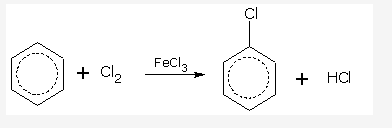
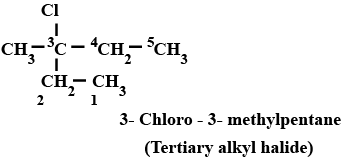
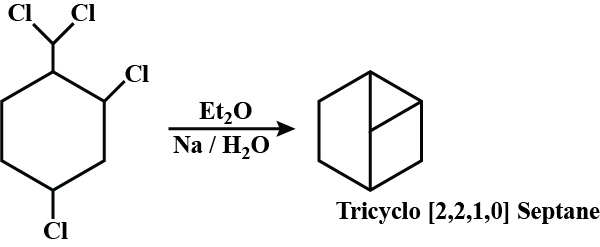
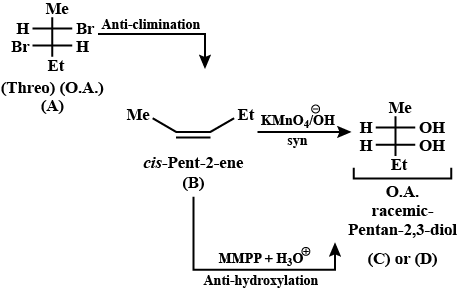
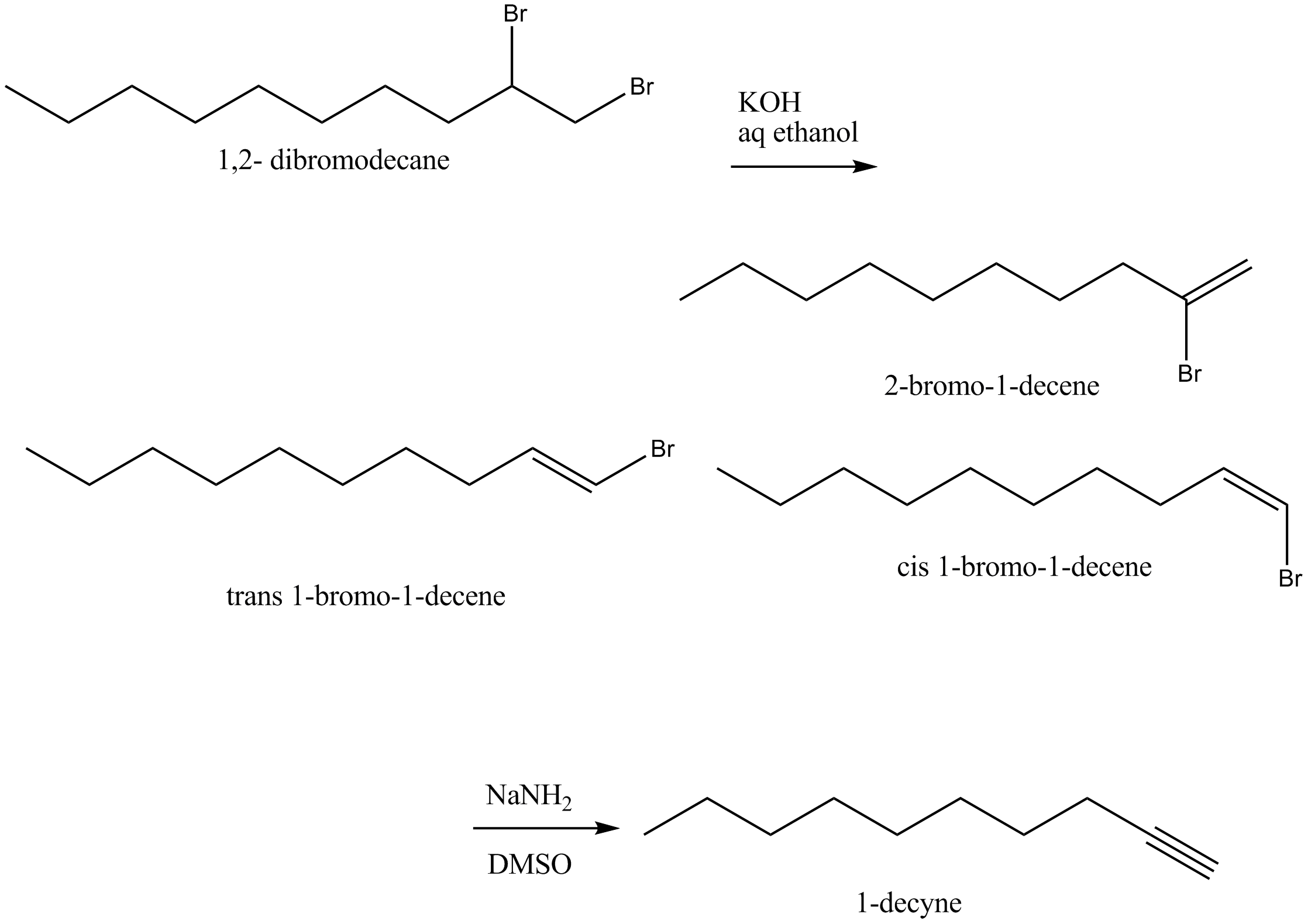
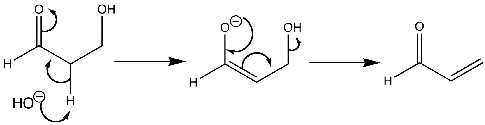
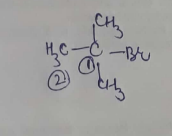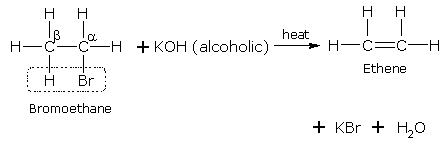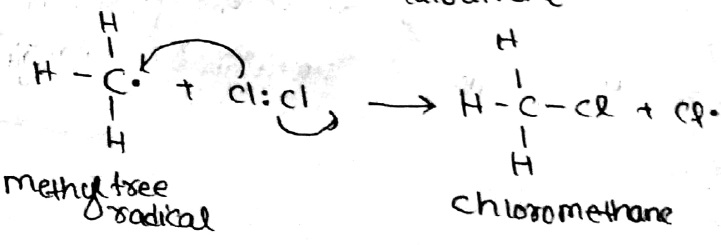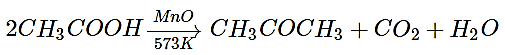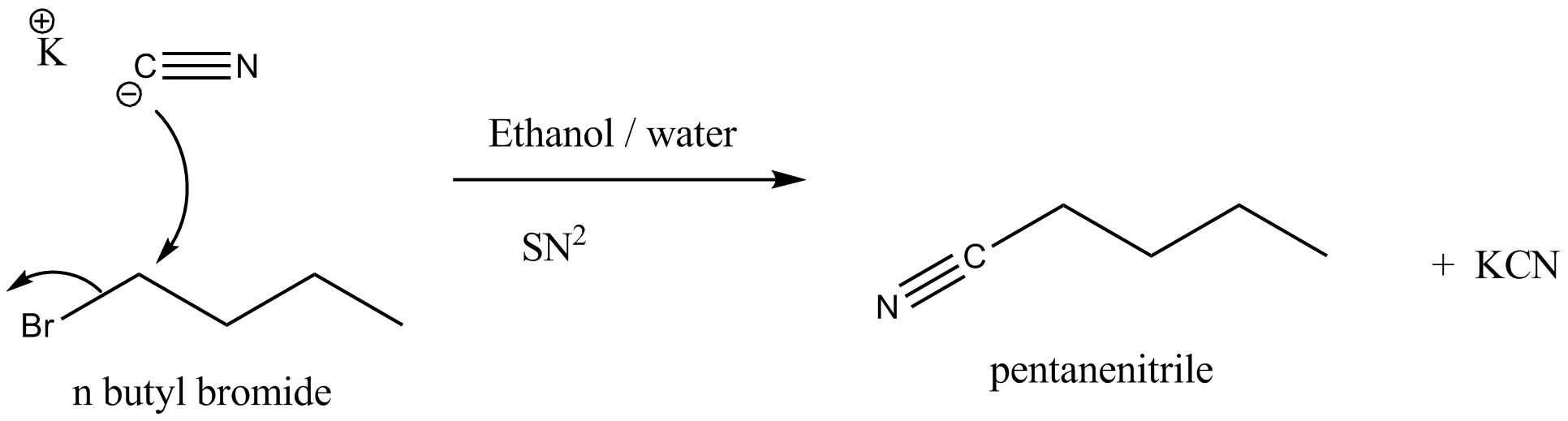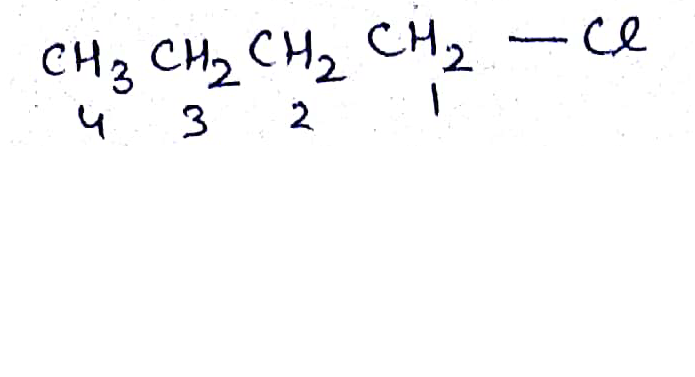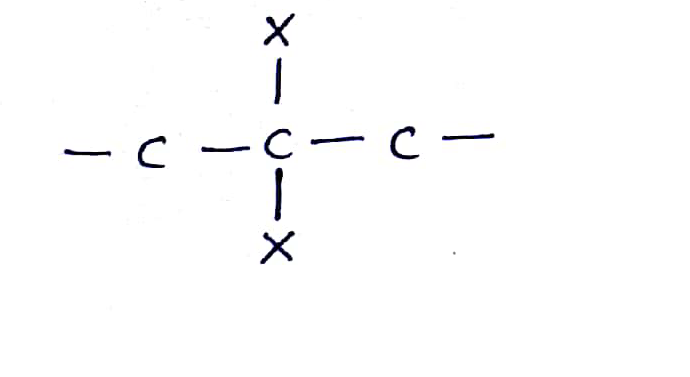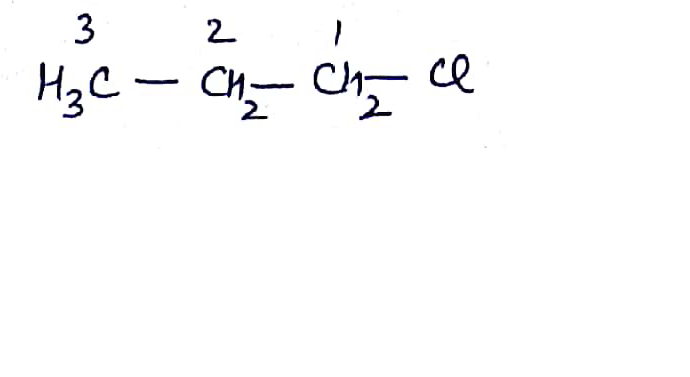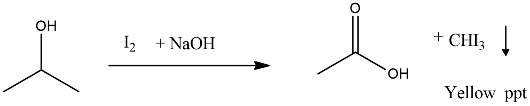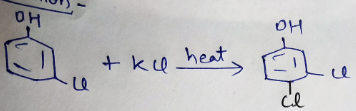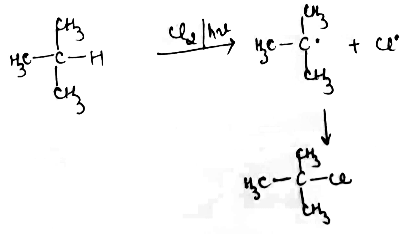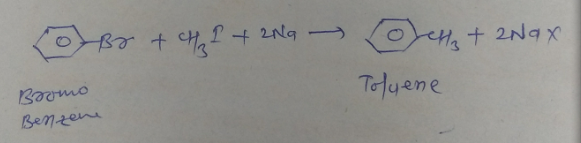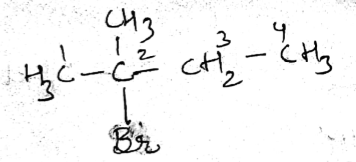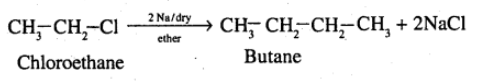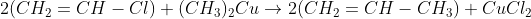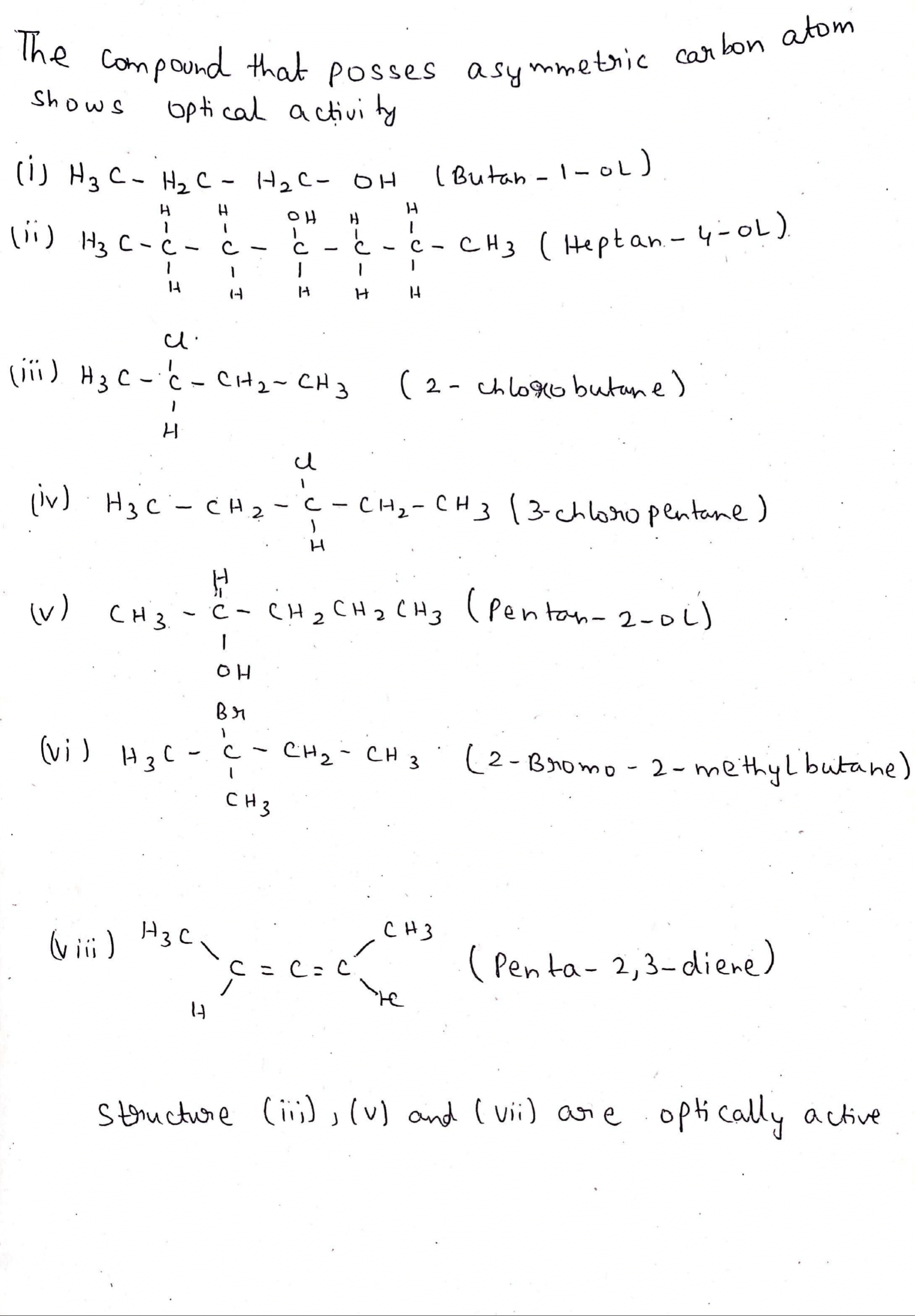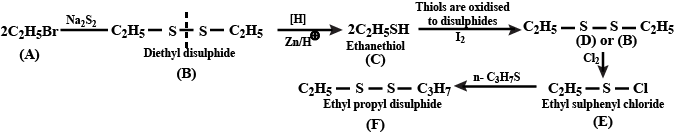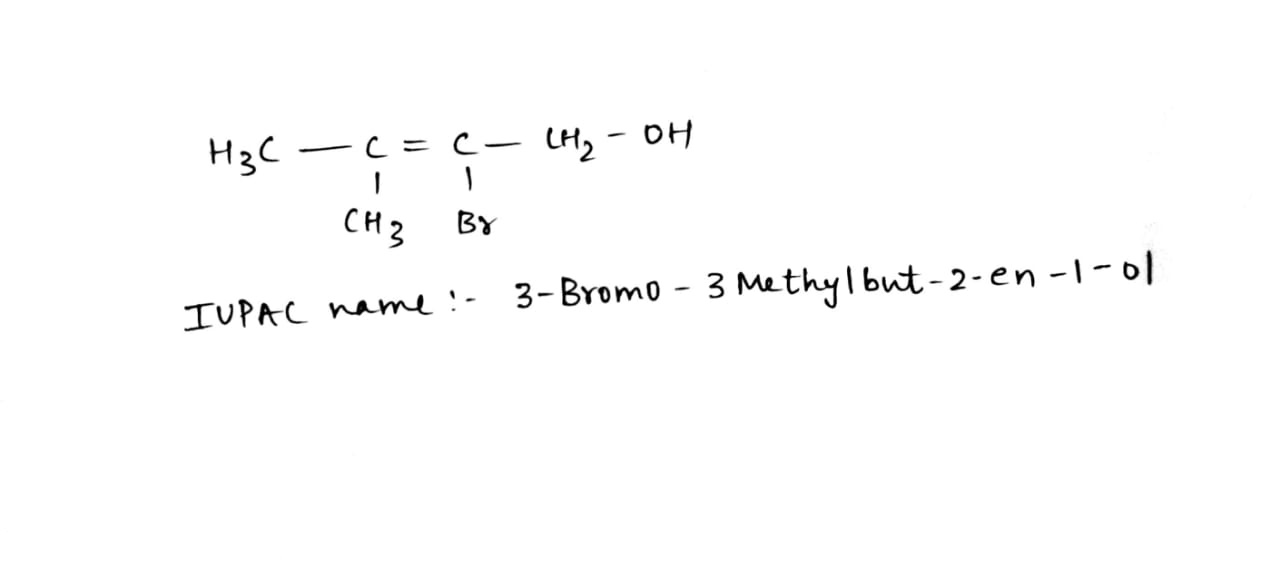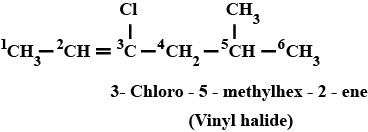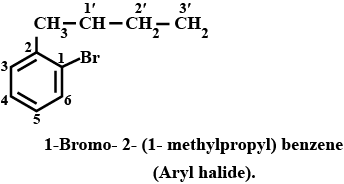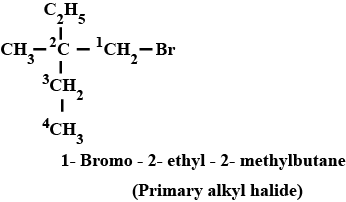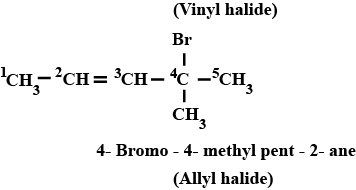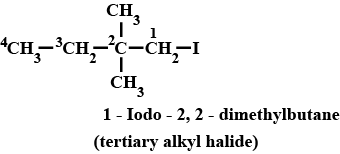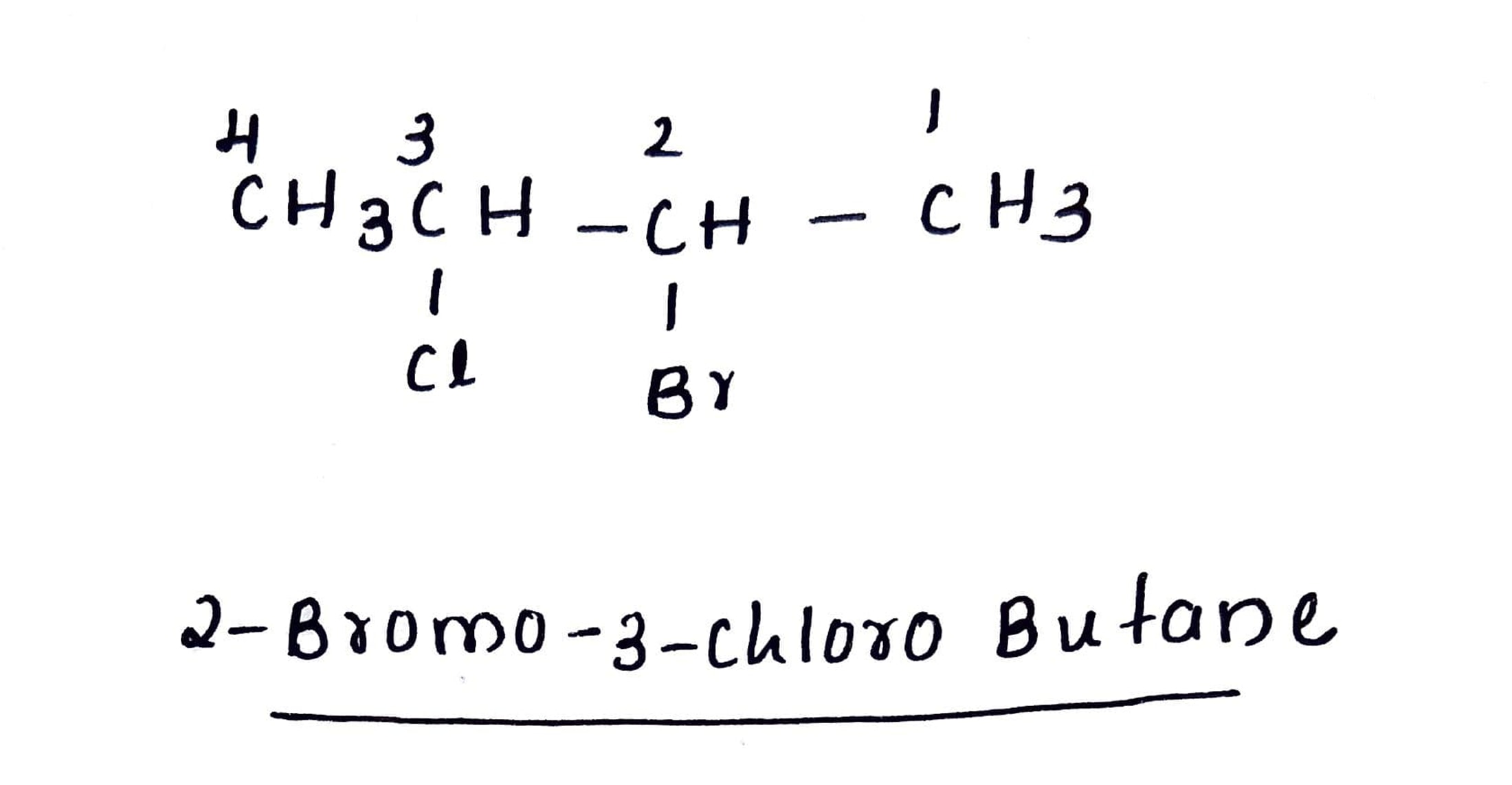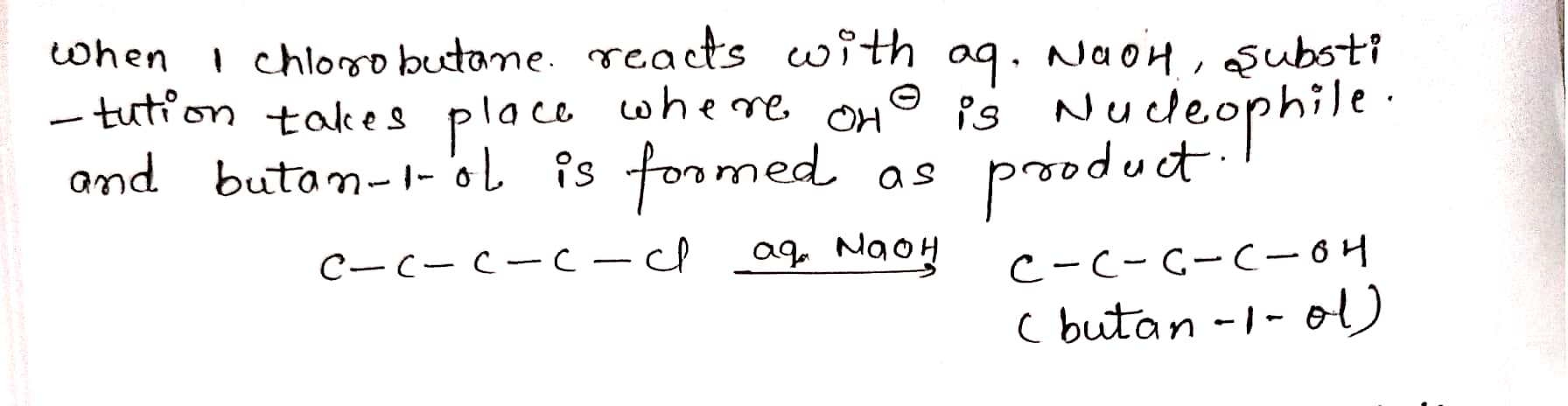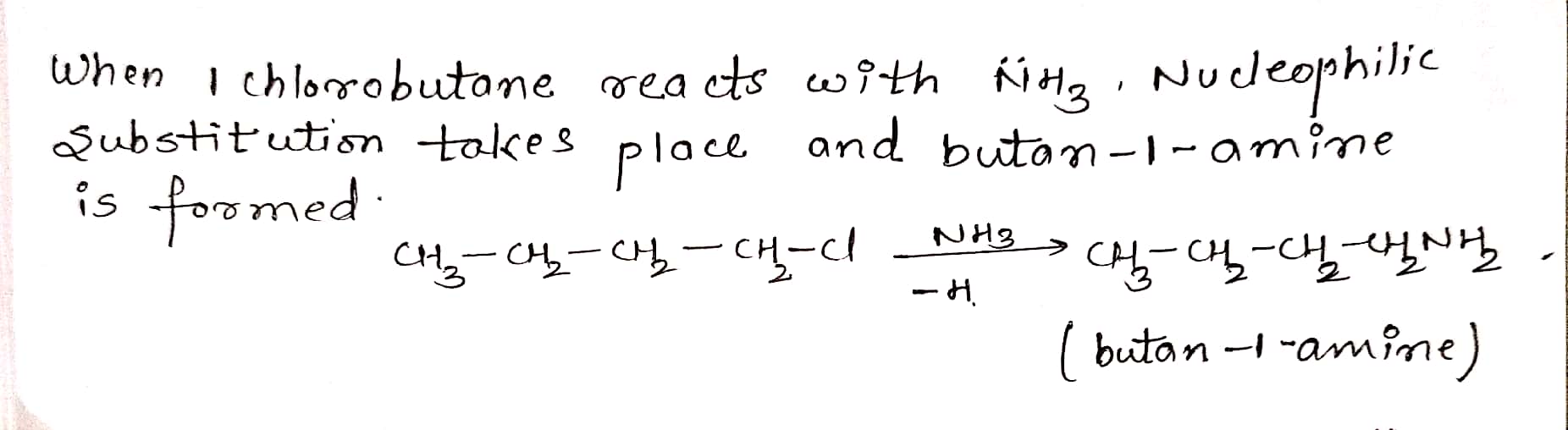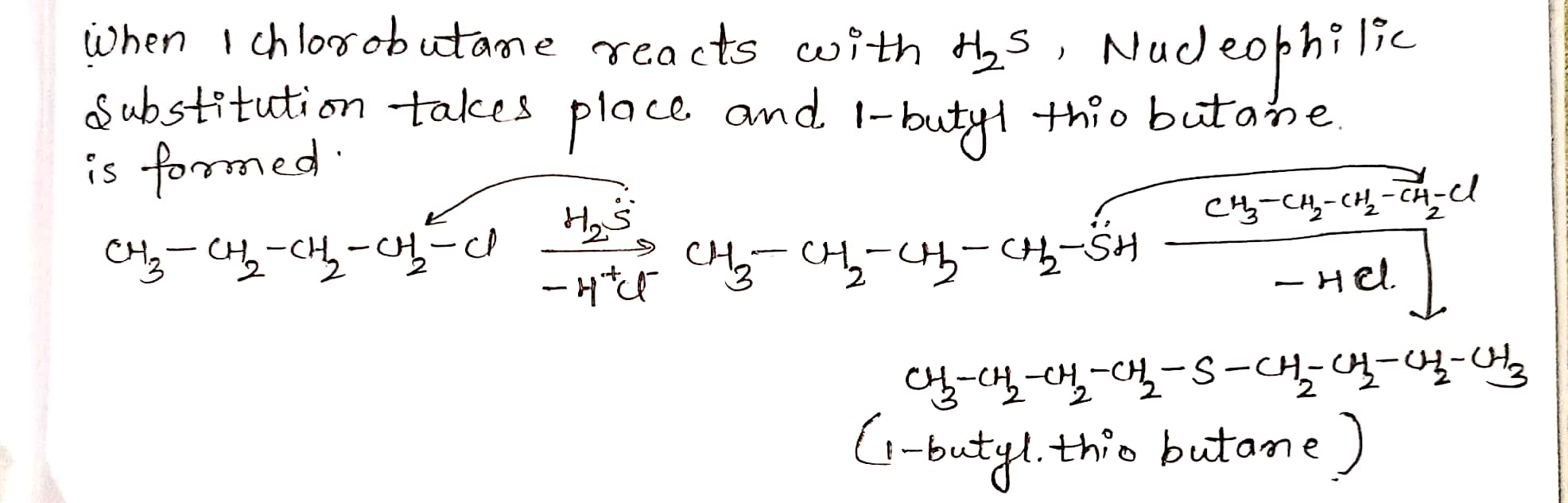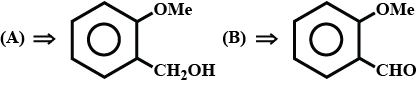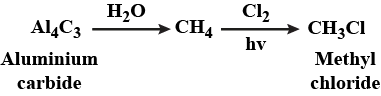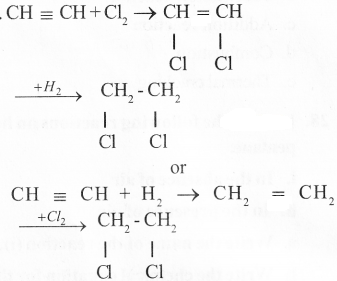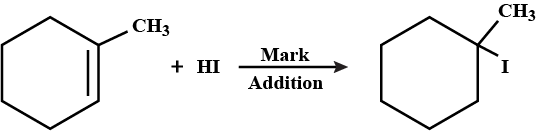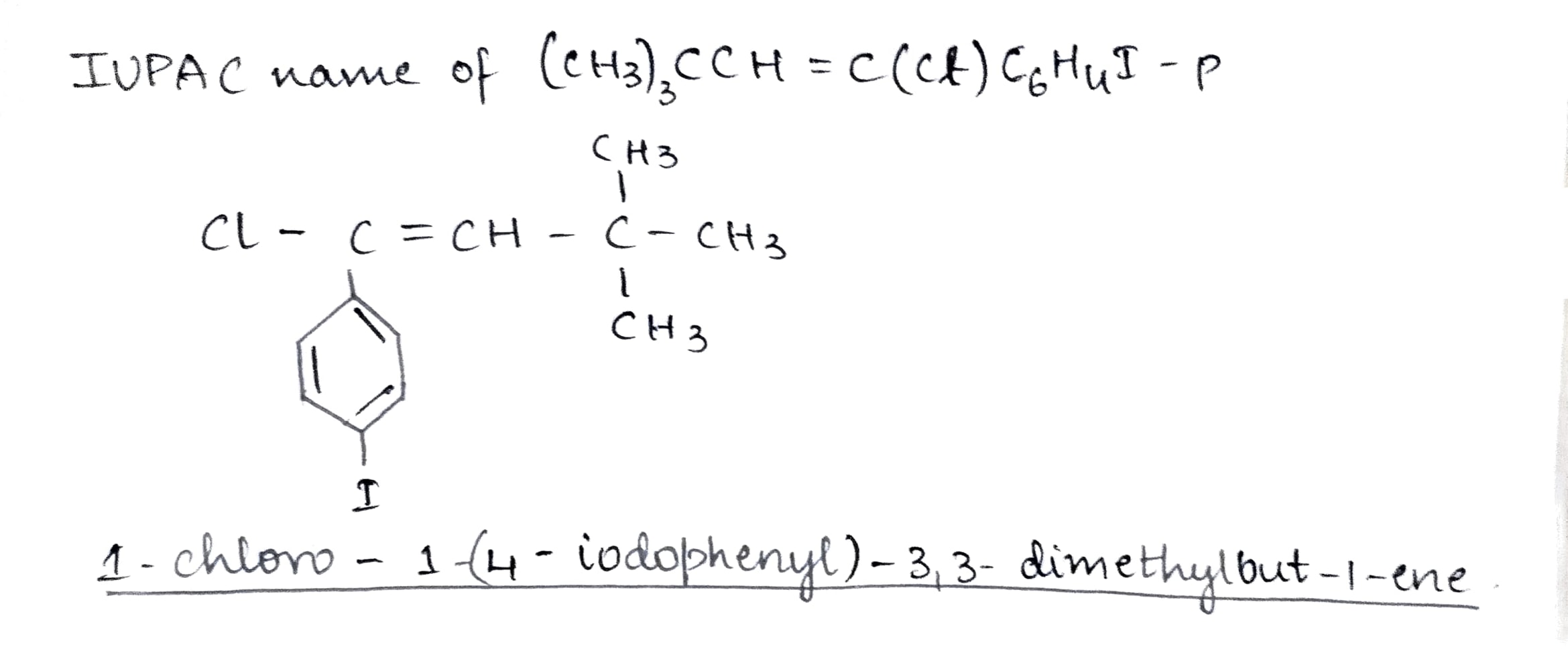Haloalkanes And Haloarenes - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
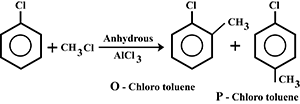
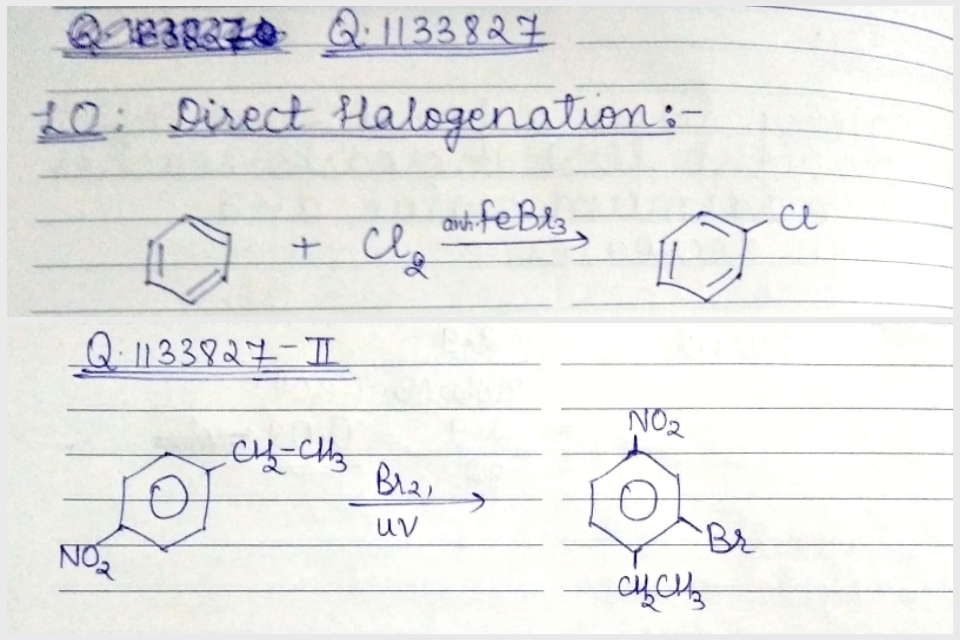
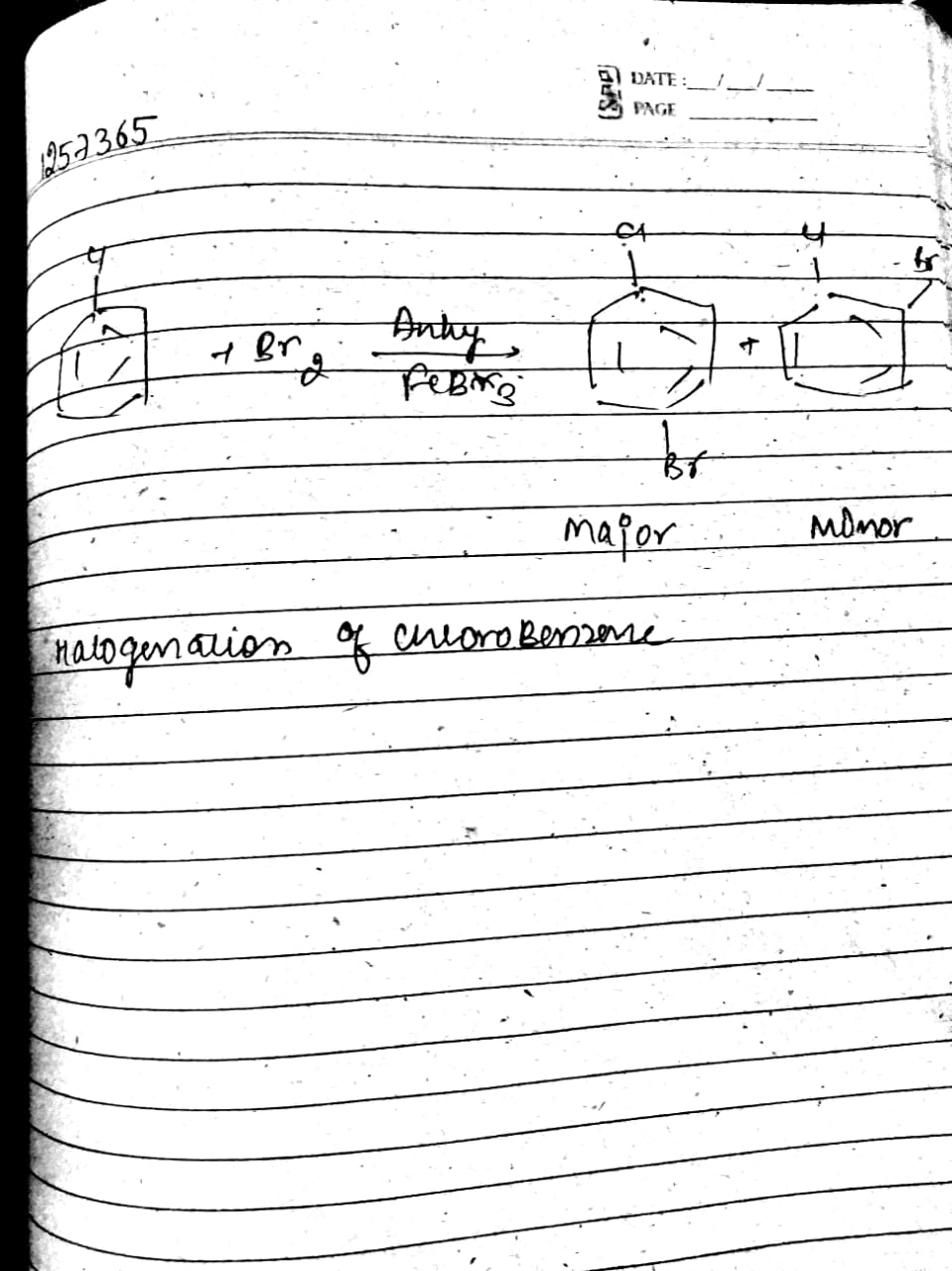
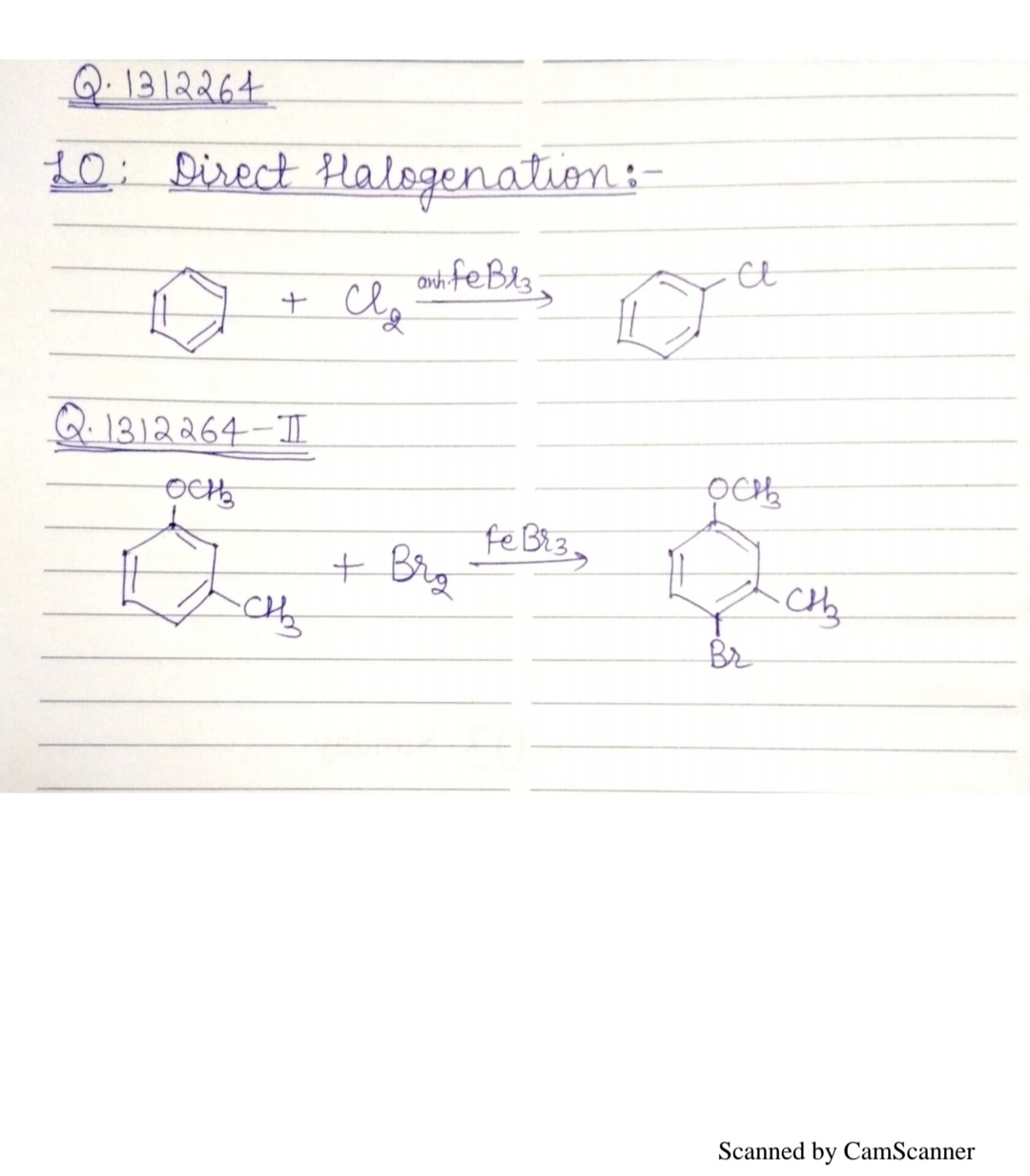
Write the equation of reaction of chlrobenzene:
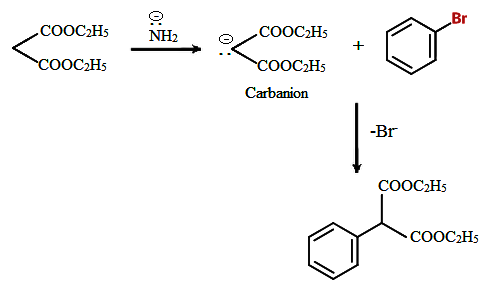
Alkylation
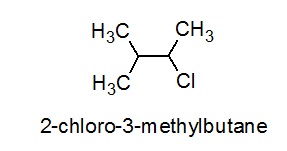
IUPAC name of the compound is:$$ CH_{ 3 }-\overset { \overset { CH_{ 3 } }{ | } }{ \underset { \underset { { CH }_{ 3 } }{ | } }{ C } } -Br $$
$${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }Br\xrightarrow {alkKoH}$$
Complete the above reaction:
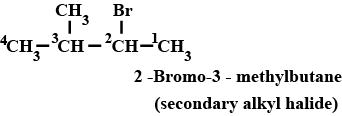
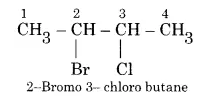
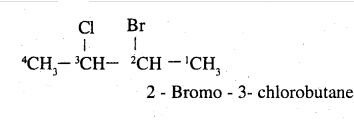
How would you name the following compounds?
$$CH_{3} - CH_{2} - Br$$
Write a mechanism of Halogenation of alkanes.
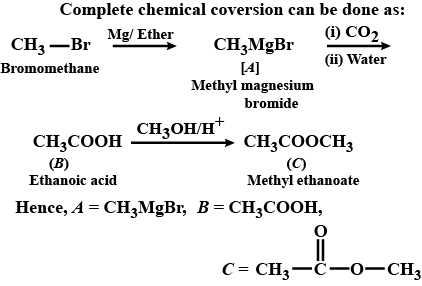
How will you convert: Bromomethane to Propanone
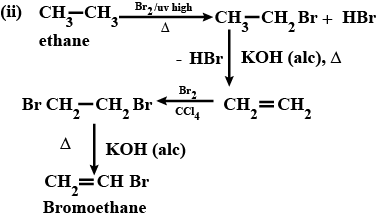
(i) Mention experimental conditions involved in obtaining ethene from ethanol. (ii) Write the chemical equation for the above reaction
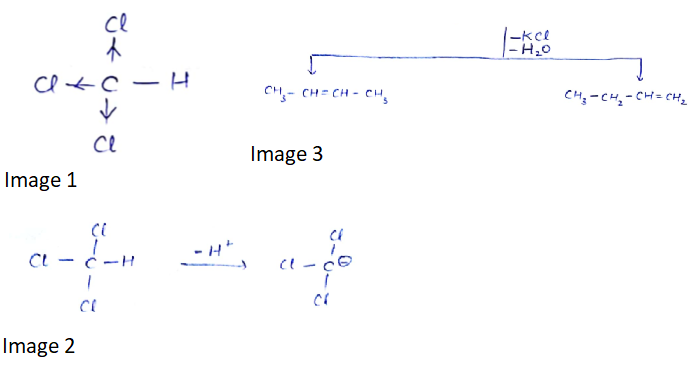
Suggest a mechanism for the given reaction:
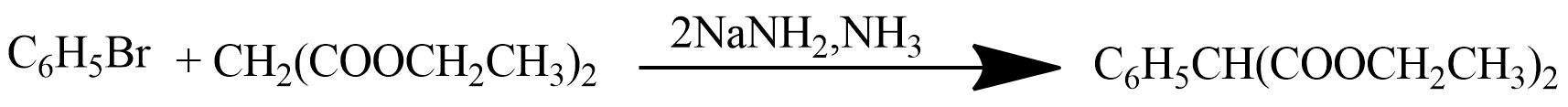
The mechanism of decomposition of $$Me_{3}S^{+}OH^{-} is S_{N}$$1
If true enter 1 else enter 0.
$$C_6H_6CI_6C_6H_6CI_6$$ on treatment with alcoholic KOHKOH yields .A : $$C_6H_6C_6H_6$$ B : $$C_6H_3CI_3C_6H_3CI_3$$ C : ($$C_6H_6$$) $$OH$$ ($$C_6H_6$$)$$OH$$ D : $$C_6H_6CI_4$$
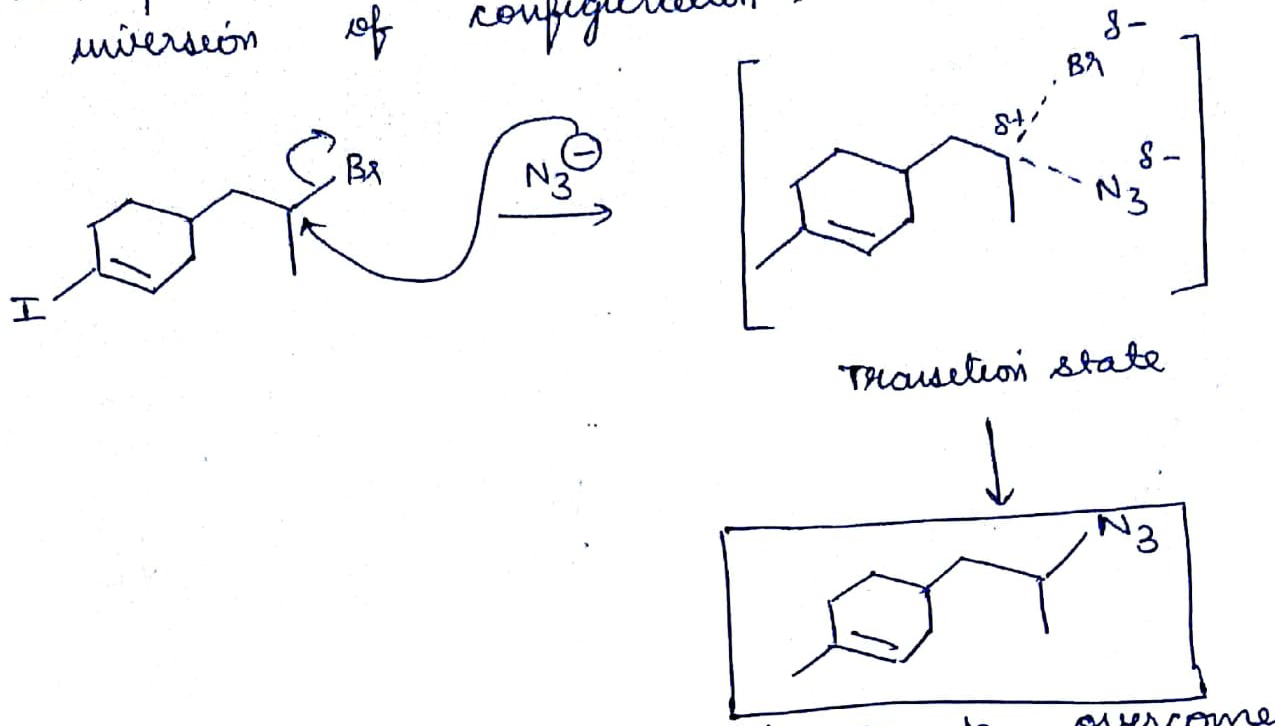
The first compound in the given pair undergoes solvolysis in aqueous ethanol more quickly. State if the given statement is true or false
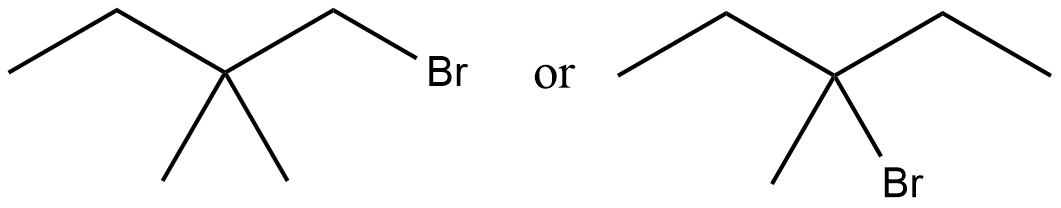
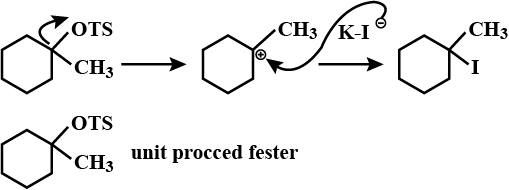
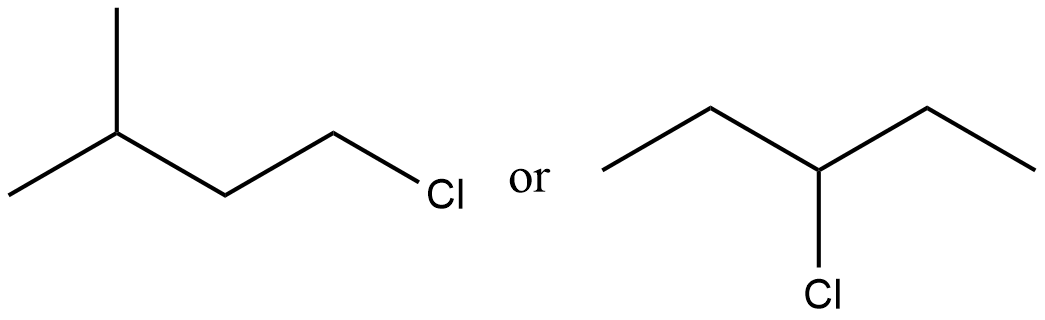
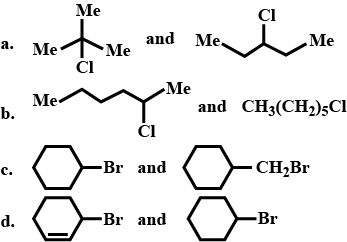
Which of the given pair of $${ S }_{ N }1$$ reaction would you expect to proceed faster? Explain your answer.
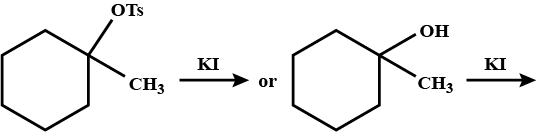
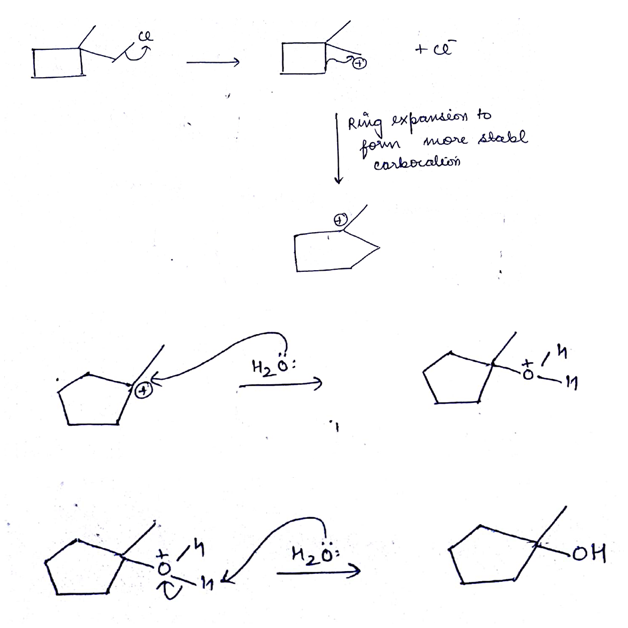
Which compound in the given pair undergoes solvolysis in aqueous ethanol more quickly?
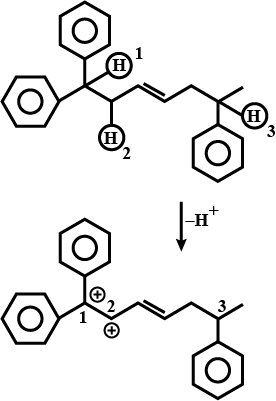
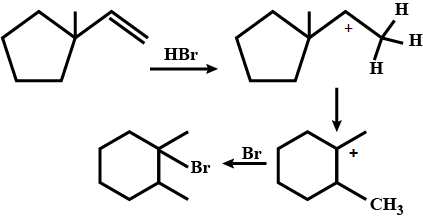
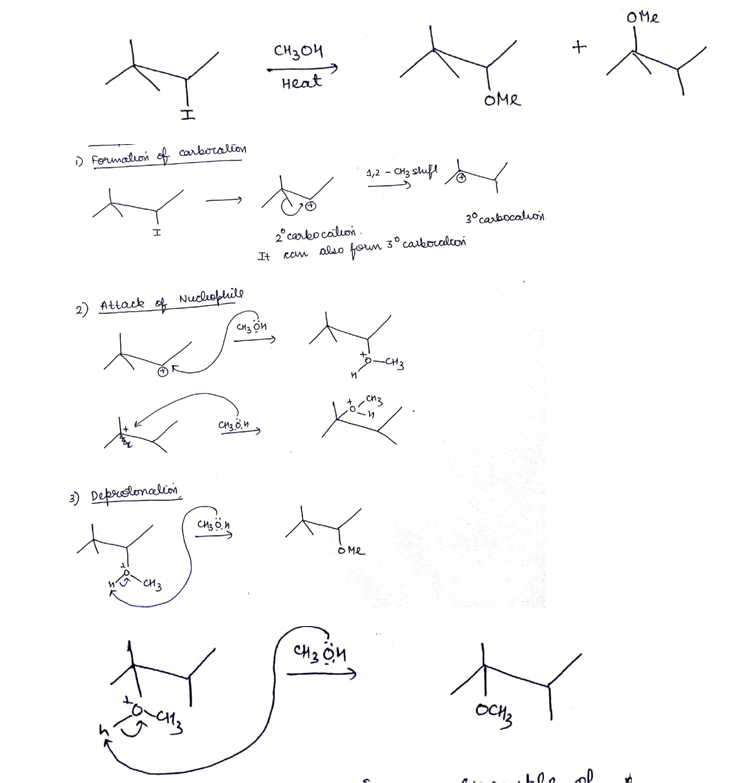
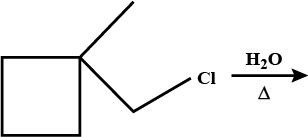
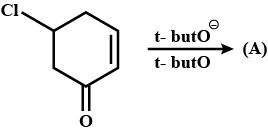
Predict major product in the reaction given.
Which of the given pair of $${ S }{ N }_1$$ reaction would you expect to proceed faster? Explain your answer.
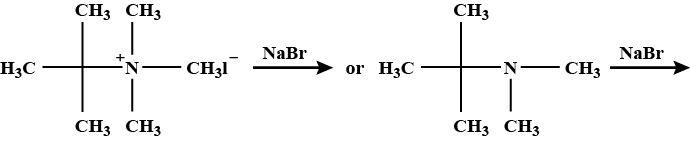
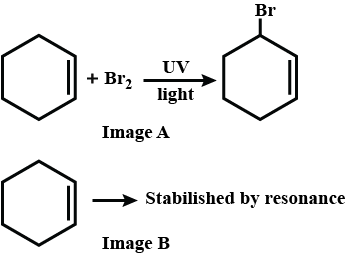
The dihalides in which halogen atoms are attached to same carbon atom are termed as alkylene dihalides
What is the correct statement for the given reactions?
a) B reacts faster than A
b) Both give the same product
c) A gives trans and B gives c is product
d) A gives cis and B gives trans product
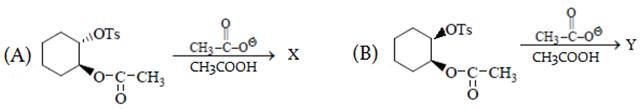
b) Both give the same product
c) A gives trans and B gives c is product
d) A gives cis and B gives trans product
Write the expected substitution product(s) for given reaction and predict the mechanism by which the product is formed.
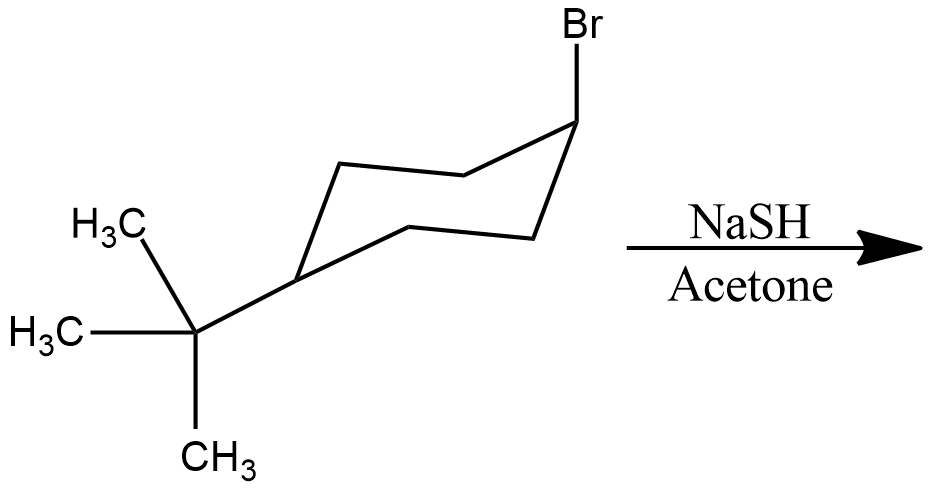
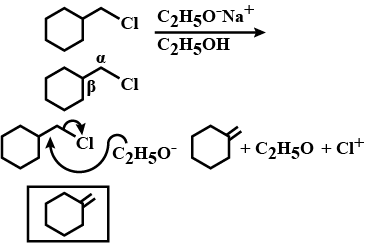
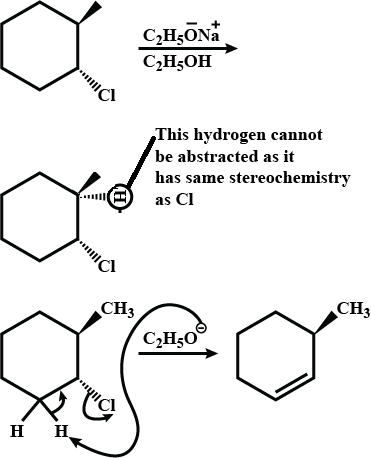
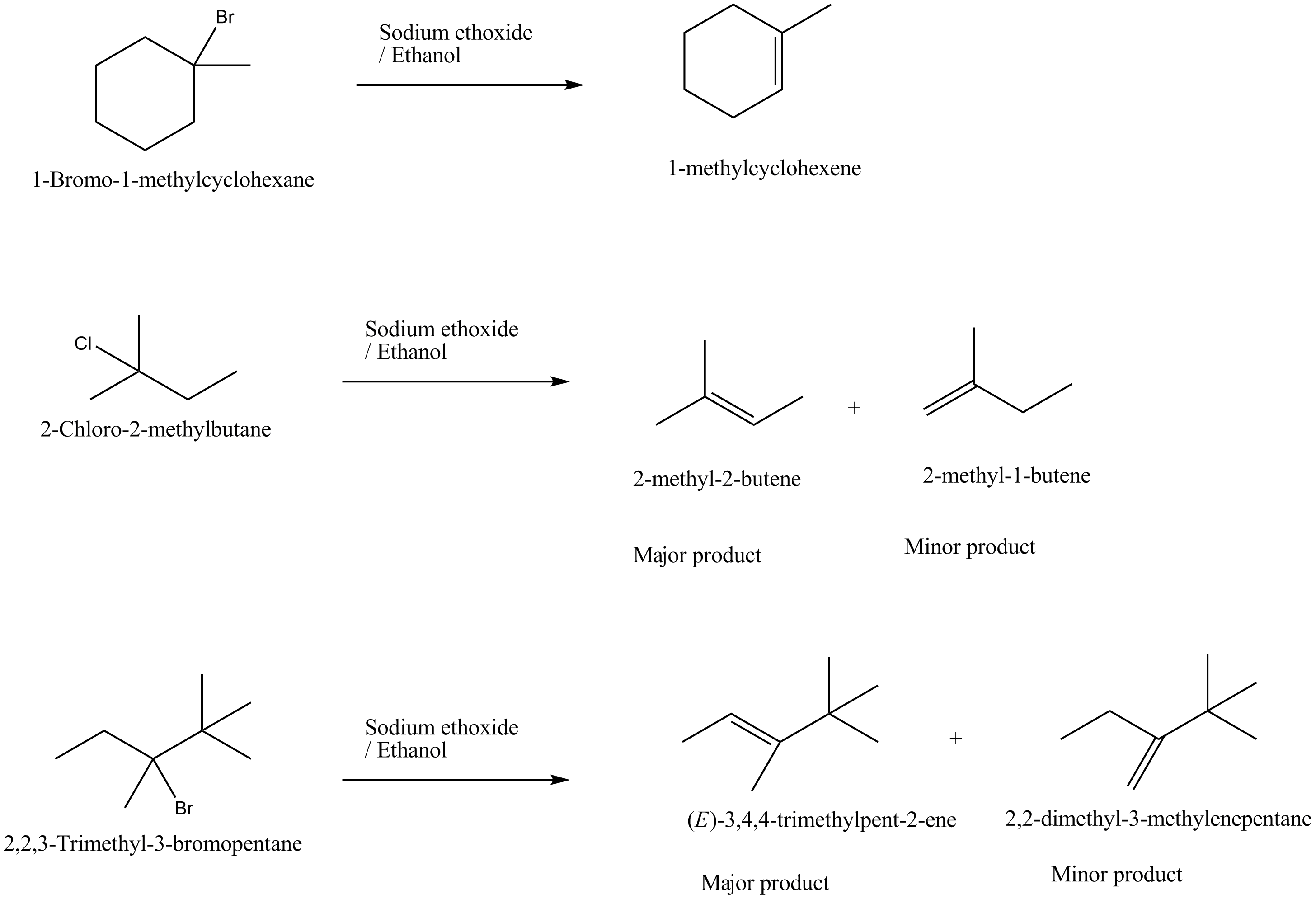
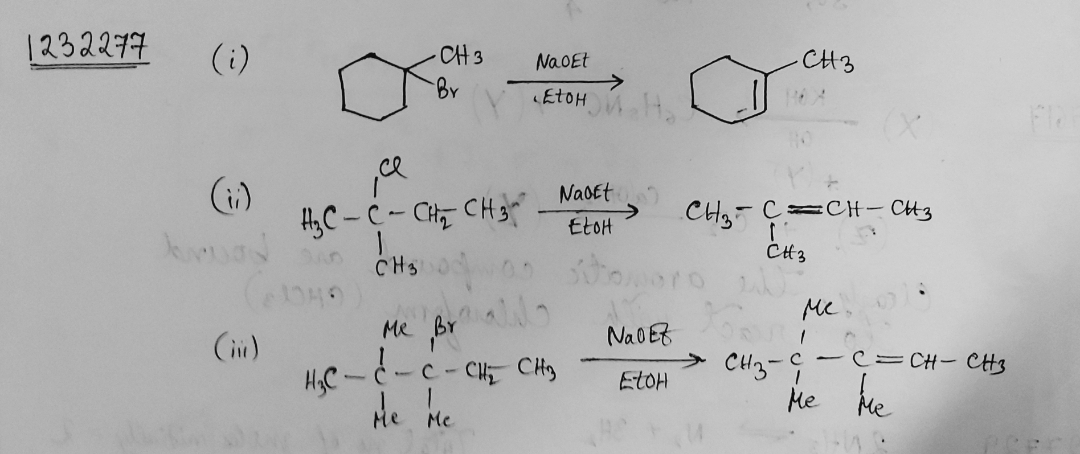
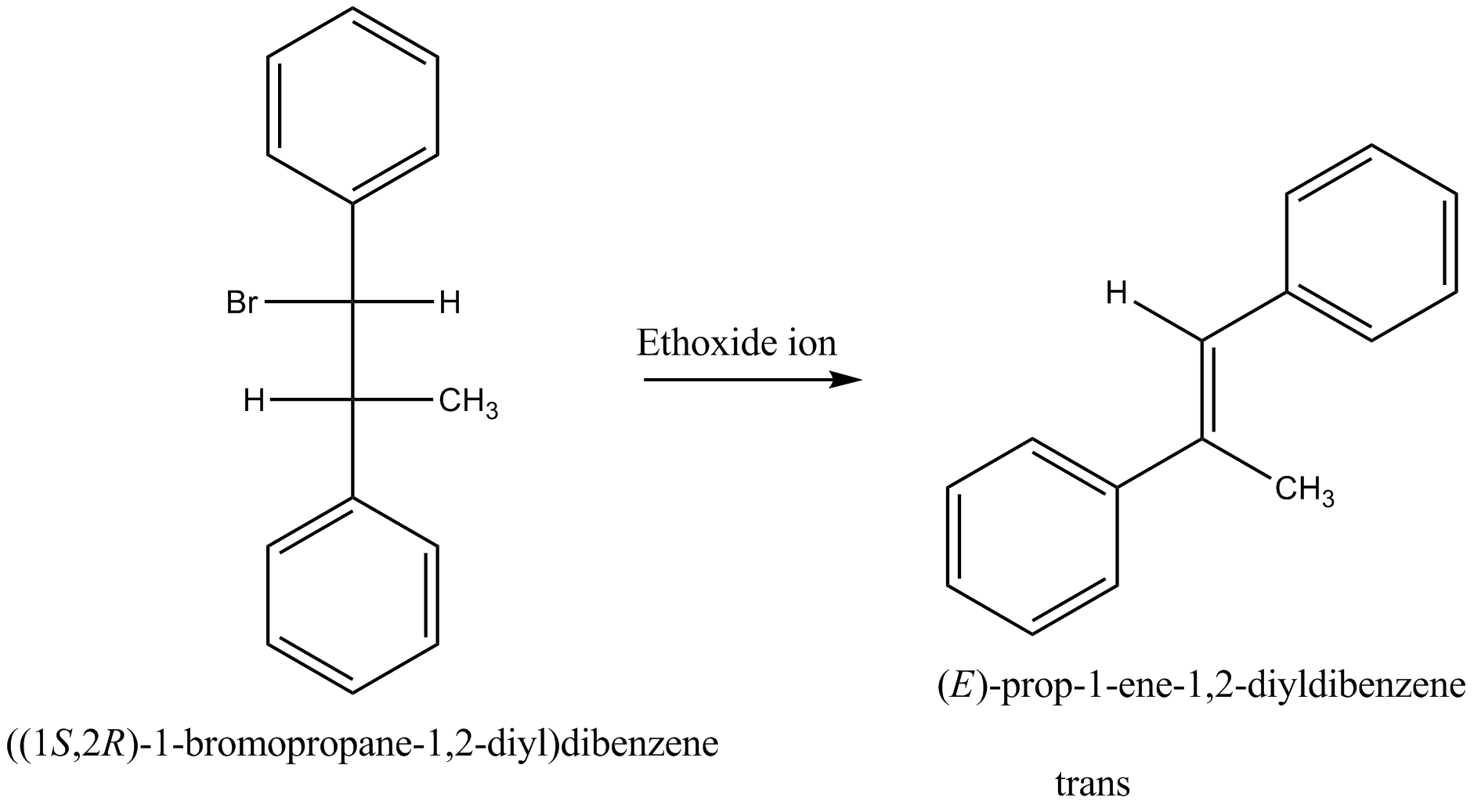
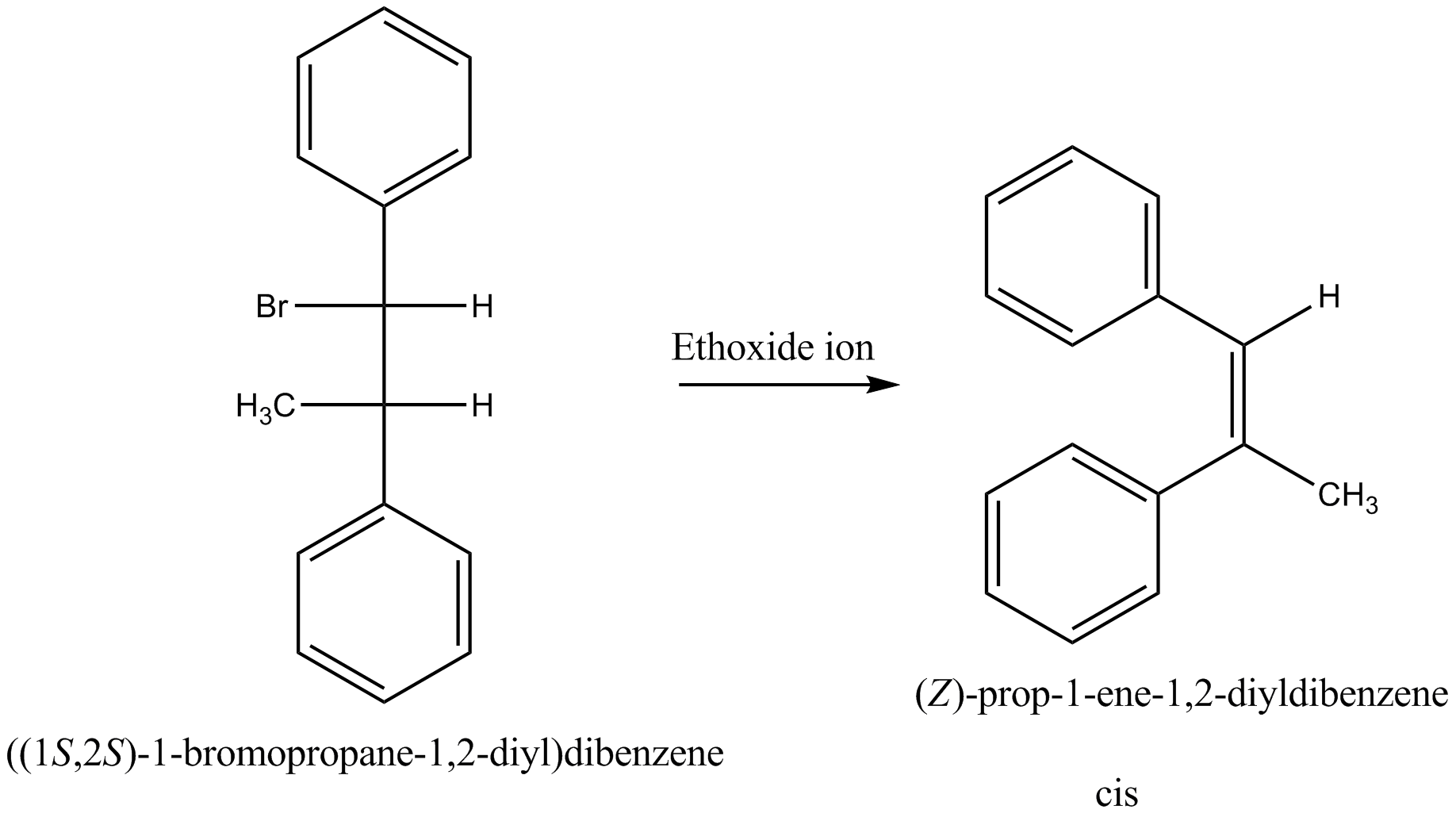
Draw structural formulas for the alkene(s) formed by treatment of each haloalkane or halocycloalkane with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Assume that elimination occurs by an $$E_2$$ mechanism.
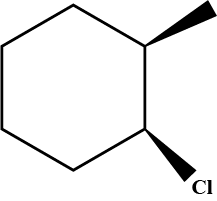
Draw a structural formula for the alkene(s) formed by treatment of each haloalkane with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.Assume that elimination occurs by an $$E_2$$ mechanism.
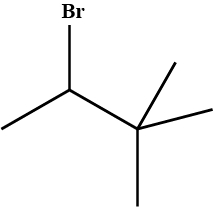
Draw structural formulas for the alkene(s) formed by treatment of each haloalkane or halocycloalkane with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Assume that elimination occurs by an $$E_2$$ mechanism.
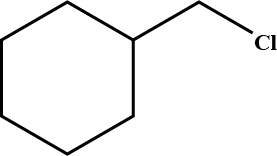
Draw structural formulas for the alkene(s) formed by treatment of each haloalkane or halocycloalkane with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Assume that elimination occurs by an $$E_2$$ mechanism.
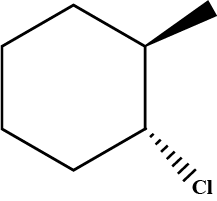
Predict product in the given reaction.
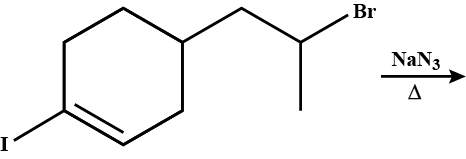
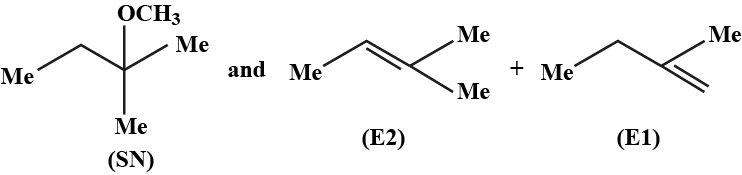
What will be the correct order of $$SN_2$$ / $$E_2$$ ratio for the %yield of the product of the following halide?
a) III > IV > II > I
b) III > II > IV > I
c) I > III > IV > II
d) II > I > III > IV
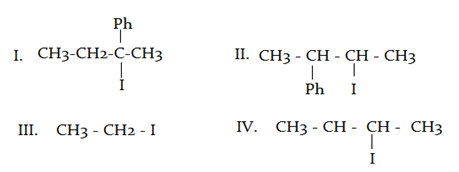
b) III > II > IV > I
c) I > III > IV > II
d) II > I > III > IV
Match the reaction in Column-I with their reaction type given in Column-II. Matching can be one or more than one
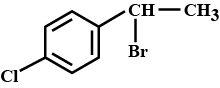
The IUPAC name of the given compound is:
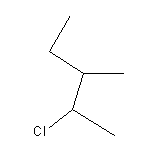
The vapour of a carboxylic acid HA when passed over MnO2 at 573 K yields propanone. What is the acid HA?
a) Methanoic acid
b) Ethanoic acid
c) Propanoic acid
d) Butanoic acid
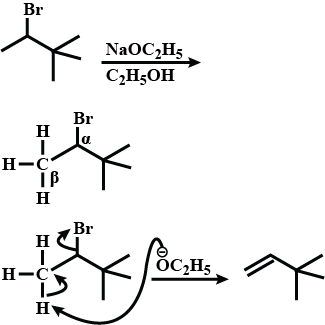
Predict the $$\beta-$$ elimination product(s) formed when each chloroalkane is treated with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. If two or more products might be formed predict which is the major product.
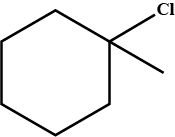
An alkyl halide of formula $$C_6H_{13}Br$$ on treatment with potassium t-butoxide gives two isomeric alkenes $$(C_6H_{12})$$. Both alkenes on hydrogenation give 2.3- dimethyl butane. Isomeric alkenes are:
Wurtz reaction involves the reduction of alkyl halide with ____ in ether.
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.
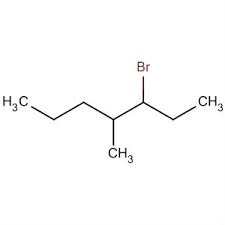
Which of the following statement is incorrect about nucleophiles?
a) Nucleophiles have an unshared electron pair and can make use of this to react with an electron deficient species
b) The nucleophilicity of an element (an electron donor) generally increases on going down a group in the periodic table
c) A nucleophile is electron-deficient species
d) All good nucleophiles are good bases when we deal across the period
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in $$SN^2$$ reaction with $$OH^{-}$$?
(i) $$CH_3Br$$ or $$CH_3I$$
(ii) $$(CH_3)_3CCl$$ or $$CH_3Cl$$
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
$$nBuBr + KCN\xrightarrow [ ]{EtOH - H_2O} nBuCN$$
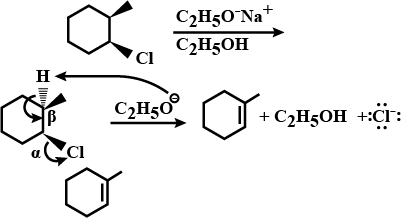
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
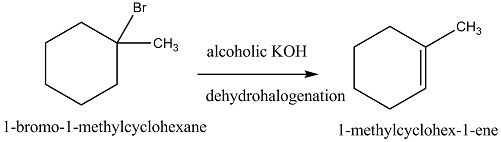
(i) 1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
(ii) 2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
(iii) 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.
(ii) 2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
(iii) 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.
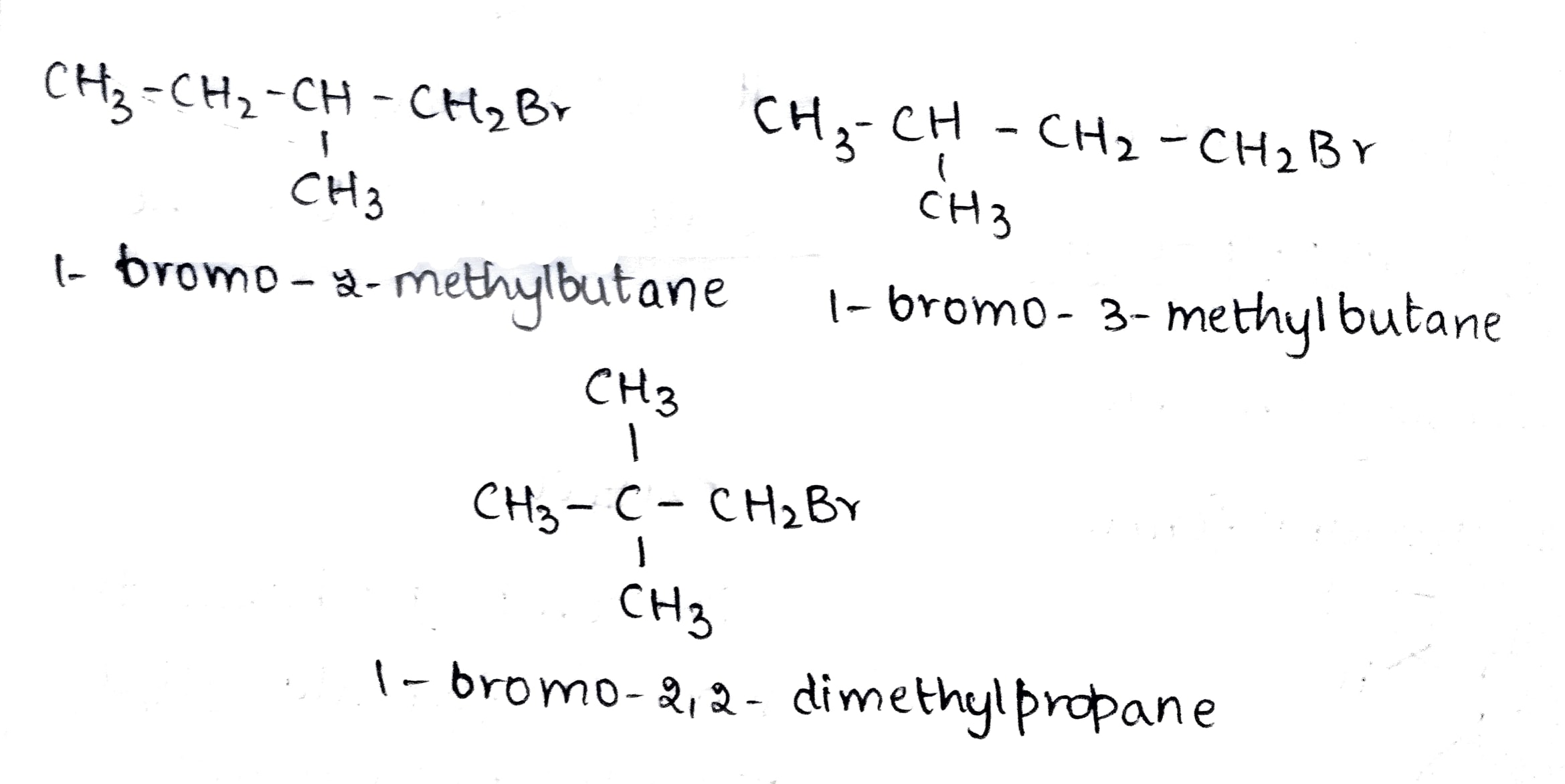
Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards $$S_N2$$ displacement.
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane,1-Bromo-3-methylbutane.
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane,1-Bromo-3-methylbutane.
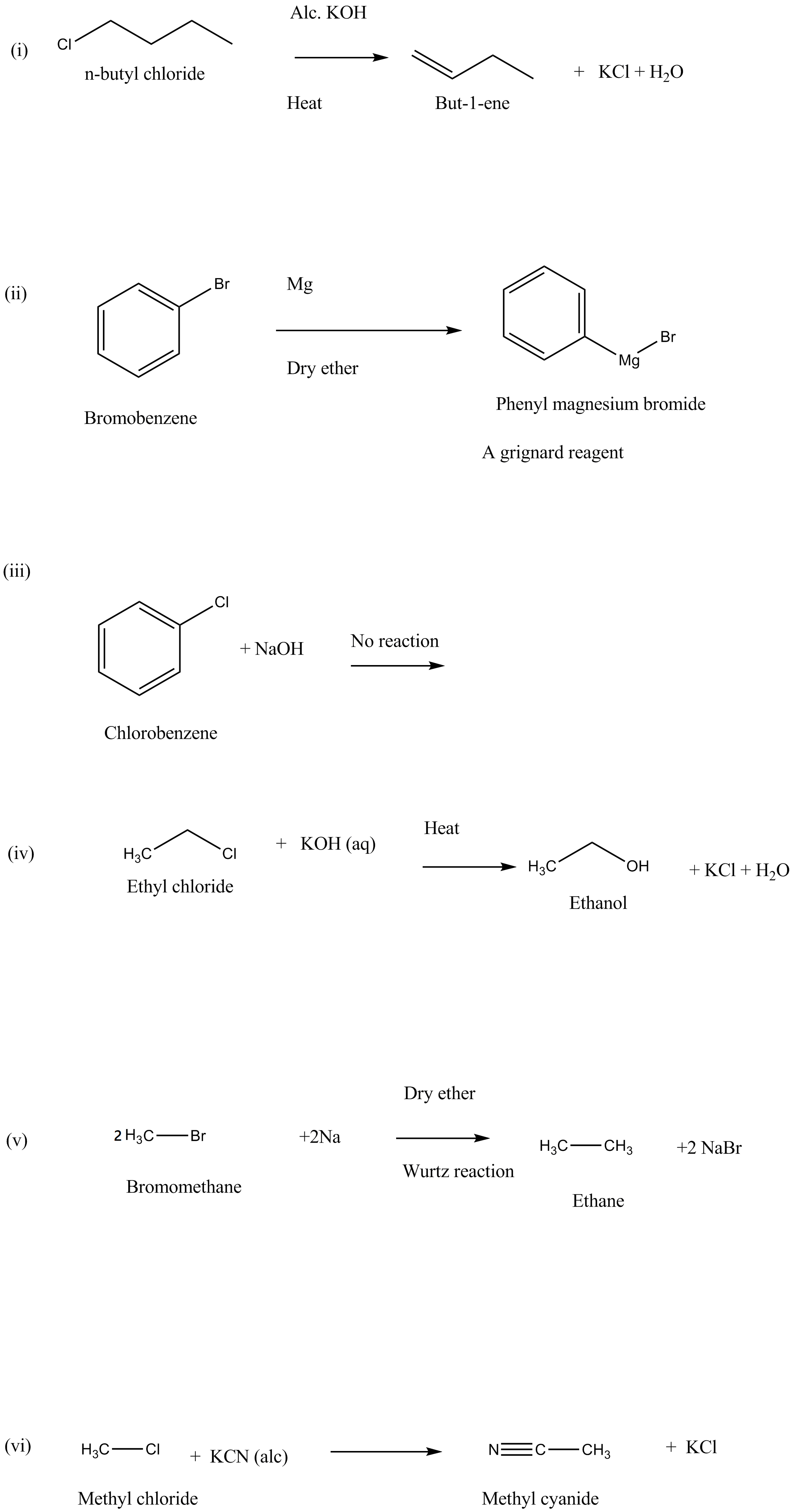
What happens when:
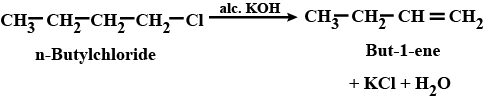
(i) n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
(ii) bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether.
(iii) chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis.
(iv) ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH.
(v) methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether.
(vi) methyl chloride is treated with KCN.
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol (ii) Ethanol to but-1-yne
(iii) 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane (iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene (vi) Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenylethanoic acid
(vii) Ethanol to propanenitrile (viii) Aniline to chlorobenzene
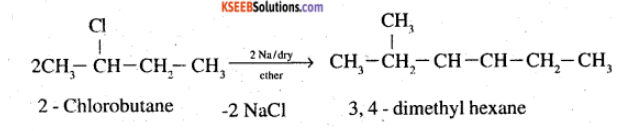
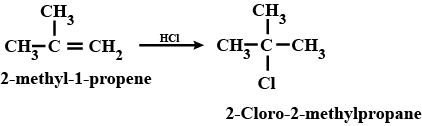
(ix) 2-Chlorobutane to 3, 4-dimethylhexane (x) 2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
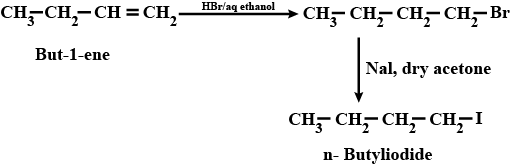
(xi) Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid (xii) But-1-ene to n-butyliodide
(xiii) 2-Chloropropane to 1-propanol (xiv) Isopropyl alcohol to iodoform
(xv) Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol (xvi) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
(xvii) Chloroethane to butane (xviii) Benzene to diphenyl
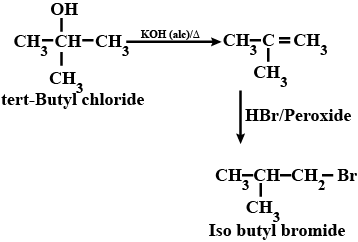
(xix) tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide (xx) Aniline to phenylisocyanide
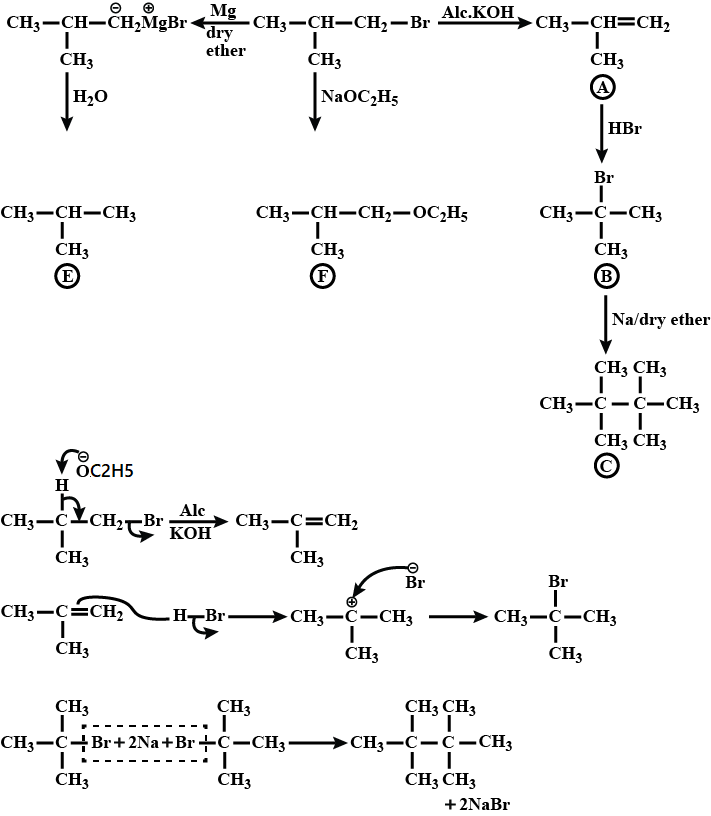
Primary alkyl halide $$C_4H_9Br$$ (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b). Compound (b) is reacted with $$HBr$$ to give (c) which is an isomer of (a). When (a) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (d), $$C_8H_{18}$$ which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formula of (a) and write the equations for all the reactions.
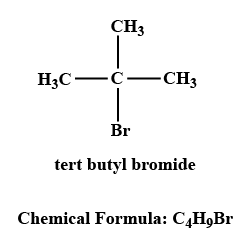
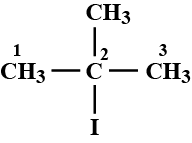
Write the structure of an isomer of compound $$C_4H_9Br$$, which is most reactive towards $$S_N1$$ reaction.
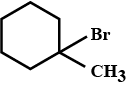
Write the IUPAC name of given compund.
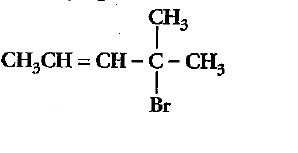
Chlorobenzene is extremely less reactive towards a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Give two reasons for the same.
Give the IUPAC name of the above compound.
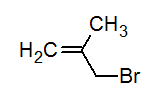
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound.
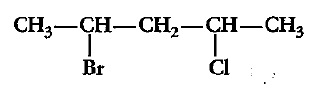
Which compound in the above pair undergoes faster $$S_{N}1$$ reaction?
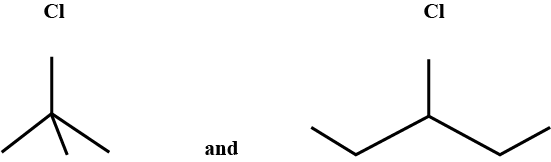
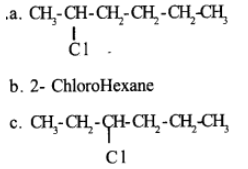
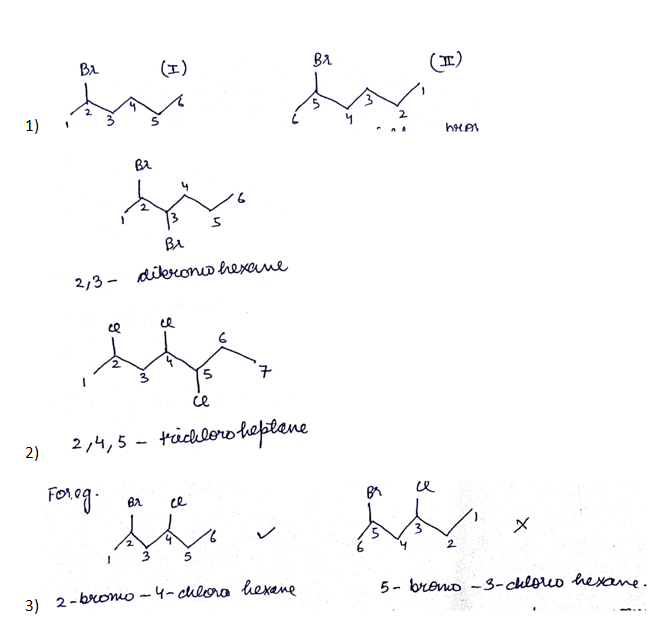
Write the common and IUPAC name of $$CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2Cl$$
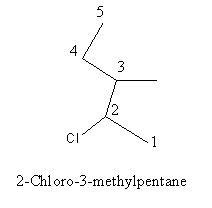
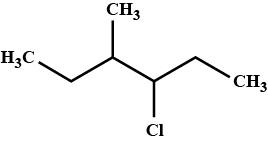
Write the IUPAC name of $$(CH_{3})_{2}CHCH(Cl)CH_{3}$$.
What is the IUPAC name of the above compound?
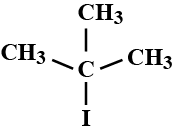
What are the compounds in which two same halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon called?
Write the common and IUPAC name of $$CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl$$.
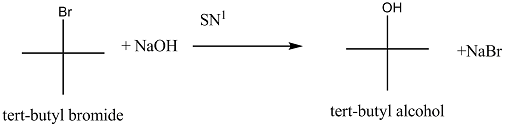
Explain $$SN^1$$ and $$SN^2$$ reactions.
Explain $$SN^1$$ reaction with appropriate example.
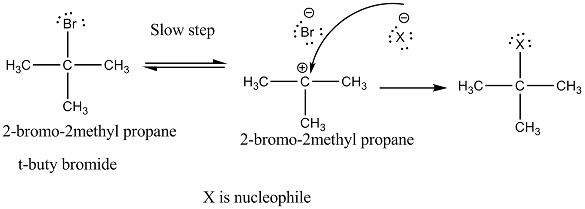
Explain the mechanism of $$S_N1$$ reaction taking 2-bromo-2methyl propane (t-buty bromide)
Write the equations for the following reactions:
(a) Wurtz reaction
(b) Wurtz-Fittig reaction
Explain the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of t-butyl bromide with energy profile diagram.
How is ethyl methanoate converted into propan-$$2$$-ol?
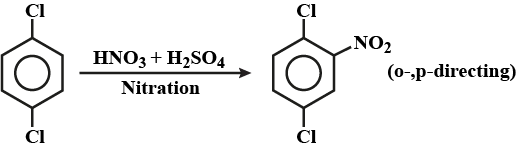
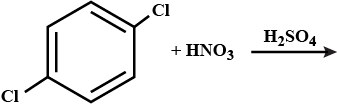
Write the equation of reaction of chlrobenzene:
Nitration
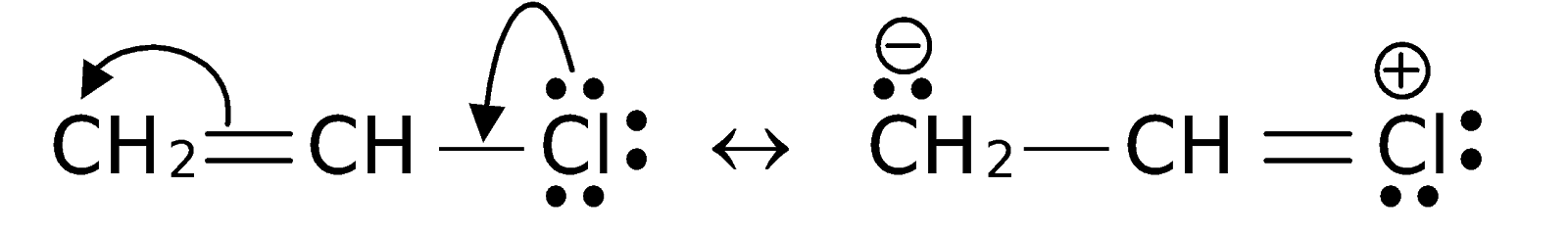
Give reasons: Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes.
Aryl halides are less reactive in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
(i) Write any two reasons for less reactivity.
(ii) Give one example for nucleophilic substitution reactions of aryl halides.
(i) The hydrogen atom of chloroform is acidic. Explain.
(ii) Why is dehydrohalogenation reaction in haloalkanes termed as Beta - elimination reaction?
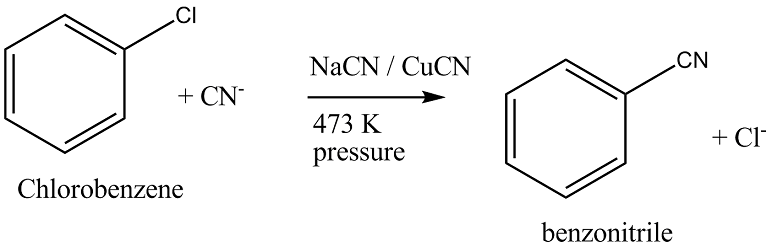
Complete and rewrite the balanced chemical equation.
Chlorobenzene $$\overset{NaCN+CuCN}{\underset{473K, pressure}{\rightarrow}}?$$
In the given compound, the ease of removal of hydrogen is in :
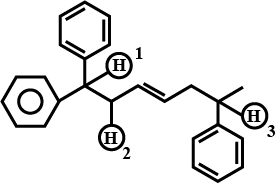
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(square pyramidal, electrical, 74, 26, $$sp^3d^2$$, $$sp^3d$$, chemical, 68, 32, tetrahedral, yellow, white, iodoform, Lucas)
Propan-2-ol on reaction with iodine and sodium hydroxide gives _________ precipitate and the reaction is called _________ test.
Complete the reaction.
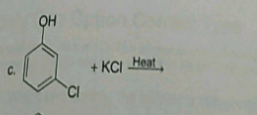
Identify the IUPAC name of the compound.$$H_2-C = CH - CH_2-Cl$$
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. Give any two reasons.
Give reasons:
a) Alkyl halides are insoluble in water although they contain polar C-X bond.
b) Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous condition.
c) Vinyl chloride is less reactive than ethyl chloride towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Convert 1-Chlorobutane into the following compounds.
- Butan-1-ol
- 1-Iodobutane
- $${ CH }_{ 3 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-CN$$
How can you change bromoethane to propanal?
Explain Halogenation reaction with conversion of $$CH_4$$ to $$CCl_4$$ in alkanes.
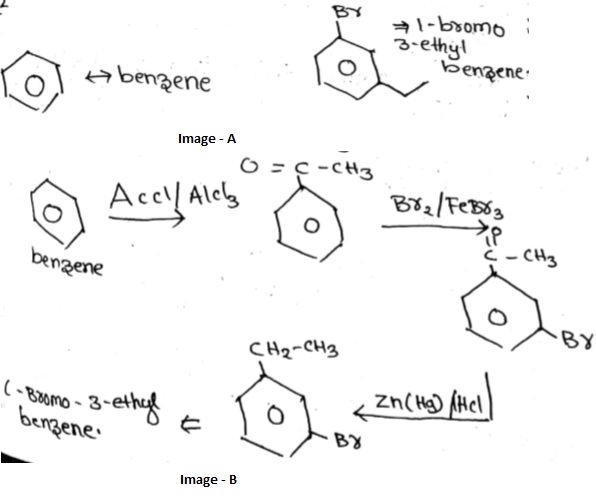
Convert benzene to $$1-bromo-3-ethylbenzene.$$
Predict the major product formed in the following reaction.
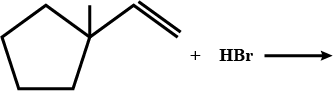
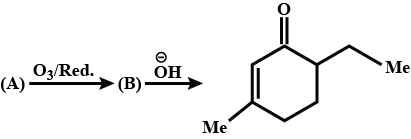
What is $$B$$?
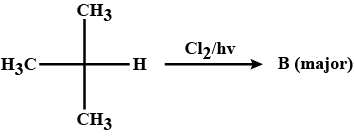
Identify the major product in the following reaction.
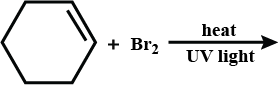
Complete the reaction.
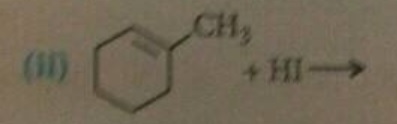
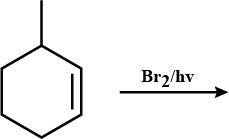
The major mono halo product in the reaction is X. Identify the product X.
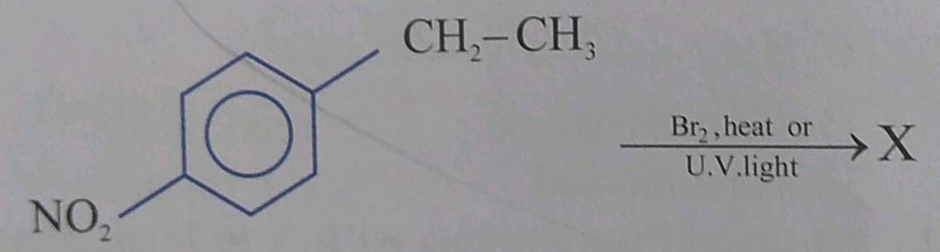
What are the advantages of chlorofluorocarbons?
The product (B) will be
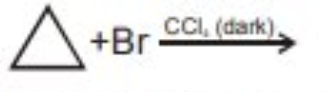
Write the structures and IUPAC names of possible isomers of $$C_5H_{11}Br$$ and classify them as $$1^0/2^0/3^0$$.
In the following sequence of reaction:
$$CH_2CH_2CH_2Br \xrightarrow[]{KOH(alc)} (A) \xrightarrow[]{HBr} (B) \xrightarrow[]{KOH(aq)} (C)$$.
Draw the structure of A?
Convert chlorobenzene to p-chloranitrobenzene.
How is ethyl bromide prepared from
(i) Ethyl alcohol (ii) ethane (iii) ethene
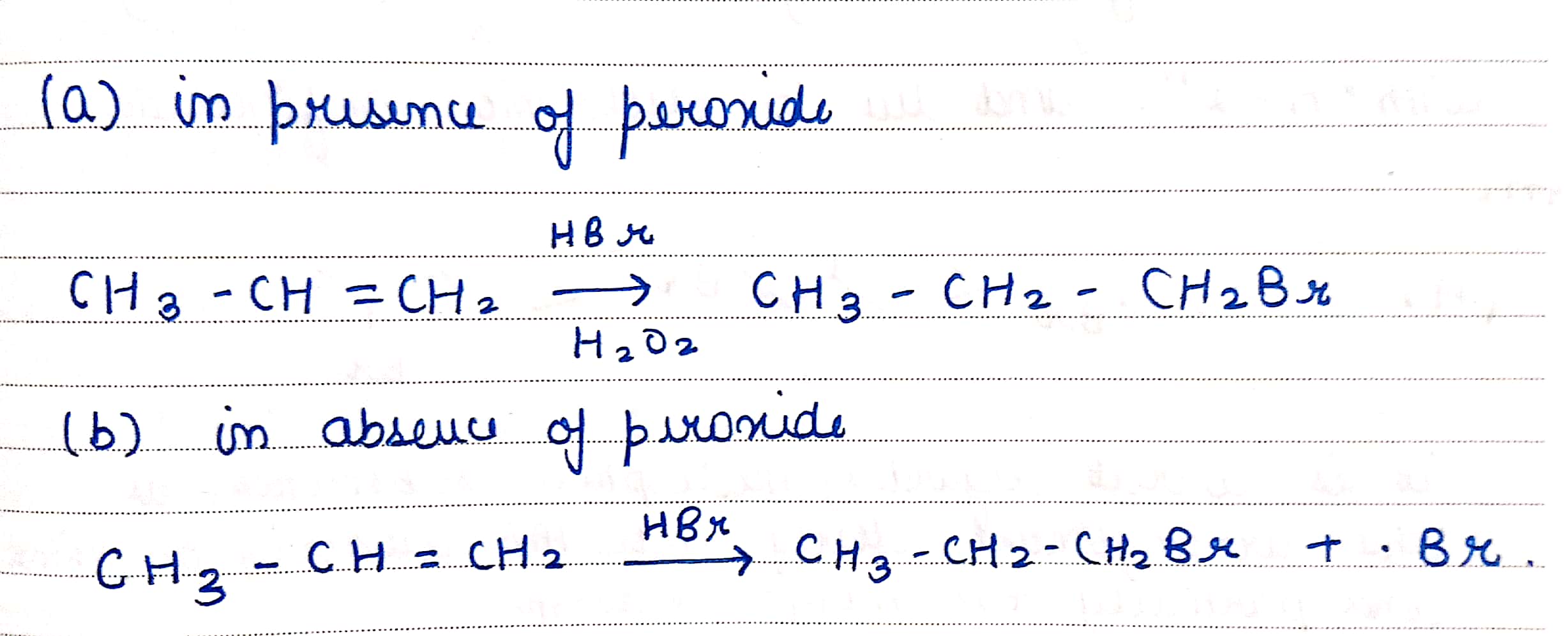
Write the structure of the alkyl halide obtained by the action of hydrogen bromide on pent-1-ene
a) In presence of peroxide
b) In absence of peroxide
Explain wurtz fitting reaction with example
Find out the number of dimerize products obtained by following reaction.
$$H_3C-Cl+H_3C-CH_2-Cl+H_3C-CH_2-CH_2-Cl\xrightarrow[Dry ether]{Na}$$
$$(CH_3)_2 C BrCH_2 CH_3$$Give IUPAC name of the compound.
Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
Consider the given reaction. Compounds $$A$$ and $$B$$ respectively are.
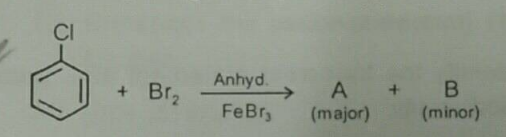
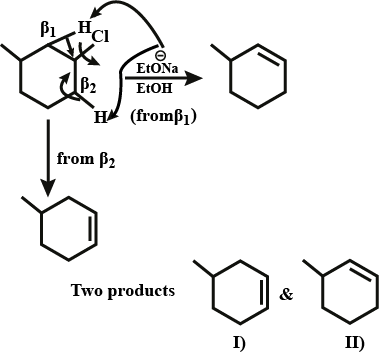
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene?
(i) $$1$$ -Bromo-$$1$$-methylcyclohexane (ii) $$2$$ -Chloro-$$2$$-methylbutane
(iii) $$2,2,3$$ -Trimethyl- $$3$$ -bromopentane.
List four characteristic of the images formed by plane mirrors.
How many of the following compounds are more acidic than ethyne?
$$C{H_2} = C{H_2},N{H_3},{H_2}O;C{H_3} - C{H_3}HF,C{H_3}C{H_2} - OH,C{H_3} - C{H_{2 - }}SH,$$
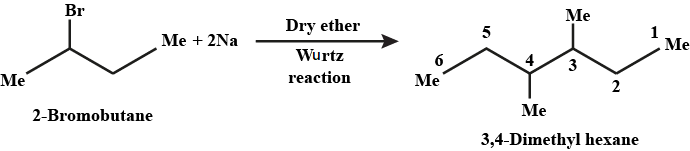
How are the following conversions carried out? (ix) 2- Chlorobutane to 3, 4-dimethylhexane
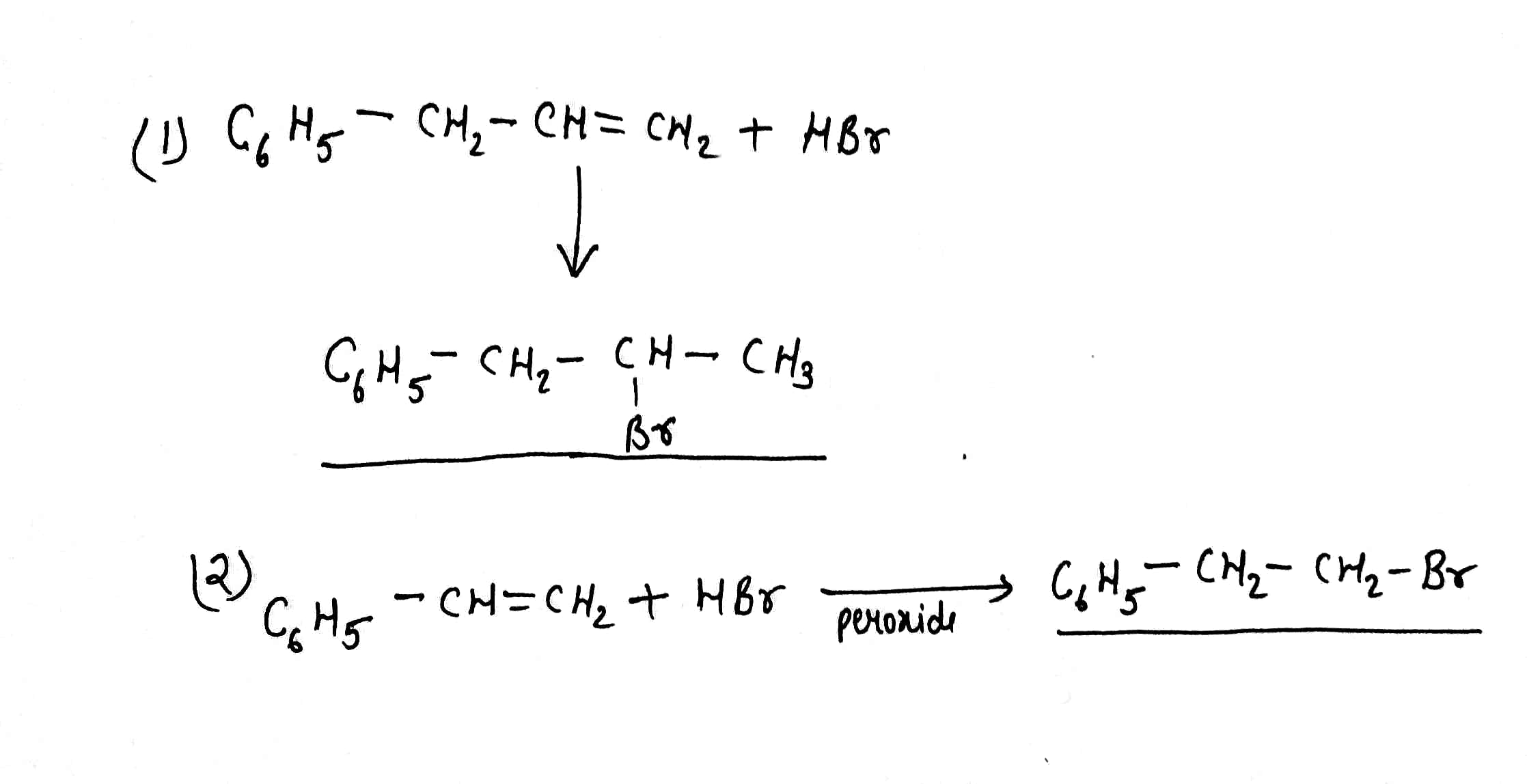
Write the products of:(1)$${C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr\xrightarrow[{}]{}$$
(2)$${C_6}{H_5} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr\xrightarrow{{Peroxide}}$$
How are the following conversions carried out? (x) 2- Methyl-1- propene to 2-chloro-2- methylpropane
How the following conversions can be carried out?
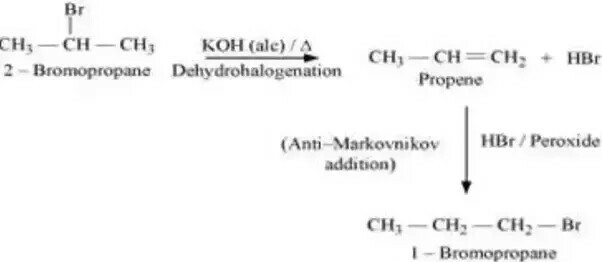
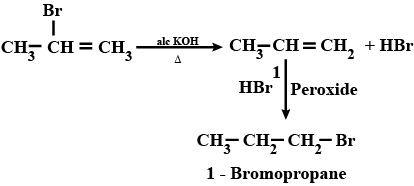
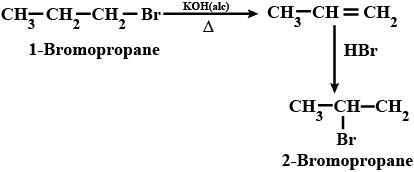
$$2-$$Bromopropane to $$1-$$bromopropane
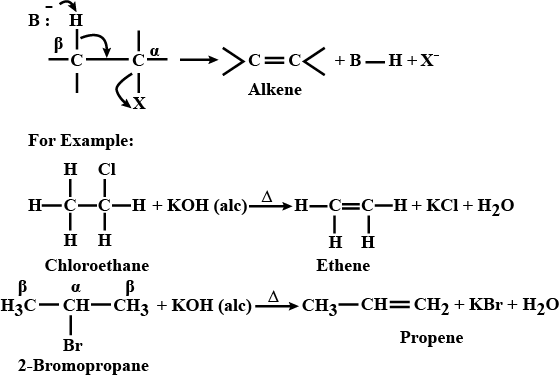
Write and name the reaction when alkyl halide is treated with alcoholic KOH.
How are the following conversions carried out? (xii) But I- ene to n-butyliodide
How are the following conversions carried out?( xvi) 2-Bromopropane to 1-Bromopropane
The major product of the following reaction is:
How are the following conversions carried out? (xix) tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide
How are the following conversions carried out? (xvii) chloroethane to butane
Name the process associated with the following phenomenon:
Fine beam of light entering a small hole in a dark room, illuminates the particles in its path.
How will you convert the following ?
Bromoethane to iodoethane.
What is the action of the alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide on ethyl bromide?
How will you bring the following conversion is not more than two steps
(ii) 1- Bromopropane to 2- Bromopropane
Write chemical equation of Wurtz reaction.
Fill in the blanks :
Alkyl chloride is a ________ compound while vinyl chloride is inert towards nucleophilic substitution.
Vinyl chloride on reaction with dimethyl copper gives ____.
Fill in the blanks :
Another name of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane is ___________.
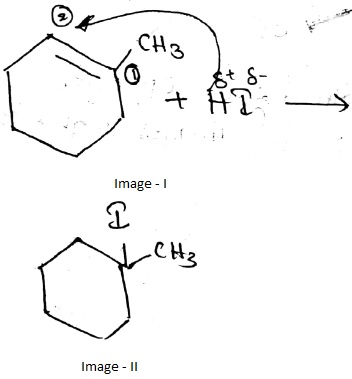
What is the final product in the given reaction?
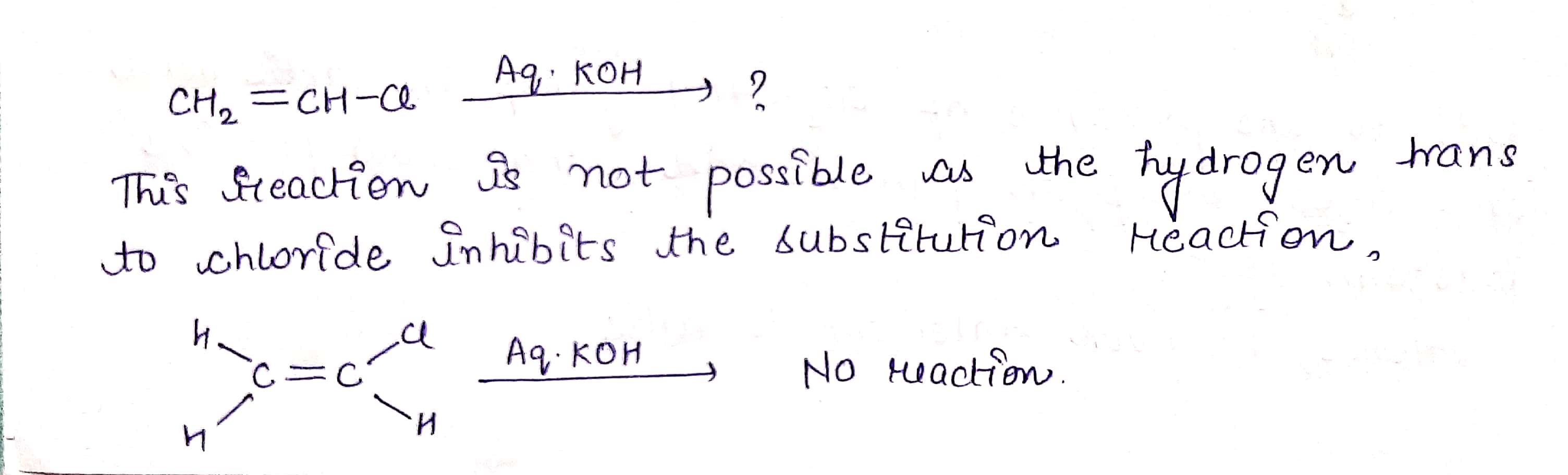
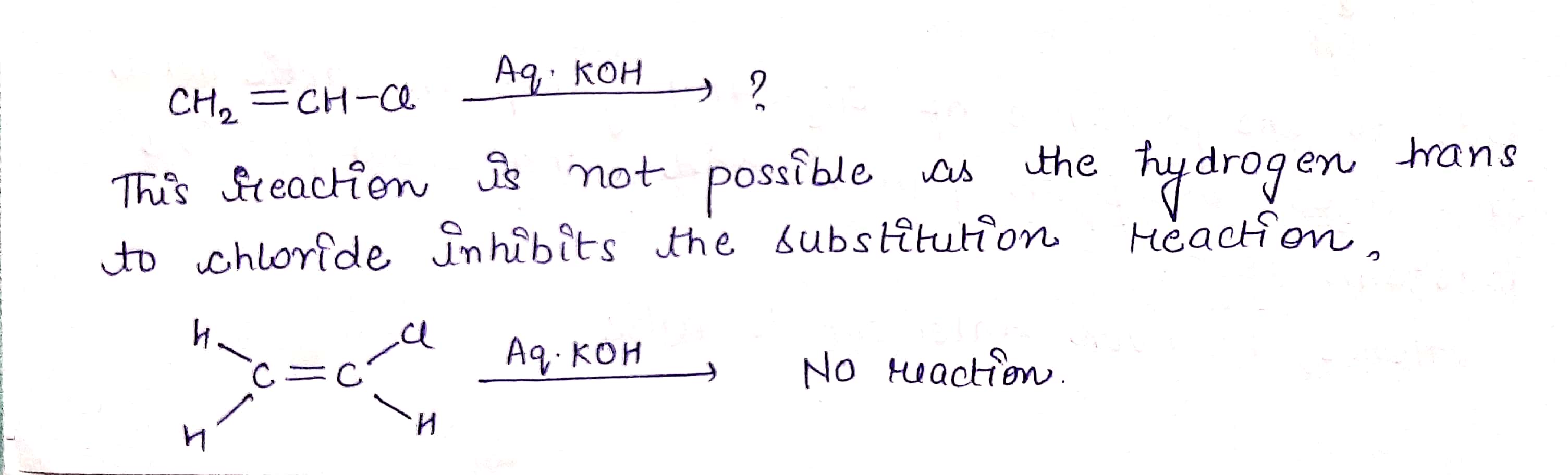
H2C=CHCl −→−−−−aq.KOHH2C=CHCl →aq.KOH ?
H2C=CHCl −→−−−−aq.KOHH2C=CHCl →aq.KOH ?
What is the final product in the given reaction?
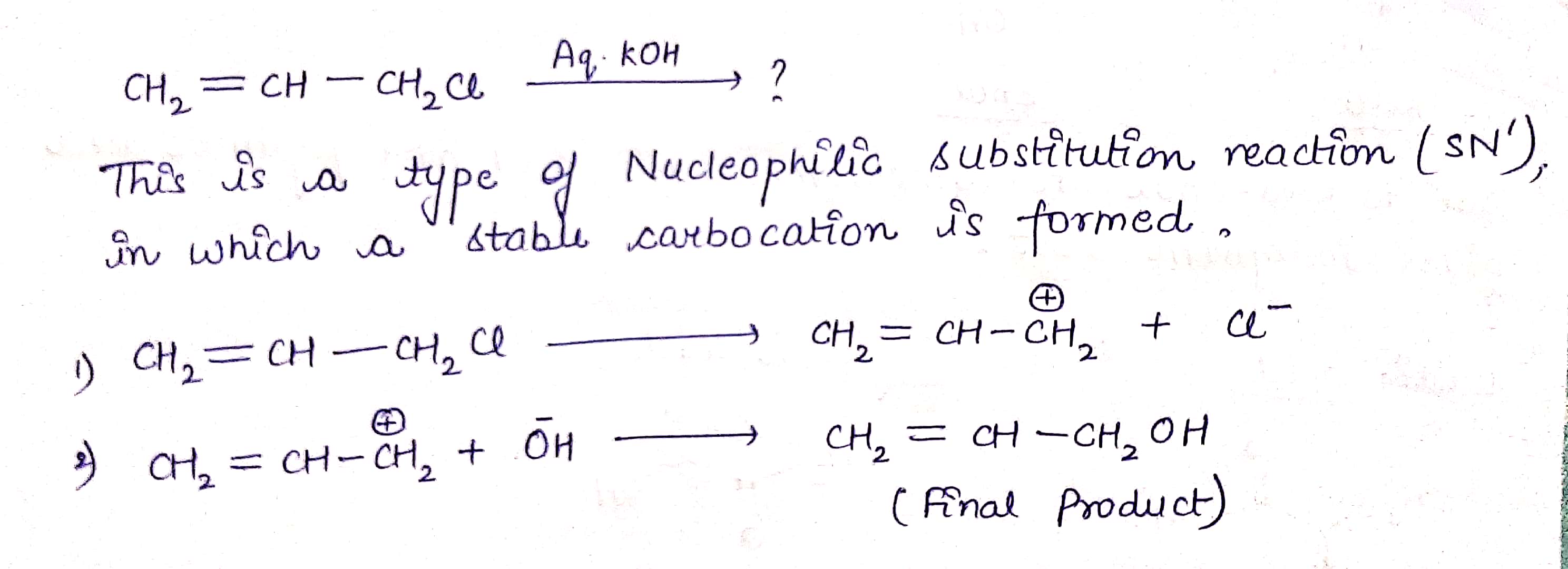
$$ H_2C=CH -CH_2Cl \ \ \xrightarrow { Aq.KOH } $$ ?
$$ H_2C=CH -CH_2Cl \ \ \xrightarrow { Aq.KOH } $$ ?
What is the final product in the given reaction?
CH3Li−→−−−−−CH2=CH2CH3Li→CH2=CH2 ?
CH3Li−→−−−−−CH2=CH2CH3Li→CH2=CH2 ?
What is the final product in the given reaction?
$$ H_2C=CHCl \ \ \underrightarrow {Aq. KOH} $$ ?
$$ H_2C=CHCl \ \ \underrightarrow {Aq. KOH} $$ ?
Complete the following by providing (A), (B), (C) and (D):
$$ CH_2CH_2CH=CH_2 \xrightarrow [Light]{NaI} (A) \xrightarrow {AlcKOH} (B) \xrightarrow {HBr}(C) $$
What is the final product in the given reaction?
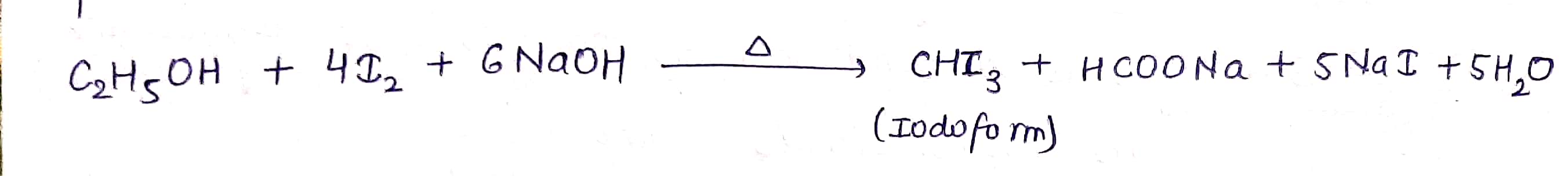
$$ C_2H_5OH \xrightarrow [NaOH]{I_2 } ? $$
What happens when ethyl bromide is treated with alcoholic caustic soda? Give equations only.
Explain the following:
Alkyl iodides become darken on standing in presence of light.
Alkyl iodides become darken on standing in presence of light.
How will you prepare the following compounds from benzene?
Chlorobenzene.
Which of the following compounds are optically active compound?
(i) Butan-1-ol
(ii) Heptan-4-ol
(iii) 2-Chlorobutane
(iv) 3-CHloropentane
(v) Pentan-2-ol
(vi) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(vii) Penta-2, 3-diene
Answer the following:
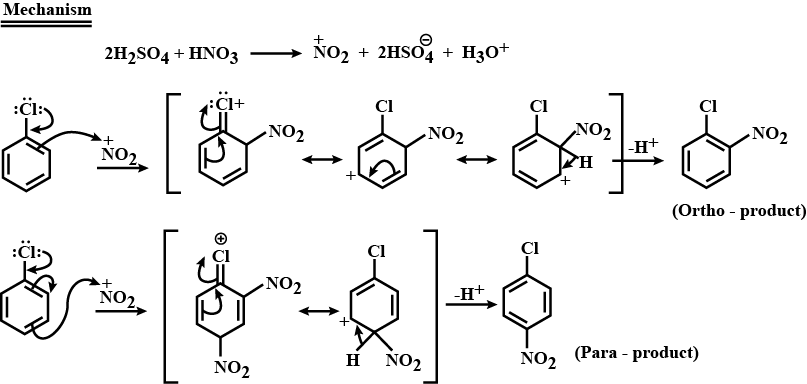
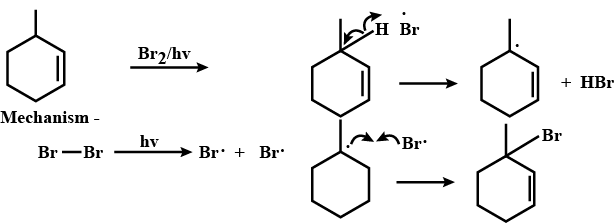
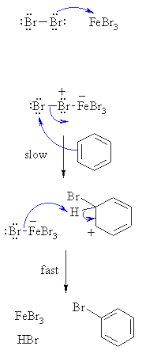
Give the mechanism of halogenation of benzene.
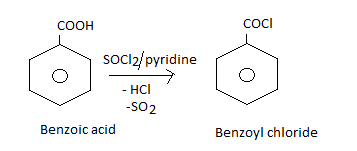
How will you obtain the following from benzoic acid?
Benzoyl chloride.
Identify the following compounds:

Complete the above :
Identify (B)
Identify the following compounds:

Write IUPAC name of (i).
Identify (X), (Y), and (Z) in the following synthetic scheme and write their structures.
$$ CH_3CH_2C \equiv C - H \xrightarrow[CH_3CH_2Br]{NaNH_2} X \xrightarrow[]{H_2 / Pd-BaSO_4} Y \xrightarrow[]{Alkaline \ KMnO_4} Z$$
Is the compound (Z) optically active? Justify your answer.
What do you understand by the term optical activity of compounds?
Draw the structure of the major monohalo product for the above reaction:
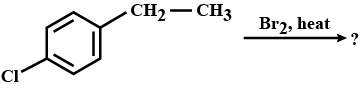
Write IUPAC name of (ii)
Give the IUPAC name of $$ (CH_{3})_{3}CCH_{2}Br $$
Write IUPAC name of (iii)
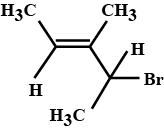
Write the major product (s) in the following reaction:
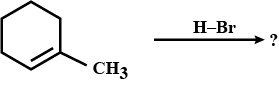
Identify the compounds $$A,B$$ and $$C$$ in the following reaction:
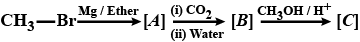
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
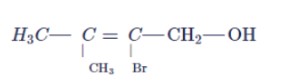
Give balanced equation when: "Ethene reacts with chlorine"
Write the IUPAC name of the above compounds:
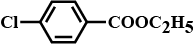
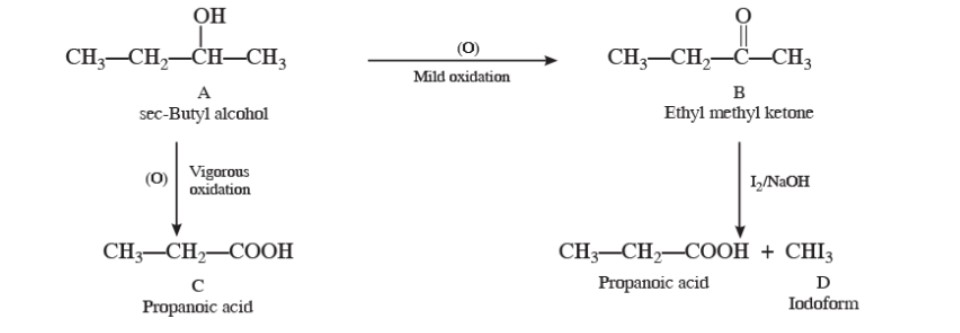
A compound 'A' is optically active. On mild oxidation, it gives a compound 'B' but on vigorous oxidation gives another compound 'C'. C along with D is also formed from B by reaction with iodine and alkali. Deduce the structures of A, B, C, and D.
Name the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and classify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$(CH_3)_2CHCH(Cl)CH_3$$
Identify the product of the following reaction:
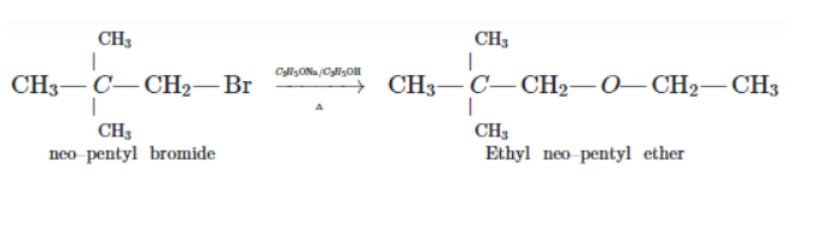
$$CH_3 - \underset{CH_3}{\underset{|}{\overset{\,\,\,\,\, CH_3}{\overset{|}{C}}} -} CH_2 - Br \xrightarrow {C_2H_5OH}$$
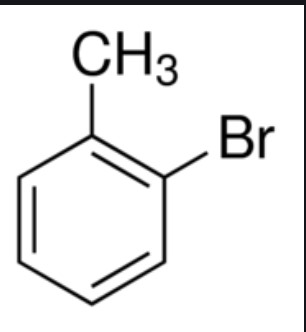
Give the IUPAC name of the following organic compound:
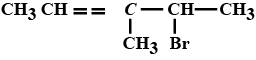
Write structures of compounds $$A, B$$ and $$C$$ in each of the following reactions:
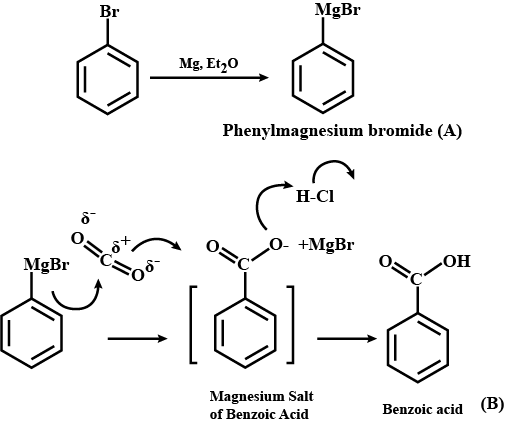
$$C_6H_5Br \ \underrightarrow {Mg/dry\ ether}\ \ A \ \ \ \underset{(b)\ H_3O^+}{\underrightarrow{(a)\ CO_2(g)}}\ \ \ B \ \ \ \underrightarrow {PCl_5}\ \ \ C$$
Give the IUPAC name of the following organic compound:
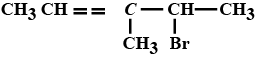
Name the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and classify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$CH_3CH_2CH(CH_3)CH(C_2H_5)Cl$$
Name the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and classify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
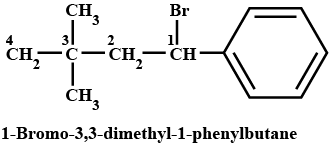
$$(CH_3)_3CCH_2CH(Br)C_6H_5$$
Name the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and classify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$CH_3CH=C(Cl)CH_2CH(CH_3)_2$$
Name the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and classify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
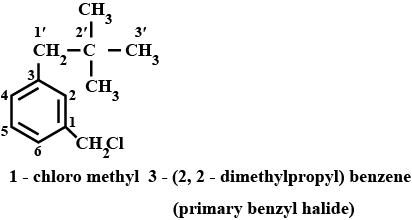
$$m-ClCH_2C_6H_4CH_2C(CH_3)_3$$
Name the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and classify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$CH_3C(Cl)(C_2H_5)CH_2CH_3$$
Name, the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and calssify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$o-Br-C_6H_4CH(CH_3)CH_2CH_3$$
Name the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and classify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$CH_3C(C_2H_5)_2CH_2Br$$
Name, the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and calssify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$CH_3CH=CHC(Br)(CH_3)_2$$
Name, the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and calssify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$CH_3CH_2C(CH_3)_2CH_3l$$
Name, the following halides according to $$IUPAC$$ system and calssify as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
$$CH_3CH(CH_3)CH(Br)CH_3$$
How will you bring about the following conversions?
Ethane to bromoethene
The parts of the structure of an organic compound are given above.
a. Write a completed structure of an organic compound by connecting all the groups given above.
b. Write the IUPAC name of the compound
c. Write the structure of a position isomer of the compound.
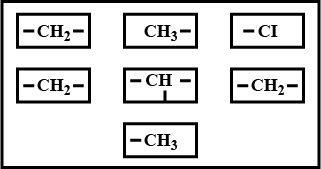
Chloroform can be prepared from methane. Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Chloroform can be prepared from methane. What is the name of reaction when chloroform is prepared from methane?
Write down the IUPAC name of the given compound.
$$CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2-Cl$$
What happens when
methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether,
What happens when
n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic $$KOH$$
Complete stages $$2,3$$ and $$4$$ in the respective order.

Write the IUPAC name of the above:
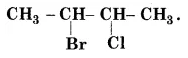
Give the $$IUPAC$$ name of the following compounds:
$$CH_3CH(Cl)CH(Br)CHCH_3$$
Ethyne is a compound that belongs to the class of alkynes.
Write the chemical equation for the preparation of following compounds from ethyne.
Chloro ethane
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound:
$$CH_{3} - CH_{2} - \underset{Br} {\underset {|} {\overset{\,\,\,CH_3}{\overset{|}{C}}}} - \underset{Br} {\underset {|} {C}}H-CH_{2}Cl $$
Give the IUPAC name of the following:
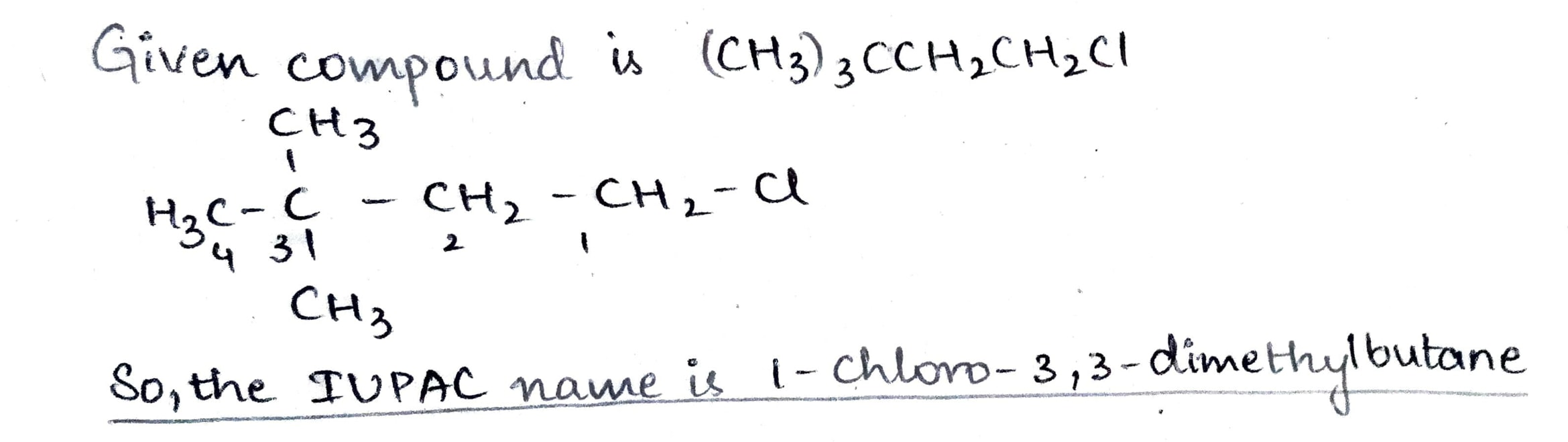
$$(CH_{3})_{3} CCH_{2} CH_{2} Cl$$
Write the structural formula and give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
Allyl chloride
Write the structures of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
$$(CH_{3})_{2} CH - CH(Br) CH_{2} CH_{3} \xrightarrow[ethanol/heat]{C_2H_5ONa} $$
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
$$CH_{3} CH (Cl) CH (Br) CH_{3} $$
$$CH_{3} CH (Cl) CH (Br) CH_{3} $$
How can the following reactions be used to prepared alkanes?
Wurtz reaction
Wurtz reaction
Give the structure of the products $$(X)$$ in the following reactions:
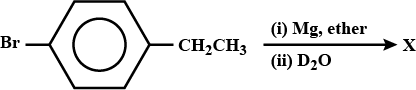
Wat are haloalkanes ? How are they named according to IUPAC system. How can haloalkanes be prepared from
(i) alcohols (ii) alkenes and (iii) alkanes ?
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
$$Cl CH_{2} CH_{2} Cl $$
Wurtz reaction is a good method for the preparation of alkanes containing even number atoms but not for alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms. Comment.
Match the following
| Column I | Column II |
is eliminated through as a base
(B) A molecule of the HBr E1cb mechanism. Ethoxide ion acts as is eliminated through as a base
(C) A molecule of HBr is E1 mechanism. Moist silver oxide eliminated through (silver hydroxide) acts as a base
Is the above reaction an example of solvolysis reaction? Give the reason for your answer.
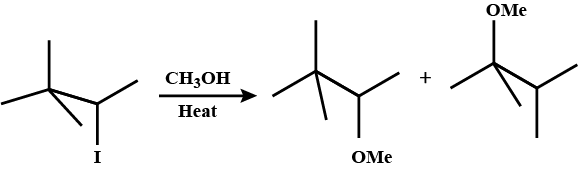
Draw structural formulas for the alkene(s) formed by treatment of each haloalkane or halocycloalkane with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Assume that elimination occurs by an $$E2$$ mechanism.
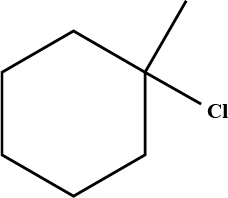
Predict the $$\beta$$-elimination product(s) formed when each chloroalkane is treated with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. If two or more products might be formed, predict which is the major product.
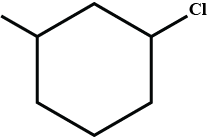
What is the product of the reaction?
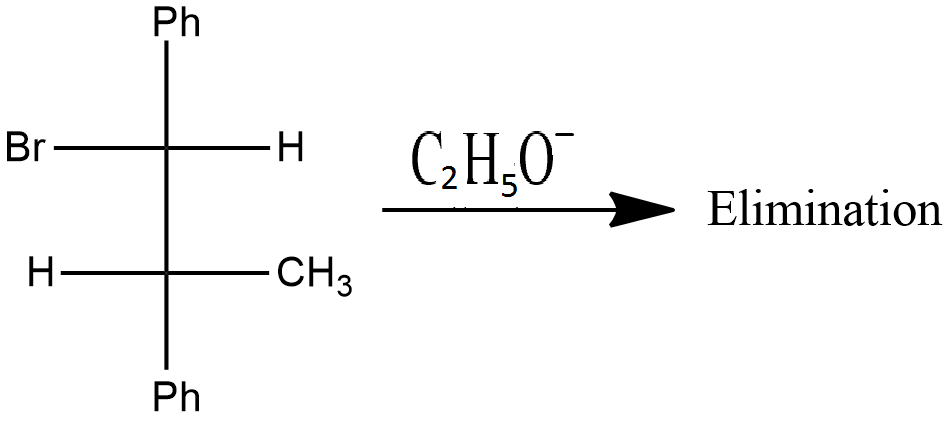
Is the above reaction an example of solvolysis reaction? Give the reason for your answer.
Which compound in the given pair undergoes solvolysis in aqueous ethanol more quickly?
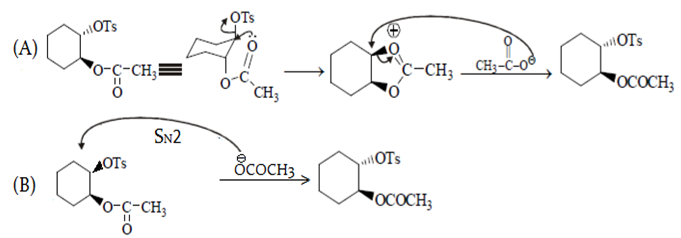
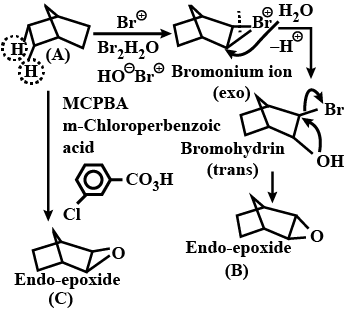
Products is $$Cis-Ph({ CH }_{ 3 })C=CHPh$$.
State whether the statement is true or false
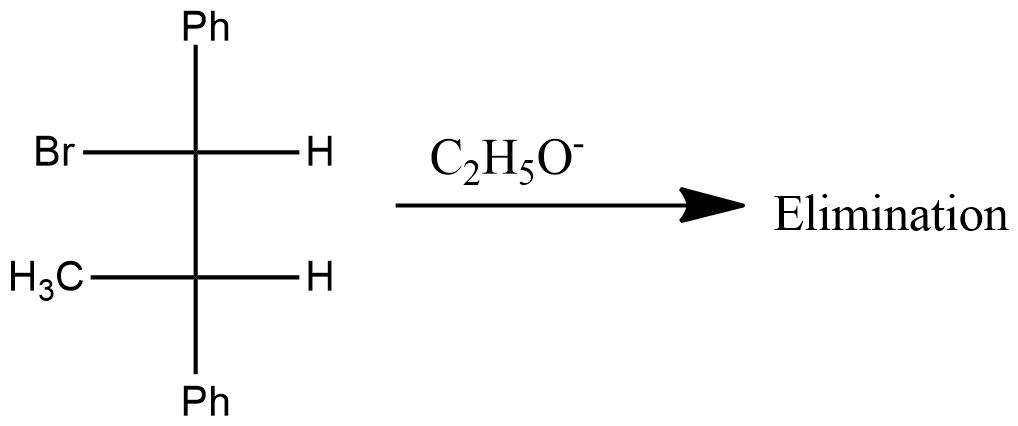
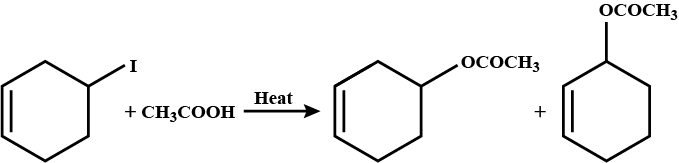
What is the product(s) of the following reaction?
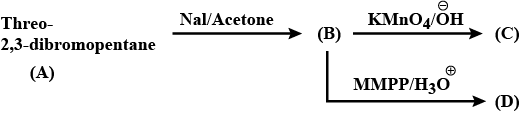
Give the stereochemical structures of B and C.$$\begin{matrix}Threo- & & & & \\ 2, 3 - dibromobutane & \xrightarrow{NaI / Acetone} & (B) & \xrightarrow[KMnO_4]{Cold\ alk.} & (C) \\ (A) \end{matrix}$$
Give the stereochemical structures of B, C, and D.
When $$1,2-$$ dibromodecane was treated with potassium hydroxide in aqueous ethanol, it yielded a mixture of three isomeric compounds was converted to 1-decyne on reaction with sodium amide in dimethyl sulphoxide. Identify these three compounds.
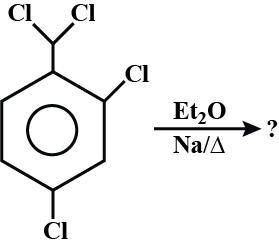
What is the product(s) of the following reaction?
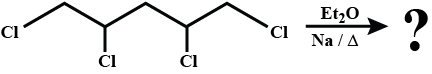
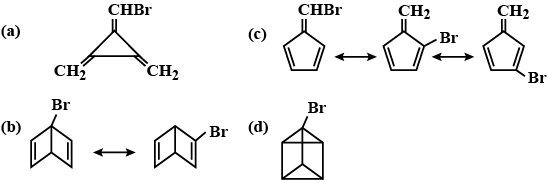
Match the compounds/reactions in List I with their stereochemistry in List II. Matching can be one or more than one.
Match the compounds/reactions in column I with their number of isomers in column II. Matching can be one or more than one.
Match the compounds/reactions in column I with their correct number of isomers in column II. Matching can be one or more than one.
Match the compounds/reactions in List 1 with their mechanism in ListMatching can be one or more than one.
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
(i) $$CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl + NaI \xrightarrow [heat ]{acetone} $$
(ii) $$(CH_3)_3CBr+KOH \xrightarrow [heat]{ ethanol }$$
(iii) $$CH_3CH(Br)CH_2CH_3 + NaOH \xrightarrow []{water} $$
(iv) $$(CH_3)_3CBr+KOH \xrightarrow [heat]{ ethanol }$$
(v) $$C_6H_5ONa + C_2H_5Cl \longrightarrow$$
(vi) $$CH_3CH_2CH_2OH + SOCl_2 \longrightarrow$$
(vii) $$CH_3CH_2CH = CH_2 + HBr \xrightarrow [ ]{peroxide}$$
(viii) $$CH_3CH = C(CH_3)_2 + HBr \longrightarrow $$
How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Ethanol to but-1-yne (ii) Ethane to bromoethene
(iii) Propene to1-nitropropane (iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Propene to propyne (vi) Ethanol to ethyl fluoride
(vii) Bromomethane to propanone (viii) But-1-ene to but-2-ene
(ix) 1-Chlorobutane to n-octane (x) Benzene to biphenyl.
(i) Ethanol to but-1-yne (ii) Ethane to bromoethene
(iii) Propene to1-nitropropane (iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Propene to propyne (vi) Ethanol to ethyl fluoride
(vii) Bromomethane to propanone (viii) But-1-ene to but-2-ene
(ix) 1-Chlorobutane to n-octane (x) Benzene to biphenyl.
Write the IUPAC name of the above compound.
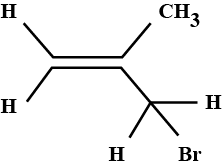
What are the IUPAC rules for naming alkyl halides?
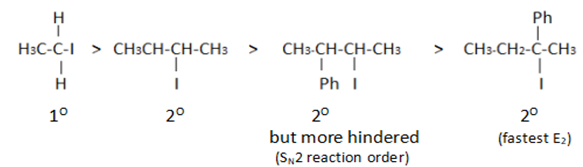
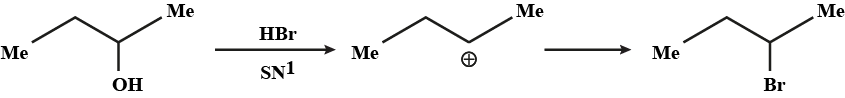
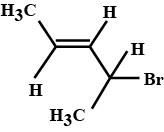
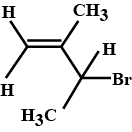
Which would undergo $$S_{N}1$$ reactions faster in the following pair?
$$CH_{3}-CH_{2}-CH_{2}-Br\; $$ and $$\;CH_{3}-CH-CH_{3}$$
|
$$Br$$
|
$$Br$$
(i) $$CH_{2}-Br + KOH \rightarrow CH_{3}OH + KBr$$
Write types of nucelophillic substitution reaction in the above reaction (i) and (ii)?
(b) Write two differences between mechanism of reaction (i) and (ii)?
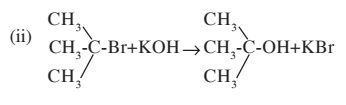
Write the chemical equation of following reaction?
(a) Wurtz reaction
(b) Finkelstein reaction.
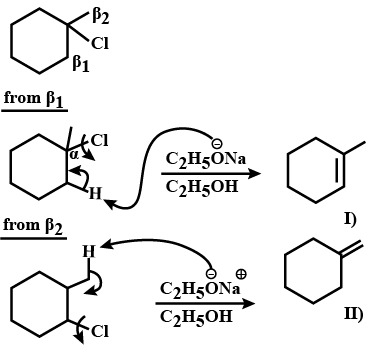
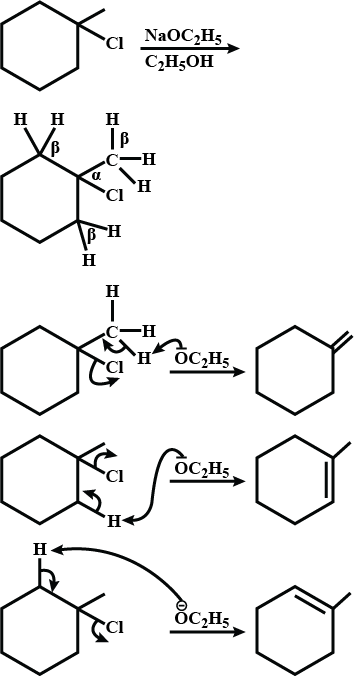
Write the structure of the alkene formed by dehydrohalogenation of $$1$$-bromo-$$1$$-methylcyclohexane with alcoholic KOH.
Name the following reaction.
$$H_3C-Br+AgF\rightarrow H_3C-F+AgBr$$.
Wurtz reaction fails in case of tert-alkyl halides. Why?
The major product obtained on monobromination $$\left( {B{r_2}/FeB{r_3}} \right)$$ of the following compound A is
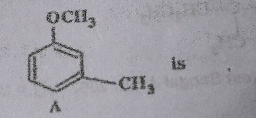
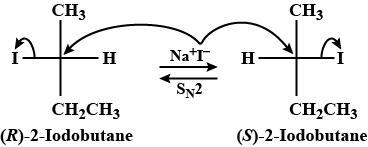
Optically active $$2$$ -iodobutane on treatment with Nal in acetone gives a product which does not show optical activity. Explain briefly.
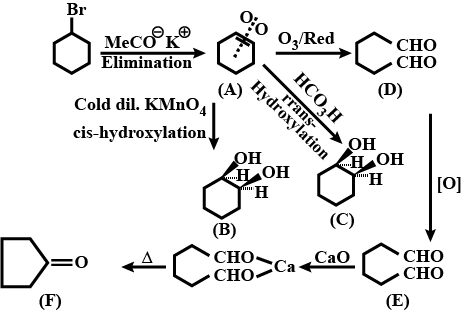
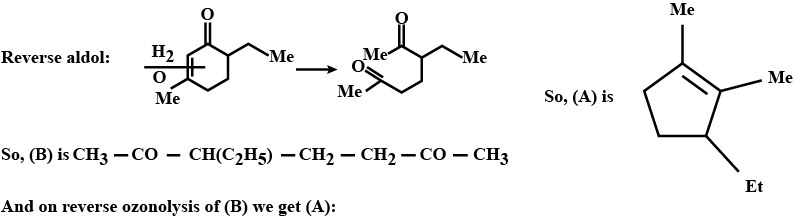
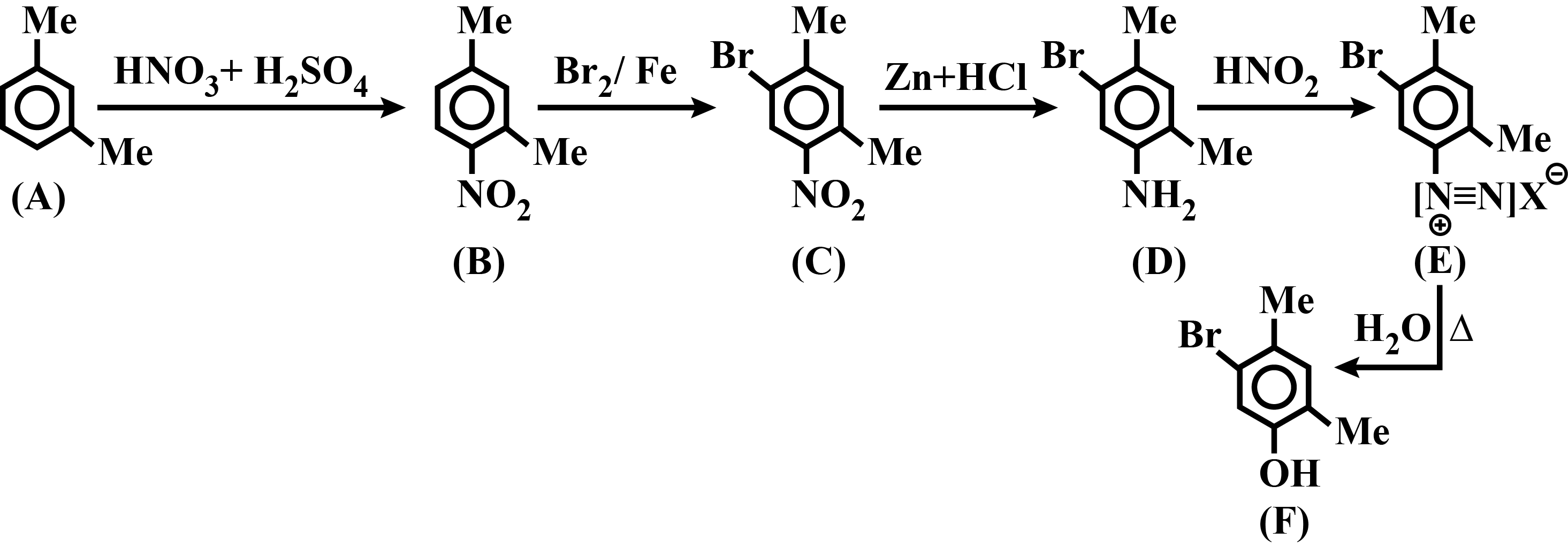
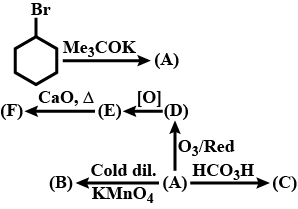
Identify $$A,B,C,D,E$$ and $$F$$ in the following:

Give structure IUPAC names of the products expected from reaction between 1-Chlorobutane and KOH.
Give structure and IUPAC names of the products expected from reaction between 1-Chlorobutane and NaOH(aq).
Give structure and IUPAC names of the products expected from the reaction between 1-Chlorobutane and $$NH_3 $$.
Give structure and IUPAC names of the products expected from reaction between 1-Chlorobutane and $$ C_2H_5ONa $$.
Give structure and IUPAC names of the products expected from the reaction between 1-Chlorobutane and $$ H_2S $$.
Give structure and IUPAC names of the products expected from the reaction between 1-Chlorobutane and $$ C_6H_6 +AlCl_3 $$.
Identify the major and minor products.
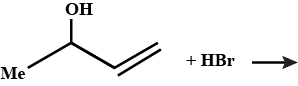
$$2-Butanol+HBr\to$$
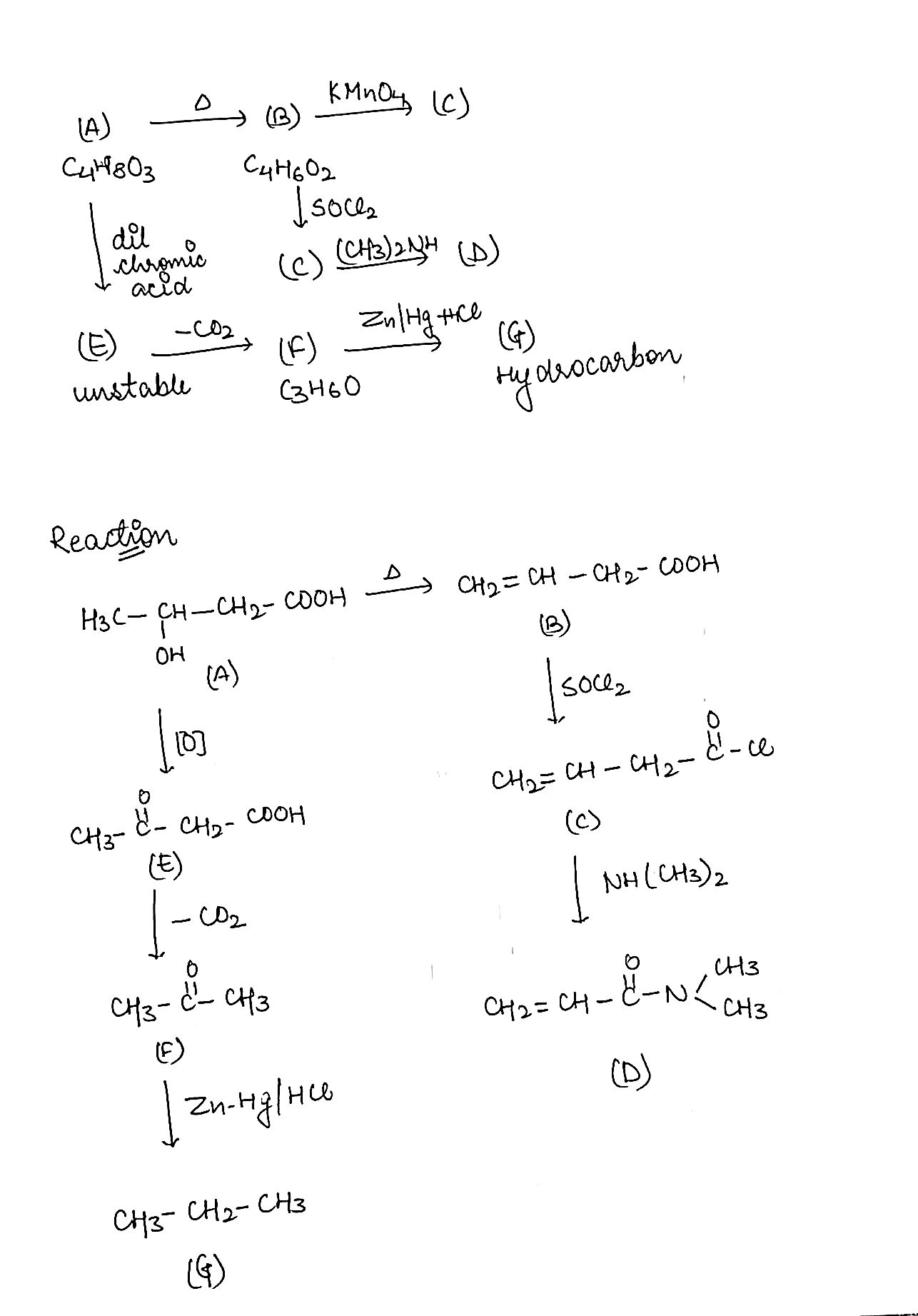
An acidic compound $$(A)$$. $$({C}_{4}{H}_{8}O)$$ loses its optical activity on strong heating yielding $$(B)$$ $$({C}_{4}{H}_{6}{O}_{2})$$ which reacts readily with $$KMn{O}_{4}$$. $$(B)$$ forms a derivative $$(C)$$ with $$SO{Cl}_{2}$$ which on reaction with $${({CH}_{3})}_{2}NH$$ gives $$(D)$$. The compound $$(A)$$ on oxidation with dilute chromic acid gives an unstable compound $$(E)$$ which decaboxylates readily to give $$(F)$$ ($${C}_{3}{H}_{6}O$$). The compound $$(F)$$ gives a hydrocarbon $$(G)$$ on treatment with amalgamated $$Zn$$ and $$HCl$$. Give the structures of $$(A)$$ to $$(G)$$ with proper reasoning.
Identify the following compounds:
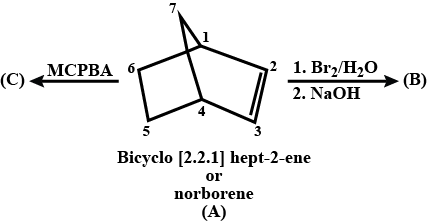
Complete the above :
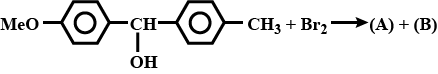
Identify the major and minor products.
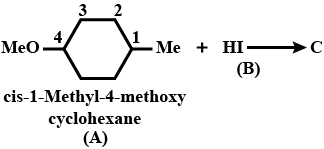
Identify the following compounds:
Identify the following compounds:
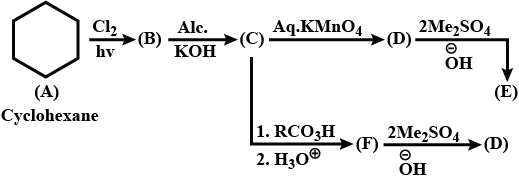
Complete the above:

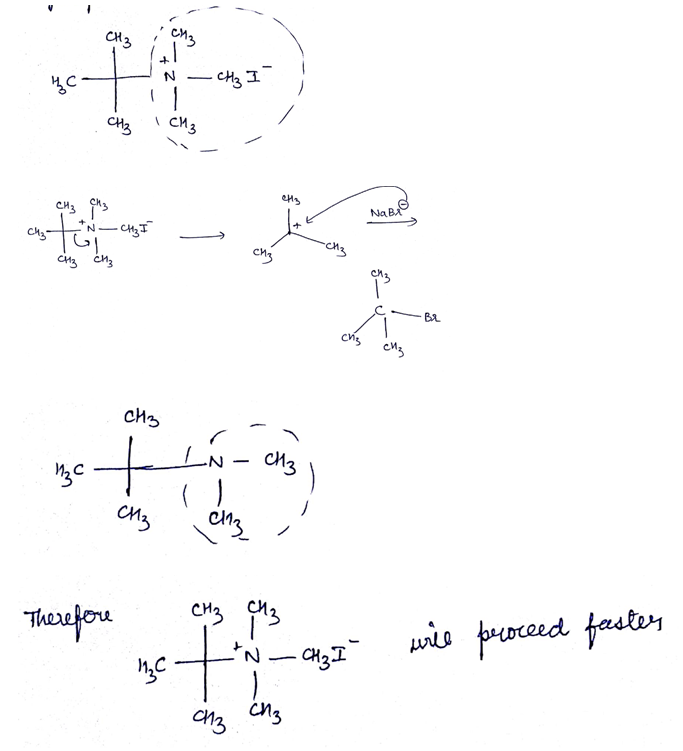
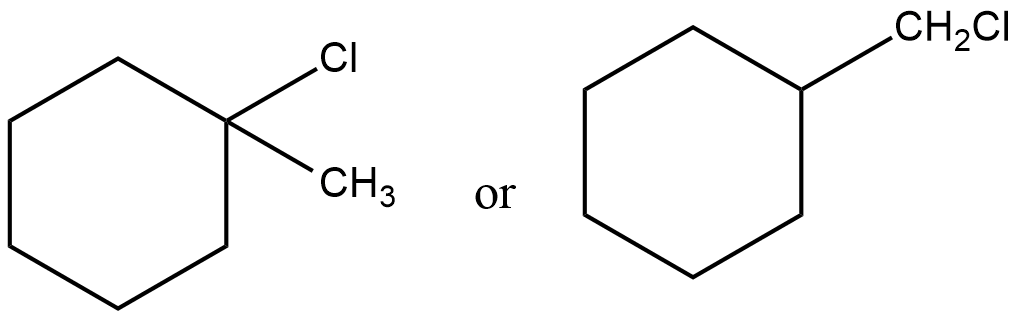
Of the following pairs, which is the faster $$SN^1$$ reactions?
How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
$$1-$$ Chlorobutane to $$n-$$octane
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
$$ CH_3CH_2Cl+SbF_3 \xrightarrow [ ]{ Heat } $$
Show both substitution and elimination products in these reactions.
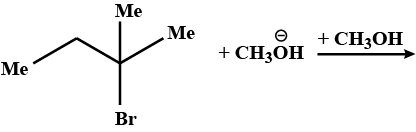
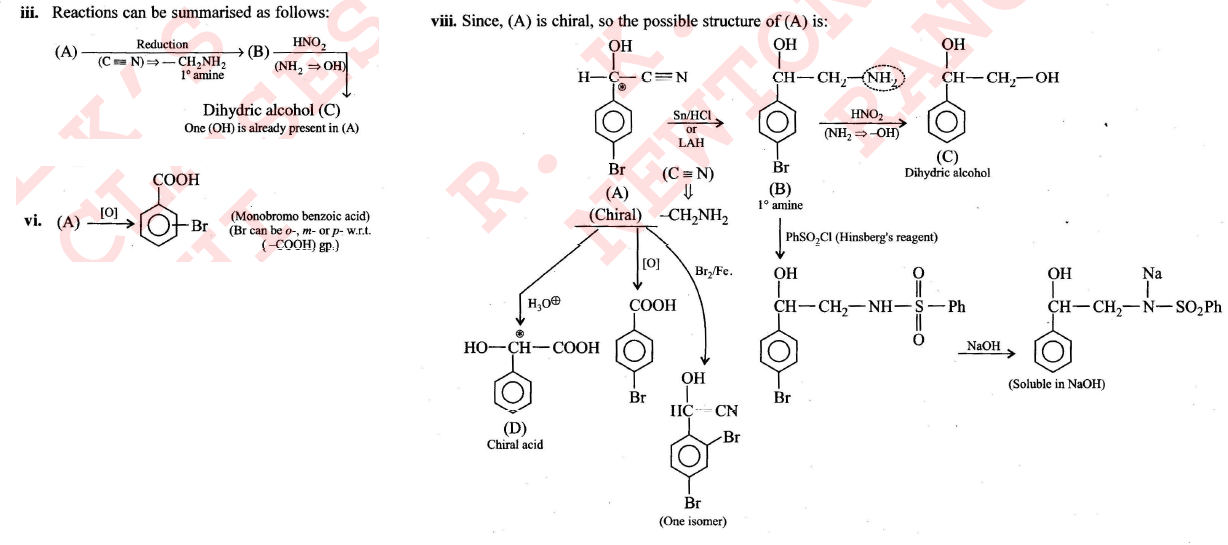
Compound $$(A), C_8H_6NOBr$$, is optically active. Reduction of $$(A)$$ gives $$(B)$$ which reacts with nitrous acid to form $$(C)$$, dihydric alcohol. Benzene sulphonyl chloride reacts with $$(B)$$ to give a product soluble in $$NaOH$$. Hydrolysis of $$(A)$$ gives $$(D)$$ which is an optically active acid. $$(A)$$ does not give any precipitate with aqueous $$AgNO_3$$. Controlled oxidation of $$(A)$$ gives monobromo benzoic acid. Compound $$(A)$$ on reaction with $$Br_2/Fe$$ gives only one compound. Identify $$(A), (B), (C)$$, and $$(D)$$.
Convert the following:
$$2$$-bromobutane to $$3, 4$$-dimethylhexane
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the above reactions:
State the conditions under which following preparations are carried out. Give the necessary equations which need not to be balanced.
Methyl chloride from aluminium carbide
Match the compounds in Column 1 with their characteristic(s)/test(s)/reaction(s)/streochemistry, etc., given in Column 2.
Matching can be one or more than one.
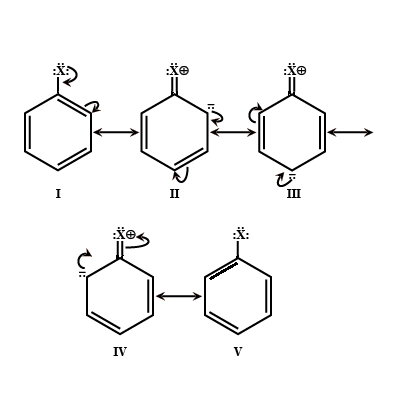
Aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic reagents. Give reason.
An optically active alcohol $$A(C_{6}H_{10}O)$$ absorbs $$2mol$$ of hydrogen per mole of $$A$$ upon catalytic hydrogenation and gives a product $$B$$. The compound $$B$$ is resistent to oxidation by $$CrO_{3}$$ and does not show any optical activity. Deduce the structures of $$A$$ and $$B$$.
Write the structure of the major organic product expected from each of the following reactions:
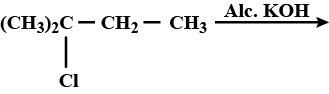
What would be the major product in each of the above reactions?
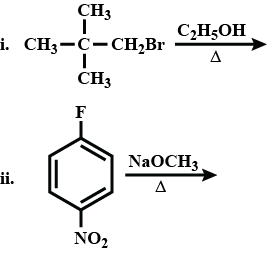
Wurtz reaction fails in case of ter-alkyl halides why?
Complete the following giving the structures of major organic products.
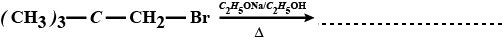
Complete the above reaction.

Identify A to G.
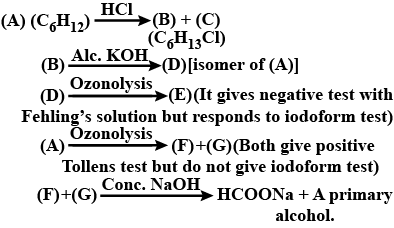
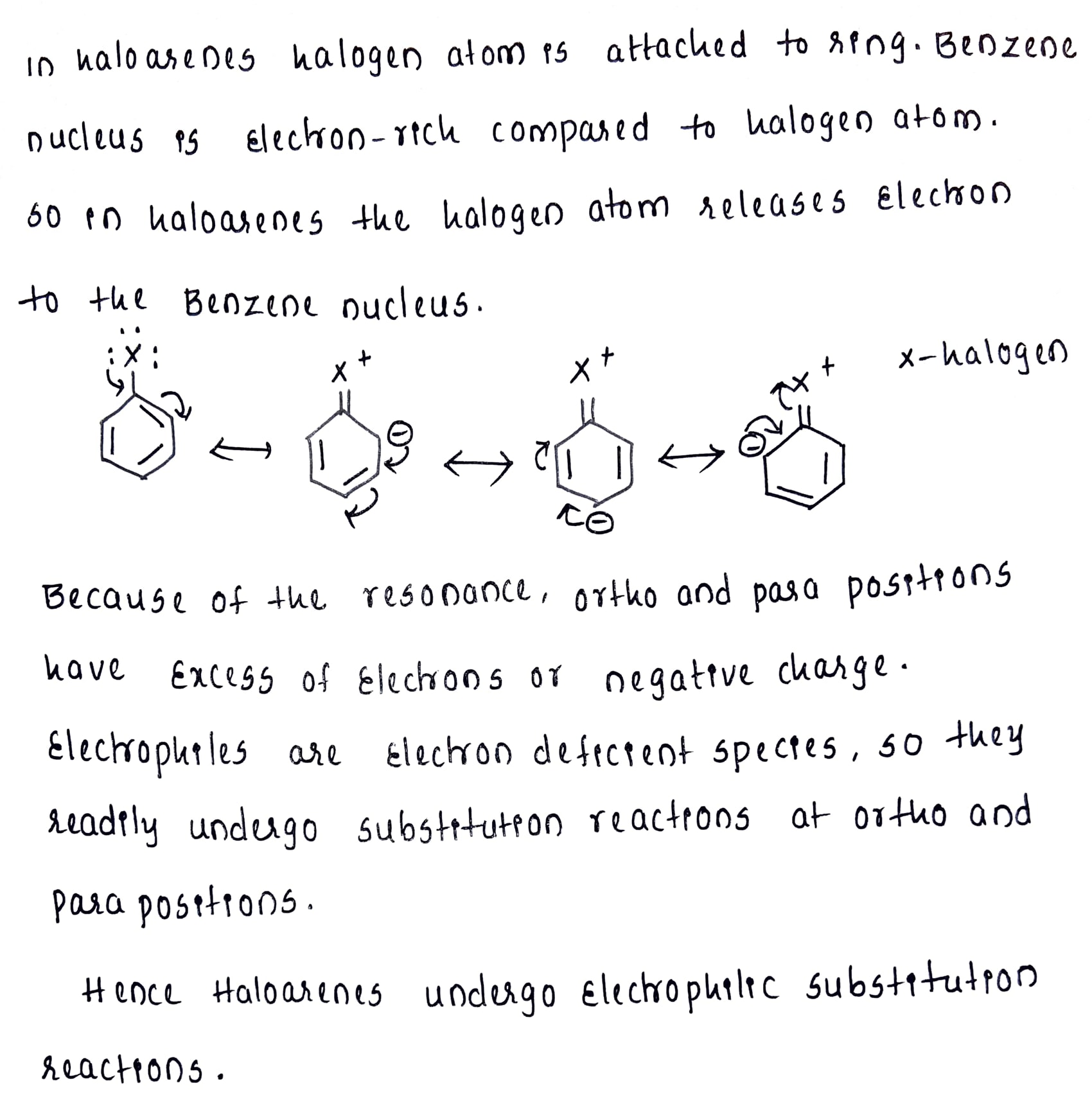
Electrophilic reactions in haloarenes occur slowly. Why?
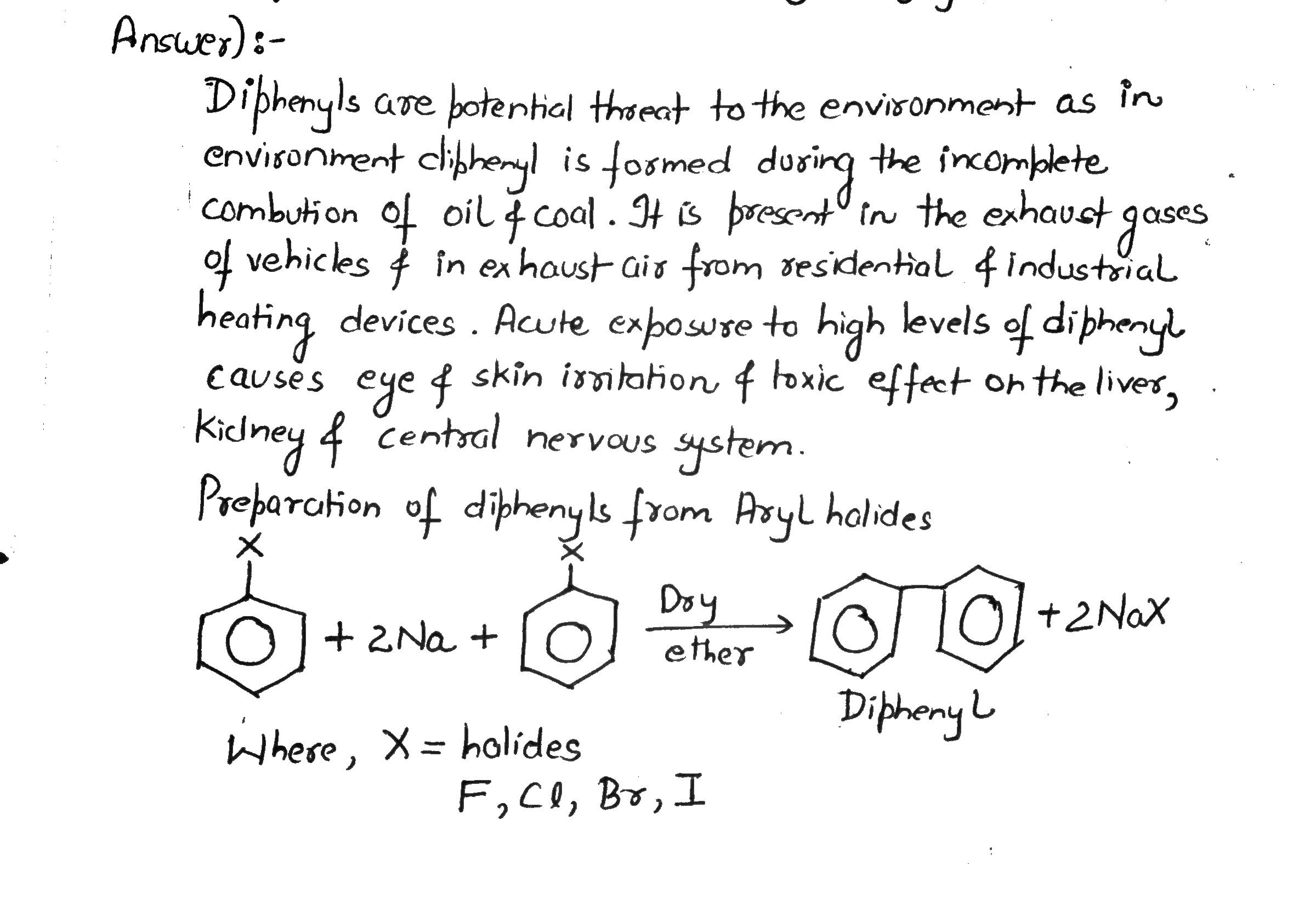
Diphenyls are potential threat to the environment. How are these produced from arylhalides
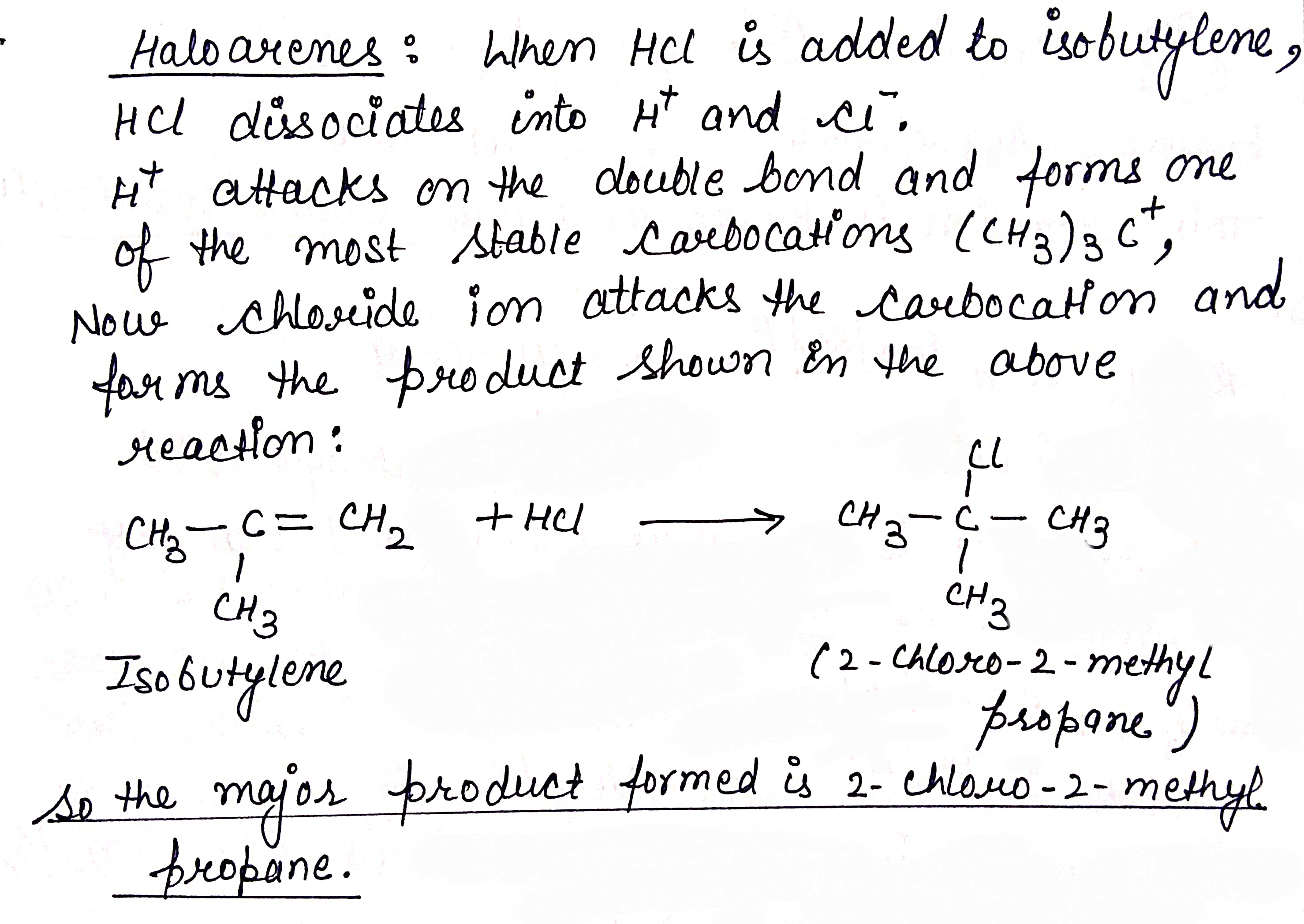
Predict the major product formed when HCl is added to isobutylene. Explain the mechanism involved.
Aryl chloride and bromide can be easily prepared by electrophilic substitution of arenes with chlorine and bromine respectively in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts. But why does preperation of aryl iodides requires presence of an oxidising agent?
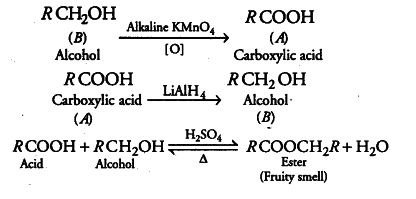
Compound 'A' was prepared by oxidation of compound 'B' with alkaline $$KMnO_{4}$$. Compound 'A' on reduction with lithium aluminum hydride gets converted back to compound 'B'. When compound 'A' is heated with compound B in the presence of $$H_{2}SO_{4}$$ it produces the fruity smell of compound C to which family the compounds 'A', 'B', and 'C' belong to?
Elimination reactions (especially $$ \beta $$ - elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the regents used in both cases.
An alkane $$ C_8H_{18} $$ is obtained as the only product on subjecting a primary a primary alkyl halide to Wurtz reaction. On monobromination this alkane yields a single isomer a tertiary bromide. Write the structure of alkane and the tertiary bromide.
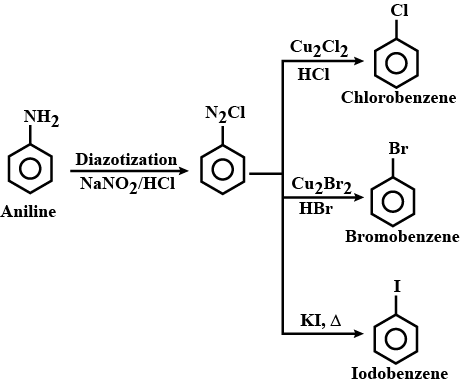
How will you prepare the following from aniline ?
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Bromobenzene
(c) Iodobenzene
Ethyne is a compound that belongs to the class of alkynes.
Write the chemical equation for the preparation of following compounds from ethyne.
$$1,2-$$ dichloroethane
Explain the following:
Directive influence of halogen atom in haloarene.
Explain $$\beta$$- elimination.
Why are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than alkyl halides. How can we enhance the reactivity of aryl halides?
Explain the following:
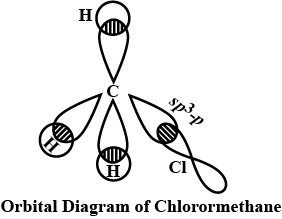
Nature of $$C-X$$ bond in halogen derivatives.
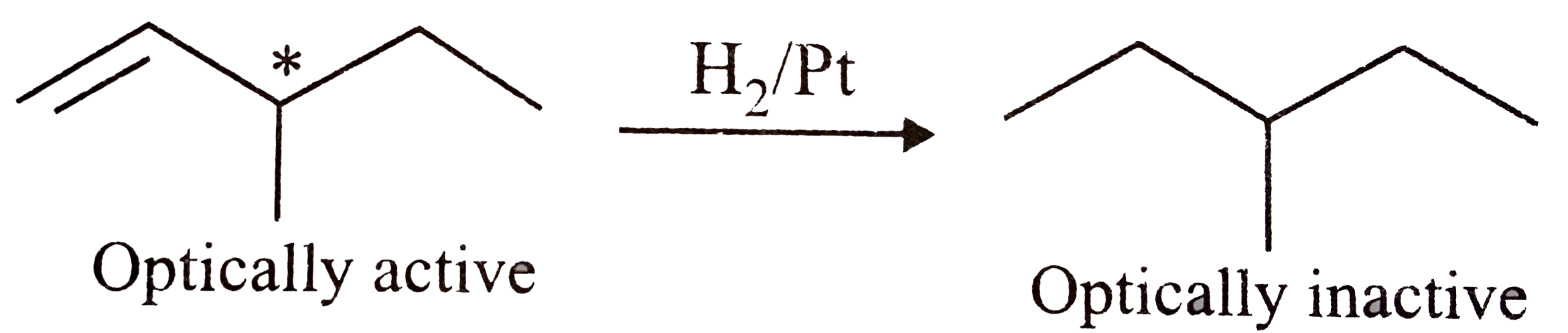
Give the structure of an optically active hydrocarbon $$(C_6H_{12})$$ which on catalytic hydrogenation gives an optically inactive compound $$(C_6H_{14})$$.
What is Wurtz reaction? How can it be used to prepare butane?
What is Wurtz reaction? What are its limitations? How have these limitations been overcome?
Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, $$E^+$$.
(i) Chlorobenzene, $$2,4-$$dinitrochlorobenzene, $$p-$$nitrochlorobenzene
(ii) Toluene, $$p-H_3C-C_6H_4-CH_3, p-H_3C-C_6H_4-NO_2, p-O_2N-C_6H_4-NO_2$$
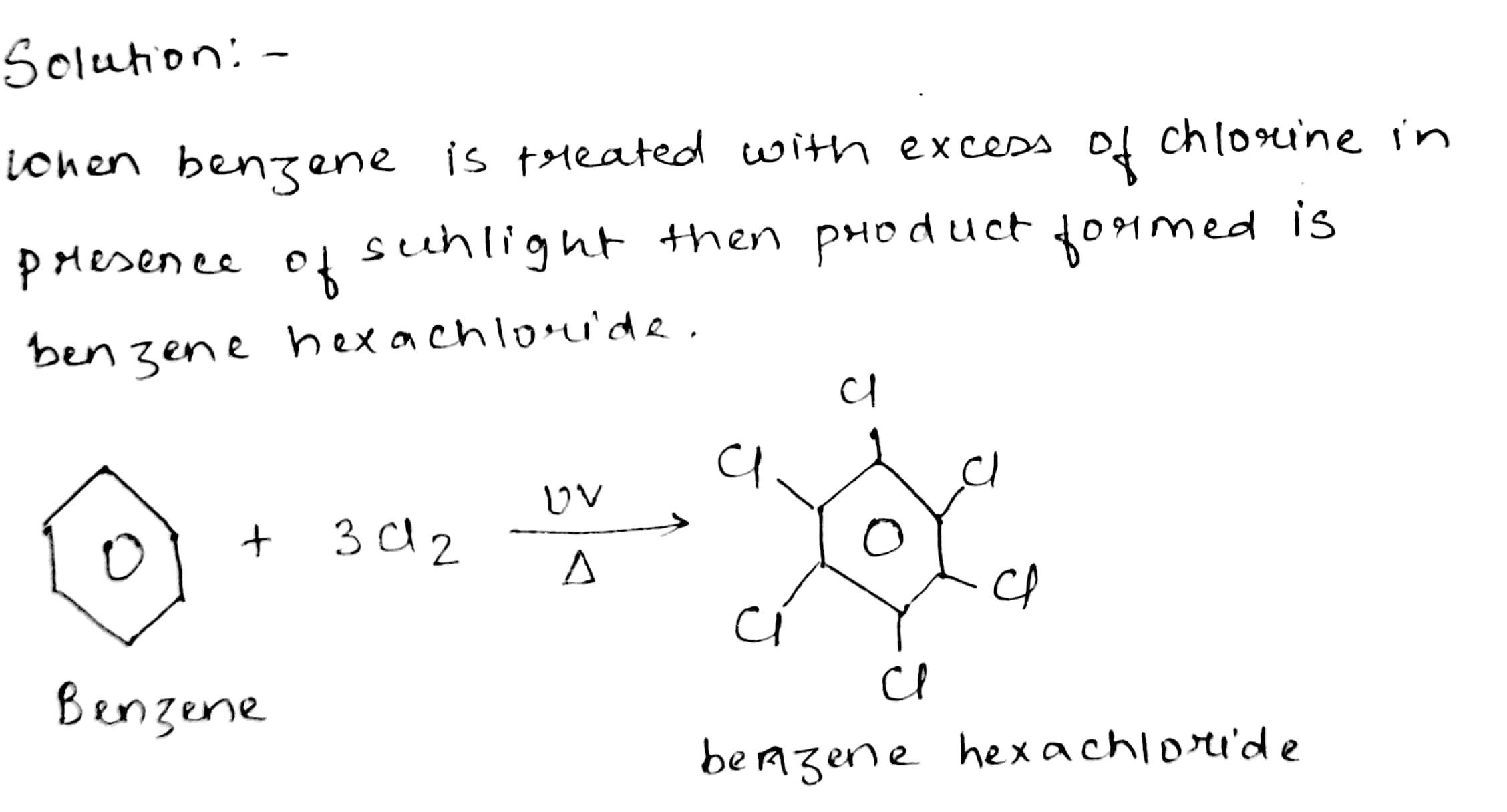
Name the product formed when benzene is treateded with excess of chlorine in presence of sunlight.
Draw the structures of the major monohalo product in each of the following reactions:
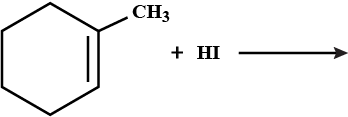
Draw the structures of the major monohalo product in each of the following reactions:
$$CH_{3} CH_{2} C \equiv CH + HCl $$ (1 equiv) $$ \rightarrow $$
Will you get any precipitate if you add silver nitrate solution to chloromethane? If not, why?
Draw the structures of the major monohalo product in each of the following reactions:
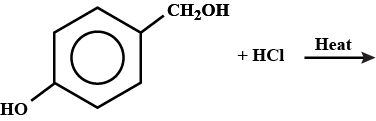
Draw the structures of the major monohalo product in each of the following reactions:
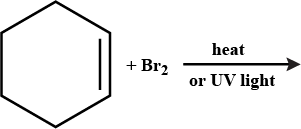
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl (primary, secondary, tertiary) allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl, or aryl halide.
(i) $$CH_{3} CH (CH_3)CH(Br)CH_{3} $$
(ii) $$CH_{3} CH_{2} C (CH_3)_{2} CH_{2} I $$
(iii) $$p-ClC_6H_4CH_2CH(CH_3)_2$$
(iv) $$CH_3CH=CHC(Br)(CH_3)_2$$
(i) $$CH_{3} CH (CH_3)CH(Br)CH_{3} $$
(ii) $$CH_{3} CH_{2} C (CH_3)_{2} CH_{2} I $$
(iii) $$p-ClC_6H_4CH_2CH(CH_3)_2$$
(iv) $$CH_3CH=CHC(Br)(CH_3)_2$$
How many monochloro products would you expect when $$2-$$methylbutane is chlorinated? Write their structures and $$IUPAC$$ names. One of them may have stereoisomer. Indicate it.
Give the structure of an alkene $$(C_4H_8)$$ which when treated with $$H_2O / H_2SO_4$$ gives $$C_4H_{10}O$$ which cannot be resolved into optical isomers.
Write the structural formula and give the IUPAC name of the given compound :
o-bromotoluene
Explain why alkyl halides are generally not prepared in the laboratory by free radical halogenation of alkanes.
How many primary halides are possible for the molecular formula, $$C_{5}H_{11}Br$$? Give their structures and IUPAC names.
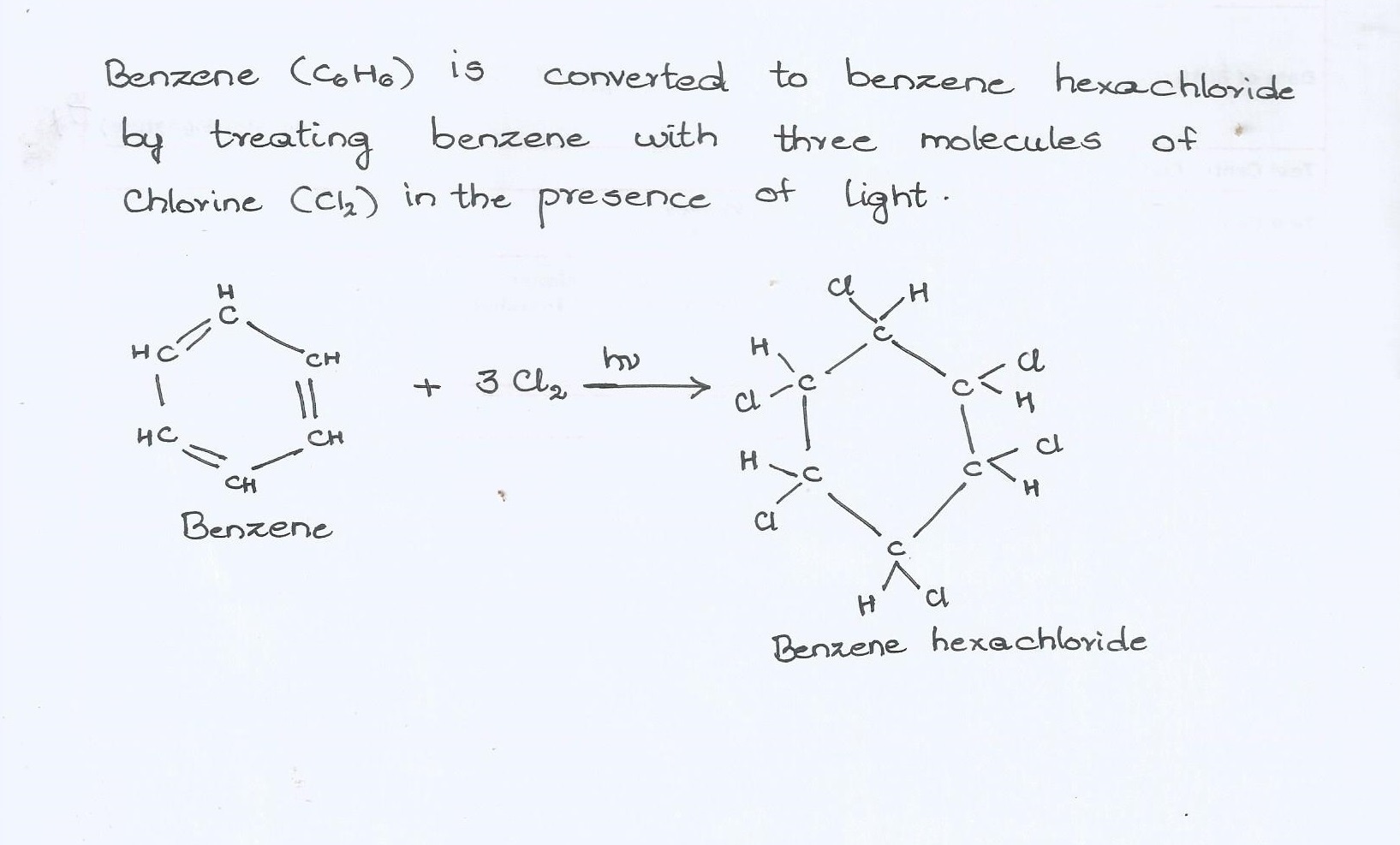
How are the following conversions carried out ?
Benzene into benzene hexachloride
Explain why free radical bromination of n-butane yields $$2$$-bromobutane as the major product.
Account for the following:
Haloarenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
What are haloarenes ? How are they classified ? Give one method each for the preparation of nuclear and side chain substituted haloarenes.
Give a brief account of the following with one example of each.
Wurtz reaction.
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
$$(CH_{3})_{3} CCH = C (Cl) C_{6}H_{4} I - p $$
$$(CH_{3})_{3} CCH = C (Cl) C_{6}H_{4} I - p $$
How do the products differ when ethyl bromide reacts separately with aqueous $$KOH$$ and alcoholic $$KOH$$ ?
n-Butane is produced by monobromination of ethane followed by Wurtz reaction. Calculate the volume of ethane at NTP required to produce $$55\ g $$ of n-butane, if the bromination takes place with $$90$$ percent yield and Wurtz reaction with $$85$$ percent yield.
Explain why chlorination of n-butane in presence of light at $$298\ K $$ gives a mixture of $$72\%$$ of 2-chlorobutane and $$28\%$$ of 1-chlorobutane.
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions