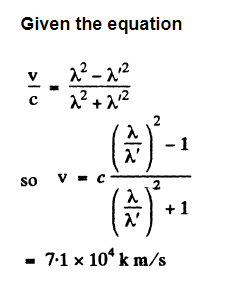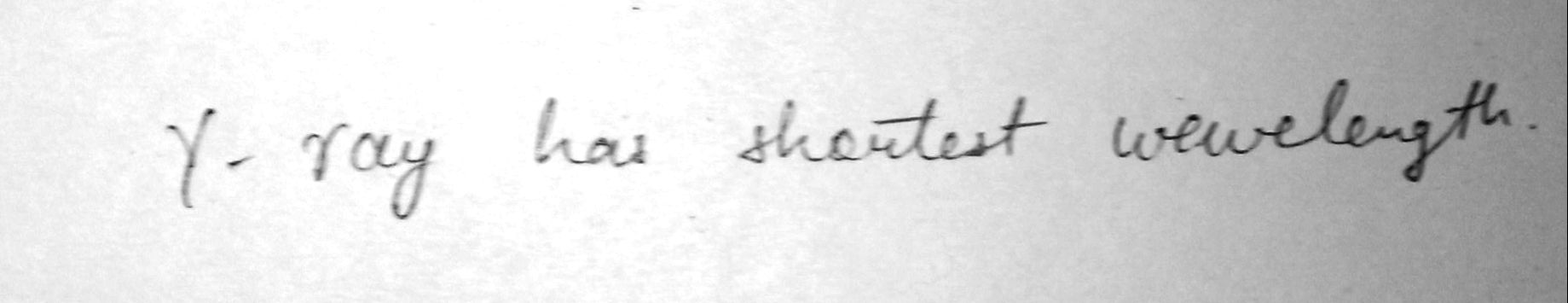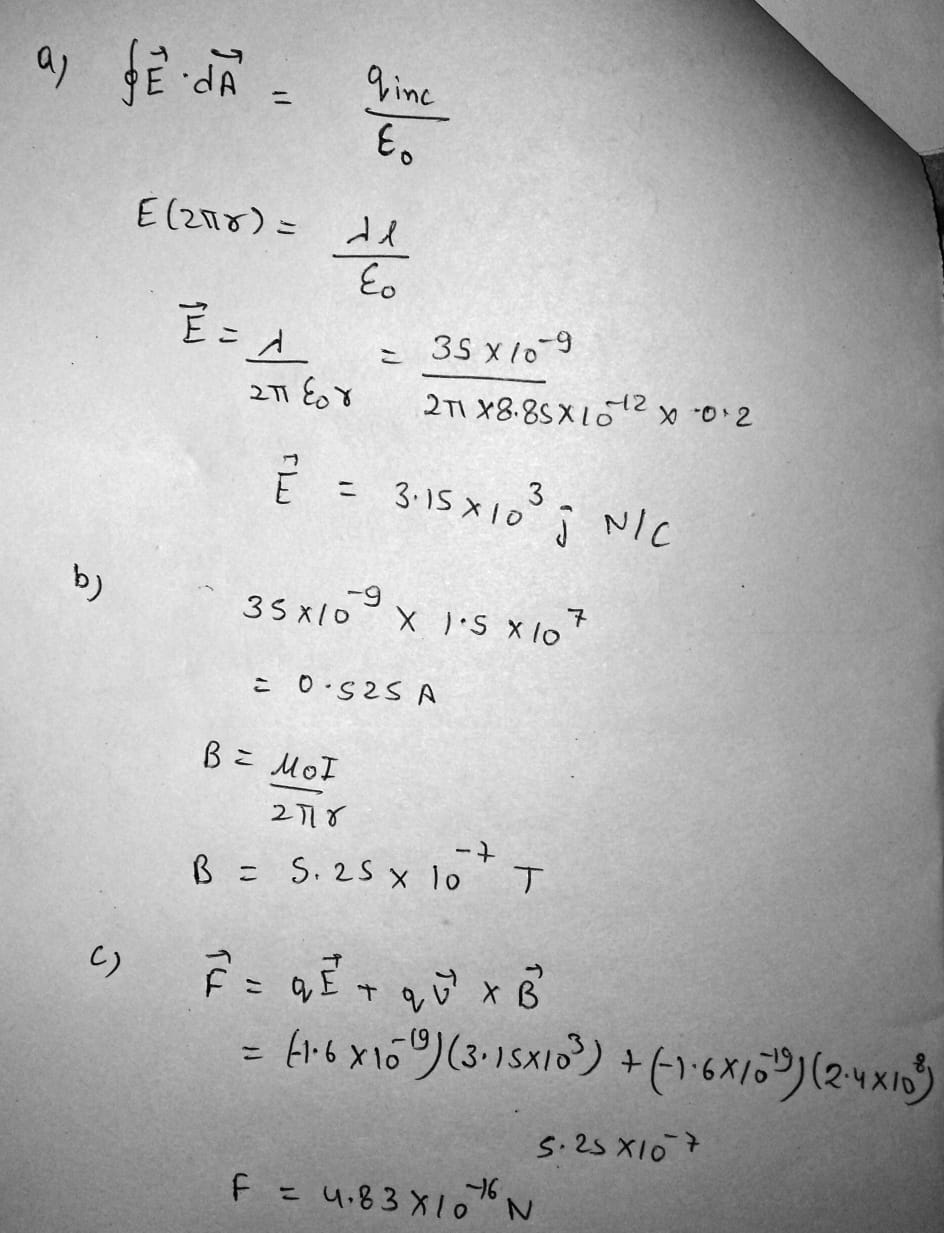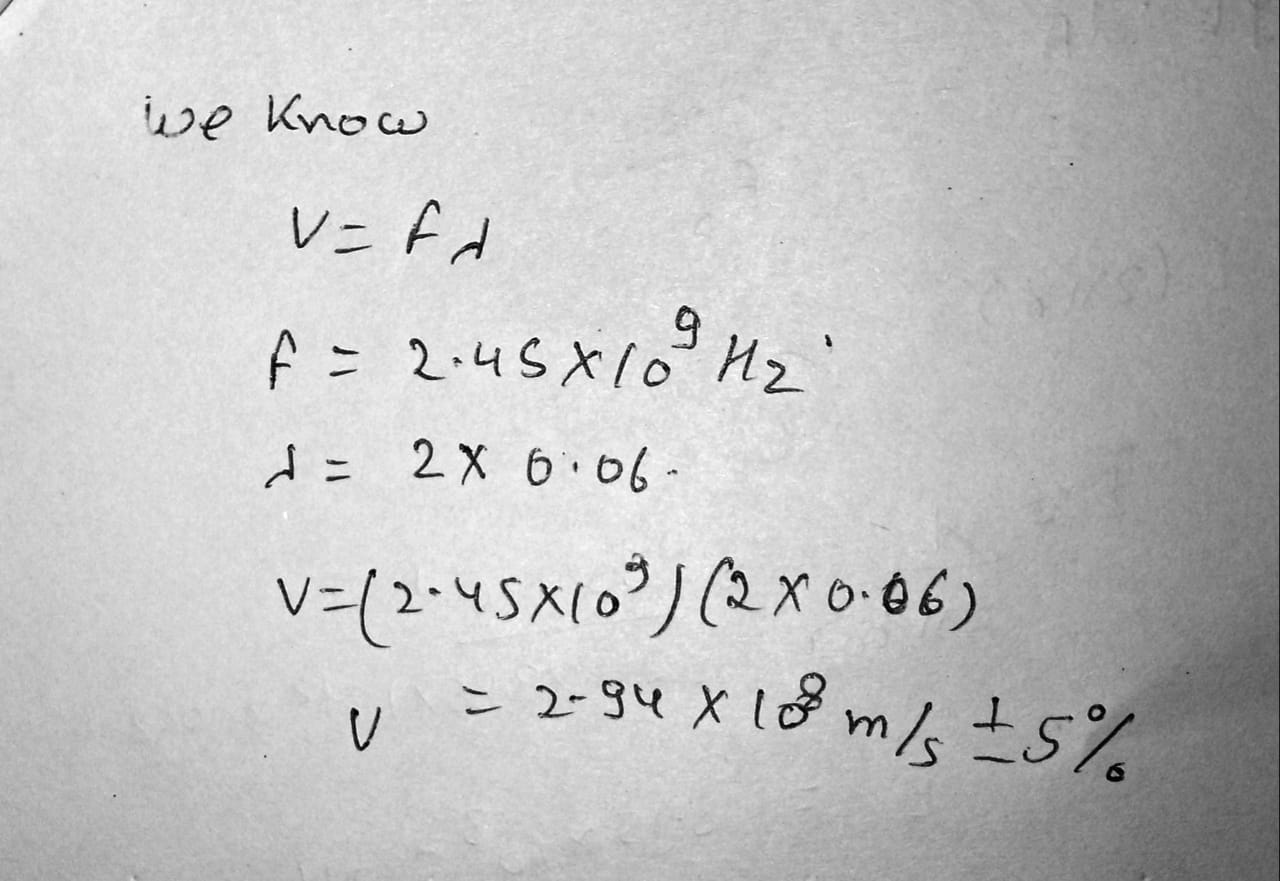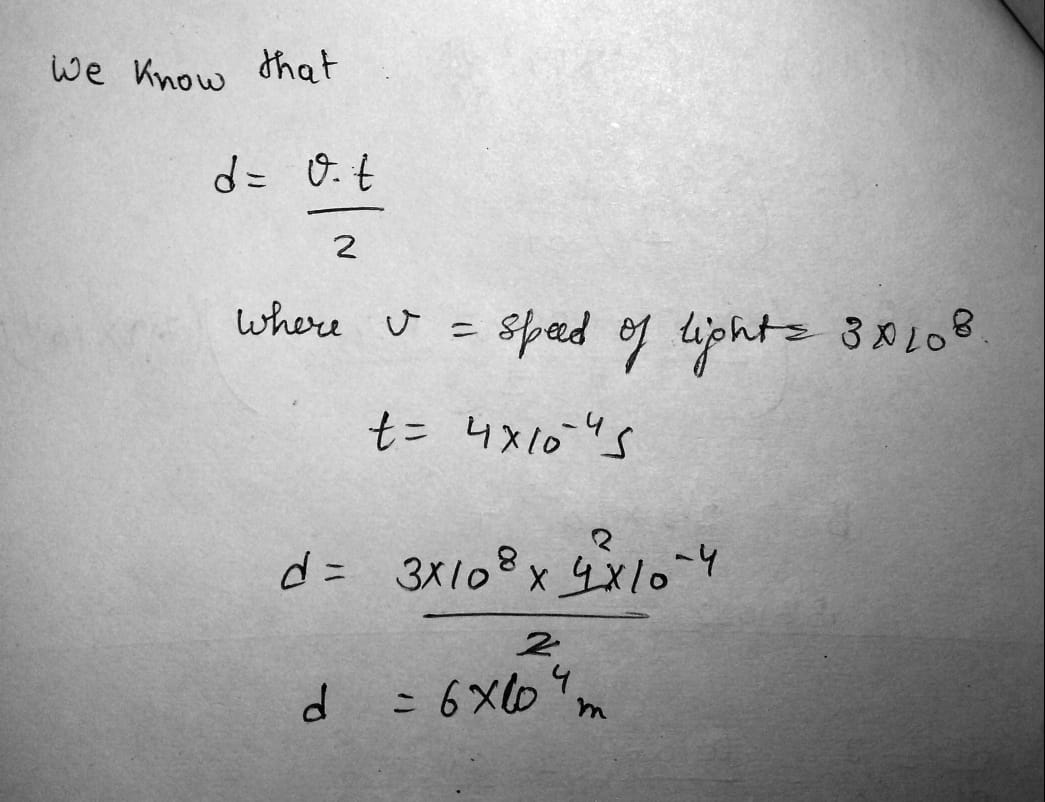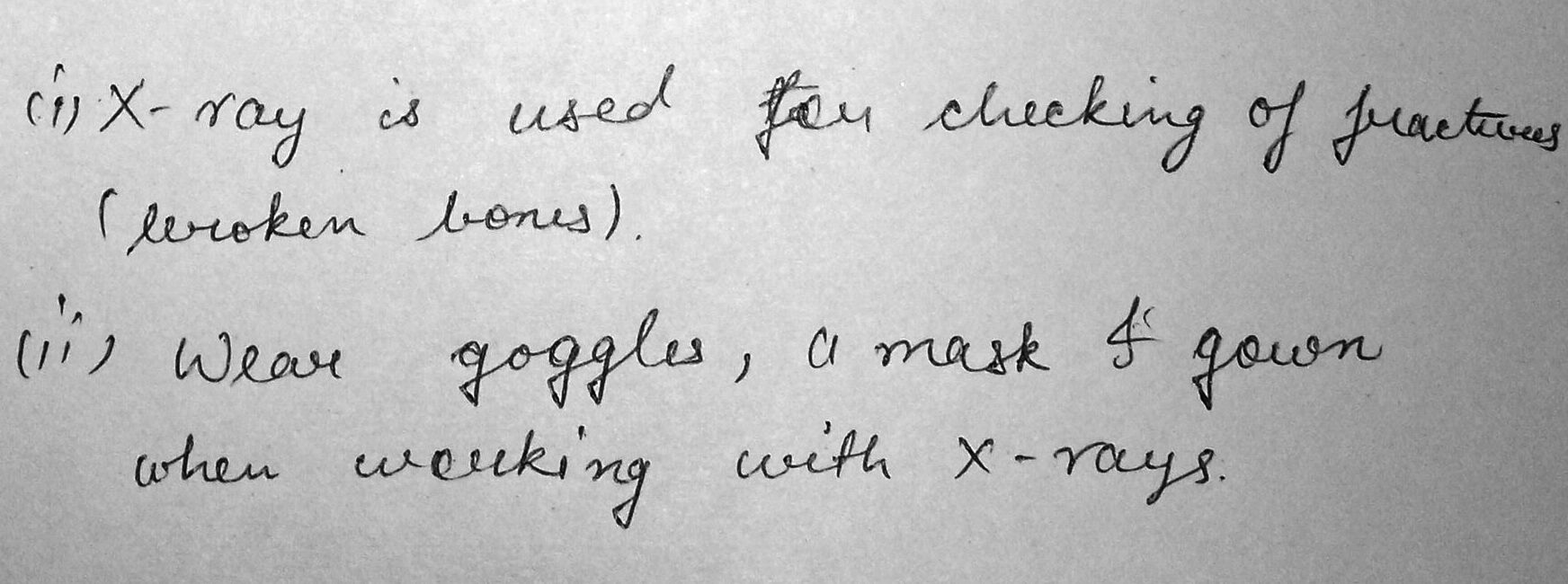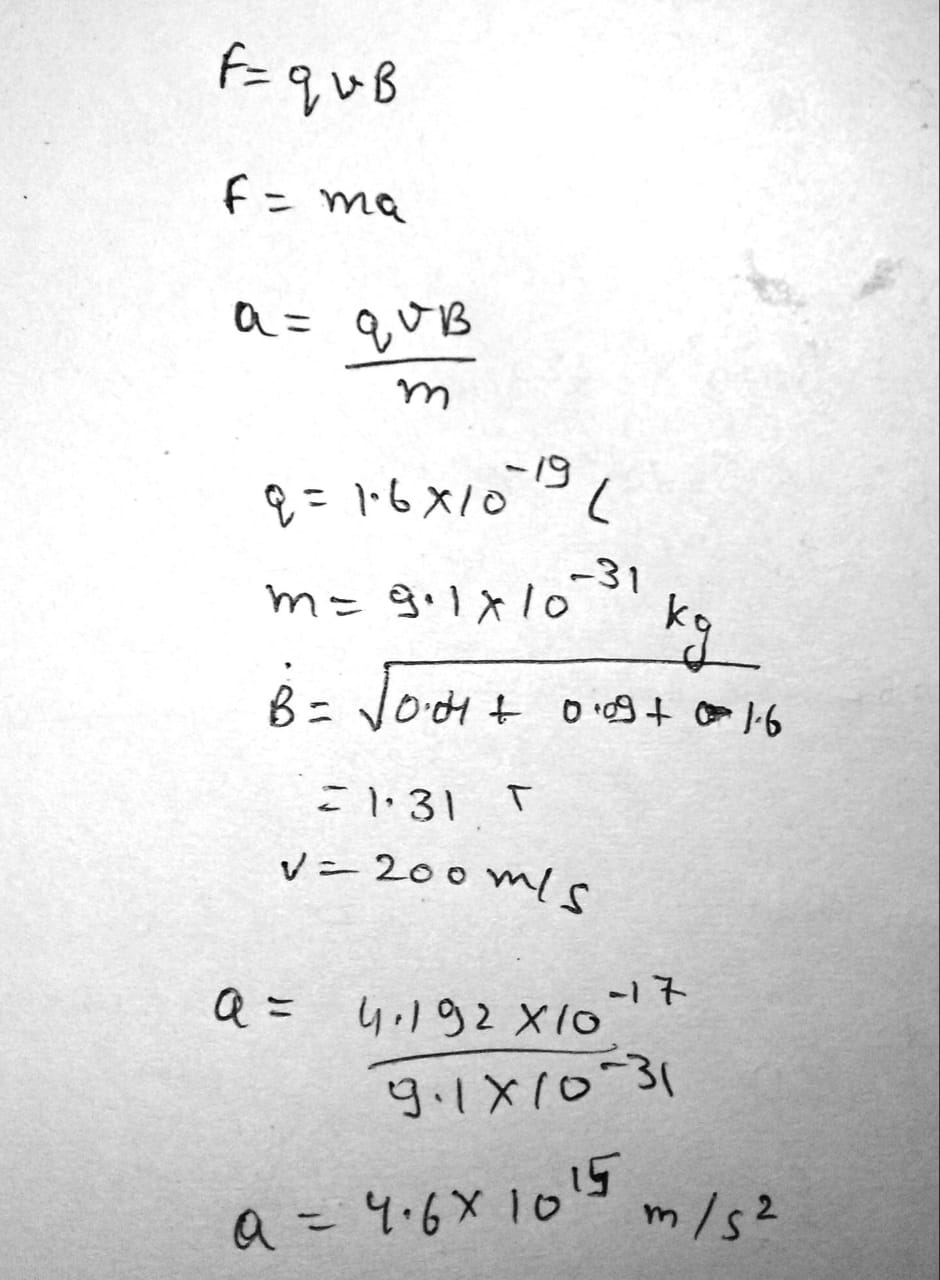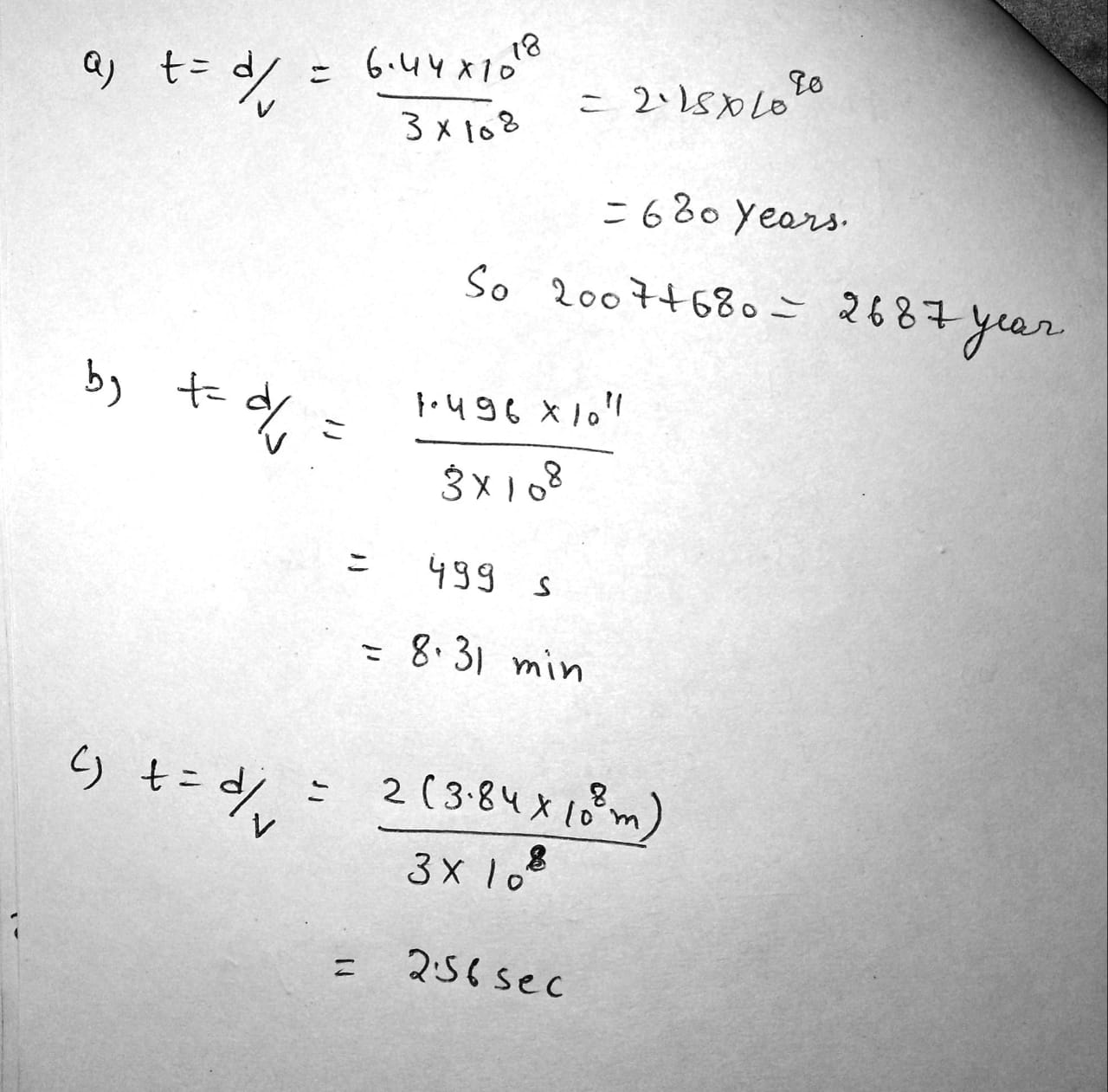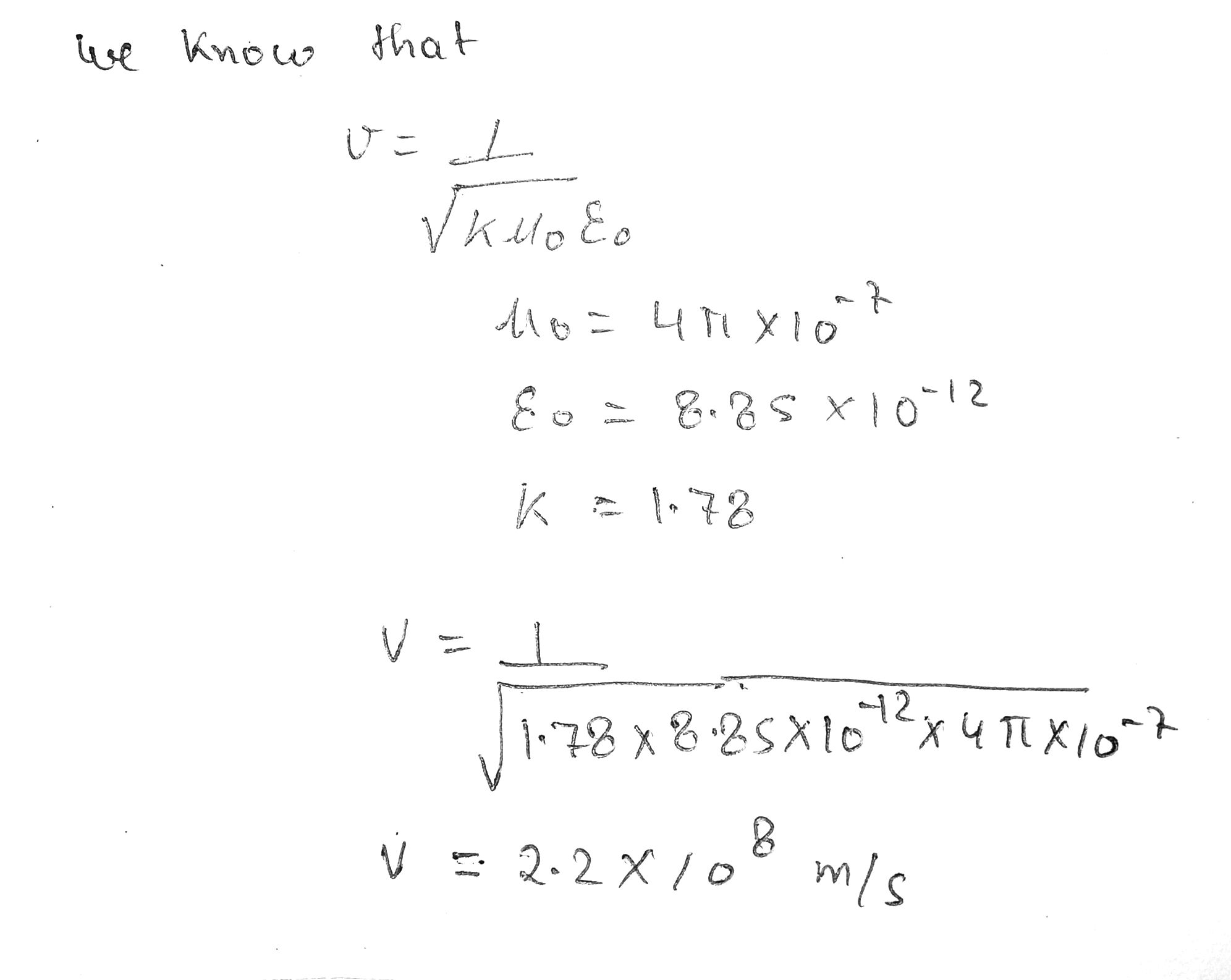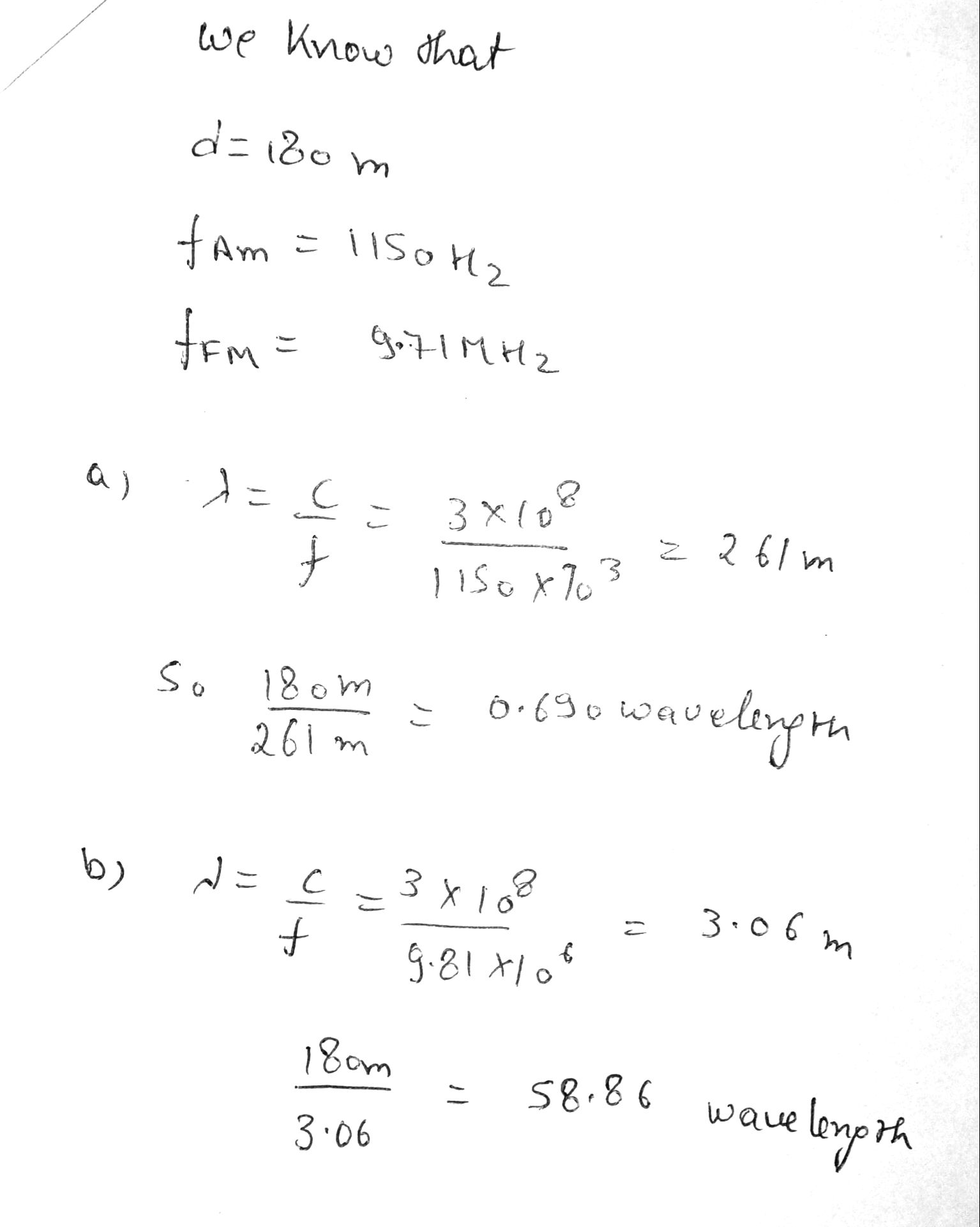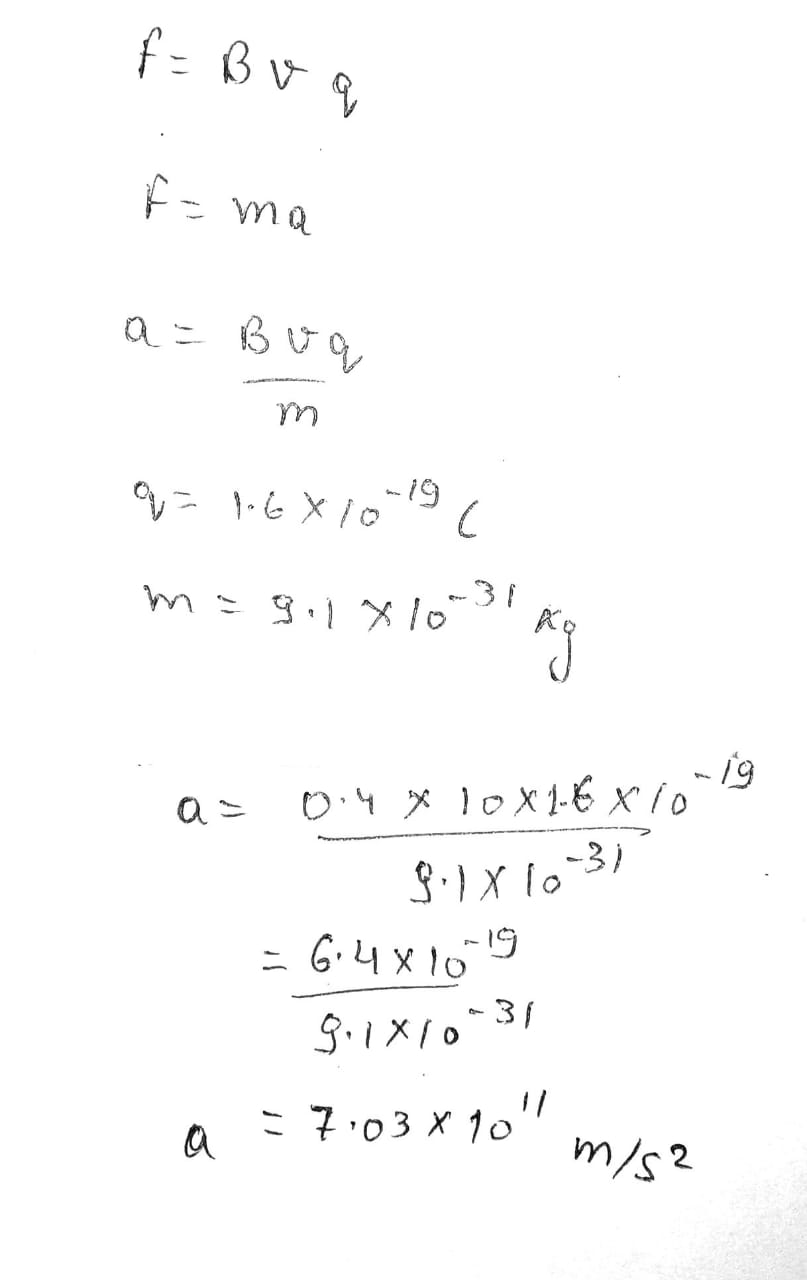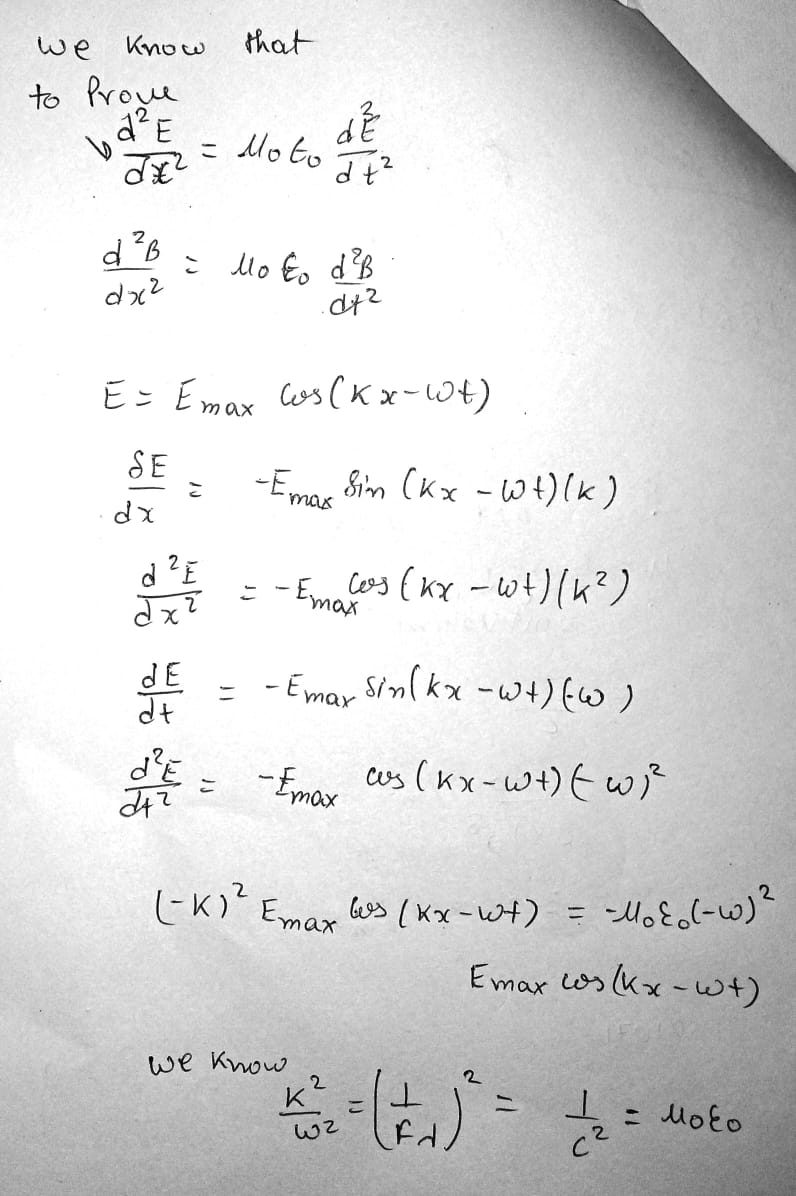Electromagnetic Waves - Class 12 Medical Physics - Extra Questions
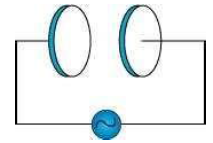
A parallel plate capacitor (fig.) made of circular plates each of radius R=6.0 cm has a capacitance C=100μF. The capacitor is connected to a 230 V ac supply with a (angular) frequency of 300 rad s−1.
Is the conduction current equal to the displacement current?
A parallel plate capacitor of plate separation 2 mm is connected in an electric circuit having source voltage 400 V. What is the value of the displacement current for 10−6 second if the plate area is 60 cm2.?
How electromagnetic waves are produced ?
In which situation is there a displacement current but no conduction current?
What is ratio of electric field and magnetic field in EM wave?
(i) What is main difference between electromagnetic waves theory and Planck's quantum theory.
(ii) Which rule is violated in the following orbital diagram:

Answer the following questions:
(i) How are infrared waves produced? Write their one important use.
(ii) The thin Ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival.
State two properties of ultra violet radiations which differs from visible light.
What is meant displacement current?
Analyse the diagram of solar spectrum and write answer.
a. Which radiation has a wavelength greater than visible light in this spectrum ?
b. Which color has the highest frequency in the visible part of the solar spectrum ?
c. Write one merit and demerit of infrared and ultraviolet radiations.
Write any two Maxwell's equation.
Name the characteristics of electromagnetic waves that
(i) increases
(ii) remains constant.
In the electromagnetic spectrum as one moves from radio wave region towards ultraviolet region.
______ was the first scientist who produced electromagnetic waves in a laboratory.
Write a short note on sky wave propagation.
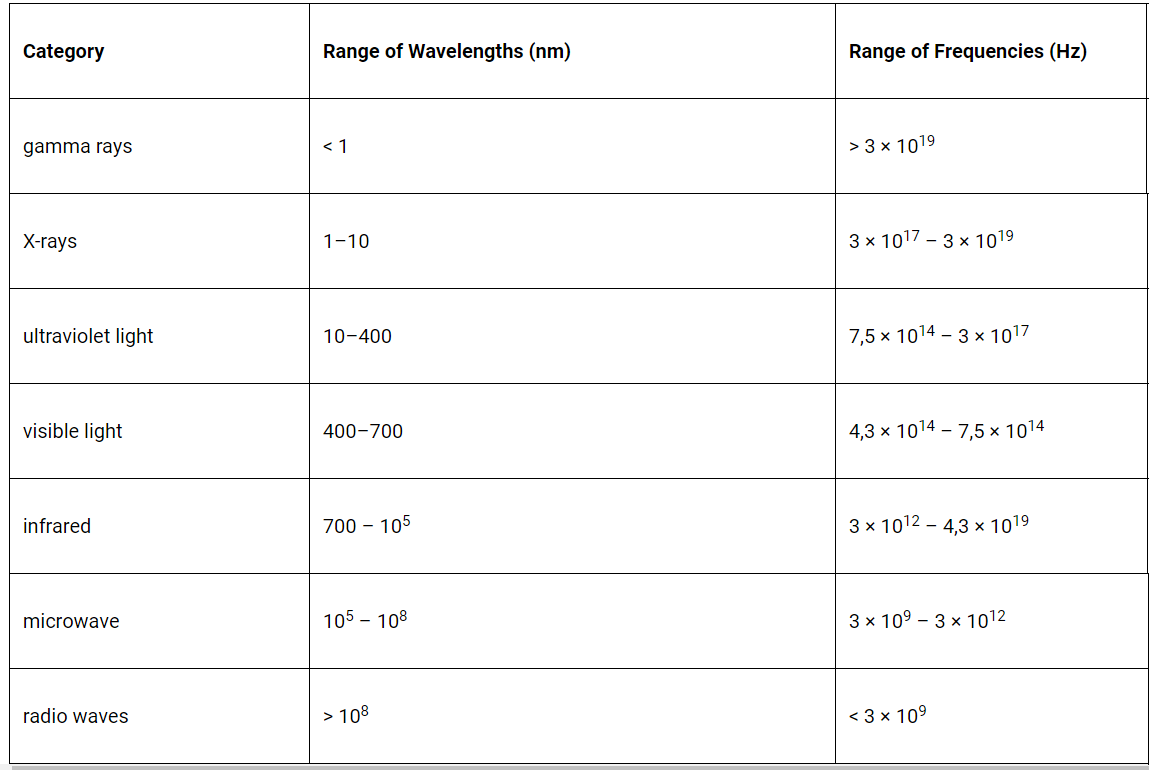
The table lists possible orders of magnitude of the wavelengths of some of the principal radiations
of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Which row shows the correct orders of magnitude of the wavelengths?
| wavelength / m | wavelength / m | wavelength / m | wavelength / m | |
| microwaves | infra-red | ultraviolet | X-rays | |
| A | 10−6 | 10−10 | 10−12 | 10−14 |
| B | 10−4 | 10−8 | 10−10 | 10−12 |
| C | 10−2 | 10−6 | 10−8 | 10−10 |
| D | 102 | 10−4 | 10−6 | 10−8 |
Which of thee following electromagnetic waves has (a) minimum wavelength, and (b) minimum frequency? Write one use of each of these two waves.
Infrared waves, Microwaves, y-rays and X-rays
A pint charge is moving along a straight line with a constant velocity v. Consider a small area A perpendicular to the direction of motion of the charge (figure 40-E1). Calculate the displacement current through the area when its distance from the charge i x. The value of z is not large so that the electric field at any instant is essentially given by Coulomb's law.

The speed of electromagnetic waves (which include visible light, radio, and x rays ) in vacuum is 3.0×108m/s. X-ray wavelengths range from about 5.0nm to about 1.0×10−2nm. What is the frequency range for x rays?
Name the type of waves which are used by astronauts to communicate with one another on moon.
Monochromatic light (that is, light of a single wavelength) is to be absorbed by a sheet of photographic film and thus recorded on the film. Photon absorption will occur if the photon energy equals or exceeds 0.6eV, the smallest amount of energy needed to dissociate an AgBr molecule in the film.(a) What is the greatest wavelength of light that can be recorded by the film?(b) In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum is this wavelength located?
What is Maxwell's corkscrew rule ? For what purpose is it used ?
Using B=μ0H find the ratio E0/H0 for a plane electromagnetic wave propagating through vacuum. This ratio is a universal constant called the impedance of free space.
The figure gives the variation
of an electric field that is perpendicular to a circular area of 2.0m2.
During the time period shown, what
is the greatest displacement current
through the area?
Why are infra-red radiations referred to as heat waves? Name the radiations which are next to these radiations in the electromagnetic spectrum having (i) shorter wavelength (ii) longer wavelength.
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in order of increasing frequency:
\gamma-rays, microwaves, infrared rays and ultraviolet rays.
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum is absorbed from sunlight by ozone layer?
A parallel-plate capacitor with circular plates of radius 0.10 m
is being discharged. A circular loop of radius 0.20 m is concentric with the capacitor and halfway between the plates. The displacement current through the loop is 2.0 A. At what rate is the electric
field between the plates changing?
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum is used in operating a RADAR?
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in order of decreasing frequency:
\gamma-rays, infrared rays, X-rays and microwaves.
Assume that lasers are available whose wavelengths can be precisely tuned to anywhere in the visible rangethat is, in the range 450 nm < \lambda < 650 nm. If every television channel occupies a bandwidth of 10 MHz, how many channels can be accommodated within this wavelength range?
Name the electromagnetic waves, which (i) maintain the Earth's warmth and (ii) are used in aircraft nagivation.
A parallel-plate capacitor with circular plates is being charged. Consider a circular loop centered on the central axis and located between the plates. If the loop radius of 3.00 cm is greater than the plate radius, what is the displacement current between the plates when the magnetic field along the loop has a magnitude 2.00 \mu T?
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which the following wavelengths belong:
(i) 10^{-1} m
(ii) 10^{-12} m.
Which of the following radiations are (i) heat radiation and (ii) used for long distance transmission? Infrared rays, gamma rays, ultraviolet rays, microwaves.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum does the wavelength 10^{-10}m correspond to?
Identify the type of waves which are produced by the following way and write one application for each:
(i) Radioactive decay of the nucleus
(ii) Rapid acceleration and decelerations of electrons in aerials
(iii) Bombarding a metal target by high energy electrons.
Which of the following has the minimum wavelength and which has the maximum wavelength?
Blue light, infrared rays, gamma rays, green light.
Which of the following has the least wavelength? Gamma rays, blue light, infrared radiation and ultraviolet, radiation.
How are X-rays produced?
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum of wavelength 10^{-2}m and mention its one application.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which the following wavelengths belong:
(i) 1\ mm
(ii) 10^{-11} m.
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for studying the crystal structure of solids.
Name the part of electromagnetic spectrum of wavelength 10^2\ m and mention its one application.
Special devices, like the klystron valve or the magnetro valve, are used for production of electromagnetic waves. Name the waves and also write one of their applications.
Give a reason to show that microwaves are better carriers of signals for long range transmission than radio waves.
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for viewing objects through haze and fog.
How are infrared waves produced?
Professor C.V. Raman surprised his students by suspending freely a tiny light ball in a transparent vacuum chamber by shining a laser beam on it. Which property of em waves was he exhibiting? Give one more example of this property.
From the following, identify the electromagnetic waves having the (i) Maximum (ii) Minimum frequency.
(a) Radio waves
(b) Gamma-rays
(c) Visible light
(d) Microwaves
(e) Ultraviolet rays, and
(f) Infrared rays.
The following table gives the wavelength range of some constituents of the electromagnetic spectrum.
| S.No. | Wavelength Range |
| 1. | 1\ mm to 700\ nm |
| 2. | 400\ nm to 1\ nm |
| 3. | 1\ nm to 10^{-3} nm |
| 4. | < 10^{-3} nm |
(i) Widely used in the remote switches of household electronic devices.
(ii) Produced in nuclear reactions.
Name the part of electromagnetic spectrum which is used for taking photographs of earth under foggy conditions from great heights.
Name the electromagnetic waves that have frequencies greater than those of ultraviolet light but less than those of gamma rays.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Which segment of electromagnetic waves has highest frequency? How are these waves produced? Give one use of these waves.
(ii) Which EM waves lie near the high frequency end of visible part of EM spectrum? Give its one use. In what way this component of light has harmful effects on humans?
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum whose wavelength lies in the range 10^{-10} m. Give its one use.
Answer the following questions:
(i) How are electromagnetic waves produced by oscillating charges?
(ii) State clearly how a microwave oven works to heat up a food item containing water molecules.
(iii) Why are microwaves found useful for the radar systems in aircraft navigation?
To which regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, the following wavelengths belong? 2,000\overset {\circ}{A}, 5,000\overset {\circ}{A}, 10,000\overset {\circ}{A} and 1.0\overset {\circ}{A}.
Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths lie in the range
(a) 10^{-11} m < \lambda < 10^{-8} m
(b) 10^{-4} m < \lambda < 10^{-1} m
Write one use of each.
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
(i) \lambda_{1} is used in satellite communication.
(ii) \lambda_{2} is used to kill germs in water purifier,
(iii) \lambda_{3} is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines.
(iv) \lambda_{4} is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
(1) Identify and name the part of electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong.
(2) Arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
(3) Write one more application of each.
Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths vary as
(a) 10^{-12} m < \lambda < 10^{-8} m
(b) 10^{-3} m < \lambda < 10^{-1} m
Write one use for each.
Identify the following electromagnetic radiations as per the wavelengths given below.
(a) 10^{-3} nm
(b) 10^{-3} m
(c) 1\ nm
Write one application of each.
Answer the following questions:
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
(i) Suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation
(ii) Produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons.
(iii) Why does a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of charging or discharging a capacitor? Write the necessary expression to explain this observation.
Write the following in descending order of wavelength:
Gamma rays, Hertzian waves, yellow light, blue light, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, \gamma-rays.
Which part of Sun's energy is responsible for drying clothes and exposure to which part could be a health hazard?
A variable frequency a.c source is connected to a capacitor. How will the displacement current change with decrease in frequency?
Professor C.V.Raman surprised students by suspending freely a tiny light ball in a transparent vacuum chamber by shining a laser beam on it. Which property of EM waves was he exhibiting? Given one more example of this property.
Why does microwave oven heats up a food item containing water molecules most effeciently?
The charge on a parallel plate capacitor varies as q={q}_{0}\cos{2\pi vt}. The plates are very large and close together (area =h, separation=d). Neglecting the edge effects, find the displacement current through? the capacitor
What is the range of wavelength of electromagnetic waves that constitute visible radiation?
Wavelength of radiation incident on a surface is 850 nm. Will the surface become visible when exposed to this radiation? Explain.
Identify the following electromagnetic radiations as per the frequencies given below:
(a) 10^{20} Hz
(b) 10^{9} Hz
(c) 10^{11} Hz
Write one application of each.
Experimental observations have shown that X-rays
(i) Travel in vacuum with a speed of 3\times 10^{8} ms^{-1}
(ii) Exhibit the phenomenon of diffraction and can be polarised.
What conclusion can be drawn about the nature of X-rays from each of these observations?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic wave : Gamma rays ?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves : Ultraviolet wave ?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves : X-rays ?
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
(i) {\lambda}_{1} is used in satellite communication.
(ii) {\lambda}_{2} is used to kill germs in water purifiers
(iii) {\lambda}_{3} is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines
(iv) {\lambda}_{4} is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions
Arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude
(a) Give a list of at least five radiations , in order of their increasing frequencies , which make up the complete electromagnetic spectrum.
(b) Which of the radiations mentioned in answer part (a) has the highest penetrating power ?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves :
Visible Light ?
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
(i) {\lambda}_{1} is used in satellite communication.
(ii) {\lambda}_{2} is used to kill germs in water purifiers
(iii) {\lambda}_{3} is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines
(iv) {\lambda}_{4} is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions
Write one more application of each
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in the order of their increasing wavelength:
(a) \gamma-rays
(b) Microwaves
(c) X-rays
(d) Radio waves
How are infra-red waves produced? What role does infra-red radiation play in (i) maintaining the Earth's warmth and (ii) physical therapy?
Answer the following
(a) Name the em waves which are used for the treatment of certain forms of cancer. Write their frequency range.
(b) Welders wear special glass goggles while working. Why? Explain
(c) Why are infrared waves often called as heat waves? Give their one application.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
Electromagnetic waves are ____ waves.
What is electromagnetic radiation?
Fill in the blanks with suitable words
The rays used to show bone structure is __________.
Match the EM waves from list I with corresponding Inventors in list II:
Fill in the blanks with suitable words
The range of wavelength of visible light is __________.
To which regions of the electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong :
(a) 250 nm
(b) 1500 nm
List the properties of electromagnetic waves.
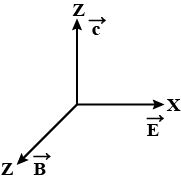
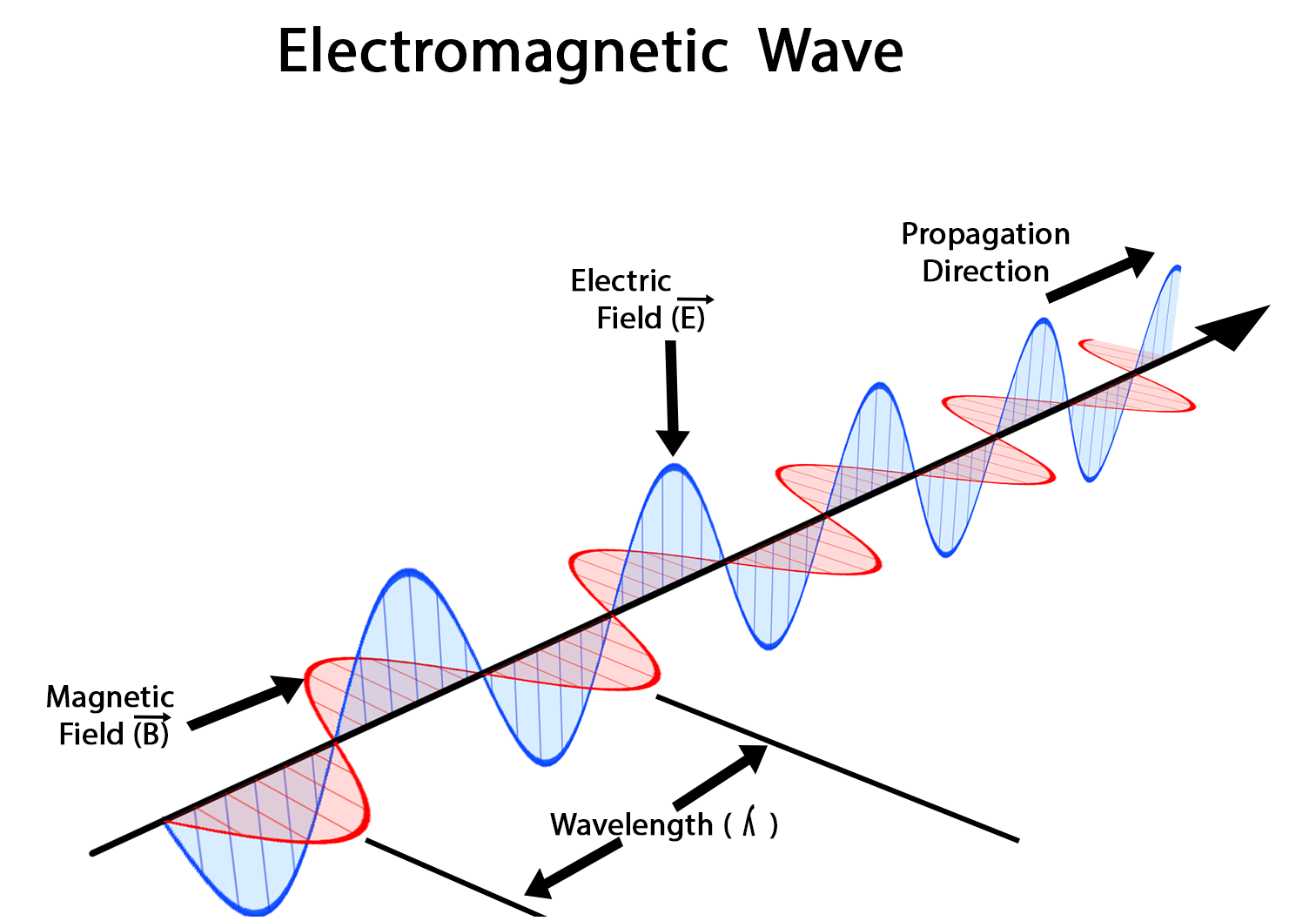
How are electric vector \vec{(E)}, magnetic vector \vec{(B)} velocity vector \vec{(c)} oriented in an electromagnetic wave ?
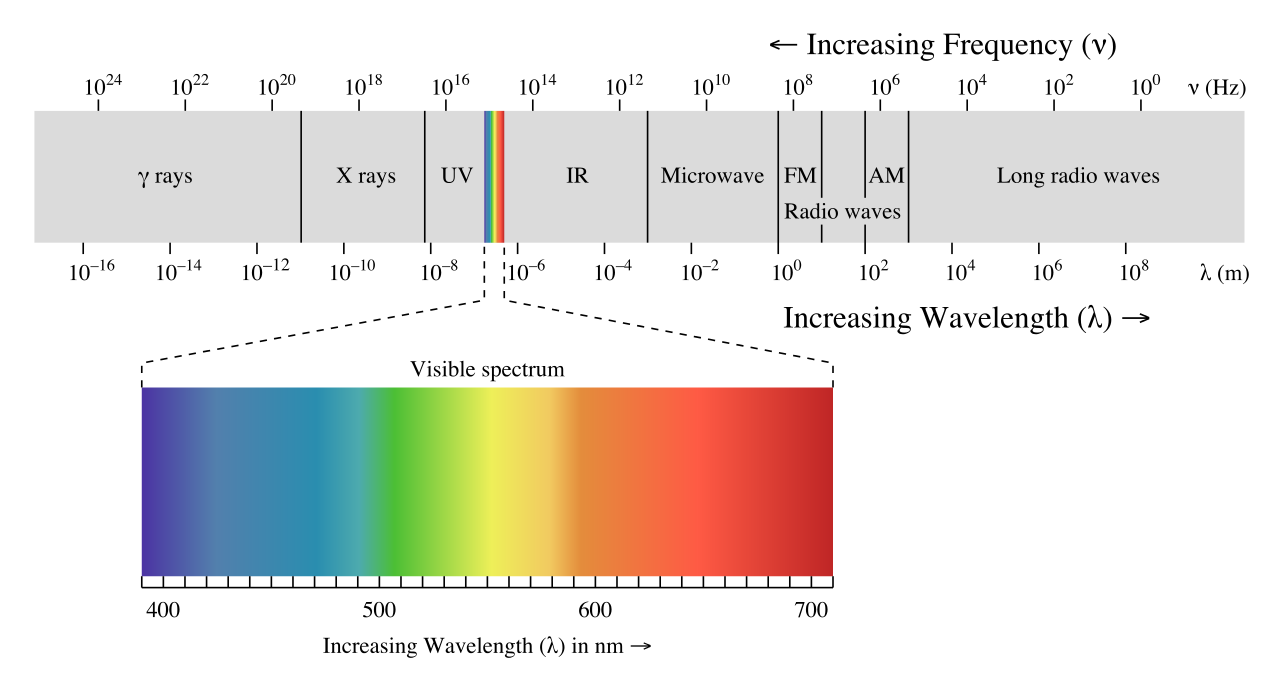
Explain the electromagnetic spectrum with a diagram.
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
(i) {\lambda}_{1} is used in satellite communication.
(ii) {\lambda}_{2} is used to kill germs in water purifiers
(iii) {\lambda}_{3} is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines
(iv) {\lambda}_{4} is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions
Identify and name the part of electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong.
Even through an electric field E exerts a force qE on a charged particle yet the electric field of an EM wave does not contribute to the radiation pressure (but transfers energy). Explain.
When an electron falls from a higher energy to a lower energy level, the difference in the energies appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why cannot it be emitted as other forms of energy ?
Give one use of ultraviolet radiations.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with the visible light .
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves : Micro waves ?
Name two electromagnetic waves of frequency greater than that of violet light. State one use of each.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with the infrared rays.
Give one use of infrared radiations .
Give one use of microwaves.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves : Infrared rays ?
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with the ultraviolet rays .
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves : Radio waves ?
Give two such properties of infrared radiations which are not true for visible light.
Name three properties of ultraviolet radiations which are similar to visible light.
What are infrared radiations ? How are they detected ? State one use of these radiations.
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively. Compare the speeds of these when they travel in vacuum.
What are ultraviolet radiations ? How they are detected ? State one use of these radiations.
Give one use of gamma rays .
Explain the following :
Infrared radiations are used for photography in fog.
Mention three properties of infrared radiations similar to the visible light.
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively. Name the two waves
Explain the following :
Infrared radiations are used as signals during war.
Explain the following :
A quartz is required for obtaining the spectrum of the ultraviolet light.
Explain the following :
The photographic darkrooms are provided with infrared lamps.
Explain the following :
A rock salt prism is used instead of a glass prism to obtain the infrared spectrum.
Explain the following : Ultraviolet bulbs have a quartz envelope instead of glass.
Write the uses of infra-red rays.
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength of 60 cm .
(a) Calculate the velocity of the wave.
(b) Name the medium through which it is travelling
Explain the inconsistency of Ampere's circuital law during charging of a capacitor. Define displacement current.
Name the rays of
1.Waves of highest frequency
2.Rays used for taking photographs in the dark
3.Rays of wavelength nearly 0.1\ nm
Fill in the blanks with the proper words.
GMRT is used for .......... waves.
Fill in the blanks with the proper words.
A certain X-ray telescope is named after scientist ............
Fill in the blanks with the proper words.
The wavelength of visible light is between .......... and ...........
Answer in brief:
Can microwaves be used in the experiment on photoelectric effect?
Name the components of electromagnetic spectrum in decreasing order of wavelength.
Name the components of electromagetic spectrum in decreasing order of wavelenght
Which type of wave is a light wave?
What physical quantity is the same for X -rays of wavelength 10^{-1} m , red light wavelength 6800 A and radio waves of wavelength 500 m,?
Given below are some fomous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiation in different contexts in physics .State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs .
1057 MH z (frequency of radiation arising from two close energy levels in hydrogen : know as lamb shift ).
Given below are some fomous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiation in different contexts in physics .State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs .
5890 A - 5890 A (double lines of sodium )
Given below are some fomous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiation in different contexts in physics .State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs .
7 K (temperature mwcrited with the isotropic radiation fHifag nil space - thought to be a reMC of the 'Mg - baugtrigbi of the universe }
What is Maxwell's displacement current?
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MH z to 12 band . What is the corresponding wavelength band ?
Given below are some fomous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiation in different contexts in physics .State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs .
21 cm (wavelength emitted by atomic hydrogen in interstellar space ).
Use the formula \lambda _{m}T = 29 cm K Obtain the charcteristic temperature ranges for different part of the electromagnetic spectrum .What do the numbers that you obtain tell you ?
Given below are some fomous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiation in different contexts in physics .State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs .
14.4 keV { energy of a particular transition in 57 Fe nucles associated with a famous highresolution spectroscopic method (Mossbauer spectrocopy )]
Find the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave of frequency 5\times 10^{19} Hz in free space identify the wave.
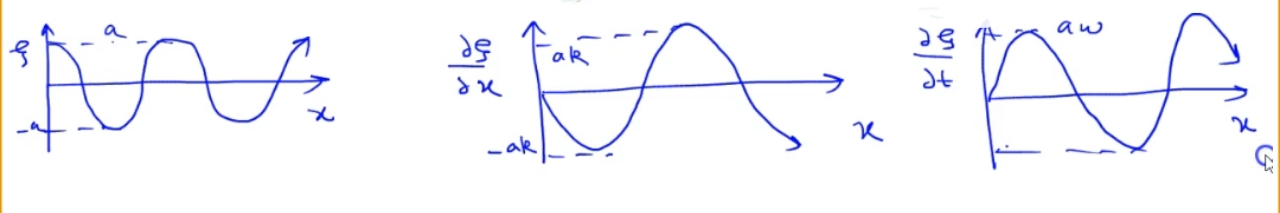
\xi and \partial\xi/\partial x as functions of x at the moments t=0 and t=T/2, where T is the oscillation period;
Analyse and describe the working of a microwave oven.
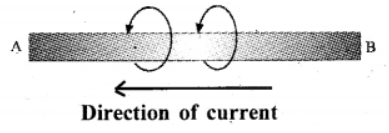
The magnetic field around the current carrying conductor AB is depicted
Based on the Maxwell's Right Hand Cork Screw Rule find out the direction of current and record it.
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. If an electron makes a transition from an energy level -1.51 eV to -3.4 eV, then calculate the wavelength of the spectral line emitted and name the series of hydrogen spectrum to which it belongs.
An electromagnetic wave is radiated by a 100 W bulb. If efficiency of the bulb is 20% then the amplitude of magnetic field at a distance of 1 m is (Consider bulb as a point source)
A parallel plate capacitor (fig.) made of circular plates each of radius R=6.0\ cm has a capacitance C= 100 \mu F. The capacitor is connected to a 230\ V ac supply with a (angular) frequency of 300 rad s^{-1}. Determine the amplitude of B at a point 3.0\ cm from the axis between the plates.?
A silver wire has resistivity \rho = 1.62 \times 10^{-8}\,\Omega.m and
a cross-sectional area of 5.00\, mm^2. The current in the wire is uniform and changing at the rate of 2000 \, A/s when the current is 100 A. (a) What is the magnitude of the (uniform) electric field in
the wire when the current in the wire is 100 A ? (b) What is the
displacement current in the wire at that time? (c) What is the ratio
of the magnitude of the magnetic field due to the displacement
current to that due to the current at a distance r from the wire?
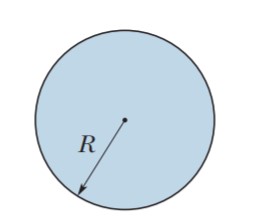
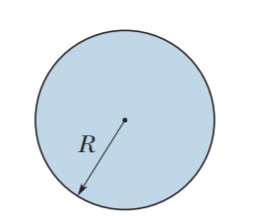
Uniform displacement current. The figure shows a circular
region of radius R = 3.00 cm in which a uniform displacement current i_d = 0.500 A is out of the page. What is the magnitude of the
magnetic field due to the displacement current at radial distances
(a) 2.00 cm and (b) 5.00 cm?
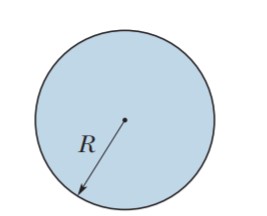
A parallel-plate capacitor having plate-area A and plate separation d is joined to a battery of emf \varepsilon and internal resistance R at t = 0 . Consider a plane surface of area A/2, parallel to the plates and situated symmetrically between them.If the displacement current through this surface as a function of time is given as: Y = \dfrac{\varepsilon }{nR}e^{-\dfrac{td}{\epsilon AR}}Then find the value of n.
Uniform displacement-current density. The figure shows a
circular region of radius R = 3.00 cm in which a displacement current is directed out of the page. The displacement current has a
uniform density of magnitude J_d = 6.00 \,A/m^2 . What is the magnitude of the magnetic field due to the displacement current at radial
distances (a)2.00 cm and (b) 5.00 cm?
Sea water at frequency v=4\times {10}^{8}Hz has permittivity \varepsilon =80{ \varepsilon }_{ 0 } permeability \mu ={\mu}_{0} and resistivity \rho =0.25\Omega-m. Imagine a parallel plate capacitor immersed in sea water an driven by an alternating voltage source V(t)={V}_{0}\sin {(2\pi vt)}. What fraction of the conduction current density is the displacement current density?
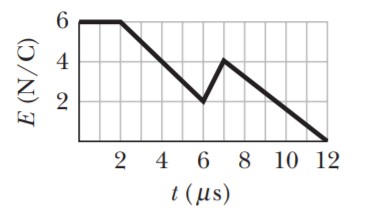
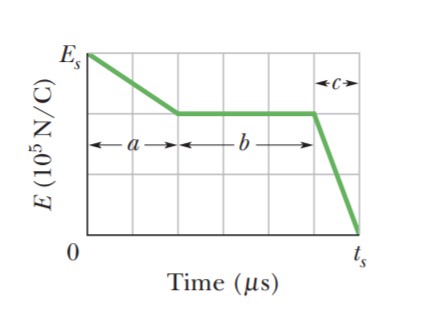
In Figure, a uniform
electric field collapses. The vertical axis scale is set by E_s = 6.0 \times 10^5\, N/C, and the horizontal axis scale is
set by t_s = 12.0\, \mu s. Calculate the
magnitude of the displacement current through a 1.6 \,m^2 area perpendicular to the field during each of
the time intervals a, b, and c shown
on the graph. (Ignore the behavior
at the ends of the intervals.)
There is a vacuum photocell whose one electrode is made of cesium and the other of copper. Find the maximum velocity of photoelectrons approaching the copper electrode when the cesium electrode is subjected to electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 0.22 \mu \mathrm{m} and the electrodes are shorted outside the cell.
Demonstrate that the law of electric charge conservation, i.e. \bigtriangledown \cdot j = -\partial \rho/ \partial t, follow from Maxwell's equations.
Proceeding from Maxwell's equation show that in the case of a plane electromagnetic wave (Fig 4.38) propagating in vacuum the following
\dfrac{\partial E}{\partial t}=-c^{2}\dfrac{\partial B}{\partial x}=\dfrac{\partial B}{\partial t}=-\dfrac{\partial E}{\partial x}.
Demonstrate that a closed system of charged non-relativistic particles with identical specific charges emits no dipole radiation.
Find the free electron concentration in ionosphere if its refractive index is equal to n = 0.09 for radio waves of frequency v = 100 MHz.
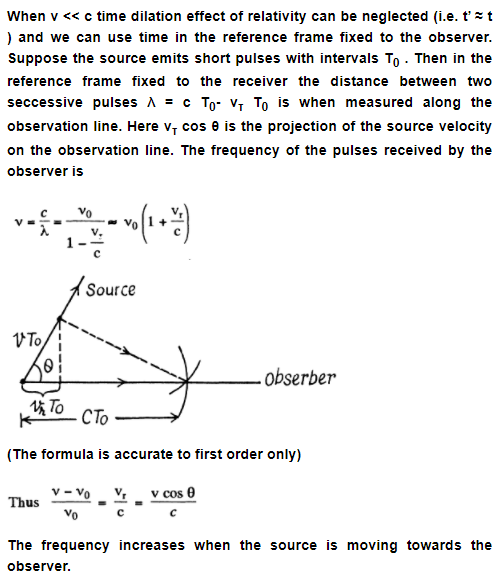
How fast should a car move for the driver to perceive a red traffic light (\lambda \approx 0.70 \mu m) as a green one (\lambda' \approx 0.55 \mu m)
A plane electromagnetic wave propagates in a medium moving with constant velocity V \ll c relative to an intertial frame K. Find the velocity of that wave in the frame K if the refractive of the wave coincides with that of the medium.
Conceptual Questions
Radio stations often advertise "instant news." If that means you can hear the news the instant the radio announcer speaks it, is the claim true? What approximate time interval is required for a message to travel from Maine to California by radio waves? (Assume the waves can be detected at this range.)
Conceptual Questions
Is Ampere’s law valid for all closed paths surrounding a conductor? Why is it not useful for calculating \overrightarrow{B} for all such paths?
Demonstrate that Maxwell's equations \bigtriangledown \times E = -\partial B/\partial t and \bigtriangledown \cdot B = 0 are compatible, i.e. the first one does not contradict the second one.
Conceptual Questions
Suppose a creature from another planet has eyes that are sensitive to infrared radiation. Describe what the alien would see if it looked around your library. In particular, what would appear bright and what would appear dim?
What does a radio wave do to the charges in the receiving antenna to provide a signal for your car radio?
An electromagnetic radiation is used for photography in fog.
Why is this radiation mentioned by you, ideal for this purpose?
An empty plastic or glass dish being removed from a microwave oven can be cool to the touch, even when food on an adjoining dish is hot. How is this phenomenon possible?
Why should an infrared photograph of a person look different from a photograph taken with visible light?
Describe the path of \gamma-rays in a magnetic field.
What new concept did Maxwell’s generalized form of Ampere’s law include?
An electromagnetic radiation is used for photography in fog.
Identify the radiation.
Do Maxwells equations allow for the existence of magnetic monopoles? Explain.
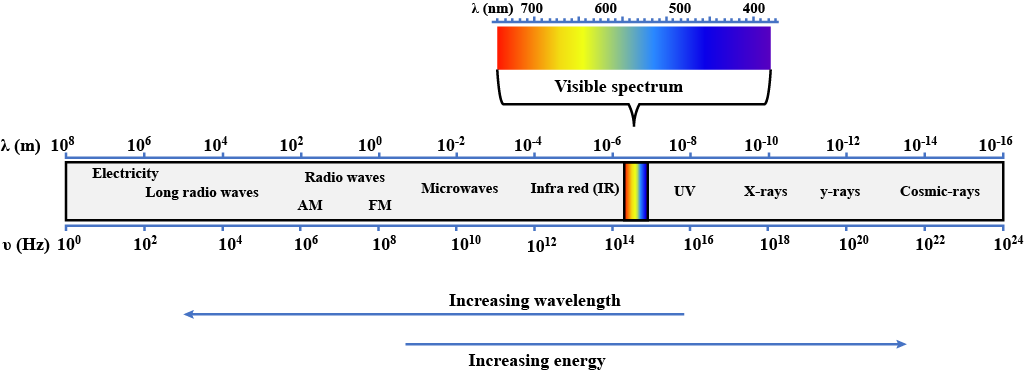
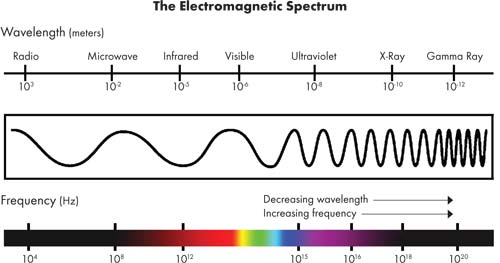
Figure represents the electromagnetic spectrum.
Fill in the blank spaces between visible light and radio waves by adding the names of the radiations.

Figure represents the electromagnetic spectrum.
State the radiation that has the shortest wavelength.

the plots of \xi,\partial\xi/\partial t, and \partial \xi/\partial x vs x;
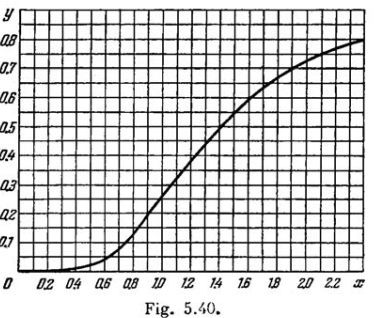
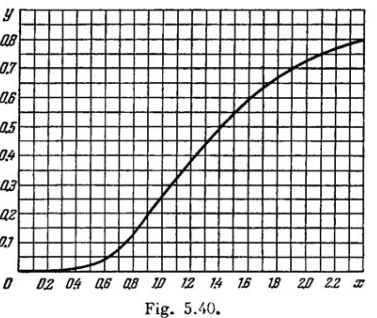
Fig. 5.40 shows the plot of the function y(x) representing a fraction of the total power of thermal radiation falling within
the spectral interval from 0 to x . Here x=\lambda / \lambda_{m}\left(\lambda_{m}\right. is the wavelength corresponding to the maximum of spectral radiation density). Using this plot, find:
(c) how many times the power radiated at wavelengths exceeding 0.76 \mu \mathrm{m} will increase if the temperature rises from 3000 to 5000 \mathrm{K}
A gas consists of atoms of mass m being in thermodyamic equilibrium at temperature T. Suppose \omega_o is the natural frequency of light emitted by the atoms.
(a) Demosntrate that the spectral distribution of the emitted light is defined by the formula
I_{\omega} = I_o e^{-a(1 - \omega/\omega_o)^2},
(I_o is the spectral intensity sorresponding to the frequency \omega_o, a = mc^2/2kT).
(b) Find the relative width \Delta \omega/ \omega_o of a given spectral line, i.e. the width of the line between the frequencies at which I_omega = I_o /2.
Fig. 5.40 shows the plot of the function y(x) representing a fraction of the total power of thermal radiation falling within
the spectral interval from 0 to x . Here x=\lambda / \lambda_{m}\left(\lambda_{m}\right. is the wavelength corresponding to the maximum of spectral radiation density). Using this plot, find:
(b) the fraction of the total radiation power falling within the visible range of the spectrum (0.40-0.76 \mu \mathrm{m}) at the temperature 5000 \mathrm{K}
A sounding of dilute plasma by radio waves of various frequencies reveals that radio waves with wavelengths exceeding \lambda_{0} = 0.75m experience total internal reflection. find the free electron concentration in that plasma.
A source of velocity relative to a receiver. Demonstrate that for v \gg c the fractional variation of frequency of light is defined by
Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(6)
A very long, thin rod carries electric charge with the linear density 35.0 \,nC/m. It lies along the x axis and moves in the x direction at a speed of 1.50 \times 10^7 \,m/s. (a) Find the electric field the rod creates at the point (x = 0, \,y = 20.0 \,cm, \,z = 0). (b) Find the magnetic field it creates at the same point. (c) Find the force exerted on an electron at this point, moving with a velocity of (2.40 \times 10^8)\hat{i} \,m/s.
Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(17)
Review. A microwave oven is powered by a magnetron,an electronic device that generates electromagnetic waves of frequency 2.45 \,GHz. The microwaves enter the oven and are reflected by the walls. The standing-wave pattern produced in the oven can cook food unevenly,with hot spots in the food at antinodes and cool spots at nodes, so a turntable is often used to rotate the food and distribute the energy. If a microwave oven intended for use with a turntable is instead used with a cooking dish in a fixed position, the antinodes can appear as burn marks on foods such as carrot strips or cheese. The separation distance between the burns is measured to be 6 \,cm \pm 5\%. From these data, calculate the speed of the microwaves.
Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(14)
A radar pulse returns to the transmitter-receiver after a total travel time of 4.00 \times 10^{-4} \,s. How far away is the object that reflected the wave?
Figure represents the electromagnetic spectrum.
(i) Describe a common uses of X-rays.
(ii) State a precaution taken by those who work with X-rays.

What are electromagnetic waves? Write its nature.
In electromagnetic spectra, the wave length and frequencies are inversely related. A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. Determine the corresponding wave length band.
The sound waves are the longitudinal waves. The electromagnetic waves are ________.
The ultraviolet radiant bulbs are made of quartz. Not of glass. Why?
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in increasing order of their frequencies (i.e., begin with the lowest frequency): Visible light, \gamma rays, X rays, micro waves, radio waves, infrared radiations and ultraviolet radiations.
Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths lie in the range
1) 10^{11}\,m < \lambda < 10^{-11}m
2) 10^{-4}\,m < \lambda < 10^{-6}m
Write one use of each.
Write any three uses of infrared radiations.
Write the following radiations in an ascending order in respect of their frequencies : X- rays, microwaves, UV (ultra - violet) rays and radio waves.
State Maxwell's theory of electromagnetic wave related to light. Write down four characteristics of electromagnetic waves.
The smoke from a fire looks white.
Which of the following statements is true?
1. Molecules of the smoke are bigger than the wavelength of light.
2. Molecules of the smoke are smaller than the wavelength of light.
Name an electromagnetic wave which is used in the radar system used in aircraft navigation. Give another use of the wave.
What do you mean by electromagnetic waves? Write the names of all electromagnetic waves from gamma rays to radio waves in order of their increasing wavelengths.
What is the ratio of the speed of gamma rays to that of radio waves in vacuum?
(a) Why are infra-red waves often called heat waves? Explain.
(b) What do you understand by the statement, "Electromagnetic waves transport momentum"?
Define displacement current.
In a cylindrical space uniform electric field varies with respect to time with rate (dE/dt). P is a point at a distance r from the axis of the space. Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at P.
A capacitor has been charged by a DC source. What are the magnitude of conduction and displacement current, when it is fully charged?
The frequency of oscillation of the electric field vector of a certain e.m. wave is 5 \times 10^{14}\ Hz. What is the frequency of oscillation of the corresponding magnetic field vector and to which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does it belong?
Plane electromagnetic wave of intensity S are incident normally on a flat surface.Only a fraction f of the incident energy is absorbed.What is the radiation pressure?
A wave travels out in all directions from a point source. Justify the expression y=(a_0/r)\sin k(r-vt), at a distance r from the source. Find the speed, periodicity and intensity of the wave.
The subjective property of light related to its wavelength is ..........(colour, refractive index).
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength 10^{-10}m, red light of wavelength 6800 \mathring A and radiowaves of wavelength 500m?
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
(i) Suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
(ii) Used to treat muscular strain.
(iii) Used as a diagnostic tool in medicine.
Write in brief, how these waves can be produced.
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
(a) suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation
(b) used to treat muscular strain
(c) used as a diagnostic tool in medicine
Write in brief, how these waves can be produced
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 5 \times 10^{11} Hz belong?
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Names the radiations and write the range of their frequency
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 3 \times 10^{13} Hz belong?
Why food placed in a microwave oven cooks more quickly than in a normal oven?
Why welders generally wear mask during welding ?
The electromagnetic spectrum that has least wave length is .......................
Name the radiations :
(i) That are used for photography at night.
(ii) Used for detection of fraction in bones.
(iii) Whose wavelength range is from 100\mathring { A } to 4000 \mathring { A } (or 10 nm to 400 nm).
Which electromagnetic radiation has wavelength greater than that of X rays and smaller than that of visible light?
A type of electromagnetic wave has wavelength 50\overset {\circ}{A}.
What is the speed of the wave in vacuum?
A type of electromagnetic wave has wavelength 50\overset {\circ}{A}.
State one use of this type of wave.
(i) Name the high energetic invisible electromagnetic waves which help in the study of the structure of crystals.
(ii) State an additional use of the waves mentioned in part (i).
A type of electromagnetic wave has wavelength 50\overset {\circ}{A}. (i) Name the wave.(ii) What is the speed of the wave in vacuum ?(iii) State one use of this type of wave.
(ii) What is the speed of the wave in vacuum ?
(iii) State one use of this type of wave.
The electromagnetic radiations that are used to take photographs of objects in darkness ...................
Which electromagnetic waves are used in remote controller (switches)?
Give the uses of ultraviolet radiation.
i) If force = mass \times acceleration, then momentum = ________
ii) If liquid hydrogen is for rocket, then _______ is for MRI
Write the name of the radiations of shortest and longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum.
What are the applications of microwaves?
Which waves are used as signal through fog and why?
Mention two applications of infrared radiation.
How are Microwaves produced?
The frequency of optical waves is of the order of ________.
A radiation X is focused by a particular device on the bulb of a thermometer and mercury in the thermometer shows a rapid increase. Name the radiation X.
Give any two applications of X-rays.
Is the colour of 620 nm light and 780 nm light same? Is the colour of 620 nm light and 621 nm light same? How many colours are there in white light?
Do electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum?
Who unified electricity and magnetism?
Write the names of waves in electromagnetic spectrum having smallest and largest wavelength.
The charging current for a capacitor is 0.25\ A. What is the displacement current across its plates?
Is the ratio of frequencies of ultraviolet rays and infrared rays in glass more than, less than or equal to 1?
Which out of the following are electromagnetic waves: X-rays, sound waves and radio waves?
If phase Difference between E and 1 is \dfrac{\pi}{4} and f = 50 Hz then calculate time difference.
Answer the following questions .
Long - distance radio brodcasts use shorts -wave bands ,Why ?
Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being charged, show how one is required to generalize Ampere's circuital law to include the term due to displacement current.
An electron beam passes through a transverse magnetic field of 2\times 10^{-3} tesla and electric field E of 3.4\times 10^{4}V/m acting simultaneously. If the path of the electrons remain undeviated, calculate the speed of the electrons
Write the relation for the speed of electromagnetic waves in terms of the amplitudes of electric and magnetic fields.
Why are microwaves used in radars?
Who predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves? Give the wavelength range of electromagnetic spectrum.
Draw and label the diagram showing various regions of Electro-magnetic spectrum and their wavelength ranges.
You have learned that the temperature of stars can be guessed from their colour.
Rewrite the following list in the ascending order (lower to higher) of temperature.
(a) Orange star
(b) Blue star
(c) Red star
Fill in the blanks in the following passage(s) from the words given inside the box.
magnet, carrying magnetic effect, electricity, the magnitude of current deflection increases, eastwards, southwards.
Oersted was the first to put forth the direct relation between _______ and magnetism. He conducted several experiments to determine the _______ of a current _______ wire. The following describes the Oersted experiment conducted to establish that a current carrying wire acts as a _______.
A long straight wire is connected to an external battery and an electric current is passed through it. When a magnetic needle is placed below the wire such that the wire is parallel to the axis of the magnetic needle and the current flows in the south to north direction, a deflection in the needle is observed. It is observed that the north pole of the needle is deflected westwards and as the _______ is increased, the deflection, _______ till the north pole of the needle turns towards exact west. It is also observed that if instead of placing the magnetic needle below the wire, if it was placed above the wire, the north pole of the magnetic needle is deflected _______ .
Oersted was the first to put forth the direct relation between _______ and magnetism. He conducted several experiments to determine the _______ of a current _______ wire. The following describes the Oersted experiment conducted to establish that a current carrying wire acts as a _______.
A long straight wire is connected to an external battery and an electric current is passed through it. When a magnetic needle is placed below the wire such that the wire is parallel to the axis of the magnetic needle and the current flows in the south to north direction, a deflection in the needle is observed. It is observed that the north pole of the needle is deflected westwards and as the _______ is increased, the deflection, _______ till the north pole of the needle turns towards exact west. It is also observed that if instead of placing the magnetic needle below the wire, if it was placed above the wire, the north pole of the magnetic needle is deflected _______ .
How are microwaves produced ? Why is it necessary in microwave ovens to select the frequency of microwaves to match the resonant frequency of water molecules ?
Write two important uses of infra-red waves.
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
Find the
(a) maximum frequency(b) Minimum wavelength of X-rays produced by 30 kV electrons.
A charged particle oscillates about its mean (equilibrium) position with a frequency of 10^{9} Hz. What is the frequency of the electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator?
Given below are some famous numbers associated with electromagnetic radiations in different contexts in physics. State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which each belongs.(a) 21 cm (wavelength emitted by atomic hydrogen in interstellar space).
(b) 1057 MHz (frequency of radiation arising from two close energy levels in hydrogen; known as Lamb shift).
(c) 2.7 K [temperature associated with the isotropic radiation filling all space thought to be a relic of the big-bang origin of the universe].
(d) 5890 \mathring A- 5896 \mathring A [double lines of sodium]
(e) 14.4 ke V [energy of a particular transition in ^{57}Fe nucleus associated with a famous high resolution spectroscopic method (\text{M}\ddot o \text{ssbauer spectroscopy})].
Write the expression for the generalized form of Ampere's circuital law. Discuss its significance and describe briefly how the concept of displacement current is explained through charging/discharging of a capacitor in an electric circuit
Write the uses of the following:
a. Radio waves
b. Microwaves
c. Ultraviolet radiation
d. X-rays
e. Infrared radiation
f. Gamma rays
Draw the diagram of electromagnetic wave.
Write the name of electromagnetic wave produced by vacuum tube magnetron.
How long would gamma radiation take to travel from sun to earth, a distance of 1.5\times 10^{11}m?
What is displacement current? Obtain an expression of displacement current for a charged capacitor. Write Ampere-Maxwell's law.
Identify the constituent radiations of electromagnetic spectrum which
(a) is obsorbed by ozone layer in the atmosphere
(b) i produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons
(c) is used in satellite communication
(d) has wavelength range between 400 nm to 700 nm.
(a) In free space at a point magnitude of electric field vector \left( \overrightarrow { E } \right) is 9.3V/m. Find the magnitude of magnetic field vector \left( \overrightarrow { B } \right) at the point.
(b) Out of ultraviolet, infrared and X-rays whose wavelength is maximum?
Write the mathematical equation of 'Ampere-Maxwell law'.
Write an expression for the displacement current.
Give two uses of Infrared Rays.
Screen S is illuminated by two point sources A and B. Another source C sends a parallel beam of light towards point P on the screen. Line AP is normal to the screen and the lines AP, BP and CP are 6, 3 and 3m respectively. The radiant powers of sources A and B are 45 and 90 W respectively. The beam from C is of intensity 0.4 W/m^2. The total incident intensity at P is
Write the name of any four waves (radiations) produced in electromagnetic spectrum.
The monoenergetic beams of electronics moving along + y direction enters a region of uniform electric and magnetic fields. If the beam goes straight through, then in which direction these simultaneously field \vec{B} and \vec{E} are directed ?
What are electromagnetic waves? Describe Maxwell's electromagnetic theory in brief.
Name the phenomenon which shows the quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation.
Write any three medical applications of X-rays.
What is displacement current? Why was this concept introduced? Explain. Also obtain the Ampere-Maxwell equation.
A parallel plate capacitor (Fig.) made of circular plates each of radius R = 6.0 cm has a capacitance C = 100 pF. The capacitor is connected to a 230 V ac supply with a (angular) frequency of 300 rad s^{-1}.(a) What is the rms value of the conduction current?
(b)
Is
the conduction current equal to the displacement current?
(c)
Determine the amplitude of B at a point 3.0 cm from the axis between
the plates.
(b) Is the conduction current equal to the displacement current?
(c) Determine the amplitude of B at a point 3.0 cm from the axis between the plates.
When the voltage applied to an X-ray tube increased emitted from { V }_{ 1 }=10\ KV to { V }_{ 2 }=20\ KV, the wavelength interval between the { K }_{ \alpha }-line and the short wavelength cut-off of the continuous X-ray spectrum increases by a factor of 3. Find the atomic number of the element of the target
A plane electromagnetic wave of frequency 25\ MHz travels in free space along the x-direction. At a particular point in space and time, \vec { E } =6.3\hat { j } { V }/{ m }. What is \vec {B} at this point?
An electron gun with its collector at a potential of 100V fires out electrons in a spherical bulb containing hydrogen gas at low pressure (\sim {10}^{-2}mm of Hg). A magnetic field of 2.83\times {10}^{4}T curves the path of the electrons in a circular orbit of radius 12.0cm. (The path can be viewed because the gas ions in the path focus the beam by attracting electrons, and emitting light by electron capture, this method is known as the fine beam tube method. Determine e/m from the data.
A message signal of frequency 20 KHz and peak voltage of 20 volts is used to modulate a carrier signal of frequency 2 MHz and peak voltage of 40 volts. Determine (i) modulation index, (ii) the side bands produced. Draw the corresponding frequency spectrum of amplitude modulated signal.
The electromagnetic waves of frequency range 100 to 300GHz are used in
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum has largest penetrating power?
A parallel plate capacitor (fig.) made of circular plates each of radius R=6.0\ cm has a capacitance C= 100 \mu F. The capacitor is connected to a 230\ V ac supply with a (angular) frequency of 300 rad s^{-1}. What is the rms value of the conduction current?
An observer is moving with half the speed of light towards a stationary microwave source emitting waves at frequency 10 GHz. What is the frequency of the microwave measured by the observer?\left( speed\quad of\quad light=3\times { 10 }^{ 8 }{ ms }^{ -1 } \right)
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in
(i)Treating mascular pains
(ii) Detecting flaws in crystallography
(iii)RADAR communication
Nonuniform displacement-current density. The figure shows a circular region of radius R=3.00 cm in which a displacement current is directed out of the page. The magnitude of the density of this displacement current is J_d = (4.00 \, A/m^2 )(1 - r/R),
where r is the radial distance (r \leq R). What is the magnitude of the
magnetic field due to the displacement current at (a) r = 2.00 cm
and (b) r = 5.00 cm?
The Sun is approximately an ideal blackbody radiator with a surface temperature of 5800 \mathrm{K}. (a) Find the wavelength at which its spectral radiancy is maximum and (b) identify the type of electromagnetic wave corresponding to that wavelength. (See Fig. 33-1.)(c) As we shall discuss in Chapter 44, the universe is approximately an ideal blackbody radiator with radiation emitted when atoms first formed. Today the spectral radiancy of that radiation peaks at a wavelength of 1.06 \mathrm{mm} (in the microwave region). What is the corresponding temperature of the universe?
Just after detonation, the fireball in a nuclear blast is approximately an ideal blackbody radiator with a surface temperature of about 1.0 \times 10^{7} \mathrm{K} . (a) Find the wavelength at which the thermal radiation is maximum and(b) identify the type of electromagnetic wave corresponding to that wavelength. (See Fig. 33-1.) This radiation is almost immediately absorbed by the surrounding air molecules, which produces another ideal blackbody radiator with a surface temperature of about 1.0 \times 10^{5} \mathrm{K} . (c) Find the wavelength at which the thermal radiation is maximum and (d) identify the type of electromagnetic wave corresponding to that wavelength.
In Figure, a capacitor with
circular plates of radius R= 18.0 cm is connected to a source of emf E = E_m sin \omega t, where E_m = 220 V
and \omega = 130\, rad/s. The maximum value of the displacement current is i_d = 7.60 \mu A. Neglect fringing of the electric field at the
edges of the plates. (a) What is the maximum value of the current i
in the circuit? (b) What is the maximum value of d\phi_E/dt, where \phi_E is the electric flux through the region between the plates? (c) What
is the separation d between the plates? (d) Find the maximum
value of the magnitude \vec B of between the plates at a distance of r = 11.0 cm from the center.
Answer the following questions:
Which one of the following electromagnetic radiations has least frequency:
(i) UV radiations, X-rays, Microwaves?
(ii) How do you show that electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum?
(iii) Write the expression for the energy density of an electromagnetic wave propagating in free space.
(a) What maximum light wavelength will excite an electron in the valence band of diamond to the conduction band? The energy gap is 5.50 eV. (b) In what part of the electromagnetic spectrum does this wavelength lie?
What happens to the intensity of light from a bulb if the distance from the bulb is doubled? As a lesser beam travels across the length of a room, its intensity essentially remains constant.
What geometrical characteristic of LASER beam is responsible for the constant intensity which is missing in the case of light from the bulb?
Assume that in the SternGerlach experiment as described for neutral silver atoms, the magnetic field overrightarrow B has a magnitude of 0.50 T. (a) What is the energy difference between the magnetic moment ori-entations of the silver atoms in the two subbeams? (b) What is the frequency of the radiation that would induce a transition between these two states? (c) What is the wavelength of this radiation, and (d) to what part of the electromagnetic spectrum does it belong?
Figure 8.6 shows a capacitor made of two circular plates each of the radius 12 cm , and separated by 5.0 cm .The capacitor is being charged by an external source (not shown in the figure ) .The charging current is constant and equal to 0.15 A .
Obtained the displacement current cross the plates .
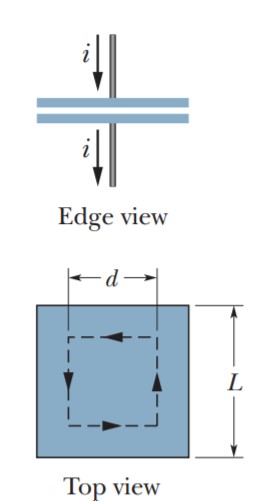
In Figure, a parallel-plate
capacitor has square plates of edge length L =1.0 m. A current of 2.0 A charges the capacitor, producing a uniform electric field
between the plates, with \vec E perpendicular to
the plates. (a) What is the displacement current i_d through the region between the
plates? (b) What is dE/dt in this region?
(c) What is the displacement current encircled by the square dashed path of edge
length d = 0.50 m? (d) What is the value of
\oint \vec B.d\vec s around this square dashed path?
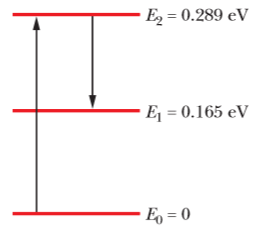
Martian CO_2 laser. Wheresunlight shines on the atmosphere of Mars, carbon dioxide molecules at an altitude of about 75km undergo natural laser action. The energy levels involved in the
action are shown in the above figure; population inversion occurs between energy levels E2 and E1.
(a) What wavelength of sunlight excites the molecules in the lasing action? (b) At what wave-length does lasing occur? (c) In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum do the excitation and lasing wavelengths lie?
Nonuniform displacement current. The figure shows a
circular region of radius R=3.00 cm in which a displacement
current id is directed out of the figure. The magnitude of the
displacement current is i_d = (3.00 A)(r/R),
where r is the radial distance (r \leq R) from the
center. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field due to id at radial distances (a) 2.00 cm and (b) 5.00 cm?
the efficient value of the displacement current density;
A conductor in the shape of a square frame with side a suspended by an elastic thread is located in a uniform horizontal magnetic field with induction B. In equilibrium the plane of the frame is parallel to the vector B Fig. Having been displaced from the equilibrium position, the frame performs small oscillations about a vertical axis passing through its centre. The moment of inertia of the frame relative to that axis is equal to I, its electric resistance is R. Neglecting the inductance of the frame, find the time interval after which the amplitude of the frame's deviation angle decreases e-fold.
the ratio of electromagnetic radiation flow densities S_{1}/S_{2} at the point P at the moments of time when the particle moves, from the standpoint of the observer P, toward him and away from him as shown in the figure.
A parallel capacitor (Fig . 8.7) made of circular plates of radius R = 6.0 cm has a capacitance C = 100 pF . The capacitor is connected to a 230 Y ac supply with an (angular)frequency of 300 rad s^{1}
Is the conduction current equal to the displacement current ?
A charged particle moves along the y axis according to the law y=a\cos \omega t, and the point of observation P is located on the x axis at a distance l from the particle (l\gg a). Find the ratio of electromagnetic radiation flow densities S_{1}/S_{2} at the point P at the moments when the coordinate of the particle y_{1}=0 and y_{2}=a. Calculate that ratio if \omega =3.3 . 10^{6}\ s^{-1} and l=190\ m.
A plane electromagnetic wave E=E_{m}\cos (\omega t-kx) propagating in vacuum induces the emf \xi_{ind} in a square frame with side l. The orientation of the frame is shown in Fig 4.37. Find the amplitude value \varepsilon_{ind}, if E_{m}=0.50\ mV/m, the frequency v=5.0\ MHz and l=50\ cm
A long straight cable of length l is placed symmetrically along z-axis and has radius a(<< l). The cable consists of a thin wire and a co-axial conducting tube. An alternating current I(t)={I}_{0}\sin { \left( 2\pi vt \right) } flows down the central thin wire and returns along the co-axial conducting tube. The induced electric field at a distance s from the wire inside the cable is
\vec { E } (s,t)={ \mu }_{ 0 }{ I }_{ 0 }v\cos { \left( 2\pi vt \right) } \log _{ e }{ \left( \cfrac { s }{ a } \right) } \hat { k }
(i) Calculate the displacement current density inside the cable
(ii) Integrate the displacement current density across the cross-section of the cable to find the total displacement current {I}_{d}
(iii) Compare the conduction current {I}_{0} with the displacement current {I}_{0}^{d}.
An electron experiences a quasi-elastic force kx and a "friction force" \dot{yx} in the field of electromagnetic radiation. The E-component of the field varies as E = E_{0} \;cos \;\omega \;t. Neglecting the action of the magnetic component of the field, find:
(a) the motion equation of the electron;
(b) the mean power absorbed by the electron; the frequency at which that power is maximum and the expression for the maximum mean power.
An isotropic point source emits light with wavelength \lambda=589 \mathrm{nm} . The radiation power of the source is P=10 \mathrm{W} . Find:
(b) the distance between the source and the point at which the mean concentration of photons is equal to n=100 \mathrm{cm}^{-3} .
AN electromagnetic wave of frequency\omega propagates in dilute plasma. The free electron concentration in plasma is equal to n_{0}. Neglecting the interaction of the wave and plasma ions, find:
(a) the frequency dependence of plasma permittivity;
(b) hows the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave depends on its wave lengthy \lambda in plasma.
In a certain medium, the relationship between the group and phase velocities of an electromagnetic wave has the form uv = c^{2}, where c is the velocity of light in vacuum. Find the dependence of permittivity of that medium on wave frequency, \varepsilon (\omega).
A light filter is a plate of thickness d whose absorption coefficient depends on wavelength \lambda as
x(\lambda) = \alpha(1 - \lambda/\lambda_{0})^{2} cm^{-1},
where \alpha \;and\lambda are constant. Find the bass band \Delta \lambda of this light filter, that is the band at whose edges the attenuation o lights is \eta the surface of the light filter is assumed to be the same at all wavelengths.
The space between two concentric metallic spheres is filled up with a uniform poorly conducting medium of resistivity \rho and permittivity \epsilon. At the moment t = 0 the inside sphere obtains a certain charge. Find:
(a) the relation between the vectors of displacement current density and conduction current density at an arbitrary point of the medium at the same moment of time;
(b) the displacement current across an arbitrary closed surface wholly located in the medium and enclosing the internal sphere, if at the given moment of time the charge of that sphere is equal to q.
Using Maxwell's equations, show that
(a) a time-dependent magnetic field cannot exist without an electric field;
(b) a uniform electric field cannot exist in the presence of a time-dependent magnetic field;
(c) inside an empty cavity a uniform electric (or magnetic) field can be time-dependent.
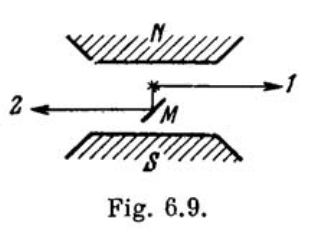
The same spectral line undergoing anomalous Zeeman splitting is observed in direction 1 and, after reflection from the mirror M (Fig. 6.9), in direction 2. How many Zeeman components are observed in both directions if the spectral line is caused by the transition
(a) ^{2}P_{3/2} \rightarrow ^{2}S_{1/2} ; (b) ^{3}P_{2} \rightarrow ^{3}S_{1} ?
Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(5)
A proton moves through a region containing a uniform electric field given by \overrightarrow{E}=50.0\hat{j} \,V/m and a uniform magnetic field \overrightarrow{B}=(0.200\hat{i}+0.300\hat{j}+0.400\hat{k}) \,T. Determine the acceleration of the proton when it has a velocity \vec{v}=200\hat{i} \,m/s.
Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(9)
The distance to the North Star, Polaris, is approximately 6.44 \times 10^18 \,m. (a) If Polaris were to burn out today, how many years from now would we see it disappear? (b) What time interval is required for sunlight to reach the Earth? (c) What time interval is required for a microwave signal to travel from the Earth to the Moon and back?
Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(13)
The speed of an electromagnetic wave traveling in a transparent nonmagnetic substance is v = 1/\sqrt{k\mu_0 \epsilon_0}, where k is the dielectric constant of the substance. Determine the speed of light in water, which has a dielectric constant of 1.78 at optical frequencies.
Maxwell’s Equations and Hertz’s Discoveries(7)
Suppose you are located 180 \ m from a radio transmitter. (a) How many wavelengths are you from the transmitter if the station calls itself 1150 \ AM? (The AM band frequencies are in kilohertz.) (b) What if this station is 98.1\ FM ? (The FM band frequencies are in megahertz.)
Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(4)
An electron moves through a uniform electric field \overrightarrow{E}=(2.50\hat{i}+5.00\hat{j}) \,V/m and a uniform magnetic field \overrightarrow{B}=0.400\hat{k} \,T. Determine the acceleration of the electron when it has a velocity \vec{v}=10.0\hat{i} \,m/s.
A small ideal mirror of mass m=10 \mathrm{mg} is suspended by a weightless thread of length l=10 cm. Find the angle through which the thread will be deflected when a short laser pulse with energy E=13 \mathrm{J} is shot in the horizontal direction at right angles to the mirror. Where does the mirror get its kinetic energy?
Figure represents the electromagnetic spectrum.
Identify one feature that is the same for all radiations that form the electromagnetic spectrum.

Maxwells Equations and Hertzs Discoveries(16)
Verify by substitution that the following equations are solutions to Equations 34.15 and 34.16, respectively:
E=E_{max}\cos(kx-\omega t)
B=B_{max}\cos(kx-\omega t)
Class 12 Medical Physics Extra Questions
- Alternating Current Extra Questions
- Atoms Extra Questions
- Current Electricity Extra Questions
- Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter Extra Questions
- Electric Charges And Fields Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Induction Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Waves Extra Questions
- Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Extra Questions
- Magnetism And Matter Extra Questions
- Moving Charges And Magnetism Extra Questions
- Nuclei Extra Questions
- Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Extra Questions
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices And Simple Circuits Extra Questions
- Wave Optics Extra Questions