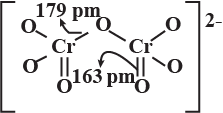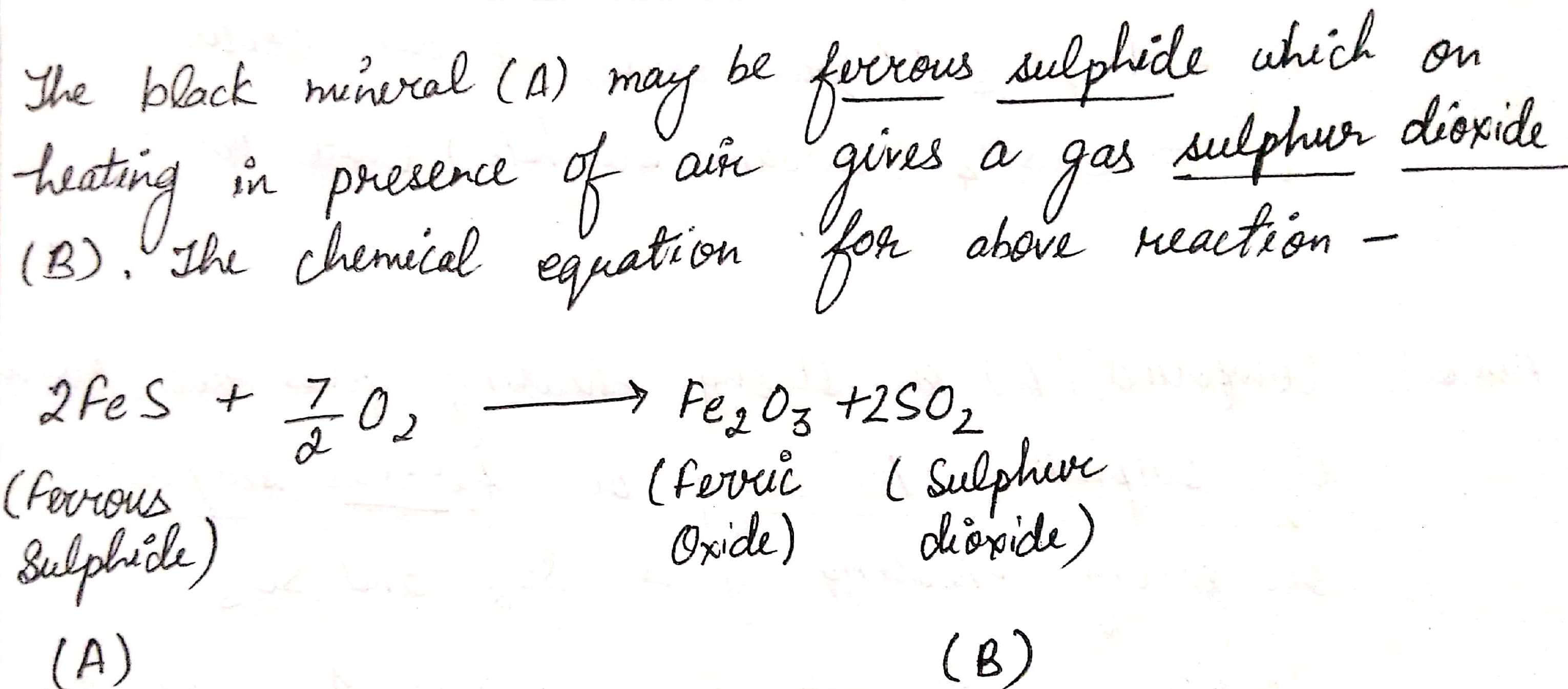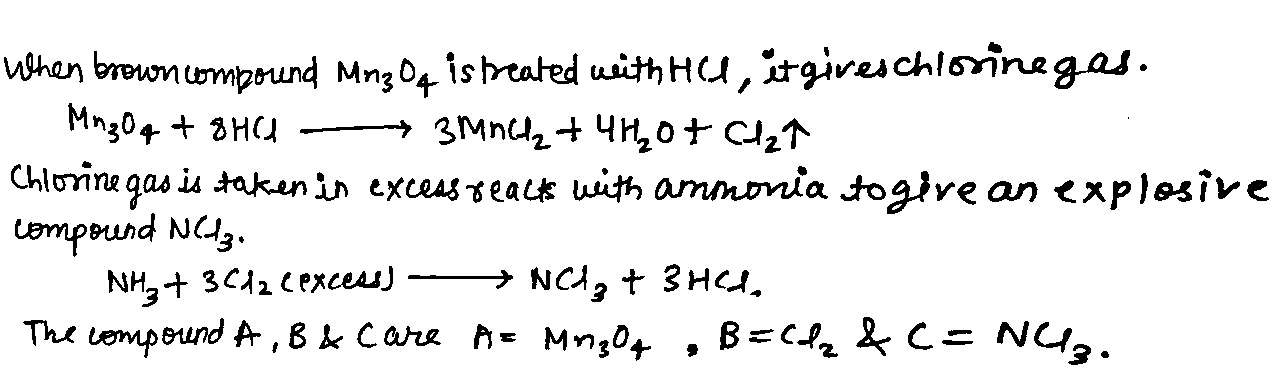The D-And F-Block Elements - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
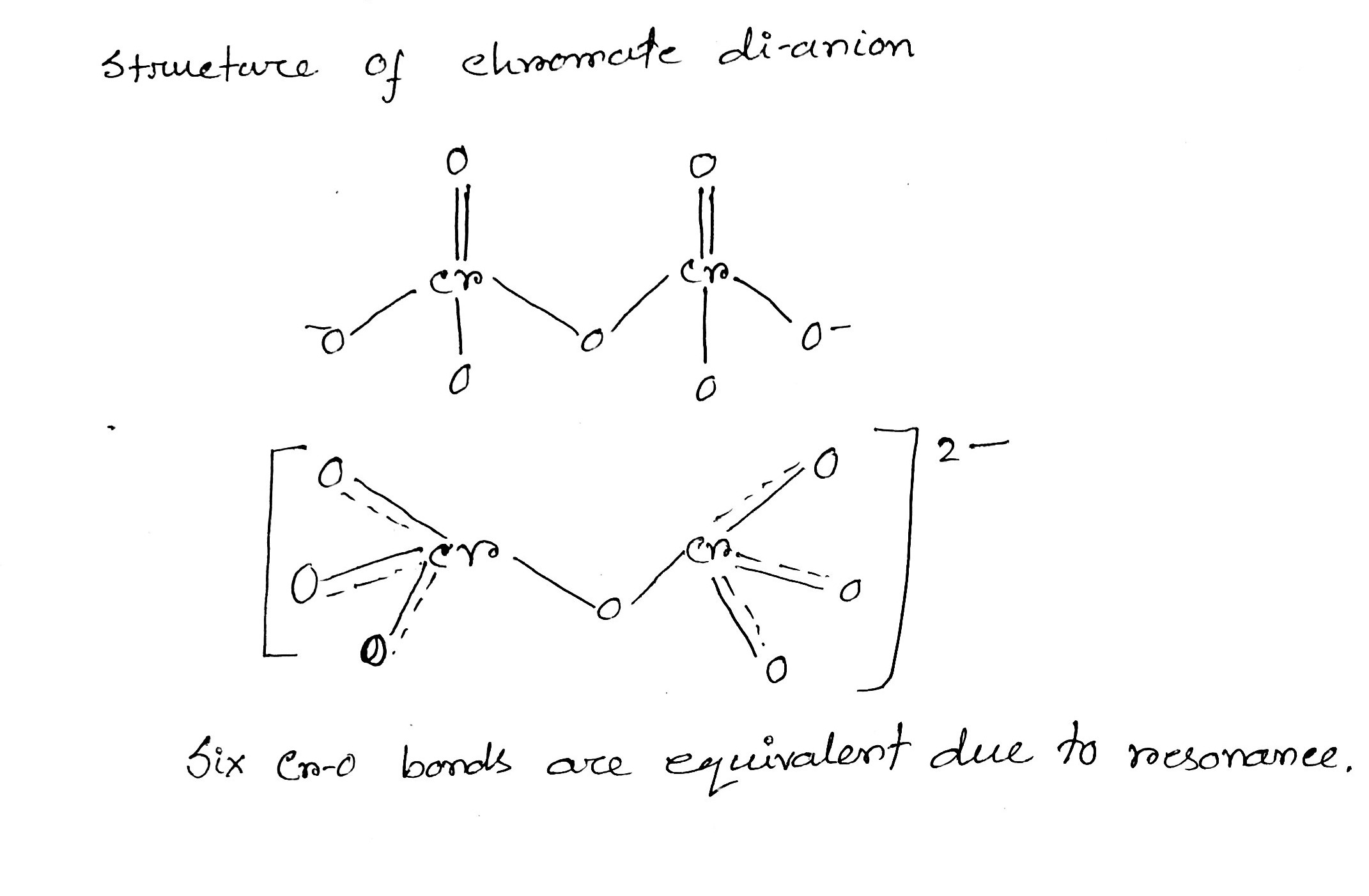
The sum of the total number of bonds between chromium and oxygen atoms in chromate and dichromate ions is ________.
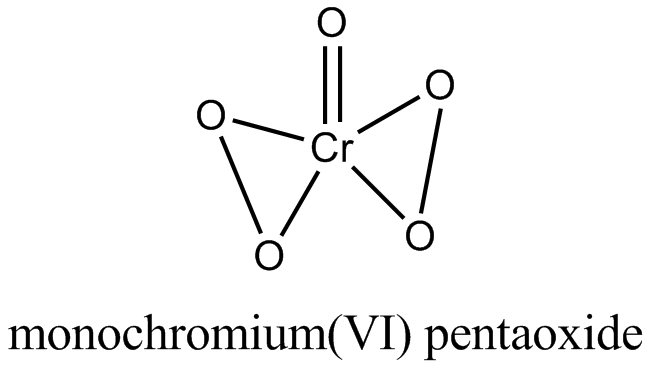
An acidified solution of potassium chromate was layered with an equal volume of amyl alcohol. When it was shaken after the addition of $$1 \ mL$$ of $$3\% \ H_2O_2$$. a blue alcohol layer was obtained. The blue color is due to the formation of a chromium (VI) compound $$‘X’$$. What is the number of oxygen atoms bonded to chromium through only single bonds in a molecule of $$X$$?
Explain why:
Transition elements form coloured compounds.
................... gives blue colour to the Glass.
Why do transition elements form complexes?
Differentiate Lanthanides and Actinides.
For the dichromate dianion, which of the following is true?
1) $$4 Cr - O$$ bonds are equivalent
2) $$6 Cr - O$$ bonds are equivalent
Transition metals are good catalytic agent. Why?
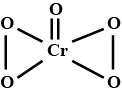
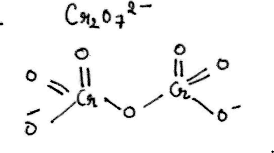
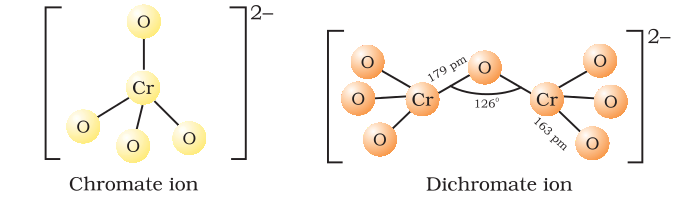
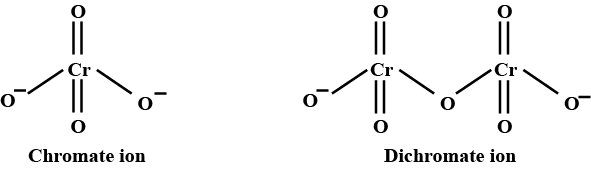
Represent the structure of dichromate ion.
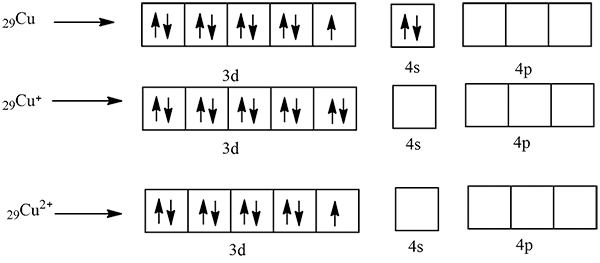
What is the magnetic property of $$Ni$$ atom $$[Z=28]$$ ?
Name the method to determine magnetic properties.
How do you account for the larger size of lanthanum than hafnium though they are successive elements?
Magnetic moment of $$V^{2+}$$ = Magnetic moment of $$Co^{2+} $$ if true enter 1, if false enter 0.
The value of 3.00 BM into SI unit is $$x \times 3.09 \times 10 ^{-24} Am^2$$. The value of $$x $$ is ______.
The colour of $$MnO^-_4$$ ion is due to charge transfer.If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Give a structure of $$Cr_2O^{2-}_7$$ ion.
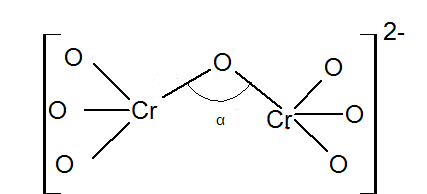
Angle $$\alpha $$ in degrees is:
Magnetic moment of $$Fe^{3+}$$ ions $$\sqrt {35}$$ BM. Determine number of unpaired electrons.
Titanium is much harder than potassium or calcium and so, it is used in making jet aircraft engines.If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Which of the following is not physically change ?
Magnetizing of a piece of iron.
No. of peroxide bonds in blue perchromate is two.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
What do you observe when water droplets fall on blue cobalt chloride ?
The transition metals (with the exception of Zn, Cd and Hg) are hard and have high melting and boiling points.If true enter 1 else 0
Transition elements show variable oxidation states . If true enter 1 else 0.
What is meant by disproportionation? Give two examples of disproportionation reaction in aqueous solution.
Give one point of dissimilarity between lanthanides and actinides.
(a) Which metal in the first transition series (3d series) exhibits $$+ 1$$ oxidation state most frequently and why?
(b) Which of the following cations are coloured in aqueous solutions and why?
$$Sc^{3+}, V^{3+}, Ti^{4+},Mn^{2+}$$
(At. Nos. $$Sc = 21,\ V = 23,\ Ti = 22,\ Mn = 25$$)
(a) How would you account for the following:
(i) The chemistry of actinoids is more complicated as compared to lanthanoids
(ii) Transition metals form complex compounds
(b) Complete the following equation:
$$2{Mn{ O }_{ 4 }}^{ - }+6{ H }^{ + }+S{{ O }_{ 3 }}^{ 2- }\longrightarrow $$
What type of magnetism is shown by a substance if magnetic moments of domains are arranged in same direction?
(i) Name the elements of $$3d$$ transition series which shows maximum number of oxidation states. Why does it show so?
(ii) Which transition metal of $$3d$$ series has positive $${ E }^{ o }_{\left( { { M }^{ 2+ } }/{ M } \right)} $$ value and why?
(iii) Out of $${Cr}^{3+}$$ and $${Mn}^{3+}$$, which is a stronger oxidizing agent and why?
(iv) Name a member of the Lanthanoid series which is well known to exhibit $$+2$$ oxidation state.
(v) Complete the following equation
$$Mn{ O }_{ 4 }^{ - }+8{ H }^{ + }+5{ e }^{ - }\longrightarrow $$
What are the transition elements ? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
(i) Why do transition elements show variable oxidation states?
(ii) Name the element showing maximum number of oxidation states among the first series of transition metals from $$Sc(Z = 21)$$ to $$Zn (Z = 30)$$.
(iii) Name the element which shows only $$+3$$ oxidation state.
(iv) What is lanthanoid contraction? Name an important alloy which contains some of the lanthanoid metals.
$$Ti^{4+}$$ ion is colourless. Give reason.
$$CuI_2$$: Brown :: $$AgCl$$ : ________
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(increases, decreases, positive, efficient, 68, non-efficient, no $$\alpha$$ -hydrogen, $$\alpha$$-hydrogen, negative, Rosenmund's, greater, Cannizzaro, 74, common-ion effect, lesser, buffer action, diamagnetic, paramagnetic)
The transition metals show ............. character because of the presence of unpaired electrons and $${Cu}^{+}$$ is ................... because its electronic configuration is $$[Ar]3{d}^{10}$$.
Give the equations for the conversion of argentite $$(Ag_2S)$$ to metallic silver.
Why is $$S{ c }^{ 3+ }$$ colourless while $${ Ti }^{ 3+ }$$ coloured ? (Atomic number $$Sc=21, Ti=22$$)
Explain the following:
$$(i)$$ Why do transition metal ions possess a great tendency to form complexes?
$$(ii)$$ The paramagnetic character in $$3d$$-transition series elements increases upto $$Mn$$ and then decreases.
What is "Spitting of Silver"? How is it prevented?
Write a note of Plumbosolvency.
How does gold react with aquaregia ?
Explain chromyl chloride test with equation.
Why do d-block elements from complexes?
Aqueous $$Cu^{+2}$$ ions are blue in color, where as aqueous $$Zn^{+2}$$ ions are colorless. Why?
What is tailing of Mercury?
Give the composition of the following alloys:
(a) German silver
(b) Brass
Write the characteristic properties of transition elements.
What is spitting of silver? How can it be prevented?
Give the composition and uses of Nichrome.
What is "Tailing of Mercury"
Write the uses of Lanthanides.
Write the equations involved in the preparation of potassium dichromate from chromite ore.
Explain:
(i) Transition elements mostly form the complex compound. Why?
(ii) Transition elements are good catalyst. Why?
(iii) Transition elements show variable valency. Why?
Write the factors which are related to the colour of transition metal ions.
Explain the following
(i) $$Cu^+$$ is colourless and $$cu^{2+}$$ is coloured,
(ii) $$Zn$$ shows only + 2 Oxidation state.
With reference to the first row transition series :
i) Name the metal which possesses maximum number of oxidation states.
ii) Among $$Zn^{+2}$$ and $$Cu^{+2}$$ which is colourless?
iii) Between $$Ti^2+$$ and $$V^{2+}$$ which ion contains more number of unpaired electrons?
(a) What are Lanthanide elements?
(b) What do you understand by Lanthanide contraction?
(c) Write chromyl chloride test with equation.
Give any two differences between lanthanoids and actinoids.
(a) Why Transition elements become paramagnetic?
(b) Explain oxidization properties of potassium permanganate in acidic medium. (any four only)
Calculate the value of magnetic moment of $$V^{+2}$$ ?
Calculate the 'spin only' magnetic moment of $$M^{2+}(aq)$$ ion (Z=27).
What is lanthanide contraction? Explain the cause of lanthanide contraction.
(i) Scandium (z = 21) is a transition element but zink (z = 30) is not. Explain.
(ii) Calculate the equivalent weight of $$KMnO_4$$in acidic medium.
(iii) What do you mean by Lanthanoid contraction ?
Out of $$C{ r }^{ 3+ }$$ and $$M{ n }^{ 3+ }$$, which is stronger oxidising agent and why?
Why do transition elements form alloys?
Explain why:
Zr and Hf exhibit similar properties.
(At. no. of Zr = 40, Hf = 72)
What happens when sulphur dioxide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a Fe(III) salt?
(i) Write down any three difference between Lanthanoid and Actinoid ?
(ii) The melting and boiling points of Zy. Cd and Hg are low. Why ?
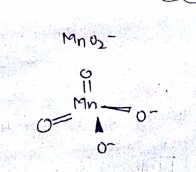
(iii) Draw the structure of manganate ion.
Explain why:
Transition elements usually form coloured ions.
What is meant by ferrimagnetism? Give any two examples.
Write any four applications of $$'f'$$ - block elements.
In the $$3$$d series from Sc$$(z=21)$$ to Zn$$(z=30)$$, enthalpy of atomisation of Zn is the lowest.
What happens when $$(NH_4)_2Cr_2O_7$$ is heated?
Magnetic momentum of an ion $${ M }^{ +3 }$$ is $$\sqrt { 35 }\ BM$$ Then, number of electron in $$d$$ orbital of $$m$$ element will be__________.
Which of the following ions is coloured in aqueous solution?
i) $$Cu^{2+}$$
ii) $$Cu^{1+}$$
Write the nomenclature and symbol of an element having atomic number 119?
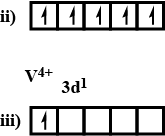
What is magnetic moment of $${ V }^{ +4 }$$?
Why are metals like chromium and molybdenum very hard?
Name the transition element of highest density.
Why basic character in lanthanoid hydroxides decreases across the period?
Transition metals and their compounds are used as catalysts. Give two reasons.
Write a chemical equation for burning of lanthanoids ($$ln$$) in oxygen.
Use hund's rule to derive the electronic configuration of $$Ce^{+3}$$ ion, and calculate its magnetic moment on the basis of 'spin only' formula. ( For Ce, Z = 58)
Give any two difference between lanthanoids and actinoids.
Answer the following question : Among the divalent cations in the first series of transition elements,manganese exhibits the maximum paramagnetism.
Calculate the magnetic moment of $$MnS{O_4}$$?
Transition elements generally forms coloured compounds. Why?
Give two reactions in which transition metals or their compound acts as catalysts.
Why $$Zn^{2+}$$ is diamagnetic whereas $$Cr^{3+}$$ is paramagnetic ?
Write short note on Lanthanide contraction.
Why do transition metals have high enthalpies of atomization?
How is potassium dichromate prepared from chrome iron ore?
Transition elements from complexes easily ? Justify.
Account for the following:
(i) Manganese shows maximum number of oxidation states in 3d series.
(ii) $$E^o$$ value for $$Mn^{3+} / Mn^{2+}$$ couple is much more positive than that for $$Cr^{3+} / Cr^{2+}$$.
(iii) $$Ti^{4+}$$ is colourless whereas $$V^{4+}$$ is coloured in an aqueous solution.
Identify the unknown compounds:
Fill in the blanks:
(N) Vegetable ghee is manufactured by the ..... of oils in presence of ..... as a catlayst.
Complete the following equations:
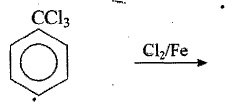
Complete the following reactions:
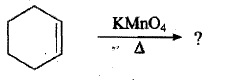
Give reason :
Transition metals and their compounds show catalytic activities.
Write two similarities between chemistry of lanthanoids and actinoids.
Write the preparation of the following :
$$Na_2 Cr_2 O_7$$ from $$Na_2CrO_4$$
Complete the following reactions.
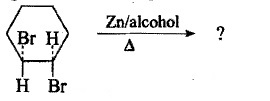
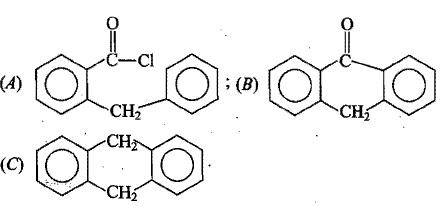
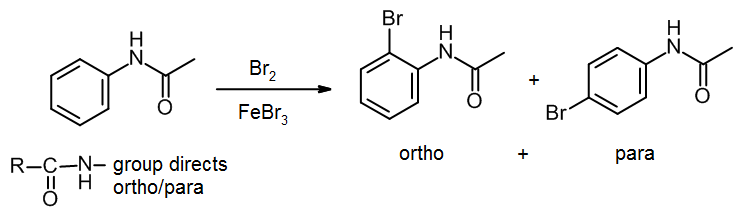
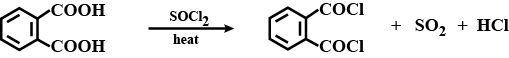
The above reaction gives two products. Write the structures of the products.
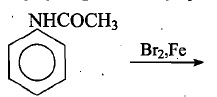
The minimum number of electrons having magnetic quantum number of zero for $$Ni$$ is :
Match the compounds in column-I with their properties in column-II
Reactivity of transition elements decreases almost regularly from Sc to Cu.Explain.
The second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row. Explain why?
Although $$Zr$$ belongs to $$4d$$ and $$Hf$$ belongs to $$5d$$ transition series but it is quite difficult to separate them why ?
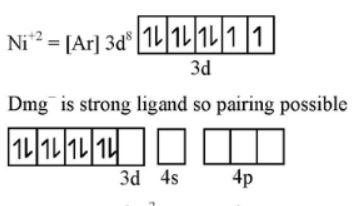
$$NiCl_2$$ in the presence of dimethyl glycoxime (DMG) gives a complex which precipitates in the presence of $$NH_4OH$$, giving a bright red color.
Predict whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
Predict the spin only magnetic moment for:
$$Mn^{2+}$$
Predict the spin only magnetic moment for:
$$Fe^{2+}$$
The type of magnetism exhibited by $$[Mn(H_2O)_6]^{2+}$$ ion is ________.
Answer the following:
Why the compounds of transition elements are coloured?
Explain the following giving proper reason:
Transition metals and their compounds act as catalysis.
Transition metals and their compounds act as catalysis.
Explain the following giving proper reason:
$$CuSO_4$$ is paramagnetic while $$ZnSO_4$$ is diamagnetic.
$$CuSO_4$$ is paramagnetic while $$ZnSO_4$$ is diamagnetic.
Predict the spin only magnetic moment for:
$$Cu^{+}$$
Explain by giving suitable reason.
Yellow coloured aqueous solution of sodium chromate changes to orange-red when $$CO_2$$ under pressure is passed.
Yellow coloured aqueous solution of sodium chromate changes to orange-red when $$CO_2$$ under pressure is passed.
Predict the spin only magnetic moment for:
$$Cr^{6+}$$
Calculate magnetic moments of $$M^{2+}$$ ions of $$Ti(Z=22), Cr(Z=24), Mn(Z=25)$$ and $$Cu(Z=29)$$ and arrange them in increasing order.
Answer the following:
Why most of the compounds of transition elements are paramagnetic?
Explain by giving suitable reason.
$$Hg^{2+}$$ and $$Hg_2^{2+}$$ salts are colourless.
$$Hg^{2+}$$ and $$Hg_2^{2+}$$ salts are colourless.
Answer the following:
Which bivalent ion of first transition series show the highest paramagnetism?
Explain:
Which divalent metal ion has maximum paramagnetic character among the first transition metals? Why?
A black mineral $$(A)$$ on heating in presence of air gives a gas $$(B)$$.
Explain by giving suitable reason.
$$Cu^{2+}$$ salts are paramagnetic while $$Cu^{+}$$ salts are diamagnetic in nature.
$$Cu^{2+}$$ salts are paramagnetic while $$Cu^{+}$$ salts are diamagnetic in nature.
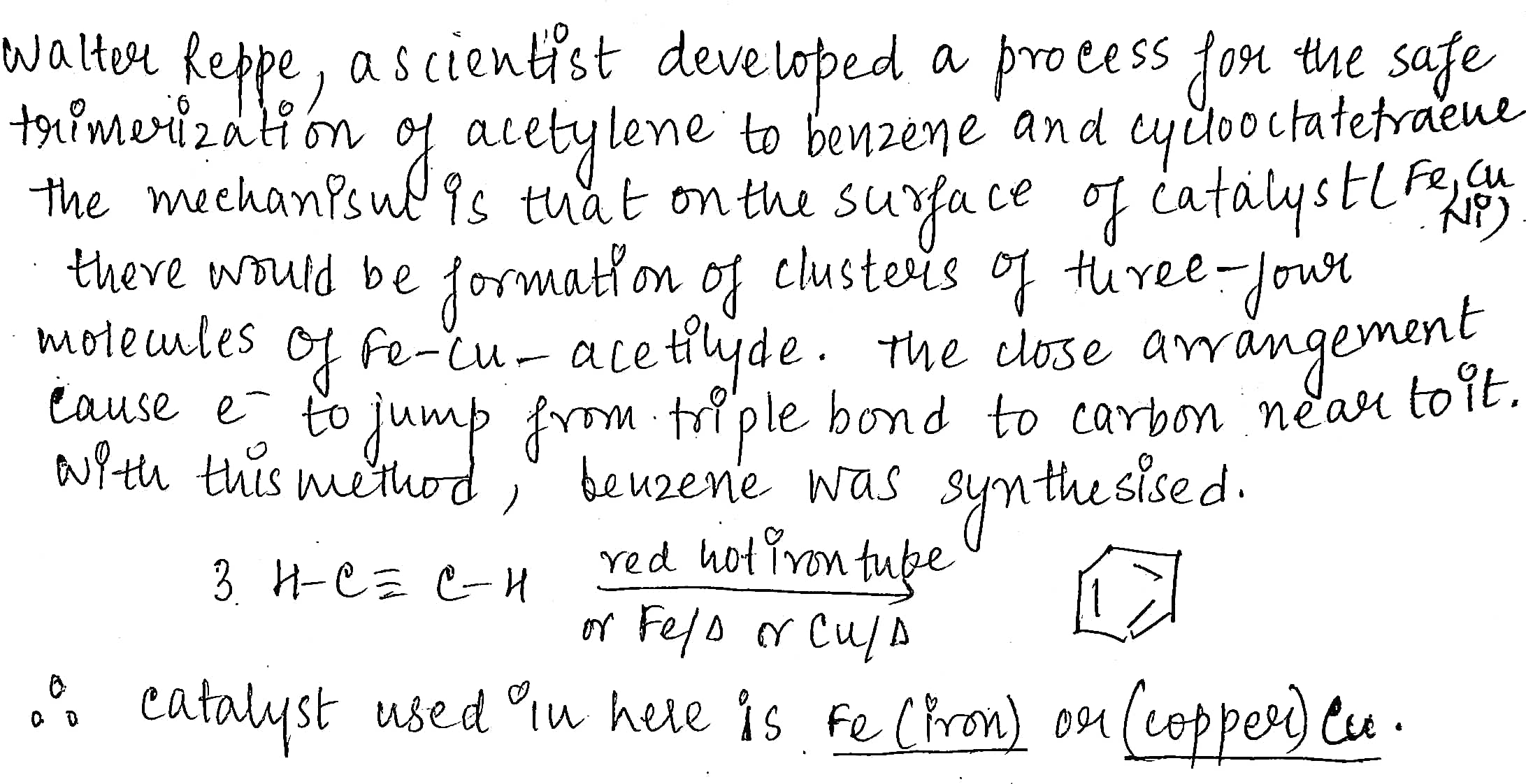
Write down the name of catalyst for the following:
Reppe synthesis of benzene.
Write down the name of catalyst for the following:
Fenton's reagent in the synthesis of aldehydes from alcohols.
Write down the name of catalyst for the following:
Deacon's process of making $$Cl_2$$ from $$HCl$$.
Write down the name of catalyst for the following:
Adams catalyst in reduction.
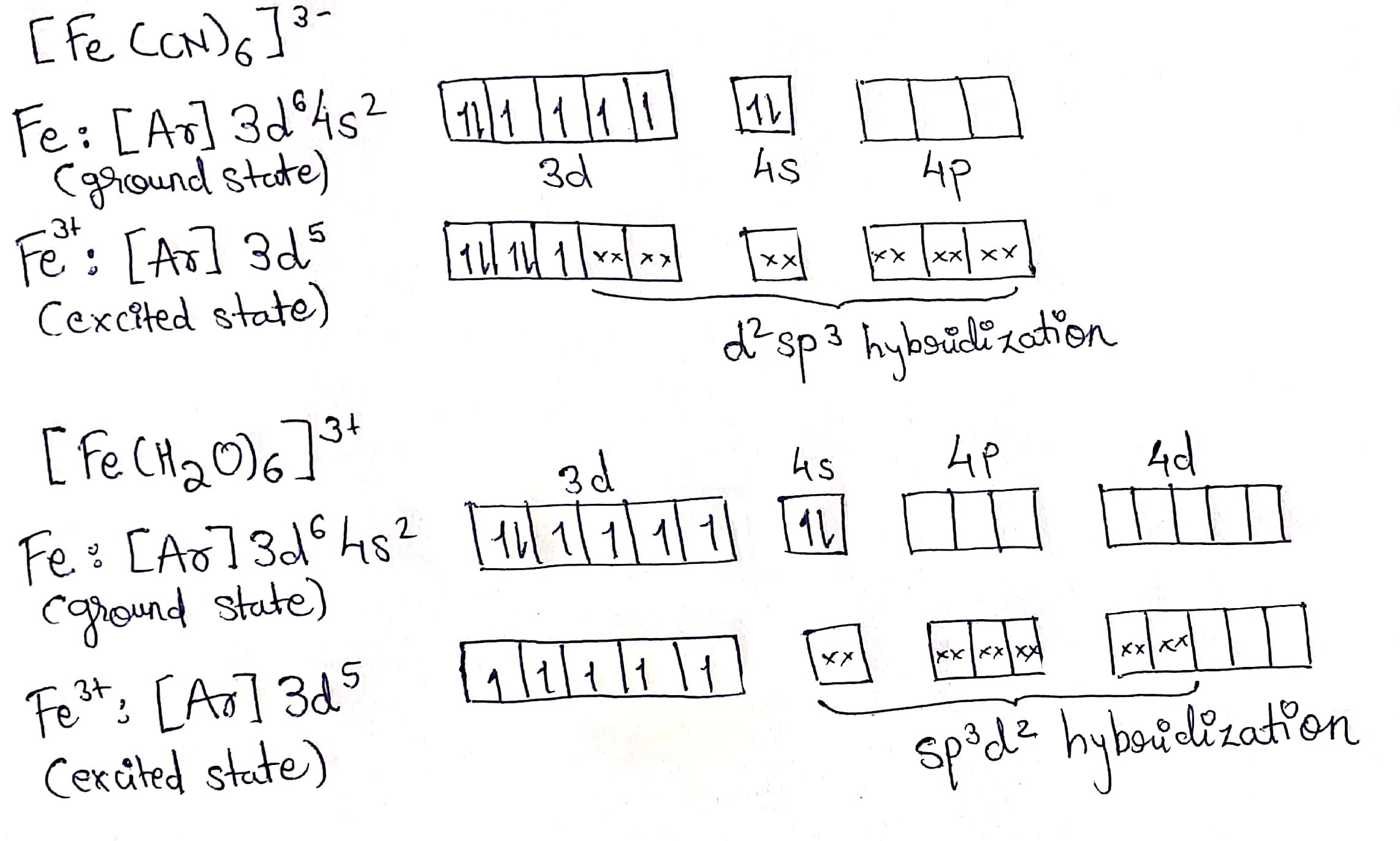
Calculate magnetic moment of $$Fe^{3+}$$ in $$[Fe(CN)_6]^{3-}$$ and in $$[Fe(H_2O)_6]^{3-}$$.
Match the List $$I$$ with List $$II$$:
Give the formula of three ions which are coloured due to charge transfer spectra.
What is the magnetic moment of $$Fe^{3+}$$?
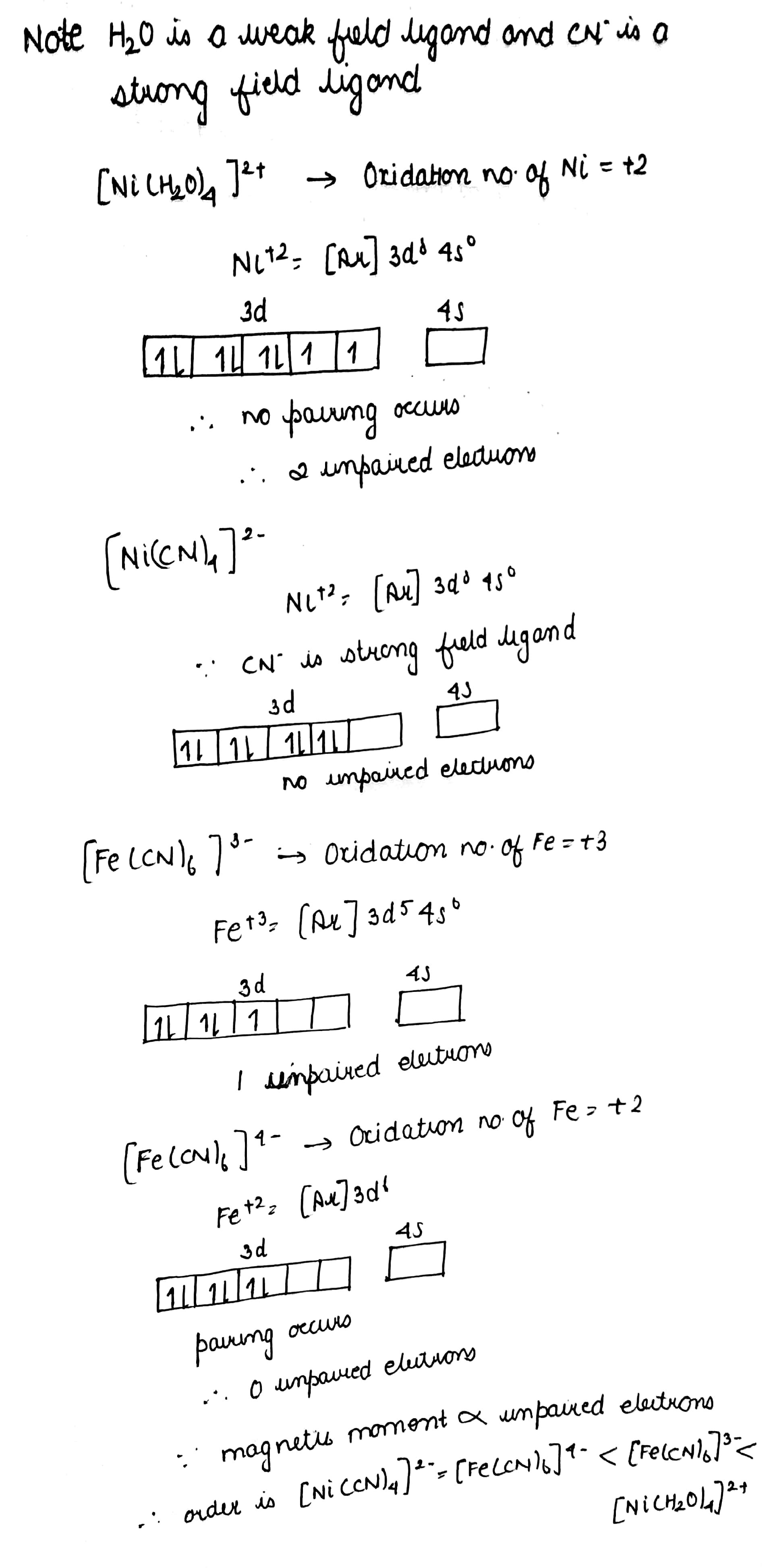
Arrange following complex in decreasing order of magnetic moment:
$$[Ni(H_2O)_4]^{2+},\ [Ni(CN)_4]^{2-},\ [Fe(CN)_6]^{3-},\ [Fe(CN)_6]^{4-}$$
What happen when?
Ammonium dichromate is heated strongly.
How many Cr-O bond are equivalent in chromate dianion?
Match the items under List 1 with the compounds in ListSelect the correct answer from the sets (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Write similarity and difference between the chemistry of lanthanoid and actinoid elements.
Explain: The metal-metal bonding is more frequently found with the second and third series of transition elements.
Which transition metal of $$3d$$ series has positive $$E^{\circ}(M^{2+}/M)$$ value and why?
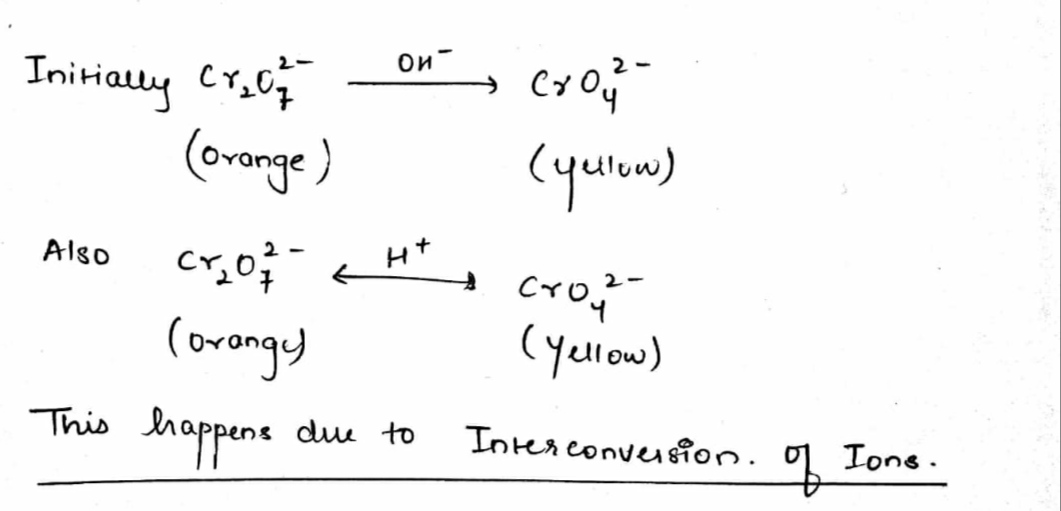
Orange colour of $$Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-}$$ ion changes to yellow when treated with an alkali. Why?
Account for: Transition metals form large number of complex compounds.
Explain: Transition elements and their compounds are known as catalysts.
Chemistry of actinoids in complicated as compared to lanthanoids. Give two reasons.
Complete and balance the following reaction:
$$Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-} + I^{-} + H^{+} \rightarrow$$
Account for: $$Zr$$ and $$Hf$$ have almost similas atomic radii.
What is lanthanoid contraction? Name an important alloy which contains some of the lanthanoid metals.
Account for: $$E_{0}$$ value for the $$Mn^{3+}/Mn^{2+}$$ couple is highly positive ($$+1.57V$$) as compare to $$Cr{3+}/Cr^{2+}$$ which is negative ($$-0.4V$$). Why?
Account for: $$Zn$$ has lowest enthalpy of atomisation in $$3d$$ series.
How do you prepare: $$Na_{2}Cr_{2}O_{7}$$ from $$Na_{2}CrO_{4}$$?
Account for: Transition metals form coloured compounds.
Account for: $$Cr^{2+}$$ is a strong reducing agent.
Define lanthanoid contraction. Write the common oxidation states of Lanthanoids
With reference to structural variability and chemical reactivity, write the differences between lanthanoids and actinoids.
Out of $$Mn^{3+}$$ and $$Cr^{3+}$$, which is more paramagnetic and why? (Atomic numbers: $$Mn=25$$, $$Cr=24$$)
Why are transition elements known as $$d-$$block elements?
Compare non transition and transition elements on the basis of their stability of oxidation states.
On the basis of lanthanoid contraction, explain the stability of the complexes of lanthanoids.
Write the equations involved in the preparation of potassium dichromate from sodium chromate ($$Na_{2}CrO_{4}$$).
Give reason: From element to element, the actinoid contraction is greater than the lanthanoid contraction.
When an oxide of manganese ($$A$$) is fused with KOH in the presence of an oxidising agent and dissolved in water, it gives a dark solution of compound ($$B$$). Compound ($$B$$) disproportionates in neutral or acidic solution to give purple compound ($$C$$). An alkaline solution of compound ($$C$$) oxidises potassium iodide solution to a compound ($$D$$) and compound ($$A$$) is also formed. Identify compounds $$A$$ to $$D$$ and also explain the reactions involved.
The elements of $$3d$$ transition series are given as :
$$Sc,\ Ti,\ V,\ Cr,\ Mn,\ Fe,\ Co,\ Ni,\ Cu,\ Zn$$
Which element is soft and why?
Which element is soft and why?
Account for: The atomic radii of the metals of the third ($$5d$$) series of transition elements are virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of the second ($$4d$$) series.
Draw the structures of chromate and dichromate ions.
Why does a transition series contain 10 elements?
Describe the trends in the Magnetic behaviour of dipositive gaseous ions ($$M^{2+}$$) of the first series of the transition elements:
Explain: There is a close similarity in physical and chemical properties of the $$4d$$ and $$5d$$ series of the transition elements, much more than expected on the basis of usual family relationship.
How would you account for: Many of the transition elements and their compounds can act as good catalysts.
Explain why $$[Fe(H_2O)_3]^{3+}$$ has magnetic moment value of $$5.92\ BM$$ whereas $$[Fe(CN)_6]^{3-}$$ has a value of only $$1.74\ BM$$.
How would you account for: Transition metals and their compounds show catalytic properties.
How would you account for: There is a greater range of oxidation states among the actinoids than among the lanthanoids.
Name an ore used in the preparation of potassium dichromate.
What is the general formula by which the electronic configuration of the transition elements is represented?
Giving the name, the stereochemistry and the magnetic behaviour of the following complex:
$$[Co(NH_3)_5 Cl]Cl_2$$
Answer the following question:
Why is $$[NiCl_4]^{2-}$$ paramagnetic while $$[Ni(CN)_4]^{2-}$$ is diamagnetic?
(Atomic number $$Ni=28$$)
Name the type of elements , which have their
Two outermost shell incomplete - ...............
How would you account for the following?
$$[Fe (CN)_6]^{3-}$$ is weakly paramagnetic while $$[Fe(CN)_6]^{4-}$$ is diamagnetic.
Mention any three processes where transition metals act as catalysts.
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
$$C_6H_5-CH_2-CH_3\ \to \ C_6H_5-COO^- K^+$$
What is the role of metal or regents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions?
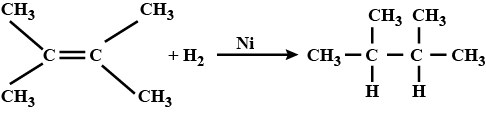
Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change their oxidation state. How does $$Fe(III)$$ catalyse the reaction between iodide and persulphate ions?
Complete each synthesis by giving missing reagents or products in the following :
What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions?(b) $$CH_3COOH + CH_3CH_2OH \xrightarrow {conc. \ H_2SO_4} CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_20$$
(c) $$CH_3CH_2OH \xrightarrow[Heat]{KMnO_4} CH_3COOH$$
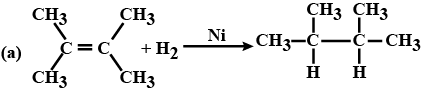
(c) $$CH_3CH_2OH \xrightarrow[Heat]{KMnO_4} CH_3COOH$$
Correct the statement.
Transition elements are placed at extreme right of the periodic table.
Name two elements in each case :
Actinides
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to:
Chemical activity.
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to:
Atomic and ionic size.
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to electronic configuration.
Explain giving reasons:
The transition metals generally form coloured compounds.
Explain giving reasons:
Transition metals and many of their compounds show paramagnetic behaviour.
Write any three differences between lanthanides and actinides.
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to:
Oxidation states.
Explain giving reasons:
Transition metals and their many compounds act as good catalyst.
Write balanced equations for the following :
NaCl is heated with sulphuric acid in the presence of $$ MnO_2 $$.
Assign reasons for the following:
The transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalyst.
When a magnetic field is applied, certain substances are attracted by the applied field. Those are called paramagnetic substances. Which is more paramagnetic $${Mn}^{2+}$$ or $${Cu}^{2+}$$? Why?
Total number of molecules which hydrolysed at room temperature and hybridization of central atom in $$sp^{3}d$$ in transition state :
$$CCl_{4}, SiCl_{4}, NCl_{3}, PCl_{3}, AsCl_{3}, SF_{6}, P_{4}O_{6}, P_{4}O_{10}, SeF_{6}$$
$$(NH_4)_2Cr_2O_7$$ is the compound which imparts odour in fire works.If true enter 1, else enter 0.
We use $$ZnO$$ in paints instead of $$Pb^{2+}$$ salts. If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Magnetic moment of $$Sc^{2+}$$ = Magnetic moment of $$Cu^{2+} $$If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the columns.
Column I lists the metal ion and Column II lists the Magnetic moment (BM) :
Match the columns:
State whether the given statement is true or false:
Dipositive zinc exhibits paramagnetism due to loss of two electrons from $$3d$$-orbitals of neutral atom.
Explain given reasons:
(i) Transition metals and many of their compounds show paramagnetic behaviour.
(ii) The enthalpies of atomisation of the transition metals are high.
(iii) The transition metals generally form coloured compounds.
(iv) Transition metals and their many compounds act as good catalyst.
(ii) The enthalpies of atomisation of the transition metals are high.
The chemistry of the actinoids is not so smooth as that of the lanthanoids. Justify this statement by giving some examples from the oxidation state of these elements.
Use Hund's rule to derive the electronic configuration of $$Ce^{3+}$$ ion and calculate its magnetic moment on the basis of spin-only formula.
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to: (i) electronic configuration (ii) atomic and ionic sizes and (iii) oxidation state (iv) chemical reactivity.
What are alloys? Name an important alloy which contains some of the lanthanoid metals. Mention its uses.
Predict which of the following will be coloured in aqueous solution? $$Ti^{3+}, V^{3+}, Cu^{+}, Sc^{3+}, Mn^{2+}, Fe^{3+}$$ and $$Co^{2+}$$. Give reasons for each
Compare the general characteristics of the first series of the transition metals with those of the second and third series metals in the respective vertical columns. Give special emphasis on the following points:
(i) electronic configurations (ii) oxidation states (iii) ionisation enthalpies and (iv) atomic sizes
Compare the chemistry of the actinoids with that of lanthanoids with reference to: (i) electronic configuration (ii) oxidation states and (iii) chemical reactivity
Comment on the statement that elements of the first transition series possess many properties different from those of heavier transition elements.
Write one similarity and one difference between the chemistry of lanthanoid and actinoid elements
Fourteen elements following Lanthanum are called Lanthanoids:
(a) What is Lanthanoid contraction? Give reason for it.
(b) $$KMn{O}_{4}$$ is a purple coloured crystal and it acts as an oxidant. How will you prepare $$KMn{O}_{4}$$ from $$Mn{O}_{2}$$?
Account for the following:
(i) Transition metals show variable oxidation states.
(ii) $$Zn, Cd$$ and $$Hg$$ are soft metals.
(iii) $$E^{\circ}$$ value of the $$Mn^{3+}/Mn^{2+}$$ couple is highly positive $$(+ 1.57\ V)$$ as compared to $$Cr^{3+}/Cr^{2+}$$
Explain why:
$$Cu^{+}$$ is diamagnetic but $$Cu^{2+}$$ is paramagnetic. $$(Z = 29)$$
Why do transition elements form complexes?
Which of the following arrangments does not represent the correct order of the property stated against it?
(1) $$V^{2+} < Cr^{2+} < Mn^2 < Fe^{2+}$$ : paramagnetic behaviour
(2) $$Ni^{2+} < Co^{2+} < Fe^{2+} < Mn^{2+}$$ : ionic size
(3) $$Co^{3+} < Fe^{3+} < Cr^{3+} < Sc^{3+}$$ : stability in aqueous solution
(4) $$Sc < Ti < Cr < Mn$$ : number of oxidation states
Consider the following list of reagents:
Acidified $${K}_{2}{Cr}_{2}{O}_{7}$$, alkaline $$KMn{O}_{4},Cu{SO}_{4},{H}_{2}{O}_{2},{Cl}_{2},{O}_{2},Fe{Cl}_{2},H{NO}_{3}$$ and $${Na}_{2}{S}_{2}{O}_{3}$$. The total number of reagents that can oxidise aqueous iodide to iodine is:
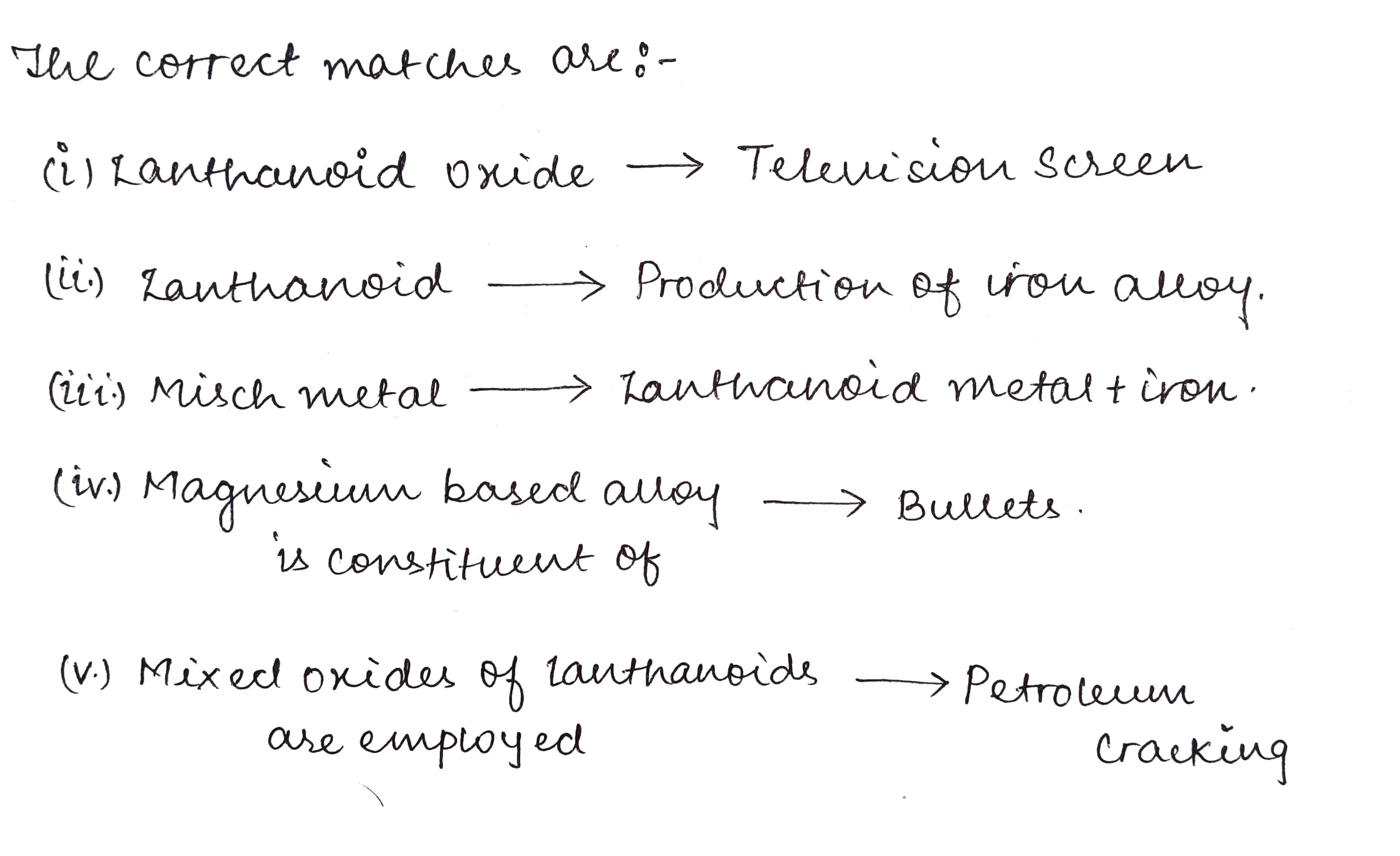
Match the compounds/elements given in Column 1 with uses given in Column 2.
Column 1:- Column 2:-
I) Lanthanoid oxide. A) production of iron alloy
II) Lanthanoid. B) television screen
III) Misch metal. C) petroleum cracking
IV) Magnesium based alloy D) Lanthanoid metal+iron
is constituent of
V) Mixed oxides of Lanthanoids E) bullets
are employed
F) in X-ray screen
Give reason :
$$[Ti(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{3+}$$ is coloured while $$[Sc(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{3+}$$ is colourless
Why salts of $$Sc^{3+},Ti^{4+},V^{5+}$$ are colourless?
Indicate the steps in the preparation of $$ \mathrm { K } _ { 2 } \mathrm { Cr } _ { 2 } \mathrm { O } _ { 7 } $$ from chromite ore.
What is lanthanoid contraction? What are the consequences of lanthanoid contraction?
Complete the following reactions:
? $$ \underset {[H^{+}]}{\xrightarrow {KMnO_{4}}}CH_{3}CH_{2}\overset {\overset {O}{\parallel}}{C}CH_{3} + HO - \overset {\overset {O}{\parallel}}{C} CH_{2} CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3}$$.
? $$ \underset {[H^{+}]}{\xrightarrow {KMnO_{4}}}CH_{3}CH_{2}\overset {\overset {O}{\parallel}}{C}CH_{3} + HO - \overset {\overset {O}{\parallel}}{C} CH_{2} CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3}$$.
Describe the structure of interstitial and substitutional alloys and outline the factor determining which is formed.
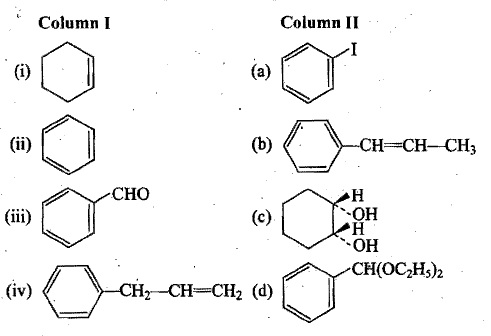
Structure of some reactants and products are given in column I and II respectively. First match the appropriate reactant-product pair from column I and II and then suggest another suitable reagent for each pair:
When orange solution containing $$ Cr_2O_7^{2-} $$ ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when $$ H^+ $$ ions are added to yellow solution,an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
When a brown compound of manganese (A) is treated with $$HCl$$ it gives a has (B). The gas taken is excess, reacts with $$ NH_3 $$ to give an explosive compound (C). Identify compounds A, B, and C.
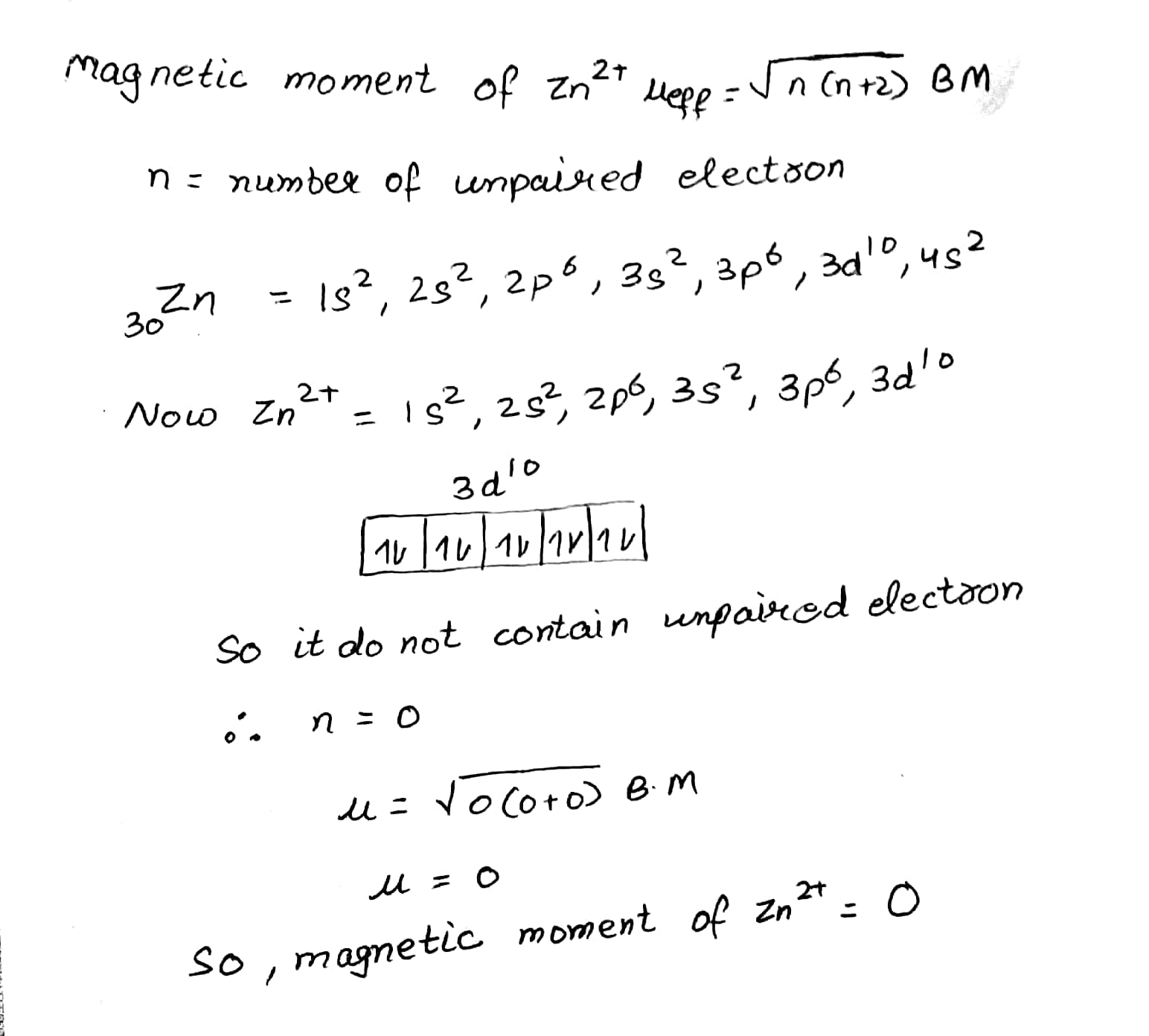
Find the magnetic moment of a salt containing $$Zn^{2+}$$ ion.
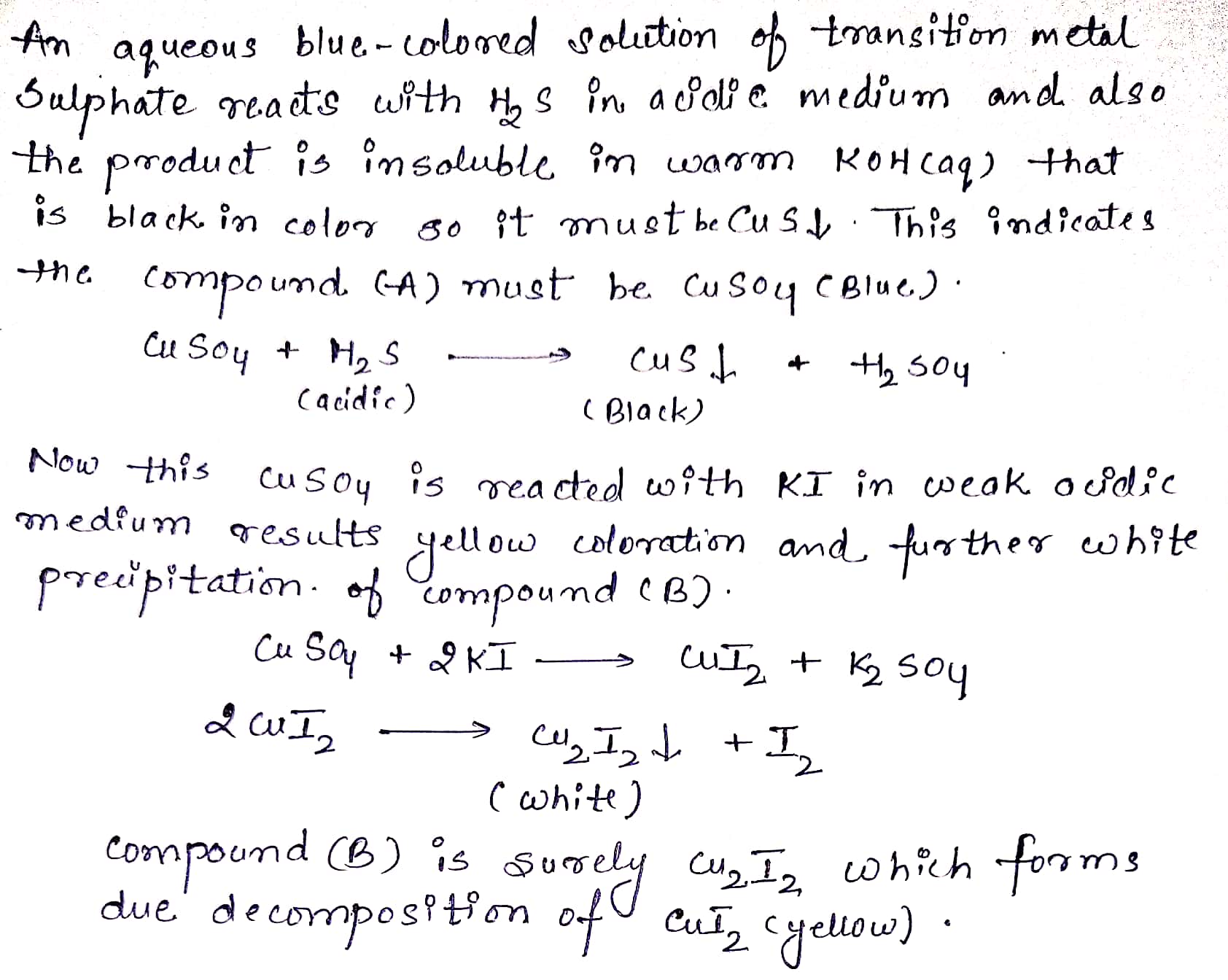
An aqueous blue-colored solution of a transition metal suphate reacts with $$ H_2S $$ in acidic medium to give a black precipitate A which is insoluble in warm aqueous solution of KOH. The blue solution on treatement with KI in weakly acidic medium turns yellow and produces a white precipitate B. Identify the transition metal ion. Write the chemical reactions involved in the formation of A and B.
Complete the following equation:
- $$Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-}+H^{+}+SO_{2}\rightarrow SO_{4}^{2-}+H_{2}O+......$$
Among $$PbS,CuS,HgS,MnS,Ag_2S,NiS,CoS,Bi_2S_3$$ and $$SnS_2$$ the total number of BLACK coloured sulphides is:
Explain the following:
$$[CoF_6]^{3-}$$ is paramagnetic but $$[Co(CN)_6]^{3-}$$ is diamagnetic.
$$[FeCN)_6]^{3-}$$ ion has magnetic moment of $$1.41\ B.M$$. While $$[Fe(H_2O)_6]^{3+}$$ has a magnetic moment of $$5.92\ B.M.$$ Explain.
Match the List $$I$$ with their characteristic List in $$II$$:
On the basis of lanthanoid contraction, explain the nature of bonding in $$La_{2}O_{3}$$ and $$Lu_{2}O_{3}$$.
Why do transition elements form complexes ?
Match the compounds in Column I with its characteristics reactions given in Column II.
Some d-block elements are given below:
$$(Cr,Mn,Fe,Co,Ni)$$
(a) Identify the element which shows maximum paramagnetic behaviour
(b) Give reason for the highest paramagnetic property of that element
(c) When two electrons are lost from each atom, is there any change in magnetic properties of each? Explain.
Write the uses of lanthanides and actinides.
Write electronic configuration of $${Cu}^{2+}$$. Calculate its magnetic moment.
Describe the preparation of potassium dichromate from iron chromite ore. What is the effect of increasing pH on a solution of potassium dichromate?
The magnetic moment of a compound of transition element is $$3.9B.M$$. Write the number of unpaired electrons in the element.
Write four differences between lanthanoids and actinoids.
Predict which of the following will be coloured in aqueous solution?
$${Ti}^{3+},{V}^{3+},{Cu}^{+},{Sc}^{3+},{Mn}^{2-},{Fe}^{3+}$$ and $${Co}^{2+}$$
Give reasons for each:
Assign A, B, C, D from given type of reactions.
A for precipitate formation reaction.
B for precipitate dissolution reaction.
C for precipitate exchange reaction.
D for no reaction.
$$2BaCrO_4+4HCl \longrightarrow 2BaCl_2+H_2Cr_2O_7+H_2O$$
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions