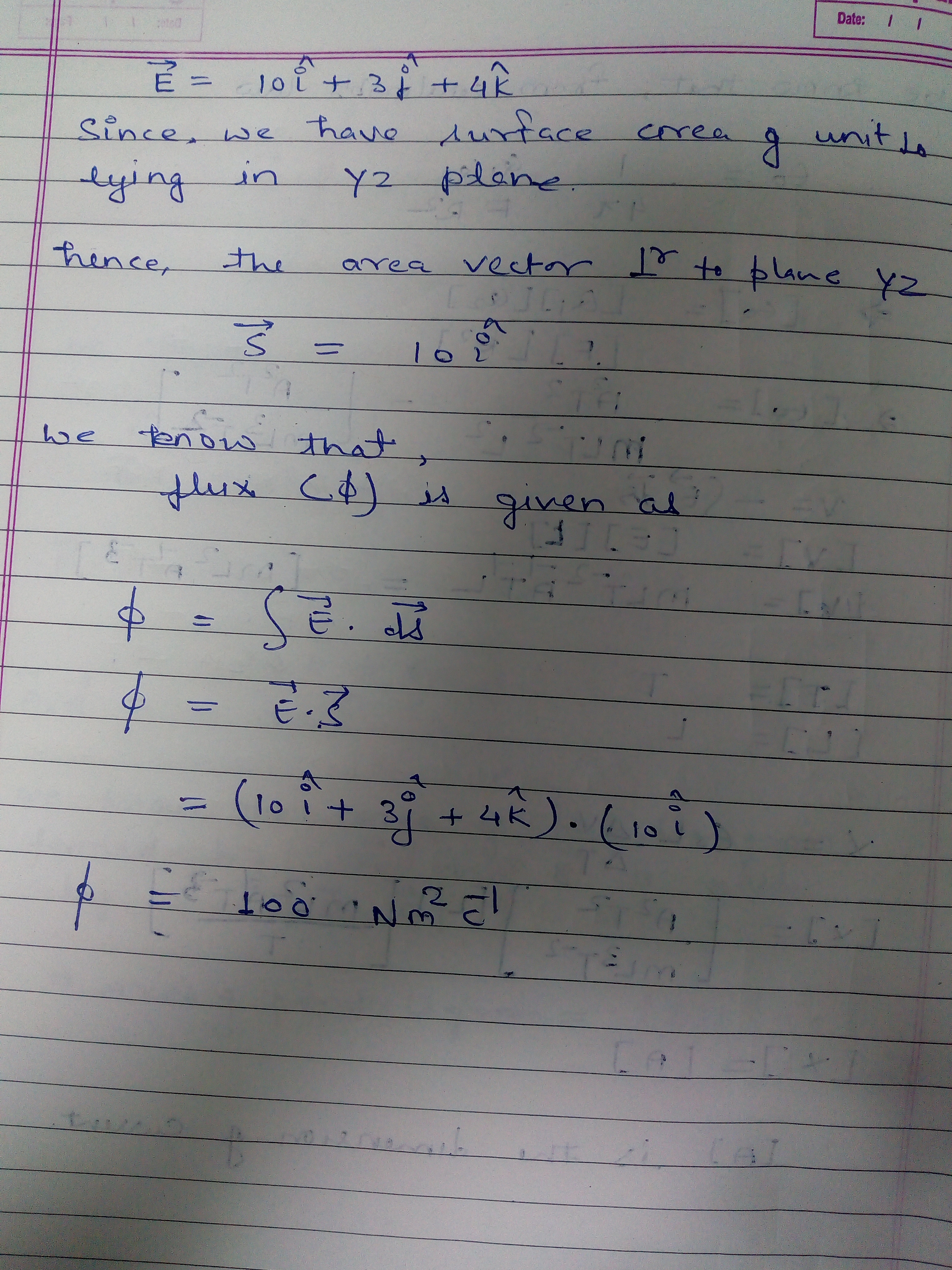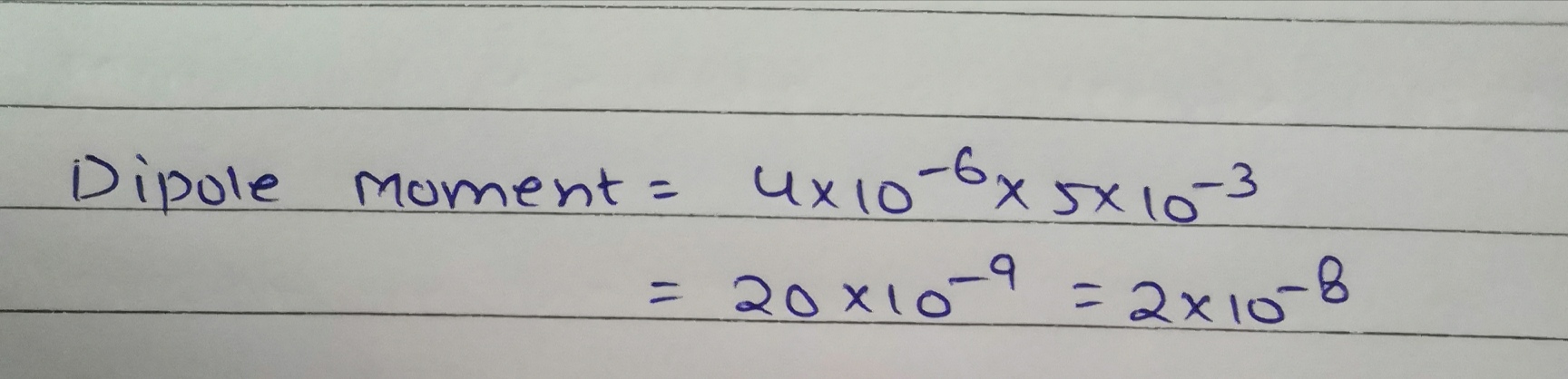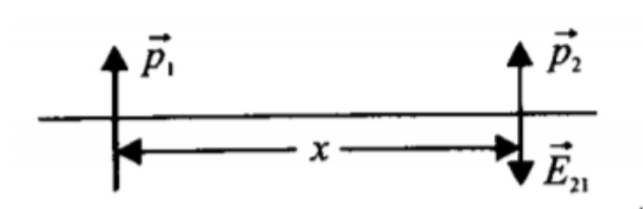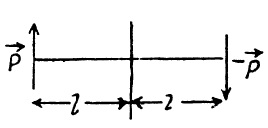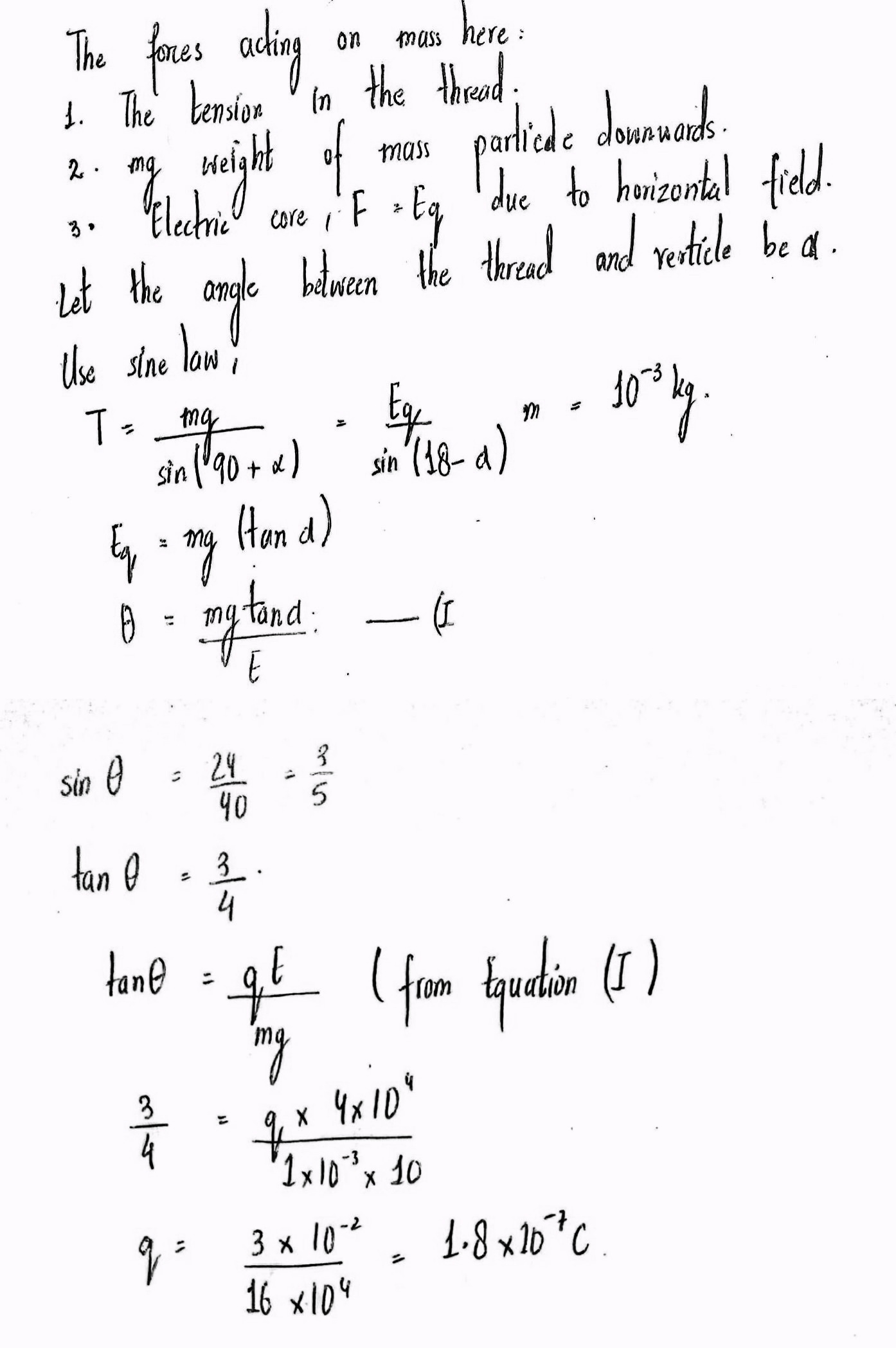Electric Charges And Fields - Class 12 Medical Physics - Extra Questions
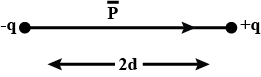
Find an expression for the oscillation frequency of an electric dipole of dipole moment →p and rotational inertia I for small amplitudes of oscillation about its equilibrium position in a unit form electric field of magnitude E.
A point charge Q is placed at point O as shown in the figure. The potential difference VA-VB is positive. Is the charge Q negative or positive

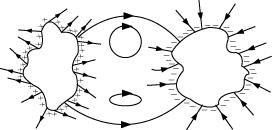
The figure shows the electric field lines around three point charges A, B and C. Which charges are positive?

During dry weather, clothes made of synthetic fiber often stick to the skin. Which type of force is responsible for this phenomenon?
Why does a plastic comb rubbed with dry hair attract bits of paper?
What are the two kinds of charges?
Name the physical quantity of which the units are:
Coulomb
Describe an experiment to demonstrate that there are two r kinds of charges.
How will you show that like charges repel and unlike charges attract each other?
What is the condition of an ideal electric dipole?
On what factors does the constant k=14πϵ0 depends?
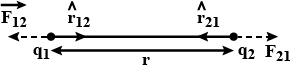
State the Coulombs law for the force acting between two definite point charges.
Can electric potential be zero at a point in a vacuum, the electric field at that point is not zero. Give example.
To determine the electric field due to a point charge, the test charge should be small. Explain why?
An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field. Show that it will not accelerate.
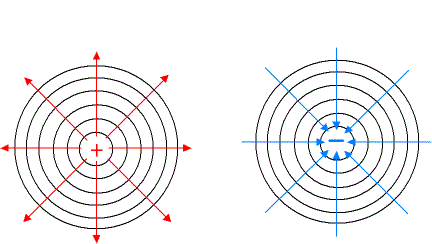
What is the electric field lines? Write any two of its properties.
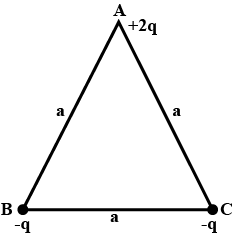
In given fig., an equilateral triangle ABC of side a has charges +2q,−q and −q at the vertices A, B, and C respectively. Calculate the dipole moment of this system.
Explain why two field lines never cross each other at any point?
The electric field components due to a charge inside the cube of side 0.1 m are shown in figure.
where, Ex=α, where α = 500 N/C-m, Ey = 0, Ez=0.Calculate(a) the flux through the cube and
(b) the charge inside the cube.
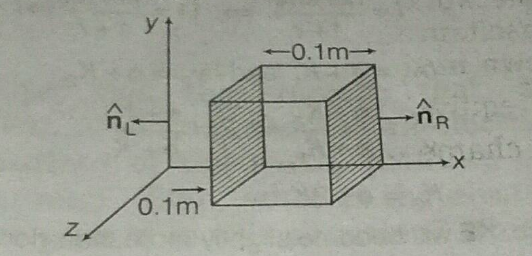
(a) the flux through the cube and
(b) the charge inside the cube.
(b) the charge inside the cube.
A hollow cylinder has a charge q coulomb within it. If ϕ is the electric flux in units of volt-meter associated with the curved surface B, the flux linked with the plane surface A in units of volt-meter will be?

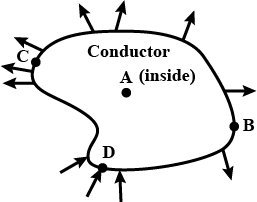
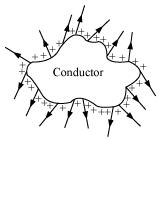
The figure shows the electric field lines around a conductor.
(a) At which of the four points is the field strongest?
(b) At which point is there a negative charge?
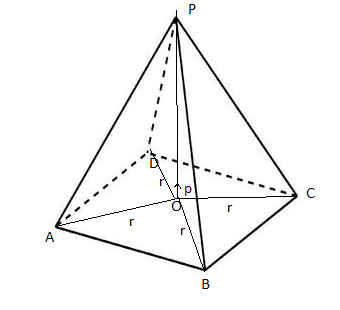
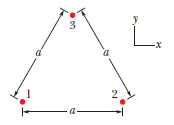
In figure, particle 1 ( of charge +1.00μC), particle 2 ( of charge +1.00μC), and particle 3 ( of charge Q) form an equilateral triangle of edge length a. For what value of Q ( both sign and magnitude) does the net electric field produced by the particles at the centre of the triangle vanish?
Given a uniform electric field →E=2×103ˆiN/C. Find the flux of this field through a square of side 20 cm, whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane. What would be the flux through the same square, if the plane makes an angle of 30o with the x-axis?
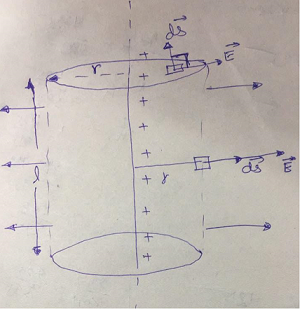
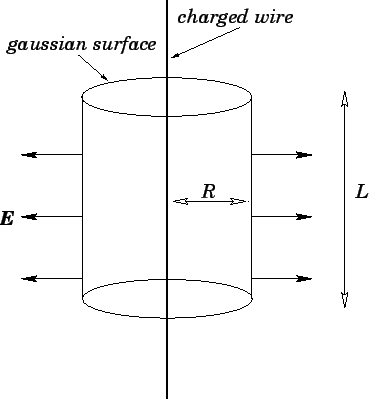
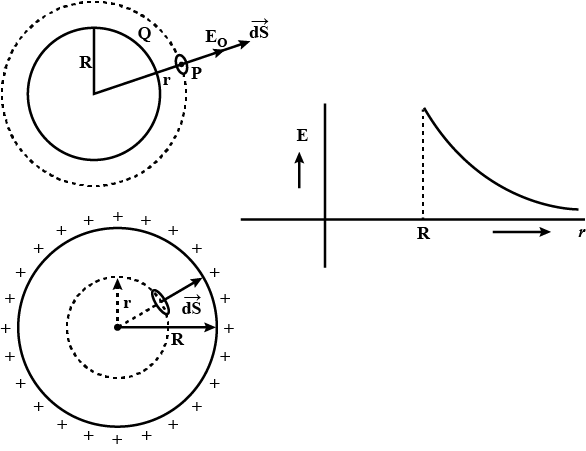
State Guass law in electrostatics. Derive an expression of electric field due to an infinitely long straight uniformly charged wire. Draw necessary diagram.
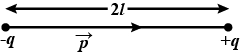
What is an electric dipole? Define electric dipole moment?
Obtain the expression for the intensity of electric field near a uniformly charged straight wire of infinite length with the help of Gauss theorem.
Write Gauss's theorem of electrostatics. Obtain an expression for the intensity of electric field near a uniformly charged straight wire of infinite length with its help.
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a rod of length l. Consider a hypothetical cube of edge l with the centre of the cube at one end of the rod. Find the minimum possible flux of the electric field through the entire surface of the cube.
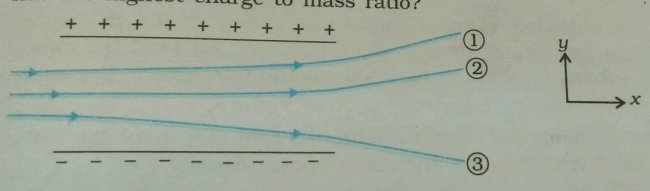
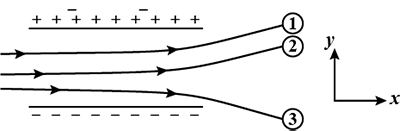
Figure shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Given the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio.
State and explain coulomb's inverse square law
Valence band
An infinite line charge produces an electric field of 9.0\times 10^4N C^{-1} at a distance of 2.0cm. What is the linear charge density?
A small test charge is released at rest at a point in an electrostatic field configuration. Will it travel along the line of force?
If an electric field is given by 10\hat i + 3\hat j + 4\hat k, calculate the electric flux through a surface of area 10 units lying in yz plane
Find the dimensions of permittivity of vacuum(\in_0).
In electric dipole what is the locus of Zero potential?
NaCI molecule is bound due to the electric force between the sodium and the chlorine ions when one electron of sodium is transferred to chlorine. Taking the separation between the ions to be 2.75\times10^{-8}cm, find the force of attraction between them. State the assumptions (if any) that you have made.
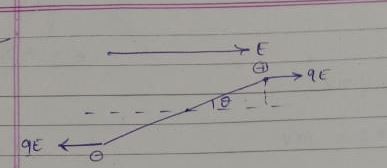
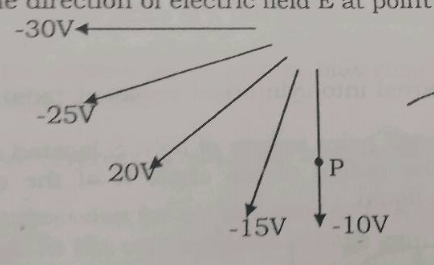
What is the direction of electric field E at point P in the following diagram
Why do electric lines of force never intersect each other?
What is electric dipole moment state its SI unit and dimension.
A person standing on an insulating stool touches a charge insult conductor . will the conductor get complete discharged ?
State Coulomb's law of force in electrostatics.
Depict the orientation of the dipole moment. Is it a scalar or a vector quantity? What are its SI unit?
Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4 cm away from a line charge of density 2 \times 10^{-6} Cm^{-1}.
Calculate the number of coulombs of positive charge in 250\ cm^{3} of (neutral) water. (Hint: A hydrogen atom contains one pro eight protons.)
We know that the negative charge on the electrons and the positive charge on the proton are equal. Suppose, however, hat these magnitudes differ from each other by 0.00010 \%. With what force would two copper coins, placed 1.0\ m apart, repel reach other? Assume that each coin contains 3 \times 10^{22} copper atoms. (Hint: A neutral copper atom contains 29 protons and 29 electrons.) What do you conclude?
Calculate the electric dipole moment of an electron and a proton 4.30\ nm apart.
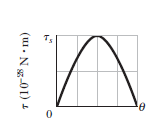
A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field \vec{E} of magnitude 20\ N/C. Figure 22-62 gives the potential energy U of the dipole versus the angle \theta between \vec{E} and the dipole moment \vec{p}. The vertical axis scale is set by U_{s}=100\times 10^{-28}J. What is the magnitude of \vec{p}?
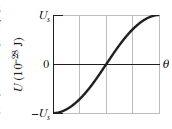
A certain dipole is placed in a uniform electric field \vec{E} of magnitude 40\ N/C. Figure gives the magnitude \tau of the torque on the dipole versus the angle \theta between field \vec{E} and the dipole moment \vec{p}. The vertical axis scale is set by \tau_{s}=100\times 10^{-28}N.m. What is the magnitude of \vec{p}?
If a cat repeatedly rubs against your cotton slacks on a dry day, the charge transfer between the cat hair and the cotton can leave you with an excess charge of -2.00 \mu C.
Just before the spark appears, do you induce positive or negative charge in the faucet?
An electric dipole consisting of charges of magnitude 1.50\ nC separated by 6.20\ \mu m is in an electric field of strength 1100\ N/C. What are
the magnitude of the electric dipole moment
Calculate the solid angle subtends by the periphery of an area 1 cm^2 at a point situated symmetrically at a distance of 5 cm from the area.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Write SI unit of electric field intensity.
(ii) Write SI unit of electric dipole moment.
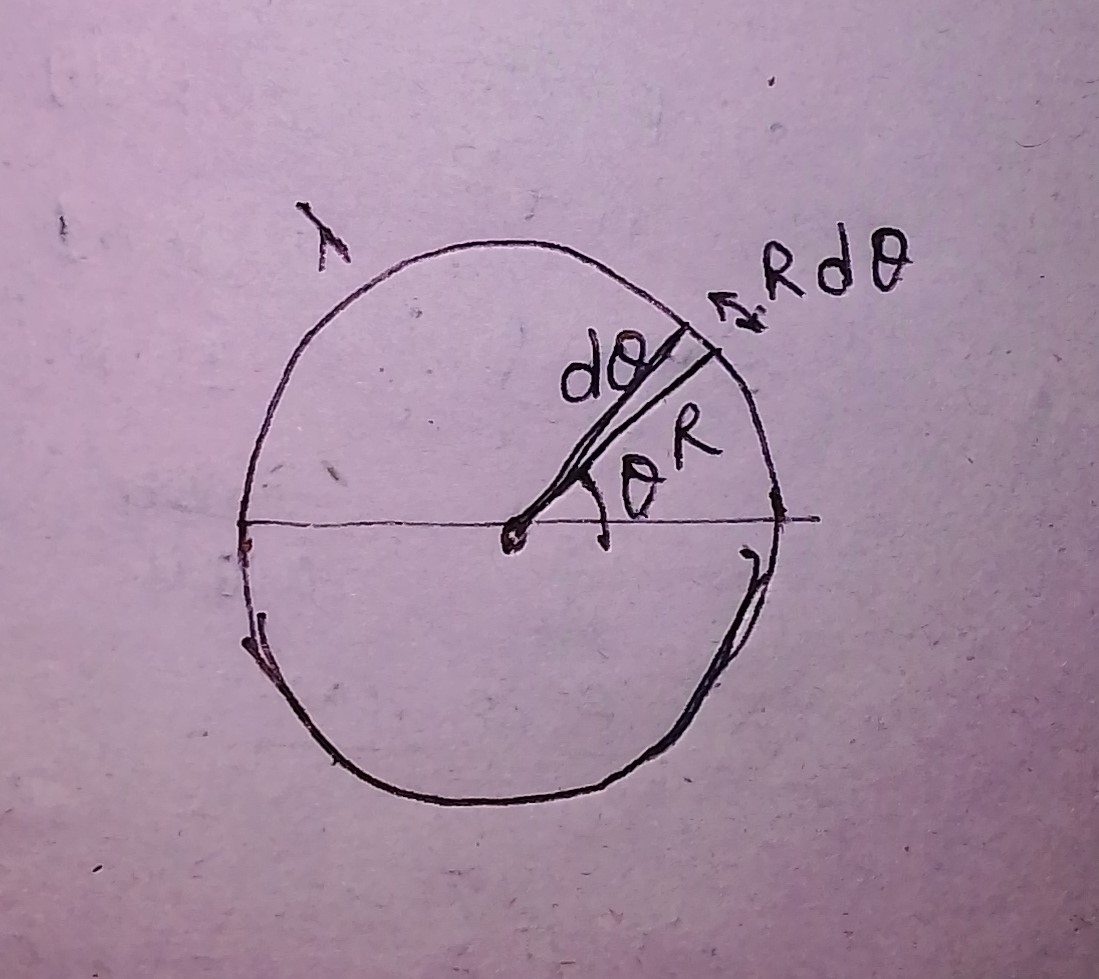
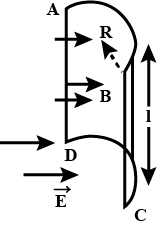
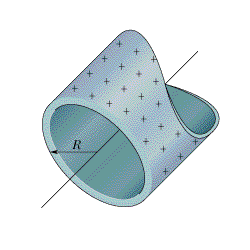
A hollow half cylinder surface of radius R and length l is placed in a uniform electric field \vec{E}. Electric field is acting perpendicular on the ABCD. If the flux through the curved surface of the hollow cylindrical surface is E\times X Rl. Find X?
Match \: the \: statements \: in \: Column \: A, \: with \: those \: in \: Column \: B.
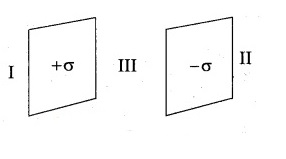
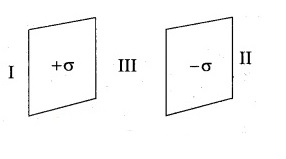
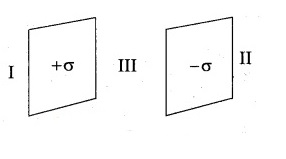
If the electric field to the left of two sheets is K\sigma/\varepsilon_0. Find K?
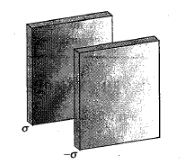
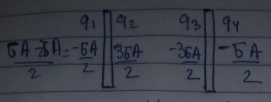
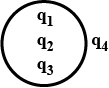
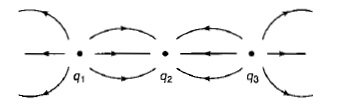
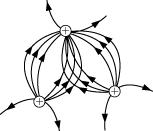
Figure shows some of the electric field lines due to three point charges q_1, q_2 and q_3 of equal magnitude. What are the signs of each of the three charges?
State and explain Coulomb's law in electrostatics.
Write any three properties of electric lines of force.
If \vec { E } =3\hat { i } +4\hat { j } -5\hat { k } , calculate the electric flux through a surface of area 50 units in z-x plane
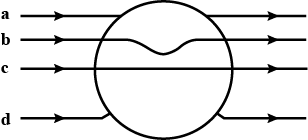
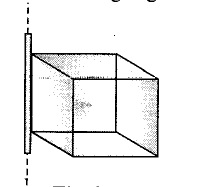
A metallic sphere is placed in a uniform electric field as shown in the figure. Which path is followed by electric field line and why?
A,B and C are three charged bodies. If A and B repel each other and A attracts C, what is the nature of the force between B and C?
An electric field \vec E - \vec iAx exists in the space, where A = V/{m^2}. take the potential at (10m, 20m) to be zero. Find the potential at the origin.
An electric dipole is formed by charge \pm\ 4\mu C, separated by 5\ mm. Calculate dipole moment and its direction.
Two point dipoles of dipole moment \overline { { P }_{ 1 } } and\overline { { P }_{ 2 } } are at a distance x from each other and \overline { { P }_{ 1 } } ||\overline { { P }_{ 2 } }
The force between the dipoles is
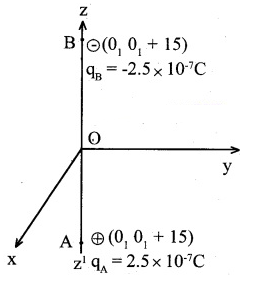
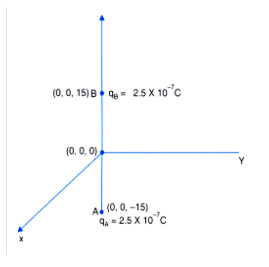
A system has two charges qA = 2.5\times 10^{-7}C and qB = -2.5\times 10^{-7}C located at point A(0, 0, -15) cm and B(0, 0, 15) cm respectively. What are the total charge and electric dipole moment vector of the system?
Complete the table:Objects
Electron exchange
Positive
Negative
Glass, Silk
From glass rod to silk
....a....
Silk
Ebonite, Wool
Wool to ebonite
...b...
...c...
Rubber rod, Wool
...d...
Wool
...e...
| Objects | Electron exchange | Positive | Negative |
| Glass, Silk | From glass rod to silk | ....a.... | Silk |
| Ebonite, Wool | Wool to ebonite | ...b... | ...c... |
| Rubber rod, Wool | ...d... | Wool | ...e... |
From which one to which does electronic transfer occur when the pair of substances given below are rubbed against each other?
Glass rod Silk cloth.
Why must hospital personnel wear special conducting shoes while working around oxygen in an operating room? What might happen if the personnel wore shoes with rubber soles?
From which one to which does electronic transfer occur when the pair of substances given below are rubbed against each other?
Ebonite Wool.
Conceptual question:
On the basis of the repulsive nature of the force between like charges and the freedom of motion of charge within a conductor, explain why excess charge on an isolated conductor must reside on its surface.
Answer to conceptual questions.
A student who grew up in a tropical country and is studying in the United States may have no experience with static electricity sparks and shocks until his or her first American winter. Explain.
Conceptual Questions :
A person is placed in a large, hollow, metallic sphere that is insulated from ground. If a large charge is placed on the sphere, will the person be harmed upon touching the inside of the sphere?
You might have seen iron chains, suspended from the body of lorries and trucks touching the earth. What is this for?
Application of Gausss Law to Various Charge Distributions
A large, flat, horizontal sheet of charge has a charge per unit area of 9.00 \mu C/m^{2}. Find the electric field just above the middle of the sheet.
Find the initial acceleration of the rod
A circle, having radius "r" has line charge distribution over its circumference having linear charge density \lambda =\lambda_0\cos^2\theta. Calculate the total electric charge residing on the circumference of the circle.
\left[\overset{2\pi}{\underset{0}{\displaystyle\int}}\cos^2\theta d\theta =\pi\right]
Define relative premittivity. Write its unit.
What are electric lines of force? State the properties of lines of force.
Do we have to include the signs (positive or negative)of the charges while solving problems?
No two electric lines of intersect each other. Why ?
Why do the electrostatic filed lines not from clossed loop ?
An electrostatic field line is a continuous curve. That is, a field line cannot have sudden breaks. Why not ?
Define one coulomb charge.
Define Permitivity of vacuum (E_0)
A uniform electric field a\hat{i}+b\hat{j} intersects a surface of area A. What is the flux through this area if the the surface lies (a) in the yz plane, (b) in the xz plane, (c) in the xy plane?
If coulomb's law involved 1/r^3 instead of (1/r^2), would Gauss's law still be true?
The branch of electricity which deals with the properties of electrified bodies due to a moving charge is called electrostatics. True/False?
An electric dipole is free to move in a uniform electric field. Explain its motion when it is placed (i) parallel to the field and (ii) perpendicular to the field:
Coulomb's law states that the electric force becomes weaker with increasing distance, Suppose that instead, the electric force between two charged particles were independent of distance. In this case, would a neutral insulator still be attracted towards the comb.
What is the electric flux through a cube of side 1 cm whose encloses an electric dipole?
Why do the electric field lines never cross each other?
Write Coulomb's law in vector form. Also explain the terms.
Draw a diagram of equipotential surface for a single charge.
State the SI unit of magnetic dipole moment
Write the definition of electric dipole moment.
What is an electric dipole?
Why do the electrostatic field lines not form closed loop?
What happens to the electrostatic force when both charges are doubled?
State Coulomb's law.
Define an electric line of force.
Tick the correct one:
Object with same charge
(attract / repel)
Tick the correct one:
Bodies with different charges
(attract / repel)
When a glass rod is rub with silk, electron loses from the glass rod. If we bring another glass rod near to it what can be observed? Give reason.
Tick the correct one:
The charged body ............ the neutral body.
(attract / repel)
State and explain coulomb's law of electric charges in scalar form.
If a charged plastic straw is brought near another uncharged plastic straw, what will happen?
If the metal clip used in the electroscope is replaced by an ebonite rod and a charged body is brought in contact with it, will there be any effect on the aluminium strips? Explain.
How many point charges of same magnitude are required to constitute an electric dipole?
The aluminium strips in an electroscope as shown in fig. 15.1 are replaced by plastic strips and a charged body is brought in contact with the metal clip. What will happen?

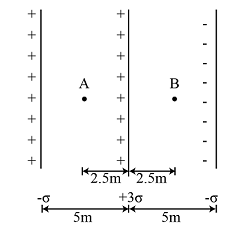
The figure shows three infinite non-conducting plates of charge perpendicular to the plane of the paper with charge per unit area + \sigma, \: +3 \sigma \: and \: - \sigma . The ratio of the net electric field at that point A to that at point B is 1/x. Find x:
A point charge +q & mass 100 gm experiences a force of 100N at a point at a distance 20cm from a long infinite uniformly charged wire. If it is released its speed is 20\sqrt { l{ n }x } m/s when it is at a distance 40cm from wire. Find x.
If the total electric flux through the paraboloidal surface due to a uniform electric field of magnitude E_0 in the direction shown in fig is \phi=XE_0 \pi r^2/2. Find out the value of X?
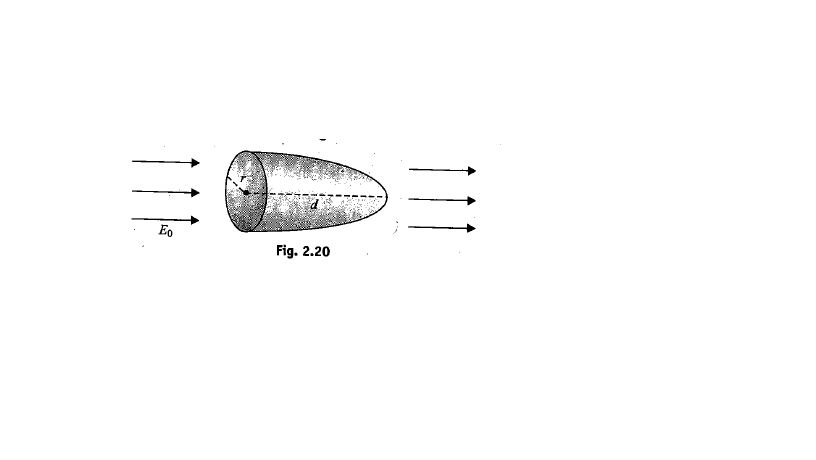
A ring of diameter d is rotated in a uniform electric field until be position of maximum electric flux is found. The flux is found to be \phi. If the electric field strength is \ E=\frac{X \phi}{\pi d^2}. Find out X ?
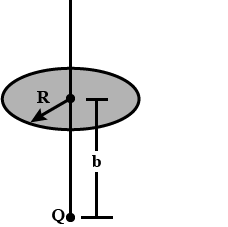
A point charge Q is located on the axis of a disc of radius R at a distance b from the plane of the disc (figure). Show that if one-fourth of the electric flux from the charge passes through the disc, then R = \sqrt 3b.
What is the charge per unit area in C/m^2, of an infinite plane sheet of charge if the electric field produced by the sheet of charge has magnitude 3.0 N/C?
Net charge within an imaginary cube drawn in a uniform electric field is always zero. Is this statement true or false.
Find the net electric flux through the entire cube.
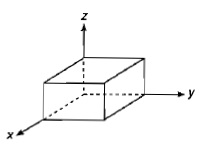
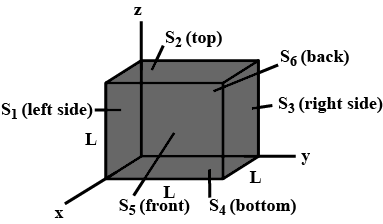
A cube has sides of length L = 0.2 m. It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in figure.The electric field is uniform and given by \vec{E}=(2.5 N/C) \dot{I} - (4.2 N/C) \dot{J}. Find the electric flux through the entire cube.
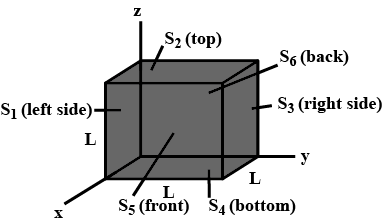
Find the electric flux through each of the six cube faces S_1, S_2, S_3, S_4, S_5 and S_6
Given the following data, calculate the electrostatic force and gravitational force between two electrons. Show that the electrostatic force is much greater than the gravitational force for the electrons separated by a certain distance.
Charge on the electron = 1.6 \times 10^{-19} C
Mass of the electron = 9.1 \times 10^{-31} kg
Gravitational constant = 6.67 \times 10^{-11} Nm^{2} kg^{-2}
Calculate the electrostatic force of attraction between a proton and an electron in a hydrogen atom. The radius of the electron orbit is 0.05 nm and charge on the electron is 1.6 \times 10^{-9} C.
Answer the following questions.
(i) An electrostatic field line is a continuous curve. That is, a field line cannot have sudden breaks. Why is it so?
(ii) Explain why two field lines never cross each other at any point.
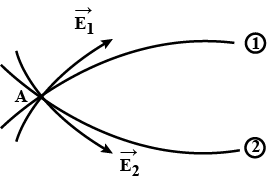
(a) Consider an arbitrary electrostatic field configuration. A small test charge is placed at a null point (i.e., where E = 0) of the configuration. Show that the equilibrium of the test charge is necessarily unstable.(b) Verify this result for the simple configuration of two charges of the same magnitude and sign placed a certain distance apart.
Consider a uniform electric field E = 3\times 10^{3}\ \hat{i}\ NC^{-1}. (a) What is the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane? (b) What is the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes a 60^o angle with the x-axis?
A system has two charges q_A = 2.5\times 10^{-7} C and q_B = -2.5\times 10^{-7}C located at points A: (0, 0, 15 cm) and B: (0,0, +15 cm), respectively. What are the total charge and electric dipole moment of the system?
Consider a uniform electric field E = 3\times 10^{3}\ \hat{i}\ NC^{-1}. What is the net flux of the uniform electric field through a cube of side 20 cm oriented so that its faces are parallel to the coordinate planes?
Figure shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
What is the electric flux through a cube of side 1\ cm which encloses an electric dipole?
Why do the electrostatic field lines not form closed loops?
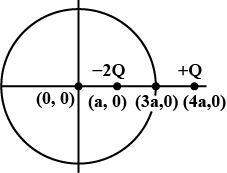
Two charges of magnitudes -2Q and +Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius '3a' with its centre at the origin?
Given a uniform electric field \vec {E} = 5\times 10^{3}\hat {i} N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of 10\ cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the Y-Z plane. What would be the flux through the same square if the plane makes a 30^{\circ} angle with the $$X-axis?
Answer the following questions:
(i) Define electric flux. Write its SI units.
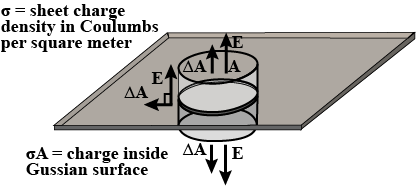
(ii) Using Gauss's law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the distance from it.
(iii) How is the field directed if (i) the sheet is positively charged, (ii) negatively charged?
Given a uniform electric field \overrightarrow E = 5 \times 10^3 \widehat i N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane. What could be the flux through the same square if the plane makes 30^o angle with the x-axis?
Symbol for steradian is ____
The lines of force exert a lateral pressure on each other. What does this property of lines of force leads to explain?
A large hollow metallic sphere has a positive charge of 35.4\mu C at its centre. Find how much electric flux will emanate from the sphere ?
Define electric dipole moment. Give its unit.
Write two properties of electric field lines.
Write the properties of electric lines of force.
Define one "Coulomb" on the basis of Coulomb's law.
State Coulomb's law in electrostatics.
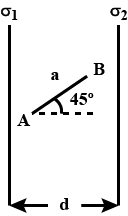
Two infinitely large sheets having charge densities { \sigma }_{ 1 } and { \sigma }_{ 2 } respectively ({ \sigma }_{ 1 } >{ \sigma }_{ 2 }) are placed near each other separated by distance d.A charge q is placed in between two plates such that there is no effect on charge distribution on plates. Now this charge is moved at an angle of {45}^{o} with the horizontal towards plate having charge density { \sigma }_{ 2 } by distance a (a<d). Find work done by electric field in the process.
Find out the magnitude of electric field intensity and electric potential due to a dipole of dipole moment \bar P = \hat i + \sqrt 3 \hat j kept at origin at following points.
(i) (2, 0, 0)
(ii) (-1, \sqrt 3 , 0)
Three identical metal plates with large surface areas are kept parallel to each other As shown in figure. The leftmost plate is given a charge Q, the rightmost a charge -2Q and the middle one remain neutral. Find the charge appearing on the outer surface of the rightmost plate.

The mutual force of repulsion between two point charges kept a fixed distance apart is 9\times {10}^{-5}N when in vacuum and 4\times {10}^{-5}N when placed in a dielectric medium. What is the value of dielectric constant of the medium?
Define electric flux. Write its SI unit.
Two field lines never intersect each other. Give reason.
If flux in a coil changes by \Delta \phi, and the resistance of the coil is R, prove that the charge flown in the coil during the flux change is \dfrac{{\Delta}\phi}{R}. (Note: It is independent of the time taken for the change in flux)
Two thin conducting plates (very large) parallel to each other carrying total charges \sigma A and -2\sigma A respectively (where A is the area of each plate), are placed in a uniform external electric field E as shown. Find the surface charge on each surface.
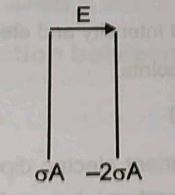
When does an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field experience
a. Maximum Torqueb. Minimum Torque
If \vec { E } =3\widehat { i } +4\widehat { j } -5\widehat { k } calculate the electric flux through the surface of area 50 units in z-x plane.
Shown as electric dipole formed by two particle fixed at the ends of a light rod of length l. The mass of each particle is m and the charges are -q and +q. The system is placed in such a way that the dipole axis is parallel to a uniform electric field E that exists in the region. The dipole is slightly rotated about its centre and released. Show that for small angular displacement, the motion is angular simple harmonic and find its time period.
Write definition of electric field intensity.
Obtain an expression for electron force and electric pressure on the surcharge of a charged conductor.
Draw necessary diagram.
Answer the following Questions.
(i) Define electric flux. Write its SI units.
(ii) A spherical rubber balloon carries a charge that is uniformly distributed over its surface. As the balloon is blown up and increases in size, how does the total electric flux coming out of the surface change? Give reason.
Who discovered the way of producing electricity by friction?
Why two electric lines of force/field cannot intersect each other?
What is the shape of equipotential surface for a given point charge q.
An infinite wire having charge density \lambda passes through one of the edges of a cube having edge length l. Find the
a. total flux passing through the cube.
b. flux passing through the surfaces which are in contact with the wire.
c. flux passing through the surfaces which are not in contact with the wire.
Two particles A and B, having opposite charges 2.0\times 10^{-6}C and -2.0\times 10^{-6}C, are placed at a separation of 1.0cm. Write down the electric dipole moment of this pair.
Fig. shows two dipole moments parallel to each other and placed at a distance x apart. What is the magnitude of force of interaction? What is the nature of force, attractive or repulsive?
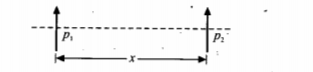
Obtain the formula for rotating the electric dipole in a uniform electric field.
Why does the ebonite rod becomes negatively charged when it is rubbed against fur?
Two large thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude 17\times 10^{-22}C/m^2. What is \vec E.
Between the plates.
A system has two charges q_A=2.5\times 10^{-7}C and q_B=2.5\times 10^{-7}C located at points
A:(0,015\ cm), respectively. What are the total charge and electric dipole moment of the system?
Two large thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude 17\times 10^{-22}C/m^2. What is \vec E.
In the outer region of the first plate.
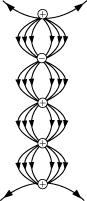
Does the curve shown in figure represent electrostatic field lines?
Does the curve shown in figure represent electrostatic field lines?
Two large thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude 17\times 10^{-22}C/m^2. What is \vec E.
In the outer region of the second plate.
Does the curves shown in figure represent electrostatic field lines?
Is it representing the electrostatic field lines?
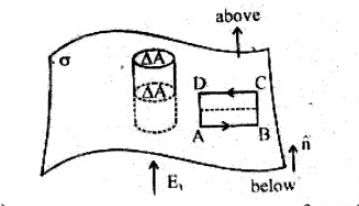
Show that the tangential component of electrostatics field is continuous from one side of a charged surface to another [Hint : For (a), use Gauss law, For (b), use the fact that work done by electrostatic field on a closed loop is zero.]
Does the curve shown in figure represent electrostatic field lines?
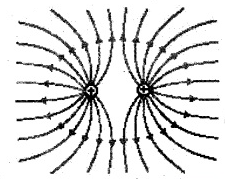
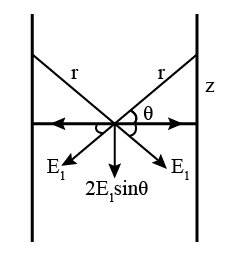
A point dipole with an electric moment p is located at a distance l from an infinite conducting plane. Find the modulus of the vector of the force acting on the dipole if the vector p is perpendicular to the plane.
Electric Flux
A nonuniform electric field is given by the expression
\overset{\rightarrow}{E}=ay\,\overset{\rightarrow}{i} + bz \,\overset{\rightarrow}{j}+cx \,\overset{\rightarrow}{k}
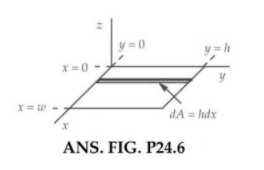
where a, b, and c are constants. Determine the electric flux through a rectangular surface in the xy plane,extending from x = 0 to x =w and from y=0 to y=h
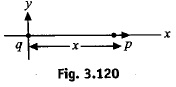
A line of charge starts at x = +x_0 and extends to positive infinity. The linear charge density is \lambda=\lambda_0 x_0/x,where \lambda_0 is a constant. Determine the electric field at the origin.
Electric Flux
An electric field of magnitude 3.50 kN/C is applied along the x axis. Calculate the electric flux through a rectangular plane 0.35 m wide and 0.700 m long
(a) if the plane is parallel to the yz plane,
(b) if the plane is parallel to the xy plane, and
(c) if the plane contains the y axis and its normal makes an angle of 40.0^{o} with the x axis.
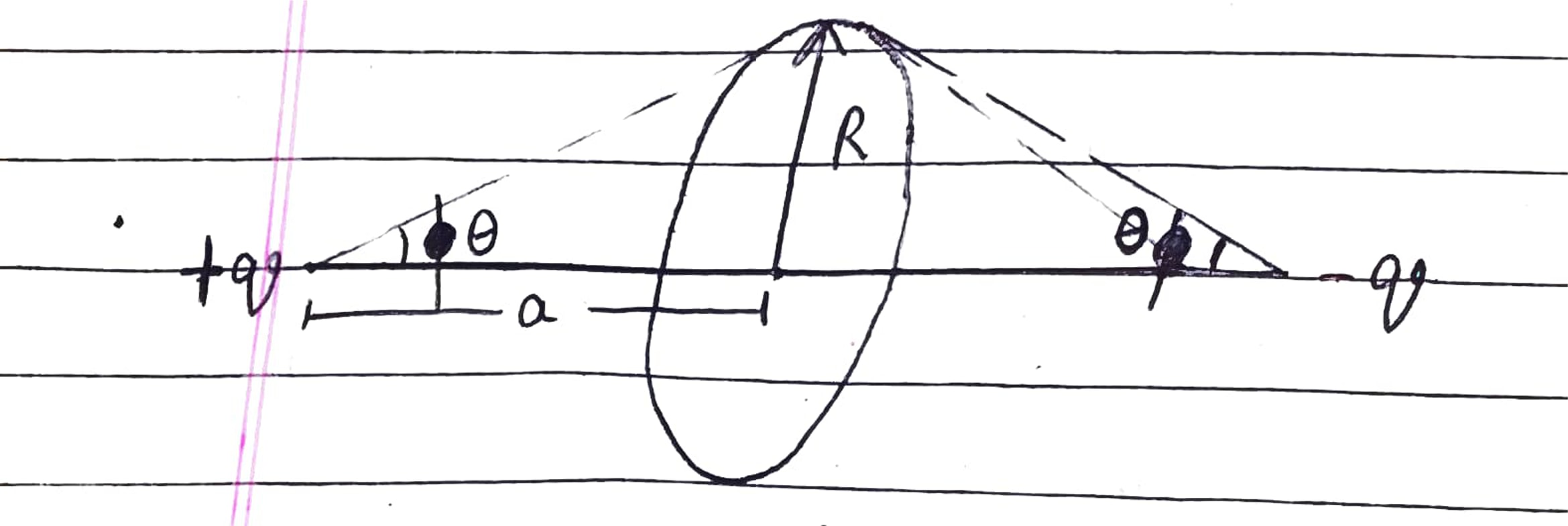
Two long parallel threads carry charge per unit length. The threads are separated by a distance l. The maximum field strength in the symmetry plane between them is given as \displaystyle \frac{\lambda}{x\pi \varepsilon_0 l}. Find x:
Two point charges q and -q are separated by a distance 2a (Fig.). Evaluate the flux of electric field strength vector across a circle of radius R.
A charged particle q of mass m is in equilibrium at a height h from a horizontal infinite line charge with uniform linear charge density \lambda. The charge lies in the vertical plane containing the line charge. If the particle is displaced slightly (vertically), prove that the motion of the charged particle will be simple harmonic. Also find its time period
Two mutually perpendicular long straight conductors carrying uniformly distributed charges of linear charge densitites \lambda_1 and \lambda_2 are positioned at a distance a from each other. How does the interaction between the rods depend on a?
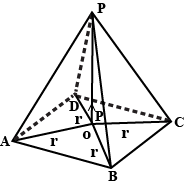
Four charge particles each having charge Q = 1 C are fixed at the corners of the base (A, B, C and D) of a square pyramid with slant length a(AP = BP = BP = PC = a = \sqrt{2}m), a charge -Q is fixed at point P. A dipole with dipole moment p = 1 Cm is placed at the center of the base and perpendicular to its plane as shown in figure. Force on the dipole due to the charge particles is \displaystyle \frac{x}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} N. Find x.
A short dipole is placed along the x-axis at x =x.
a. Find the force acting on the dipole due to a point charge q placed at the origin.
b. Find the force on the dipole if the dipole is rotated by 180^{\circ} about the z-axis.
c. Find the force on dipole if the dipole is rotated by 90^{\circ} anticlockwise about z-axis, i.e., it becomes parallel to the y-axis.
The electric field in a region is given by \displaystyle \vec{E} = \frac{3}{5} E_o \widehat{i} + \frac{4}{5} E_o \widehat{j} with E_o = 2.0 \times 10^3 N/C. Find the flux of this field (in Nm^2C^{-1}) through a rectangular surface of area 0.2 m^2 parallel to the Y-Z plane.
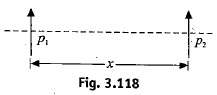
Figure 3.118 shows two dipole moments parallel to each other and placed at a distance x apart. What is the magnitude of force of interaction? What is the nature of force, attractive or repulsive?
Two point charges q and -q are separated by a distance 2l, Find the flux of electric field strength vector across the circle of radius R placed with its centre coinciding with the midpoint of line joining the two charges in the perpendicular plane.
(a) Show that the normal component of electrostatic field has a discontinuity from one side of a charged surface to another given by (E_2\,-\, E_1)\, \dot\, \hat{n}\,\displaystyle \frac{\sigma }{\varepsilon _0}
where \hat{n} is a unit vector normal to the surface at a point and \sigma is the surface charge density at that point. (The direction of \hat{n} is from side 1 to side 2.) Hence show that just outside a conductor, the electric field is \sigma \hat{n} /\epsilon _0
(b) Show that the tangential component of electrostatic field is continuous from one side of a charged surface to another. [Hint: For (a), use Gauss's law. For, (b) use the fact that work done by electrostatic field on a closed loop is zero.]
where \hat{n} is a unit vector normal to the surface at a point and \sigma is the surface charge density at that point. (The direction of \hat{n} is from side 1 to side 2.) Hence show that just outside a conductor, the electric field is \sigma \hat{n} /\epsilon _0
(b) Show that the tangential component of electrostatic field is continuous from one side of a charged surface to another. [Hint: For (a), use Gauss's law. For, (b) use the fact that work done by electrostatic field on a closed loop is zero.]
A long charged cylinder of linear charged density \lambda is surrounded by a hollow co-axial conducting cylinder. What is the electric field in the space between the two cylinders?
In a certain region of space, electric field is along the z-direction throughout. The magnitude of electric field is, however, not constant but increases uniformly along the positive z-direction, at the rate of 10^5\, NC^{-1}\ m^{-1} per metre. What are the force and torque experienced by a system having a total dipole moment equal to 10^{-7} Cm in the negative z-direction ?
Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude 17.0\times10^{-22}\,C/m^{2}. What is E: (a) in the outer region of the first plate. (b) in the outer region of the second plate, and (c) between the plates?
State Gauss' law. Using this find an expression for electric field due to an infinitely long straight charged wire uniform charge density.
Two plates A and B are placed one above the other in the gravitational field and a block of mass m is connected to the upper plate by a spring of spring constant k. Its time period is found to be T. Now the space between the plates is made gravity free and a charge +q is given to the block of mass m and an electric field E is produced in the direction shown. The new time period is?

Find the electric field intensity at a point P which is at a distance R (point lying on the perpendicular drawn to the wire at one of its end) from a semi-infinite uniformly charged wire. (Linear charge density = \lambda.)
Consider a uniform electric field E=3\times 10^3 \hat{i} N/C. (a) What is the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane? (b) What is the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes a 60^o angle with the x-axis?
A system has two charges {q}_{A}=2.5\times {10}^{-7} and {q}_{B}=2.5\times {10}^{-7}, located at point A: (0, 0, -15\ cm), B: (0, 0, 15\ cm)respectively. What are the total charge and electric dipole moment of the system?
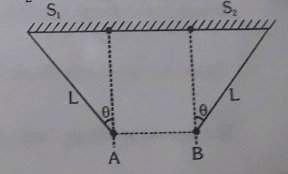
Two identical helium filled balloon A and Bm fastened to a weight of 5g by threads floats in equilibrium as shown in fig. Calculate the charge on each balloons, assuming that they carry equal charges

Two ball A and B of same mass (M) and charges Q, -Q are suspended by two strings of same length from two different suspension points {S}_{1} and {S}_{2} if {S}_{1}{S}_{2}=3x and AB=x then show that-
tension in the string is T=\dfrac { { Q }^{ 2 }L }{ 4\pi { \in }_{ 0 }{ x }^{ 3 } }
\tan { \theta } =\dfrac { { Q }^{ 2 } }{ 4\pi { \in }_{ 0 }{ x }^{ 2 }Mg }
A dipole is formed by taking two charges +8\ \mu C and -8\mu C and keeping them 5\ mm apart. Find the electric field at an axial point P situated at 20\ cm from the center of a dipole. What would be the electric intensity if the point P were on the equator of the dipole?
A particle, having a charge +5\ \mu C, is initially at rest at the point x=30\ cm on the x-axis. The particle begins to move due to the presence of a charge Q that is kept fixed at the origin. Find the kinetic energy of the particle at the instant it has moved 15\ cm from its initial position if
(a) Q=+5\mu C and (b) Q=-15\mu C
An electric dipole of momentum \vec{p} is placed in a uniform electric field. The dipole is rotated through a very small angle \theta from equilibrium and is released, find the time period of simple harmonic motion.
Write the expression for electric intensity at a point due to point charge and explain the terms.
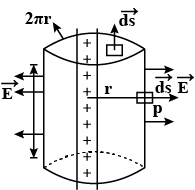
An electric field is uniform, and in the positive x direction for positive x, and uniform with the same magnitude but in the negative x direction for negative x. It is given that E = 200 \,\hat{i} \,N/C for x > 0 and E = -200 \,\hat{i} \,N/C for x < 0. A right circular cylinder of length 20 \,cm and radius 5 \,cm has its centre at the origin and its axis along the x-xis so that one face is at x = +10 \,cm and the other is at x = -10 \,cm.
(a) What is the net outward flux through each flat face?
(b) What is the flux through the side of the cylinder?
(c) What is the net outward flux through the side of the cylinder?
Two equal and opposite charges each of 2\mu C are placed at a distance of 3.0 cm. Dipole moment of the system will be
A charged particle of mass 1.0 g is suspended through a silk thread of length 40cm in a horizontal electric field of 4\times 10^{ 4 }\quad N/C. If the particle stays at a distance of 24 cm from the vertical line passing through the suspension points in equilibrium , The charges on the particle is:
An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux through this surface ?
State Coulomb's law, explain its vector form and define S.I. unit of electric charge. State two limitations of Coulomb's law.
(i) Using Gauss Theorem show mathematically that for any point outside the shell, the field due to a uniformly charged spherical shell is same as the entire charge on the shell, is concentrated at the centre.
(ii) Why do you expect the electric field inside the shell to be zero according to this theorem?
The figure shows a section of a long, thin-walled metal tube of radius R = 3.00 cm, with a charge per unit length of \lambda = 2.00 \times10^{-8} C/m. What is the magnitude E of the electric field at a radial distance (a) r= R/2.00 and (b) r = 2.00R? (c) Graph E versus r for the range r =0\ to\ 2.00R
Two identical conducting sphere, fixed in place, attract each other with an electrostatic force of 0.108\ N when their center-to-center separation is 50.0\ cm. The sphere are then connected by a thin conducing wire. When the wire is removed, the sphere repel each other with an electrostatic force of 0.0360\ N. Of the initial charges on the sphere, with a positive net charge, what was the positive charge on the other?
Two identical conducting sphere, fixed in place, attract each other with an electrostatic force of 0.108\ N when their center-to-center separation is 50.0\ cm. The sphere are then connected by a thin conducing wire. When the wire is removed, the sphere repel each other with an electrostatic force of 0.0360\ N. Of the initial charges on the sphere, with a positive net charge, what was the negative charge on one of them?
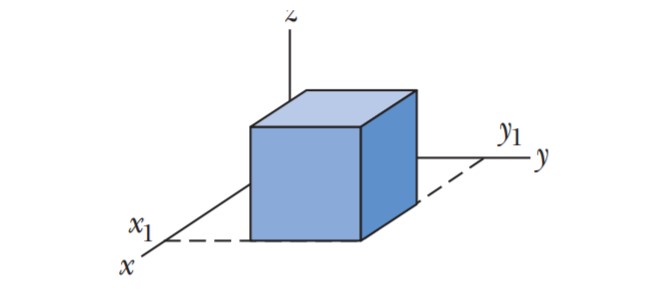
The figure shows a closed Gaussian surface in the shape of a cube of edge length 2.00 m, with one corner at x_1=5.00\, m,y_1 = 4.00 m.The cube lies in a region where the electric field vector is given by \vec E =-3.00i-4.00y^2\,j +3.00k\, N/C with y in meters. What is the net charge contained by the cube?
An electron on the axis of an electric dipole is 25\ nm from the centre of the dipole. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on the electron if the dipole moment is 3.6\times 10^{-29}\ C.m?
Assume that 25\ nm is much larger than the separation of the charged particles that form the dipole.
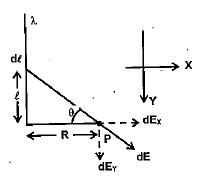
A very long straight uniformly charged thread carries a charge \lambda per unit length. Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field strength at a point which is at a distance y from the thread and lies on the perpendicular passing through one of the thread's ends.
Consider a uniform electric. Held \vec E=3\times 10^3 \hat i N/C
A point charge +10\ p\ C is a distance 5\ cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10cm, as shown in figure. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square of 10cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the plane?
Show that the normal component of electrostatic field has a discontinuity from one side of a charge surface to another given by (E_2-E_1),\ \cap n=? Where is a unit vector normal to the surface at a point and a is the surface charge density at that point (The direction of ft from side 1 to 2.) Hence show that just outside a conductor, the electric field is
Two charge q_A = 2.5 \times 10^{-7}C and q_B = -2.5 \times 10^{-7}C are at point A(0, 0, - 15\,cm) and B (0, 0, +15\,cm) respectively form a system. Determine the electric dipole moment of the system.
A nonconducting solid sphere has a uniform volume charge density \rho. Let be the vector from the center of the sphere to a general point P within the sphere. (a) Show that the electric field at P is given by \vec E=\rho \vec r/3\epsilon_0 (Note that the result is independent of the radius of the sphere.) (b) A spherical cavity is hollowed out of the sphere, as shown in the figure. Using superposition concepts, show that the electric field at all points within the cavity is uniform and equal to \vec E=\rho \vec a/3\epsilon_0 where is the position vector from the center of the sphere to the center of the cavity.
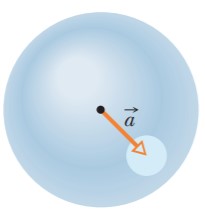
What must be the magnitude of a uniform electric field if it is to have the same energy density as that possessed by a 0.50 T magnetic field?
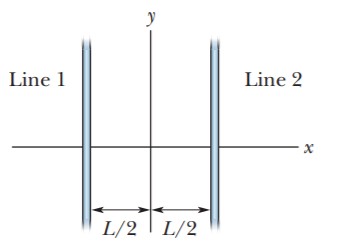
In Figure, short sections of two very long parallel lines of charge are shown, fixed in place, separated by L = 8.0 cm. The uniform linear charge densities are 6.0 \mu C/m for line 1 and 2.0 \mu C/m for lineWhere along the x axis shown is the net electric field from the two lines zero?
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the electric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that the net charge inside is zero.
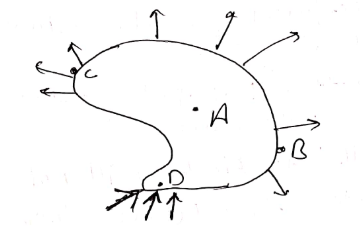
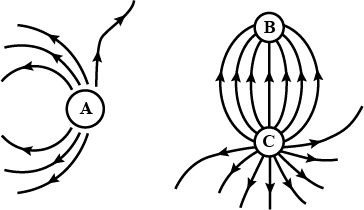
The given figure shows the electric field lines around three point charges A, B and C.
(i) Which charges are positive?
(ii) Which charge has the largest magnitude? Why?
(iii) In which region or regions of the picture could the electric field be zero?
Justify your answer.
(i) near A (ii) near B (iii) near C (iv) nowhere.
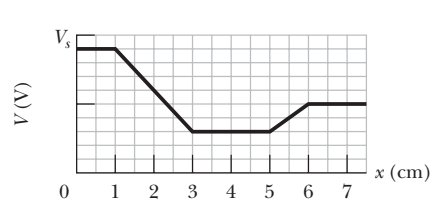
Proton in a well. The above figure shows electric potential V along an x axis. The scale of the vertical axis is set by V_s = 10.0 \ V. A proton is to be released at x=3.5 \ cm with initial kinetic energy 4.00 \ eV.
(a) If it is initially moving in the negative direction of the axis, does it reach a turning point (if so, what is the x coordinate of that point) or does it escape from the plotted region (if so, what is its speed at x=0)?
(b) If it is initially moving in the positive direction of the axis, does it reach a turning point (if so, what is the x coordinate of that point) or does it escape from the plotted region (if so, what is its speed at x=6.0 \ cm)?
What are the
(c) magnitude F and
(d)direction (positive or negative direction of the x axis) of the electric force on the proton if the proton moves just to the left of x=3.0 \ cm?
What are
(e) F and
(f) the direction if the proton moves just to the right of x=5.0 \ cm?
Electric Flux
A flat surface of area 3.20 m^{2} is rotated in a uniform electric field of magnitude E = 6.20 \times 10^{5} N/C. Deter-mine the electric flux through this area
(a) when the electric field is perpendicular to the surface and
(b) when the electric field is parallel to the surface.
Electric Flux
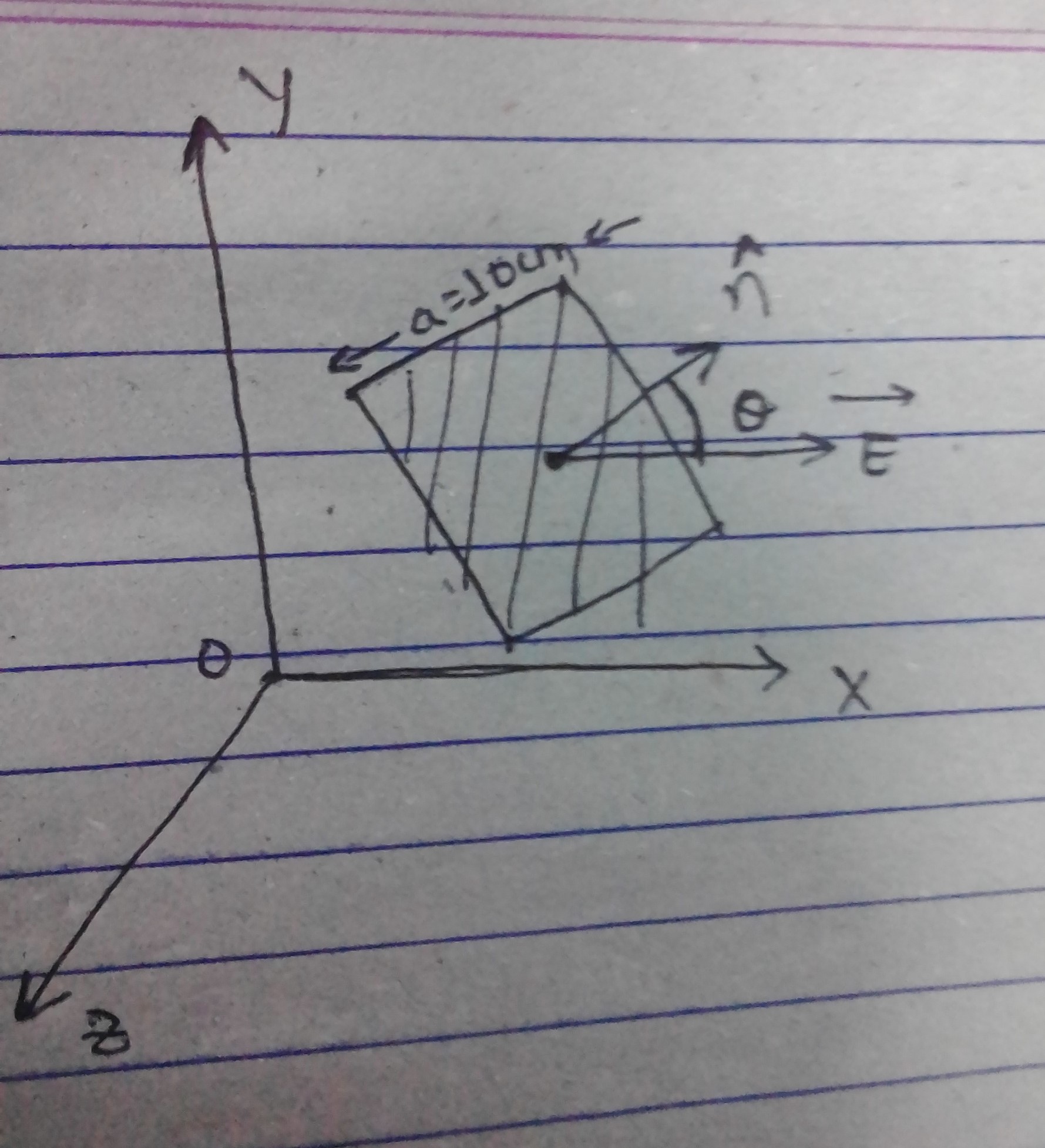
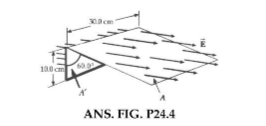
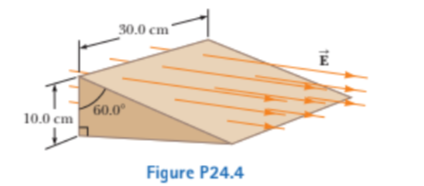
Consider a closed triangular box resting within a horizontal electric field of magnitude E=7.80 \times 10^{4} N/C as shown in Figure P24.Calculate the electric flux through
(a) the vertical rectangular surface,
(b) the slanted surface, and
(c) the entire surface of the box.
Electric Flux
A vertical electric field of magnitude 2.00 \times 10^{4} N/C exists above the Earths surface on a day when a thunderstorm is brewing. A car with a rectangular size of 6.00 m by 3.00 m is traveling along a dry gravel road-way sloping downward at 10.0^{o}. Determine the electric flux through the bottom of the car.
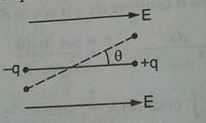
An electric field line emerges from a positive point charge +{q}_{1} at an angle \alpha to the straight line connecting it to a negative point charge -{q}_{2} (figure).
At what angle \beta will the field line enter the charge -{q}_{2}?

Application of Gausss Law to Various Charge Distributions
The charge per unit length on a long, straight filament is -90.0 \mu C/m. Find the electric field (a) 10.0 cm,(b) 20.0 cm, and (c) 100 cm from the filament, where distances are measured perpendicular to the length of the filament.
Class 12 Medical Physics Extra Questions
- Alternating Current Extra Questions
- Atoms Extra Questions
- Current Electricity Extra Questions
- Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter Extra Questions
- Electric Charges And Fields Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Induction Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Waves Extra Questions
- Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Extra Questions
- Magnetism And Matter Extra Questions
- Moving Charges And Magnetism Extra Questions
- Nuclei Extra Questions
- Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Extra Questions
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices And Simple Circuits Extra Questions
- Wave Optics Extra Questions