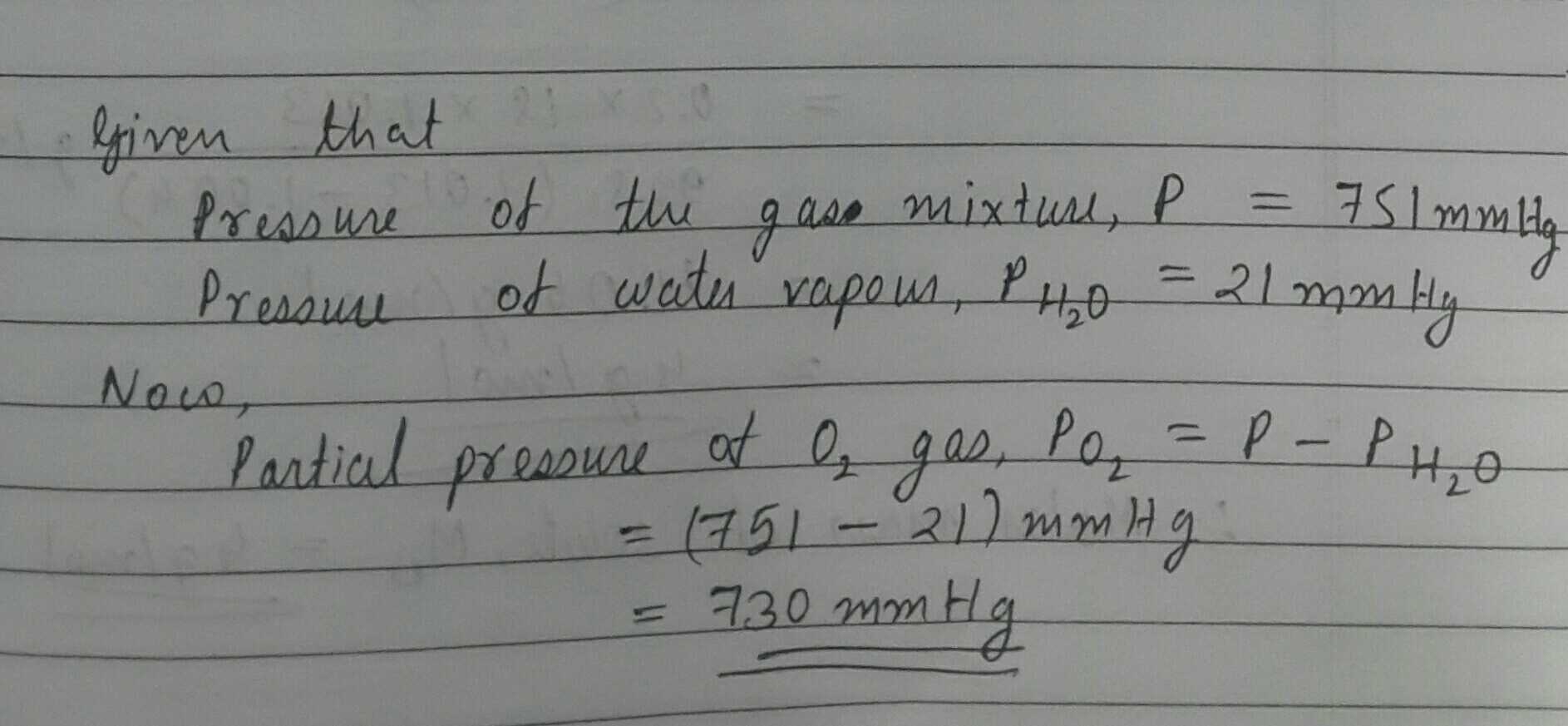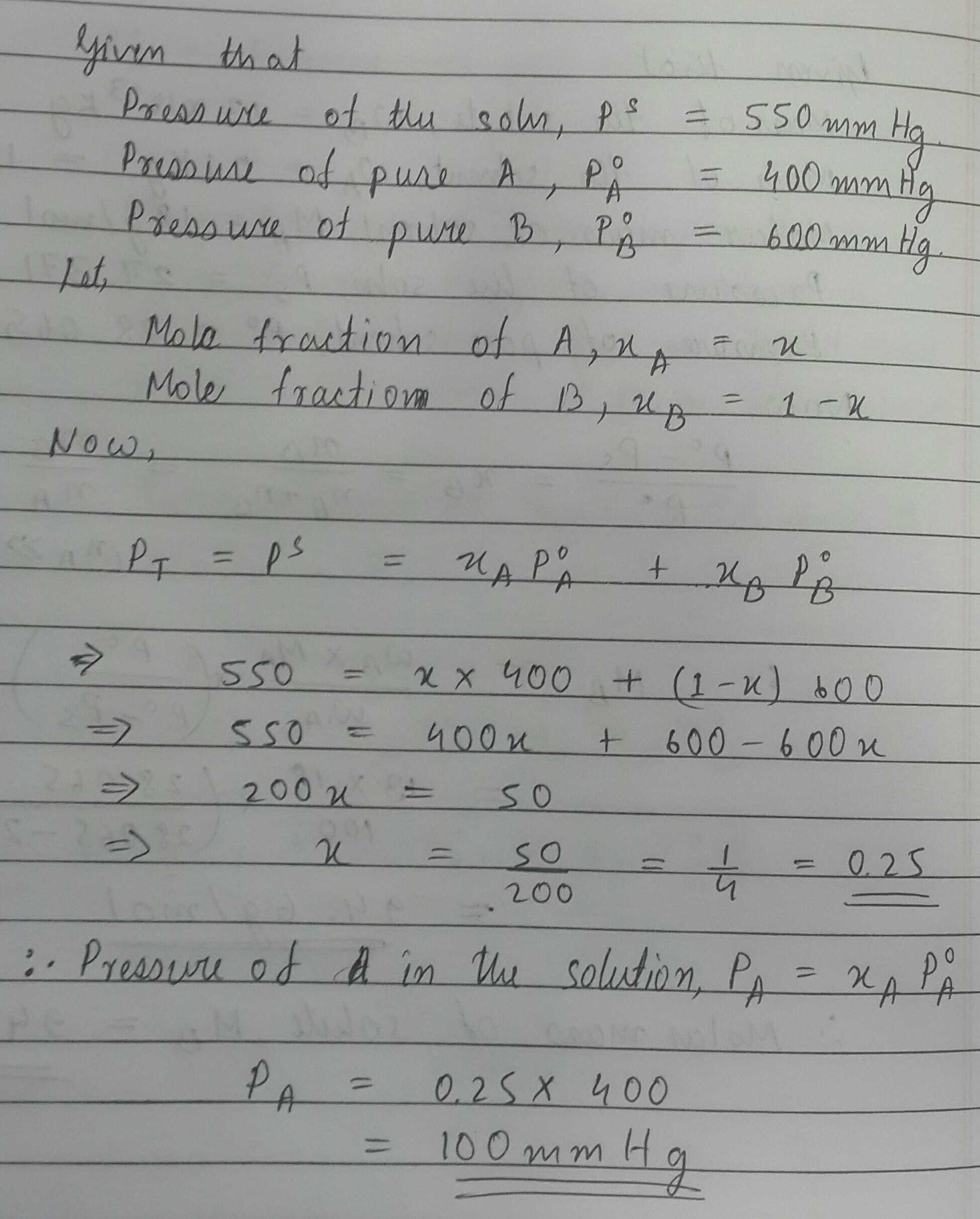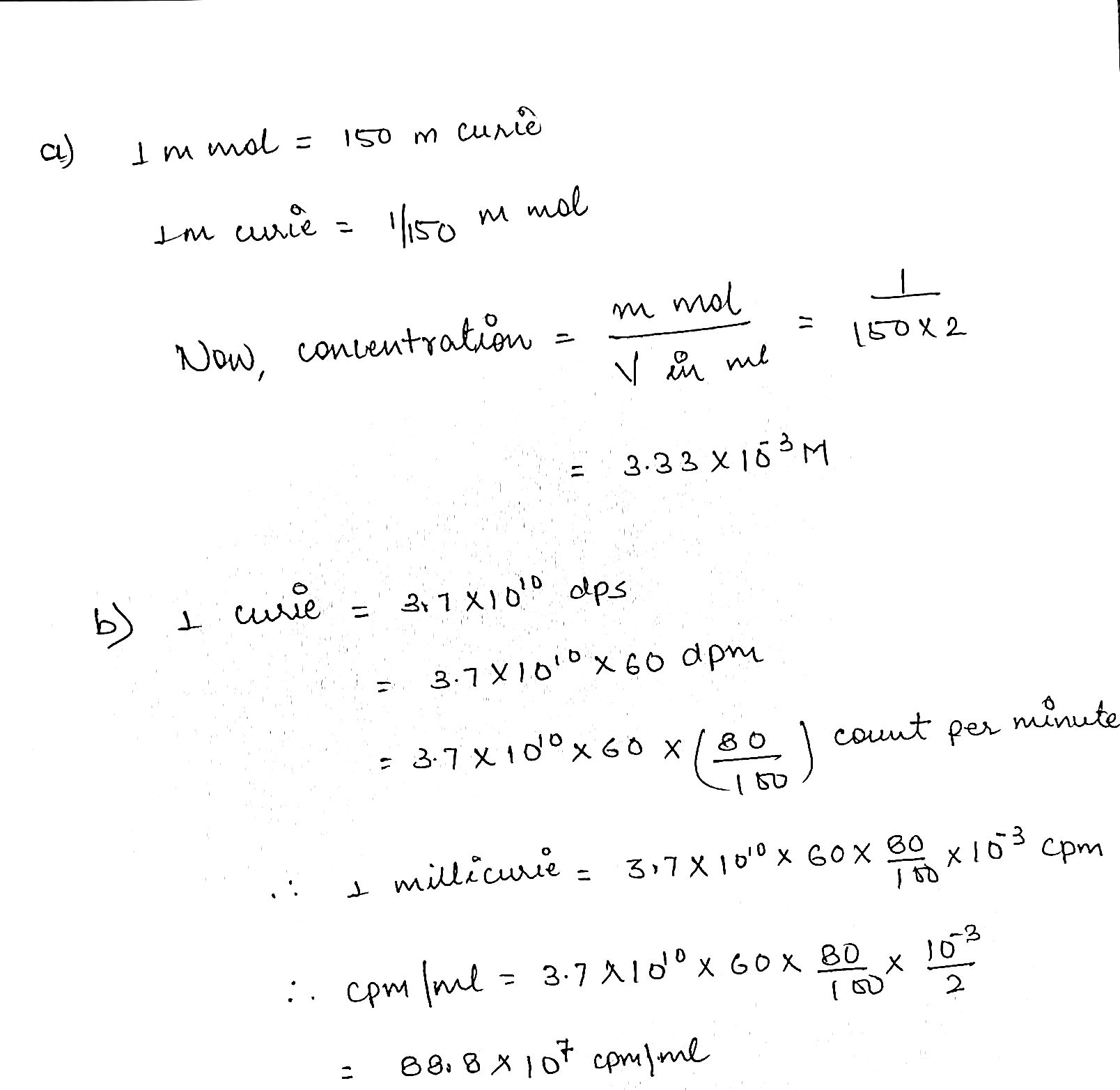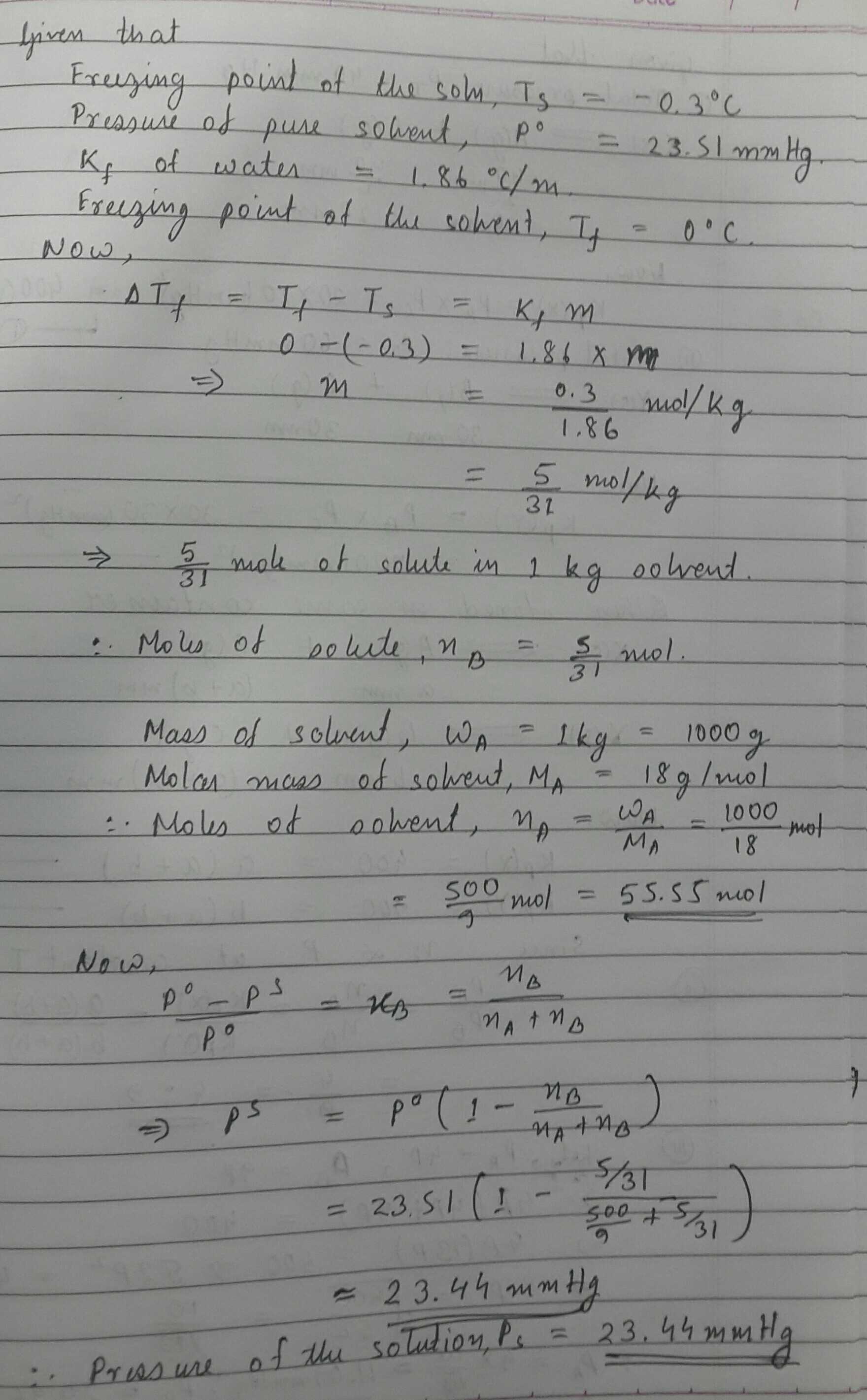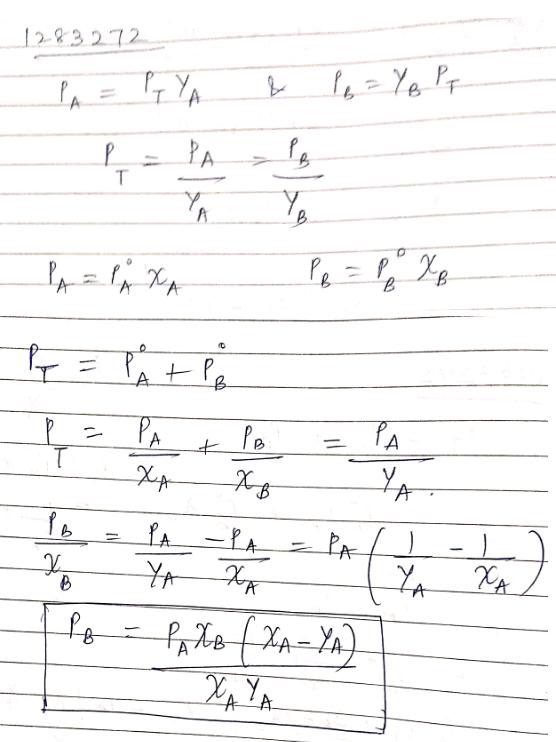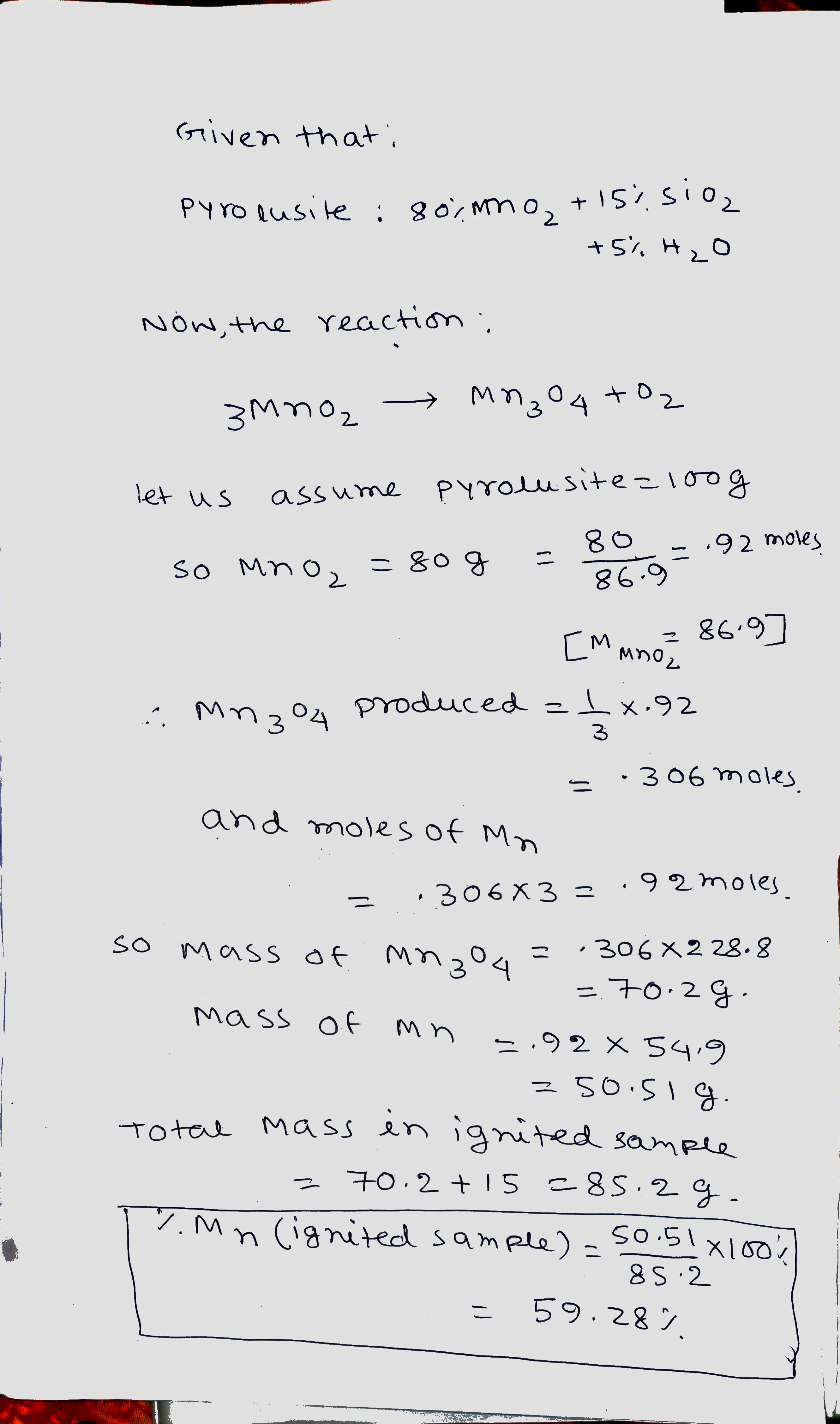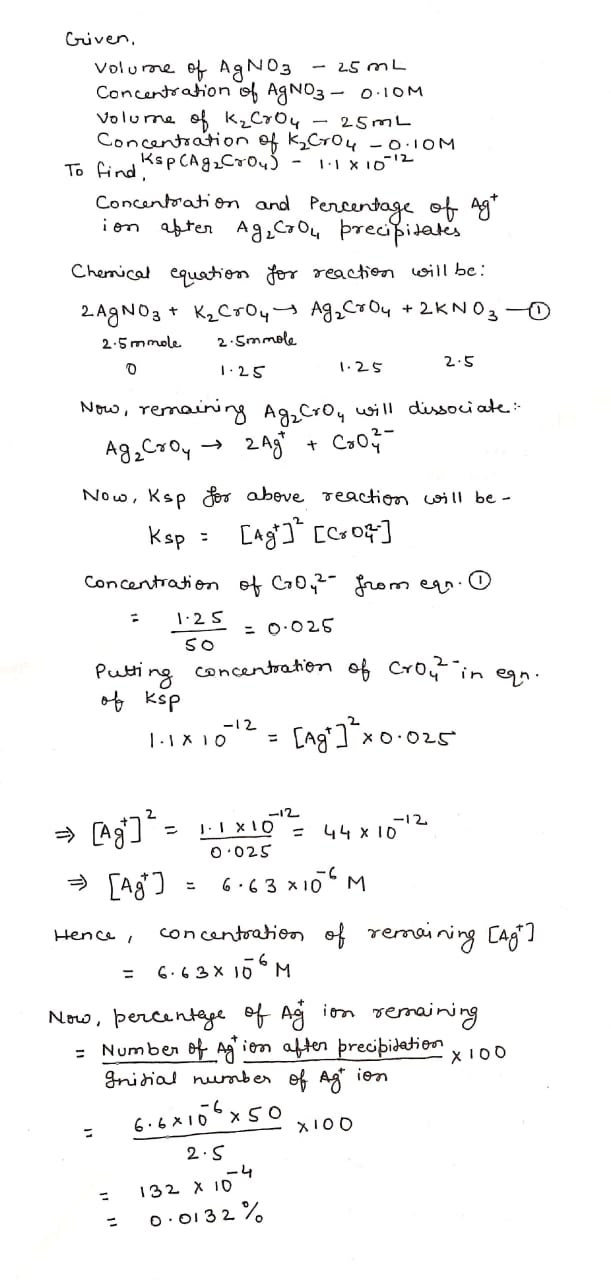Solutions - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
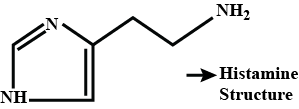
The mass percentage of nitrogen in histamine is _______.
An ideal aqueous solution containing liquid $$A(M.Wt=128)$$ $$64$$% by weight has a vapour pressure of $$145mm$$ $$Hg$$. If the vapour pressure of $$A$$ is $$x$$ $$mm$$ of $$Hg$$ and that of water is $$155mm$$ $$Hg$$ at the same temperature. Then find $$\dfrac{x}{5}$$. The solutions is ideal.
Does a new substance form when a solute dissolves in a solvent?
Calculate the percentage of magnesium in magnesium carbonate.
Mention names of four methods of expressing concentration of a solution.
Calculate percentage of oxygen present in $$CO_{2}$$. [Atomic mass of O=16u. C=12u]
At constant temperature and pressure, one mole of a pure substance free energy is identical with:
Van't Hoff factor for an electrolyte is greater than _____.
For strong electrolytes, van't Hoff factor 'i' equals to total number of _____ (ions/atoms) in the formula unit.
Van't Hoff factor for $$TH(NO_3)_4$$ in an aqueous solution is :
At $$25^oC$$ benzene and toluene have densities 0.879 and 0.867 g/mL respectively. Assuming that benzene, toluene solutions are ideal, then the equation for the density (e) of solution as: $$e=\frac {1}{100}[0.879V+0.867(100-V)]$$ where V is the volume of benzene.
If true enter 1 else enter 0.
Match column I with column II
Match column I with column II
For weak electrolytes, van't Hoff factor 'i' is a measure of the degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte.
If true enter 1, if false enter 0.
Van't Hoff factor of a mixture of two moles of KI with 1 mole $$HgI_2$$ in a solution of water is :
What is the difference between lyophobic sol and lyophilic sol ?
How is the vapour pressure of a solvent affected when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it ?
For an ideal solution, $${\Delta}_{mix}H$$ is _______ .
For an ideal solution, $${\Delta }_{mix}V$$ is
The vapour pressure of water is $$12.3\ kPa$$ at $$300\ K$$. Calculate the vapour pressure of $$1$$ molal solution of a non-volatile solute in it.
Vapour pressure of water at $$293\ K$$ is $$17.535\ mm\ Hg$$. Calculate the vapour pressure of water at $$293\ K$$ when $$25\ g$$ of glucose is dissolved in $$450\ g$$ of water.
Based on solute-solvent interactions, arrange the following in order of increasing solubility in n-octane and explain. Cyclohexane, $$KCl,\ CH_{3}OH,\ CH_{3}CN$$
Define the term solution. How many types of solutions are formed? Write briefly about each type with an example.
Define an ideal solution and write one of its characteristics.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of solubility in water:
$${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 5 }N{ H }_{ 2 },{ \left( { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 } \right) }_{ 2 }NH,{ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }N{ H }_{ 2 }$$
A 1.00 molal aqueous solution of trichloroacetic acid $$(CCl_3COOH)$$ is heated to its boiling point. The solution has the boiling point of $$100.8^oC$$. Determine the van 't Hoff factor for trichloroacetic acid. $$(K_b$$ for water 0.512 K kg $$Mol^{-1}$$)
OR
Define the following terms:
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Isotonic solutions
(iii) Van 't Hoff factor
(iv) Ideal solution
Vapour pressure of three liquids A, B, C are in their ascending order. Identify the liquid that has least critical temperature in its gaseous state.
A mixture containing four miscible liquids P, Q, R, and S are subjected to fractional distillation. Liquid P is distilled off first, into the receiver flask. Then S, followed by R and Q is left behind in the distillation flask. Based on the above observations, arrange the liquids in ascending order of their vapour pressures.
Why is be solubility of $$NaCl$$ in water $$311\,g\, l^{-1}$$ $$N$$ but is zero in benzene?
What is the value of $$\Delta H_{mix}$$ for an ideal solution ?
a. Which gas is dissolved in soft drinks?
b. What will you do to increase the solubility of this gas ?
What happens to vapour pressure of water if a tablespoon of sugar is added to it?
What will be the value of van't Hoff factor $$\left(i\right)$$ of benzoic acid if it demerises in aqueous solution? How will the experimental molecular weight vary as compared to the normal molecular weight?
What will be the value of Van't Hoff factor for ethanoic acid in benzene?
Derive van't Hoff general solution equation.
What is relative lowering of vapour pressure? How is it useful to determine the molar-mass of a solute?
The vapour pressure of pure benzene at a certain temperature is $$0.850$$ bar. A non-volatile, non-electrolyte solid weighing $$0.5$$ $$g$$ when added to $$39$$ $$g$$ of benzene (molar mass $$78$$ $$g$$ $${mol}^{-1}$$), vapour pressure becomes $$0.845$$ bar. What is the molar mass of the solid substance?
'The extent to which a solute is dissociated or associated can be expressed by Van 't Hoff factor'. Substantiate the statement.
Derive the relationship between relative lowering of vapour pressure and molar mass of solute.
Alkaline solution of $$Hg{Cl}_{2}$$ and $$KI$$ is called _________.
Mention the enthalpy of mixing $$({\triangle}_{mix}H)$$ value to form an ideal solution.
Heptane and octane form ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquids are 105.2 kPa and 46.8 kPa respectively. What will be the vapour pressure, in bar, of a mixture of 25 g heptane and 35 g of octane?
An aqueous solution containing $$28\%$$ by mass of a liquid A (mol. mass = $$140$$) has a vapour pressure of $$160$$ mm of $$37^o C$$. Find the vapour pressure of the pure liquid A (The vapour pressure of water at $$37^oC$$is $$150$$ mm).
Potassium ferrocyanide is 50% ionised in aqueous solution. Its van't Hoff factor will be:
A solution containing $$8.44 g$$ of sucrose in $$100 g$$ of water has a vapour pressure $$4.56 mm$$ of $$Hg$$ at $$273 K$$. If the vapour pressure of pure water is $$4.58 mm$$ of $$Hg$$ at the same temperature, calculate the molecular weight of sucrose.
Calculate the vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of 1.0 molal glucose solution at $$100^oC.$$
The vapour pressure of two pure liquids A and B forming an ideal solution are 400 mm Hg and 800 mm Hg respectively at temperature I. A liquid mixture containing 3:1 molar composition of A and B is present in a cylinder closed by a piston so that the pressure can be varied. The solution is slowly vaporised at temperature I by decreasing the applied pressure from a starting of 760 mm Hg. A pressure gauge (in mm Hg) is connected
A cylinder fitted with an air tight piston contains a small amount of a liquid at a fixed temperature. The piston is moved out so that the volume increases
(a) What will be the effect on the change of vapour pressure initially?
(b) How will the rates of evaporation and condensation change initially?
(c) What will happen when equilibrium is restored finally and what will be the final vapour pressure?
The freezing point of a solution containing 5.85 g of $$NaCl$$ in 100g of water is $$-3.348^o$$C. Calculate van't Hoff factor 'i' for this solution. What will be the experimental molecular weight of NaCI?
($$K_f$$ for water = $$1.86 K kg mol^{-1}$$, at. wt. Na = 23, Cl = 35.5)
Two moles of $$O_2$$ gas is collected over water at 400 K temperature in 2 litre vessel. If the pressure of dry $$O_2$$ gas is 32.20 bar then find the vapour pressure of water under the same conditions.
The vapour pressure of a pure liquid at $$25$$ is 100 mm $$Hg$$. Calculate the relative lowering of vapour pressure if the mole fraction of solvent in solution is 0.8.
Identify the solute & the solvent in the following solution:
a) sugar solution
b) Air
c) Rain water
d) Aerated drinks
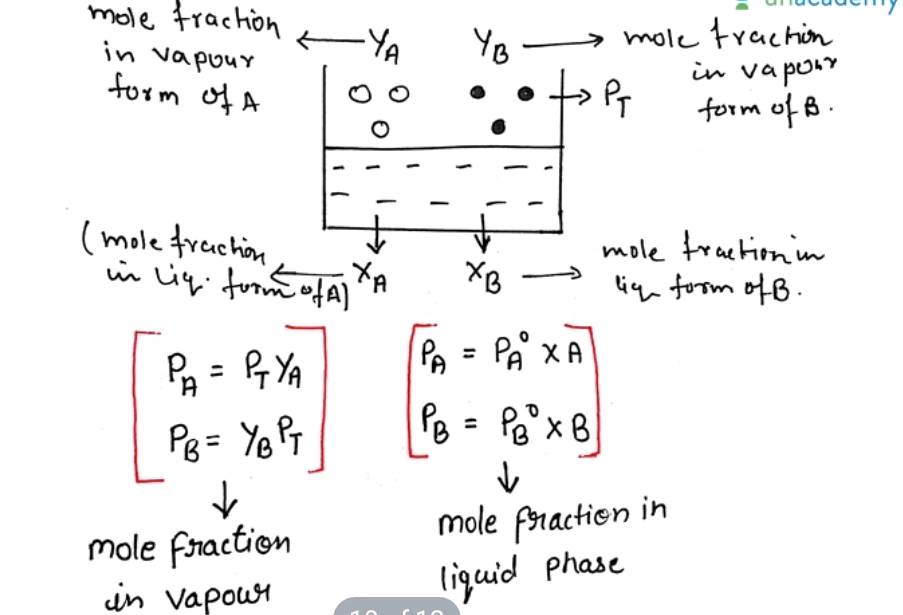
A mixture of two miscible liquids A and B is distilled under equilibrium conditions at $$1$$ atm pressure. The mole fraction of A in solution and vapour phase are $$0.30$$ and $$0.60$$ respectively. Assuming ideal behaviour of the solution and the vapour. Calculate the ratio of the vapour pressure of pure A to that of pure B.
Define an ideal solution.
At $$90^o$$C, the vapour pressure of toluene is $$400$$ Torr and that of o-xylene is $$150$$ Torr. What is the composition of the liquid mixture that boils at $$90^o$$C when the pressure is $$0.50$$ atm? What is the composition of the vapour produced?
Calculate the following.
The vapour pressure of the solution at $$298$$ K.
At $$25^o$$C the saturated vapour pressure of water is $$3.165$$ kPa ($$23.75$$ mm Hg). Find the saturated vapour pressure of a $$5\%$$ aqueous solution of urea (carbamide) at the same temperature. (Molar mass of urea $$=60.05$$ g $$mol^{-1}$$)
The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of glucose is 750mm at 373K. find molality and mole fraction
Identify the solute & the solvent in the following solutions:(a) Sugar solution (b) Air (c) Grains (d) Aerated drinks.
Derive the relationship between relative lowering of vapour pressure and mole fraction of the volatile liquid.
Out of two $$0.1$$ molal solutions of glucose and of potassium chloride, which one will have a higher boiling point and why?
$$400\ g$$ of $$20\%\ (w/w)$$ solution is cooled. $$50\ g$$ of solute is precipitated. What is the %(w/w) of solute in the remaining solution?
Vapour pressure of liquids $$A$$ and $$B$$ at $$298\ K$$ is $$300\ mm\ Hg$$ and $$450\ mm\ Hg$$. Calculate the mole fraction of $$A$$ in the mixture.
[Given total vapour pressure of solution$$=405\ mm\ Hg$$.]
The vapor pressure of water is $$12.3 \text { }KPa$$ at $$300K$$. Calculate the vapor pressure of $$1$$ molal solution of a non-volatile solute in it.
What is vapour pressure?
The vapour pressure of water is $$92$$mm at $$323$$K. $$18.1$$g of urea are dissolved in $$100$$g of water. The vapour pressure is reduced by $$5$$mm. Calculate the molar mass of urea.
If equal volume of $${ BaCl }_{ 2 }$$ and $$NaF$$ solutions are mixed , which of these combination will give a precipitate? $${ K }_{ sp } $$ of $$ { BaF}_{ 2} ={ 1.7\times 10 }^{ -7 }.$$
The vapour pressure of a pure liquid A is $$80$$ mmHg at $$300K$$. It forms an ideal solution with liquid B. When the mole fraction of B is $$0.4$$, the total pressure was to be $$88$$mmHg. The vapour pressure of liquid B would be?
The vapour pressure of solution of 5g of non electrolyte in 100 g of a water at a particular temperature is $$2985 N{ m }^{ -2 }$$. The vapour pressure of pure water at that temperature is $$3000 N{ m }^{ -2 }$$
What is the mass of a non volatile solute (molecular mass 60) that needs tobe dissolved in $$ 100 g $$ of water In order to decrease the vapour pressure of water by $$ 25% $$.What will be the velocity of solution?
If p° and p are the vapour pressure of a solvent and it's solution repetitively and N1 and N2 are the mole fractions of the solvent and solute respectively, then the relation between them is?
The vapour pressure of pure water is 23.8 mm Hg at $$25^0C$$ What is the vapour pressure of 2.50 molal $$C_6H_{12}O_6$$.
2 g benzoic acid $$(C_{6}H_{5}COOH)$$ dissolved in 25 g of benzene shoes a depression in freezing point equal to 1.62 K. Molal depression constant for benzene is 4.9 K kg $$mol^{-1}$$. What is the percentage association of acid if it forms dimer in solution?
Explain homogenous and heterogenous conditions with an example.
Derive van"t Hoff equation for osmotic pressure of a solution.
A sample of $$O_{2}$$ gas is collected over at $$23^{o}\ C$$ at a barometric pressure of $$751\ mm\ Hg$$ (vapour pressure of water at $$23^{o}\ C$$ is $$21\ mmHg)$$. The partial pressure of $$O_{2}$$ gas in the sample collected is
A $$0.2\% $$ aq. sol. of a non-volatile solution exerted a VP of $$1.004$$ bar at $$100^\circ C$$. What is the molar mass of the solute ?
(Given V.P of mass water at $$100^\circ C$$ is $$1.013$$ bar and molar mass of water is $$18\,g/mol$$).
A 821 mL $$ N_2(g) $$ was collected over liquid water at 300 K and 1 atm. If vapour pressure of $$ H_2O $$ is 30 torr then moles of $$ N_2(g) $$ in moist gas mixture is :
Define Van't Hoff's factor.
The vapour of a sodium containing $$13\times 10^{-3}\ kg$$ of solute in $$0.1\ kg$$ of water at $$298\ K$$ is $$27.371\ mm\ Hg$$. Calculate the molar mass of the solute. Given that the vapour pressure of water at $$298\ K$$ is $$28.065\ mm\ Hg$$ .
Find its mass of urea dissolved in $$100g H_2O$$ which decreese the vapour presure of solvent by $$20\%$$
110g of salt is present in 550g of solution. Calculate the mass percentage of the solution.
The vapour pressure of pure water at is 25.21 torr. What is the vapour pressure of a solution which contain 20.0 glucose, $${C_6}{H_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_6}$$ in 70 g water ?
Two A and B in a mixture produced 550 mm of Hg vapour pressure. If their vapour pressure in the pure states are 400 mm of Hg and 600 mm of Hg respectively. What is the vapour pressure of 'A' in the mixture?
Calculate the percentage by mass to volume for 0.2 M NaOH solution.
What is the number of molecules in 1.5 moles of ammonia ?
When $$HgI_2$$ is added to aqueous solution of KI, why there is an increase in vapour pressure of solution ?
Under what condition the van't Hoff factor is greater than one?
100 g of liquid A (mol. mass of = 140 g/mol) was dissolved in 1000 g of liquid B (molar mass of = 180 g/mol). The vapour pressure of pure liquid B was found to be 500 atmosphere. Calculate the vapour pressure of liquid A and its vapour pressure in the solution, if the total vapour pressure of the solution is 475 atmosphere.
Predict whether van't HOff factor $$(i)$$ is less than one or greater than one in the following:
(i) $$CH_3COOH$$ dissolved in water
(ii) $$CH_3COOH$$ dissolved in benzene
The vapour pressure of water at $$20^oC$$ is $$17$$mm Hg.Calculate the vapour pressure of a solution containing $$2.8 $$g of urea $$(NH_2CONH_2)$$ in $$50$$g of water ($$16.71$$mm Hg).
Octane is a component of gasoline. Complete combustion of octane leads to $$CO_2$$ and $$H_2O$$ while incomplete combustion produces $$CO$$ and $$H_2O$$, which not only reduced the efficiency of the engine using the fuel but is also toxic.In a certain test run, gallon of octane is burned in an engine, The total mass of $$CO, CO_2$$ and $$H_2O$$ produced is $$9.768\ kg$$. Calculate the efficiency of the process, i.e, calculate the percentage of octane converted to $$CO_2$$. The density of octane is $$2.28\ kg/gallon$$.
In $$1.684\ g$$ sample of a mixture of $$MgSO_{4}.7H_{2}O$$ and $$MgCl_{2}.6H_{2}O$$ containg some inert impurity was subjected to suitable treatment, as a result of which there were obtained $$0.699\ g$$ of $$BaSO_{4}$$ adn $$0.888\ g$$ of $$Mg_{2}P_{2}O_{7}$$. The mass percentage of impurity is $$(Ba=137, Mg=24, P=31)$$
A $$1.174\ g$$ sample of special grade steel was treated approximately with Chugaev's reagent by which nickel was precipitated as nickel dimethylglyoxime $$NiC_{8}H_{14}O_{4}N_{4}$$. The dried precipitate weighed $$0.2136\ g$$
The percentage of nickel in the steel being analysed is $$(Ni=58.7)$$
A blackened silver coin weighing $$15\ g$$ on treatment with $$HCl$$ yielded $$25\ mL$$ of $$H_{2}S$$ at $$12^{o}C$$ and $$775\ mm$$ pressure. What percentage of original silver tarnished?
$$3\ g$$ sample of blue vitrol $$(CuSO_{4}.5H_{2}O)$$ were dissolved in water. $$BaCl_{2}$$ solution was mixed in excess to this solution. The precipitate obtained was washed and dried. It weighed $$2.82\ g$$. Determine $$\%$$ of $$SO_{4}^{2-}$$ by weight in sample.
What is the percentage by volume of gases in the atmosphere?
An aqueous solution containing $$20\%$$ by weight of liquid $$X(mol. wt. =140)$$ has a vapour pressure $$160\ mm$$ at $$60^{o}C$$. Calculate the vapour pressure of pure liquid $$X$$ if the vapour pressure of water is $$150\ mm$$ at $$60^{o}C$$
Which of the following aqueous solutions has a higher vapour pressure if the density of water is $$1\ g/cc$$?
(1) Solution having mole fraction of cane sugar $$=0.1$$
(2) Solution having molal concentration = 1 m
[Give your answer in terms of 1 or 2, e.g. enter 1 if (1) is true.]
Which of the following aqueous solutions has a higher vapour pressure if the density of water is $$1\ g/cc$$?
Solution having molal concentration $$=1\ m$$
What is the vapour pressure at $$100^{o}C$$ of a solution containing $$15.6\ g$$ of water and $$1.68\ g$$ of sucrose $$(C_{12}H_{22}O_{11})$$?
Find the percentage of nitrogen in an organic compound analysed by Kjeldahl method. $$1.61 \,g$$ of the compound produced $$NH_3$$ which was absorbed in $$250 \,mL$$ of $$\dfrac{N}{2}H_2SO_4$$ solution.The remaining acid was then diluted to one litre,$$25 \,mL$$ of which required $$25.5 \,mL$$ of $$\dfrac{N}{10} NaOH$$ for exact neutralization.
One litre of water was added to $$500\ mL$$ of $$32\%\ HNO_{3}$$ of density $$1.20\ g/mL$$. What is the per cent concentration of $$HNO_{3}$$ in the solution obtained?
At $$25^{o}C$$ benzene and toluene have densities $$0.879$$ and $$0.867\ g/cc$$ respectively.
Assuming that benzene-toluene solutions are ideal. establish the equation for the density of the solution.
$$d=\dfrac{1}{100}\left\{0.879\ V+0.867 (100-V)\right\}$$where $$V$$ is the volume per cent of benzene.
$$0.5\ g$$ of a nonvolatile organic compound $$(mol.wt. 65)$$ is dissolved in $$100\ mL$$ of $$CCl_{4}$$. If the vapour pressure pure $$CCl_{4}$$ is $$143\ mm$$, what would be the vapour pressure of the solution? (Density of $$CCl_{4}$$ solution is $$1.58\ g/cc$$)
Determine the per cent concentration of a solution obtained by mixing $$300\ g$$ of a $$25\%$$ and $$400\ g$$ of a $$40\%$$ solution.
When $$10$$mL of ethanol of density $$0.7893$$ g/L is mixed with $$20$$ mL of water of density $$0.9971$$ g/L at $$25^o$$C, the final solution has a density of $$0.9571$$ g/L. Calculate the percentage change in total volume on mixing.
A solution contains $$1$$ milli-curie of L-phenyl alanine $$C^{14}$$ (uniformly labelled) in $$2.0\ mL$$ solution. The activity of the labelled sample is given as $$150$$ milli-curie/milli-mole. Calculate:
(a) The concentration of the sample in the solution in mole/litre.
(b) The activity of the solution in terms of counting per minute/mL at a counting efficiency of $$80\%$$.
Calculate the concentration of a solution obtained by mixing $$300\,g \,25$$% by weight solution of $$NH_4Cl$$ and $$150\,g$$ of $$40$$% by weight solution of $$NH_4Cl.$$
If the vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B are $$300$$ mm and $$800$$ mm Hg at $$75^o$$C, calculate the composition of the mixture such that it boils at $$75^o$$C. Find the composition of the vapour phase.
Calculate the % of free $$SO_3$$ in oleum (a solution of $$SO_3$$ in $$H_2SO_4$$) that is labelled $$109$$% $$H_2SO_4$$ by weight.
A $$0.5$$ g sample containing $$MnO_2$$ is treated with HCl, liberating $$Cl_2$$. The $$Cl_2$$ is passed into a solution of KI and $$30.0 cm^3$$ of $$0.1$$M $$Na_2S_2O_3$$ are required to titrate the liberated iodine. Calculate the percentage of $$MnO_2$$ in the sample.
What type of liquids form ideal solutions?
Explain the solubility rule "like dissolve like" in terms of intermolecular forces that exist in solutions.
State any two characteristics of ideal solutions.
Neutralisation of $$30 \,gm$$ of a mixture of acetic acid and phenol solutions required $$100 \,ml$$ of $$2M$$ sodium hydroxide solution. When the same mixture was treated with bromine water, $$33.1 \,gm$$ of precipitate was formed. Determine the mass percentage of acetic acid and phenol in the given solution.
Define w/w (percentage mass by mass) way of expressing concentrations.
Both Sarika and Mohan were asked to make a salt solution. Sarika was given a teaspoonful of salt and half a glass of water, whereas Mohan was given twenty teaspoons full of salt and half a glass of water.
(a) How would they make salt solutions?
(b) Who would be able to prepare a saturated solution?
Match the terms given in Column I with expressions given in Column II.
Match the items given in Column I with Column II.
Why is the vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of glucose lower than that of water?
Define the v/v (volume by volume percentage) mode of expressing the concentration of a solution.
Concentration terms such as mass percentage, ppm, mole fraction and molality are independent of temperature, however molarity is a function of temperature. Explain.
Will honey form a solution in water? (Yes/No)
Define saturated solution
Differentiate between the following.
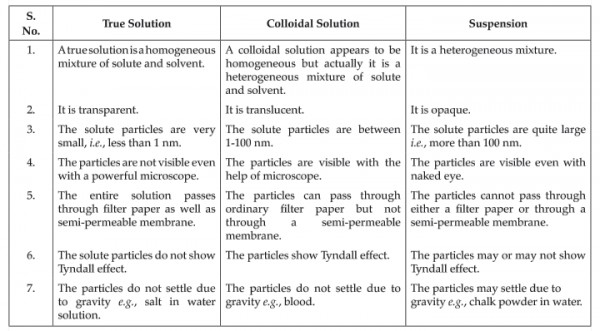
Solution and Suspension
Give an example of a reaction where the following are involved in a Solution
Define Seeding.
Explain why a solution is always clear and transparent.
Suggest a suitable technique to separate the constituents of the following mixtures. Also give the reason for selecting the particular method.
(a) Salt from sea water
(b) Ammonium chloride from sand
(c) Chalk powder from water
(d) Iron from sulphur
(e) Water and alcohol
(f) Sodium chloride and potassium nitrate
(g) Calcium carbonate and sodium chloride
Will sodium carbonate form a solution in water? (Yes/No)
What type of solutions are formed on dissolving different concentrations of soap in the water?
Calculate the mass of $$95\%$$ pure $$MnO_2$$ to produce $$35.5 \,g$$ of $$Cl_2$$ as per the following reaction:$$MnO_2 + 4HCl \rightarrow {}MnCl_2 + Cl_2 + H_2O.$$ (At. mass of $$Mn = 55$$)
A solution of sodium hydroxide contains $$4.8 \,g$$ of the substance per $$dm^3,$$
What volume of water has to be added to one $$dm^3$$ of the solution in order to make it exactly decinormal ?
Define: Mass percentage.
Which one in each of the following pairs of liquids is more viscous: coconut oil, castor oil
What do you mean by decinormal solution ?
Calculate the volume of concentrated nitric acid of normality $$14$$ required to prepared $$1 \,dm^3$$ of $$\dfrac{N}{10}$$ nitric acid.
Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in $$NH_4.$$ (Atomic mass of $$N = 14, H = 1$$ amu)
$$ 1 \cdot 5 \mathrm{g} $$ of pyrolusite ore were treated with 10 g of Mohr's salt and dilute $$ \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} $$. Atter the reaction, the solution was diluted to $$ 250 \mathrm{cm}^{3} . $$ $$50 cm ^{3} $$ of diluted solution required $$ 10 \mathrm{cm}^{3} $$ of $$ 0 \cdot 1 \mathrm{N} \mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7} $$ solution.
Find out percentage of pure $$ \mathrm{Mn} \mathrm{O}_{2} $$ in pyrolusite.
$$1 \cdot 1 $$ g of a sample of copper ore is dissolved and $$ \mathrm{Cu}^{2+}(a q) $$ is treated with KI. The iodinethus liberated required $$ 12 \cdot 12 \mathrm{cm}^{3} $$ of $$ 0.1 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{S}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3} $$solution for titration. What is the percentage of copper in the ore?
What are the factors affecting the solubility?
$$ 5 \cdot 0 $$ g of a sample of brass were dissolved in 1 litre dil. $$ \mathbf{H}_{2} \mathbf{S O}_{4} \cdot \mathbf{2 0} \operatorname{cm}^{3} $$ of this solution weremixed with KI and liberated lodine required $$ 20 \mathrm{cm}^{3} $$ of $$ 0 \cdot 0327 \mathrm{M} $$ hypo solution for titration. Calculate the percentage of copper in the alloy.
$$ 1 \cdot 5 \mathrm{g} $$ of pyrolusite ore were treated with 10 g of Mohr's salt and dilute $$ \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} $$. Atter the reaction, the solution was diluted to $$ 250 \mathrm{cm}^{3} . $$ $$50 cm ^{3} $$ of diluted solution required $$ 10 \mathrm{cm}^{3} $$ of $$ 0 \cdot 1 \mathrm{N} \mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7} $$ solution.
Find out percentage of pure $$ \mathrm{Mn} \mathrm{O}_{2} $$ in pyrolusite.
Calculate the mass percentage of different elements present in sodium sulphate.
In an ore, the only oxidisable material is $$ S n^{2+} $$. This ore is titrated with a dichromate solution containing $$ 2 \cdot 58 $$ of $$ \mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7} $$ in 0.50 litre. The $$ 0.40 \mathrm{g} $$ sample of the ore required $$ 10.0 \mathrm{cm}^{3} $$ of titrant to reach equivalent point. Calculate the percentage of the in the ore. $$ (K=39 \cdot 1, C r=52, $$ $$ S n=118 \cdot 7) $$
(i) $$200 {cm}^{3}$$ of aqueous solution of a protein contains $$1.26 g$$ of protein. The osmotic pressure of solution at $$300 K$$ is found to be $$8.3 \times {10}^{-2}$$ bar. Calculate the molar mass of protein. $$\left(R = 0.083 l bar {K}^{-1} {mol}^{-1}\right)$$
(ii) What is the significance of Van't Hoff factor?
Derive the relationship between relative lowering of vapour pressure and molar mass of non-volatile solute.
Amongst the following compounds, identify which are insoluble, partially soluble and highly soluble in water?
(i) phenol (ii) toluene (iii) formic acid (iv) ethylene glycol (v) chloroform (vi) pentanol
Two liquids A and B form an ideal solution. At 300 K, the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 mole of B is 550 mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if one more mole of B is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm of Hg. Determine the vapour pressure of A and B in their pure states.
Match the items of Column-I with its proportional term in the items of Column-II:
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (a) Kinetic energy | (p) Mole fraction |
| (b) Partial pressure of a gas | (q) Density |
| (c) Rate of diffusion | (r) Molar mass |
| (d) Vapour pressure of a liquid | (s) Absolute temperature |
The answer to this question is a single digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9.
The van't Hoff factor for aqueous solution of $$CuSO_4 \cdot 5H_2O$$ will be ...
A solution of a non-volatile solute in water freezes at $$ -0.3^0 C$$ .If vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.51 mm of Hg and $$K_f$$ for water in 1.86 degree/molal .Calculate the vapour pressure of this solution at 298 k.
At 80C, the vapour pressure of pure benzene is 753 mm Hg and of pure toluene 290 mm Hg. Calculate the composition of a liquid in mole per cent which at 80C is in equilibrium with the vapour containing 30 mole per cent of benzene.
Two solids $$X$$ and $$Y$$ dissociate into gaseous products at a certain temperature as follows:
$$X(s) \rightleftharpoons A(g) + C(g)$$, and $$Y(s) \rightleftharpoons B(g) + C(g)$$. At a given temperature, pressure over excess solid $$X$$ is $$40\ mm$$ and total pressure over solid $$Y$$ is $$60\ mm$$. When they are preset in separate containers. Calculate
(a) the values of $$K_{p}$$ for two reactions (in mm)
(b) the ratio of moles of $$A$$ and $$B$$ in the vapour state over a mixture of $$X$$ and $$Y$$.
(c)The total pressure of gases over a mixture of $$X$$ and $$Y$$.
Two solutions of A and B are available. The first is known to contain 1 mole of A and 3 moles of B and its total vapour pressure isAtm. The second is known to contain 2 moles of A and 2 moles of B; its vapour pressure is greater than 1 atm, but it is found that this total vapour pressure may be reduced to 1 atm by the addition of 6 moles of C. the vapour pressure of pure C is 0.80 atm. Assuming ideal solutions and that all these data refer to 25C, calculate the vapour pressureof pure A and of pure B.
Vapour pressure of water at certain temperature is $$155$$mm Hg and that of the another solvent 'X' is 'p' mm Hg. Molecular weight of 'X' is $$128$$. An aqueous solution of 'X'($$64\%$$ by wt) has a vapour pressure of $$145$$mm Hg. What is 'p'?
Vapour pressure of chloroform $$(CHCl_{3})$$ and dichloromethane $$(CH_{2}Cl_{2})$$ at $$298\ K$$ are $$200\ mm\ Hg$$ and $$415\ mm\ Hg$$ respectively.
(i) Calculate the vapour pressure of the solution prepared by mixing $$25.5\ g$$ of $$CHCl_{3}$$ and $$40\ g$$ of $$CH_{2}Cl_{2}$$ at $$290\ K$$ and
(ii) Mole fraction of each component in solution.
Calculate the weight of a non-volatile solute $$(mol./wt. 40)$$ which should be dissolved in $$114\ g$$ octane to reduce its vapour pressure to $$80$$%.
Vapour pressure of pure benzene is $$640\ mm$$ and its mol. wt. is $$78$$. When $$2.175\ g$$ of a non-volatile substance is dissolved in $$39g$$ benzene the vapour pressure of the solution becomes $$600\ mm$$. Calculate mol. wt. of solute.
Two gases in adjoining vessels are brought into contact by opening a stop cock between them. The one vessel measured 0.25 lit and contained NO at 800 torr and 220 K, the other measured 0.1 lit and contained $$O_2$$ at 600 torr. The reaction to form $$N_2O_4$$ (solid) exhausts the limiting reactant completely.
a) Neglecting the vapour pressure of $$N_2O_4$$ what is the pressure of the gas remaining at 220 K after completion of the reaction?
b) What weight of $$N_2O_4$$ is formed?
[Given that : $$\displaystyle \frac {342.8}{760}\,\times\, \frac {0.35}{0.082}\,\times\, \frac{1}{22}\,=\,8.75\,\times\,10$$]
The vapour pressure of chloroforms and de-chloroforms at 298 k are 200 mm Hg and 415 mm Hg? calculate the vapour pressure of solution by mixing 25.5 gram of $$CHCl_3$$ 40 gram of $$CH_2Cl_2$$. calculate the mole fraction of each component on vapour phase.
Van't Hoffs factor for a solution is less than one, what is the conclusion drawn from it.
At $$400^oC$$, the vapour pressure of water is $$55.3mm\ Hg$$. Calculate the vapour pressure at the same temperature over $$10\%$$ aqueous solution of urea $$[CO(NH_2)_2]$$?
The vapor pressure of water at $$80^ {\circ}C$$ is $$355$$ torr. A $$100\, ml $$ vessel contained water-saturated oxygen at $$80^ {\circ}C$$ the total gas pressure being $$760$$ torr. The contents of the vessel were pumped into a $$ 50.0$$ ml, vessel at the same temperature, What were the partial pressure of oxygen and of water vapor, what was the total pressure in the final equilibrated state? Neglect the volume of any water which might condense.
Three grams of activated charcoal was added to 50ml of acetic acid solution (0.06 N) in a flask. After an hour it was filtered and the strength of the filtrate was found to be 0.042 N. Amount of acetic acid adsorbed (per gram of charcoal) is:
Vapour pressure of pure water at $$298\ K$$ is $$23.8\ mm\ Hg$$. $$50\ g$$ of urea $$(NH_2CONH_2)$$ is dissolved in $$850\ g$$ of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution and its relative lowering.
Two liquids $$A$$ and $$B$$ form an ideal solution at temperature $$T$$. When the total vapour pressure above the solution if $$600\ torr$$, the amount fraction of $$A$$ in the vapour phase is $$0.40$$ and in the liquid phase is $$0.6$$. What are the vapour pressure of pure $$A$$ and $$B$$ at temperature $$T$$?
Solution of two volatile liquid $$x$$ and $$y$$ obey Raoult's law. At a certain temperature it is found that when the total pressure above a given solution is $$400\ mm$$ of $$Hg$$, the mole fraction of $$x$$ in the vapour is $$0.45$$ and in the liquid is $$0.65$$. what are the vapour pressure of two pure liquids at the given temperature?
The vapour pressure of two pure liquids $$A$$ and $$B$$ which from an ideal solution are $$500$$ and $$800$$ torr respectively at $$300\ K$$. A liquid solution $$A$$ and $$B$$ for which the mole fraction of $$A$$ is $$0.60$$ is contained in a cylinder closed by a piston on which the pressure can be varied. What will be the pressure when 1 mol of the mixture has been vaporized?
Vapor pressure of pure water at $$298 \ K$$ is $$23.8 \ mmHg$$. $$50 \ g$$ of urea is dissolved in $$850 \ g$$ of water. Calculate the vapor pressure of water for this solution and it's relative lowering.
Two liquids $$A$$ and $$B$$ boils at $$145^{o}C$$ and $$190^{o}C$$. Which of them has higher vapour pressure at $$80^{o}C$$?
The vapour pressure of pure water is $$23.8\ mmHg$$ at $$25^{0}\ C$$. What is the vapour pressure of $$2.50\ molal\ C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}$$?
The normal boiling of water is $$373 K$$. Vapour pressure of water at temperature $$T$$ is 19 mm $$Hg$$. If enthalpy of evaporation is $$40.67 kJ/mol$$, then temperature $$T$$ would be: (Use $$log 2 =0.3,R =8.3 { JK }^{ -1 }$$)
For a dilute solution containing 2.5 grams of non volatile non electrolyte solute in hundred grams of water, the elevation in the boiling point at 1 atmosphere pressure is to degree Celsius asuming concentration of solute is much lower than concentration of solvent, the vapour pressure of the solution is?
Quantity of gas occupies $$100m$$,then it is collected on surface of water at $$15C$$ and $$760mm$$ of $$Hg$$. It occupies $$91.9ml$$ in dry state at STP conditions. Calculate vapour pressure of $${H}_{2}O$$ at $$15C$$.
By adding a non-volatile salute into a solution vapour pressure is reduces.
Give the differences between colloidal solution, true solution and suspension? (at least 2 differences)
Liquids $$'A'$$ and $$'B'$$ form an ideal solution. Calculate the vapour pressure of solution having 40 mole-percent of $$'A'$$ in the vapour at equilibrium. $$ (P^0_A = 80cm Hg, P^0_B = 30cm Hg) $$
Solve it
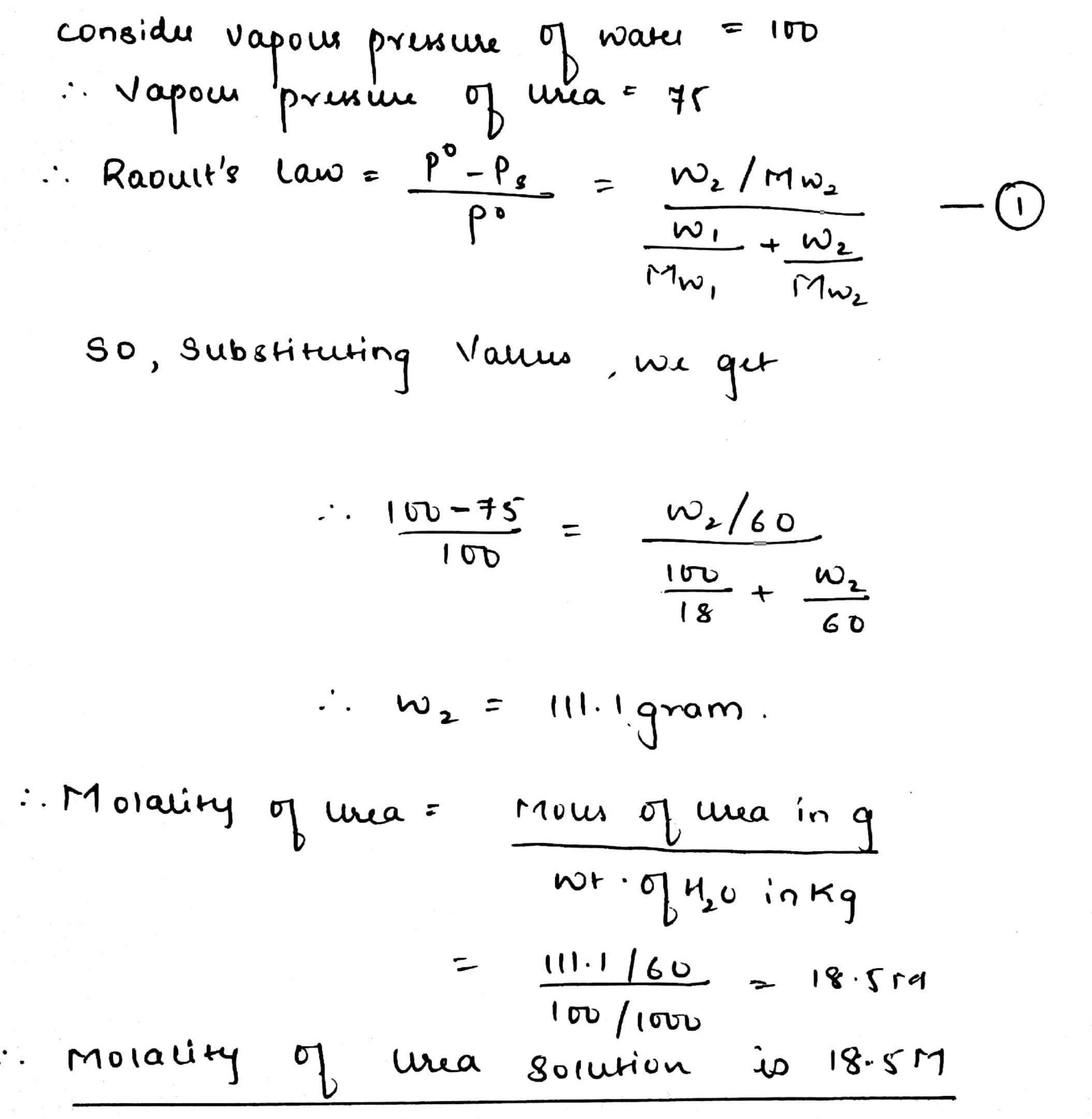
Urea forms an ideal solution in water. Determine the V.P of an aqueous solution containing $$10\% $$ by mass of urea at $$40^\circ C$$. (Vapour pressure of water at $$40^oC=55.3 mm Hg)$$
$${P_T} = P\mathop A\limits^ \circ {X_P} - P\mathop B\limits^ \circ {X_B}$$
$$P_T = P \mathring{A} X_P - P \mathring{B} (1 - X_A)$$
$${P_T} = P\mathop A\limits^ \circ {X_A} + P\mathop B\limits^ \circ - P\mathop B\limits^ \circ {X_A}$$
$${P_T} = P\mathop B\limits^ \circ + \left( {P\mathop {A - P\mathop B\limits^ \circ }\limits^ \circ } \right){X_A}$$
$${P_T} = P\mathop A\limits^ \circ {X_A} + P\mathop B\limits^ \circ - P\mathop B\limits^ \circ {X_A}$$
$${P_T} = P\mathop B\limits^ \circ + \left( {P\mathop {A - P\mathop B\limits^ \circ }\limits^ \circ } \right){X_A}$$
0.6 ml of acetic acid $$(C{H_3}COOH)$$ having density 1.06 g/ml is dissolved in 1 litre of water. The depression in freezing point observed for this strength of acid was $$0.0205\,{\,^0}C.$$ Calculate the Van't Hoff factor and the dissociation constant of acid.
Why is the vapour pressure of a solution of glucose in water lower than that of water?
A quantity of 1.245 g of $$ CuSO_{4}.xH_{2}O $$ was dissolved in water and $$ H_{2}S $$ was passed into it till CuS was completely precipitated. The $$ H_{2}SO_{4} $$ produced in the filtrate required 10 ml of M - NaOH solution. Calculate x.
A sample of chalk contain as impurity a form of clay which losses $$14.5\%$$ if its weight as water on along heating. A $$5\ g$$ of chalk sample, on heating shows a loss in weight by $$1.507\ g$$. The mass percentage of $$CaCO_3$$ in the chalk sample is $$(Ca=40)$$
A quantity of $$2.7\ g$$ of an alloy of copper and silver was dissolved in moderately concentrated $$ HNO_{3}$$, and excess of $$HCl$$ was added to this solution when $$2.87\ g$$ of a dry precipitate is formed. Calculate the percentage of copper in the alloy. $$(Cu=63.5\ ,\ Ag=108)$$
A gas mixture contains $$CH_4$$ and $$C_3H_6$$. When this mixture undergo cracking into $$C(s)$$ and $$H_ 2(g)$$m the total number of moles of $$H_2(g)$$ obtained is $$42$$. If the total volume of the initial gas mixture at $$1.5\ atm$$ and $$27^oC$$ is $$246.3\ L$$, what is the mole per cent of $$CH_4$$ gas in the initial mixture?
To analyse cast iron for its sulphur content, a $$6.4\ g$$ portion of the iron was weighed out for analysis and treated as follows: it was dissolved in hydrochloric acid, the hydrogen sulphide evolved from iron sulphide was distilled off and made to be absorbed by a solution of a cadmium salt, after which $$CdS$$ was treated with an excess of a solution of $$CuSO_{4}$$ and the $$CuS$$ precipitated formed was ignited. As a result $$0.795\ g$$ of an ignited $$CuO$$ precipitate was obtained. Calculate the percentage content of sulphur in the cast iron $$(Cu=63.5)$$
A mixture containing $$ As_{2}S_{3}$$ and $$ As_{2}S_{5} $$ requires 20 ml of 0.05 N iodine for titration. The resulting solution is then acidified and excess of KI was added. The liberated iodine required 1.24g hypo,$$ Na_{2}S_{2}O_{3}.5H_{2}O ,$$ for complete reaction.The reactions are :
$$ As_{2}S_{3}+2I_{2}+2H_{2}S \rightarrow As_{2}S_{5}+4H^{+}+4I^{-}$$
$$ As_{2}S_{5}+4H^{+}+2I^{-}\rightarrow As_{2}S_{3}+2I_{2}+2H_{2}S $$
The mole percent of $$As_{2}S_{3}$$ in the original mixture is (As= 75)
A 0.2 g sample of chromite was fused with excess of $$Na_{2}O_{2}$$ and brought into solution according to reaction:
$$2Fe\left ( CrO_{2} \right )_{2}+7Na_{2}O_{2}$$ $$\rightarrow 2NaFeO_{2}+4Na_{2}CrO_{4}+2Na_2O $$
The solution was acidified with dil. HCl and 1.96 g Mohr's Salt (molar mass = 392 g/mol ) was added. The excess of $$ Fe^{2+} $$ required 40 ml of $$ 0.05N - K_{2}Cr_{2}O_{7}$$ for titration. What is the percent of Cr in sample ? (Cr = 52, Fe = 56)
$$2Fe\left ( CrO_{2} \right )_{2}+7Na_{2}O_{2}$$ $$\rightarrow 2NaFeO_{2}+4Na_{2}CrO_{4}+2Na_2O $$
The solution was acidified with dil. HCl and 1.96 g Mohr's Salt (molar mass = 392 g/mol ) was added. The excess of $$ Fe^{2+} $$ required 40 ml of $$ 0.05N - K_{2}Cr_{2}O_{7}$$ for titration. What is the percent of Cr in sample ? (Cr = 52, Fe = 56)
A 10g mixture of $$Cu_{2}S$$ and CuS was treated with 400 ml of $$0.4M - MnO_{4}^{-}$$ in acid solution producing $$ SO_{2},Cu^{2+}$$ and $$ Mn ^{2+}. $$ The $$ SO_{2} $$ was boiled off ans the excess of $$ MnO_{4}$$ was titrated with 200ml of $$ 1M-Fe^{2+}$$ solution. The percentage of CuS in original mixture is (Cu=64)
A quantity of $$1.6\ g$$ of pyrolusite ore was treated with $$50\ ml$$ of $$1.0\ N$$ oxalic acid and some sulphuric acid. The oxalic acid left undecomposed was raised to $$250\ ml$$ in a flask. A volume of $$25\ ml$$ of this solution when titrated with $$0.1\ N\ KMnO_4$$ required $$32\ ml$$ of the solution. The percentage of available oxygen in the ore is:
One gram of commercial $$ AgNO_{3} $$ is dissolved in 50 ml of water. It is treated with 50 ml of a KI solution.The silver iodide thus precipitated is filtered off. Excess of KI is titrated with $$ M/10-KIO_{3} $$ solution in the presence of 6M - HCl till all iodide ions are converted into ICl. It requires 50 ml of $$ M/10-KIO_{3} $$ solution. A 20 ml of the same stock solution of KI requires 30 ml of $$ M/10-KIO_{3} $$ under similar conditions. The percentage of $$ AgNO_{3} $$ in the sample is (Ag=108)
Reaction:
$$ KIO_{3}+2KI+6HCl $$
$$ \rightarrow 3ICI+KCI+3H_{2}O $$
A mixture of ideal gases is cooled up to liquid helium temperature (4.22 K) to from an ideal solution. Is this statement true or false? Answer '1' or true and '2' for false.
$$50\ mL$$ if a mixture of $$CO$$ and $$H_{2}$$ gave $$20\ mL$$ of $$CO_{2}$$ after combustion in excess of air. Determine the percentage of $$CO$$ by volume in the mixture.
The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of cane sugar $$(mol. wt\ 342 )$$ is $$756\ mm$$ at $$100^{o}C$$. How many grams of sugar are present per $$1000\ g$$ of water?
Give your answer in nearest integer.
What approximate proportions by volumes of water $$(d=1\ g/cc)$$ and ethylene glycol $$C_{2}H_{6}O_{2}(d=1.12\ g/cc)$$ must be mixed ot ensure protection of an automobile cooling system to $$-10^{o}C$$?
A solution containing ethyl alcohol and propyl alcohol has a vapour pressure of $$290\ mm$$ at $$30^{o}C$$. Find the vapour pressure of pure ethyl alcohol if its mole fraction in the solution is $$0.65$$. The vapour pressure of propyl alcohol is $$210\ mm$$ at the same temperature.
Benzene and toluene fomr nearly ideal solution. If at $$27^{o}C$$ the vapour pressures of pure toluene and pure benzene are $$32.06\ mm$$ and $$103.01\ mm$$ respectively.
Calculate the vapour pressure of a solution containing $$0.60$$ mole fraction of toluene.
$$10.03g$$ of vinegar was diluted to $$100mL$$ and a $$25mL$$ sample was titrated with the $$0.0176M$$ $$Ba{(OH)}_{2}$$ solution $$34.30mL$$ was required for equivalence. What is the percentage of acetic acid in the vinegar?
Igniting $$MnO_{2}$$ converts it quantitatively to $$Mn_{3}O_{4}$$. A sample of pyrolusite is of the following composition: $$MnO_{2}= 80\%; SiO_{2}$$ and other inert constituents $$15\%$$ and rest being water.
The sample is ignited in air to constant weight. What is the percentage of $$Mn$$ in the ignited sample?
$$[Mn=54.9, O=16]$$
$$[Mn=54.9, O=16]$$
An alloy of aluminium and copper was treated with aqueous $$ HCl $$ The aluminium dissolved according to the reaction .
$$\displaystyle Al + 3H^{+} \rightarrow Al^{+3} + \dfrac{3}{2}H_2 , $$
but the copper remained as pure metal . A $$ 0.350-g $$ sample of the alloy gave $$ 415 cc $$of $$ H_2 $$ measured at $$ 273 K $$ and $$ 1 \,atm $$ pressure . What is the weight percentage of $$ Al $$ in the alloy ?
Give your answer as nearest integer.
Concentrated $$HCl$$ solution is $$37.0$$% $$HCl$$ and has a density of $$1.19g/mL$$. A dilute solution of $$HCl$$ is prepared by diluting $$4.50mL$$ of this concentrated $$HCl$$ solution to $$100mL$$ with water. Then $$10mL$$ of this dilute $$HCl$$ solution reacts with an $$Ag{NO}_{3}$$ solution. Calculate the volume of $$0.108M$$ $$Ag{NO}_{3}$$ solution required to precipitate all the chloride as $$AgCl(s)$$
Twenty grams of HI is heated at $$327^0C$$ in a bulb of 1-litre capacity. Calculate the volume percentage of $$H_2, \ I_2$$ and HI at equilibrium. Given that the mass law constant for the equation $$2HI \rightleftharpoons H_2 + I_2$$ is 0.0559 at $$327^0C$$ when concentrations are expressed in moles / litre.
The vapour pressure of water is $$3167.2$$ Pa at $$25^oC$$. What would be the vapour pressure of a solution of sucrose(with mole fraction of sucrose$$=0.1$$) and of a solution of levulose(with mole fraction of levulose$$=0.1$$)?
Liquid $$A$$ and $$B$$ form ideal solution over the entire range of composition. At temperature $$T$$, equimolar binary solution of liquids $$A$$ and $$B$$ has vapour pressure $$45\ torr$$. At the same temperature, a new solution of $$A$$ and $$B$$ having mole fraction $$x_{A}$$ and $$x_{B}$$, respectively, has a vapour pressure of $$22.5\ torr$$. The value of $$x_{A}/x_{B}$$ in the new solution is .....
$$\mathrm{(P^0_A= 20 torr)}$$
An aqueous solution freezes at $$271.5$$ K. Determine its boiling point and vapour pressure at $$298$$K. The cryoscopic constant of water is $$1.86^oC/m$$, its ebullioscopic constant is $$0.516^oC/m$$ and the water vapour pressure at $$298$$K is $$3168$$ Pa.
What weight of the nonvolatile solute, urea $$(NH_2-CO-NH_2)$$ needs to be dissolved in $$100$$g of water in order to decrease the vapor pressure of water by $$25\%$$? What will be the molality of the solution?
What are the concentration and percentage of $$Ag^+$$ ion remaining after $$Ag_2CrO_4$$ precipitates when $$25$$ mL of $$0.10$$M $$AgNO_3$$ is added to $$25$$ mL of $$0.10$$M $$K_2CrO_4$$? $$K_{sp}(Ag_2CrO_4)=1.1\times 10^{-12}$$.
The vapour pressure of pure water at $$25^{o}C$$ is $$23.62\ mmHg$$. What will be the vapour pressure of a solution of $$1.5\ g$$ of urea in $$50\ g$$ is water?
The vapour pressure of a $$0.01\ m$$ solution of a weak base $$BOH$$ in water at $$20^{o}C$$ is $$17.536\ mm$$. Calculate $$K_{b}$$ for the base. Aq. tension at $$20^{o}C=17.54\ mm.$$
Then apply $$i=1+x$$ and $$K_{b}=\dfrac{0.01 x^{2}}{1-x}$$
The rate of diffusion of a sample of ozonised oxygen is $$0.98$$ times more than that of pure oxygen. Find the percentage (by volume) of ozone in the ozonised sample.
Assume liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is a 50-50 (by mole) mixture of n -pentane and n-butane . calculate the calorific value (in kJ /mol) of gas available from a newly filled cylinder .give your answer divided by 100.
| n-butane , $$ C_4 H_{10} $$ | n-pentane , $$ C_5 H_{12} $$ | |
| Vapour pressure | 1800 Torr | 600 Torr |
| Calorific value | 2800 kJ /mol | 3600kJ /mol |
A space capsule is filled with neon gas at $$1$$ atm and $$290$$K. The gas effuses through a pinhole into outer space at such a rate that the pressure drops by $$0.3$$ mm/second. If the capsule were filled with $$30\%$$ He, $$20\%$$ $$O_2$$ and $$50\%$$ $$N_2$$(mole $$\%$$) at a total pressure of $$1$$ atm and a temperature of $$290$$K, calculate the rate of pressure drop.
A solution A (l) and B (l) with 30 mole percent of A is in equilibrium with its vapour which contains 60 mole percent of A . Assuming ideality of the solution and its vapour calculate the ratio of vapour pressure of pure A to that of pure B. (report your answer as ratio $$ \times $$ 2 )
Calculate the freezing point depression expected for $$ 0.0711 \, m $$ aqueous solution of $$ Na_2SO_4 $$ . If this solution actually freezes at $$ -0.320^{\circ}\,C $$, what would be the value of van't Hoff factor?
($$K_f $$ for water is $$ 1.86 \,K \, kg \, mol^{-1} $$ )
What do you mean by $$ 10 $$% aqueous solution of sodium carbonate?
Define van't Hoff factor.
Define the following terms :
Van't Hoff factor (i)
What do you understand by 'colligative properties'?
What is the van't Hoff factor for a compound which undergo dimerisation in an organic solvent?
What is collodion?
The dissolution of ammonia chloride in water is an endothermic process but still dissolves in water readily. Why?
Give Reasons for the Following:
Why is it said that solubility of any solute changes with a change in temperature?
Which of the liquids in each of the following pair has higher vapour pressure: Mercury, water
How many types of solutions are formed? Write briefly about each type with an example.
Which of the liquids in each of the following pair has higher vapour pressure : Petrol, kerosene
Give reason for the following :
Blue solution of copper sulphate changes to green when a piece of iron is added to this solution.
A solution of A and B with 30 mole percent of A is in equilibrium with its vapour which contain 60 mole percent of A. Assuming that the solution and the vapour behave ideally, calculated the ratio of the vapour pressures of pure A and pure B.
(a) Benzoic acid completely dimerises in benzene. What will be the vapour pressure of a solution containing 61g of benzoic acid per 500g benzene when the vapour pressure of pure benzene at the temperature of the experiment is 66.6 torr?
(b) What would have been the vapour pressure is the absence of dimerisation?
Define the terms 'Vapour pressure and 'Solubility'.
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions