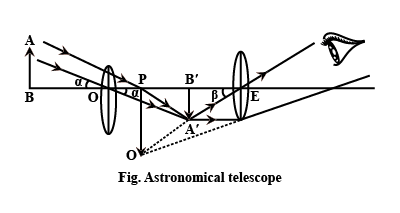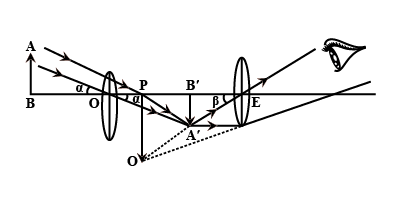Ray Optics And Optical Instruments - Class 12 Medical Physics - Extra Questions
A transparent sphere of radius 20 cm and refractive index 1.6 is fixed in a hole of the partition separating the two media: A(refractive index $$n_1$$= 1.2 ) and B (refractive index $$n_3$$ =1.7). A luminous point object is placed 120 cm from surface of sphere in medium A. It is viewed from D in medium B in a direction normal to the sphere. Find the position of the image formed by the rays, from point N.
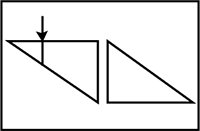
A ray of light incident normally on face AB of an isosceles prism travels as shown in figure. The least value of the refractive index the prism must be:
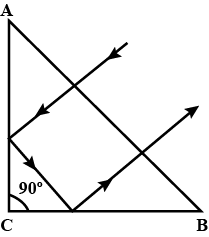
How many times does a ray of light undergo refraction when it passes through a water droplet?
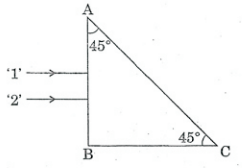
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.38 and 1.Trace the path of these rays after entering through the prism.
With the help of labelled ray diagram show the formation of an image in.
a) A simple microscope.
b) A compound microscope.
c) An astronomical telescope.
What is the magnifying power of a telescope whose objective and eye - piece have focal length 180 cm and 3 cm respectively?
Fill in the blanks.
The lens placed towards the object in an optical instrument is called _______.
A convex lens is made up of three different materials as shown in the figure. How many of images does it form

Fill in the blanks:
The equation of mirror formula is ___
Fill in the blanks
In minimum deviation position of prism, the angle of incidence is equal to angle of ____________.
'Chandra' is a telescope operating in space to unveil the secrets of universe.
a) Write the type of radiation that 'Chandra' picks up to study the universe.
b) What are the advantages of setting up a telescope outside the earth's atmosphere?
When light of wavelength $$5000\mathring{A}$$ in vacuum travels through same thickness in glass and water, the difference in the number of waves is $$400$$. Find the thickness (Refractive index of glass and water are $$\cfrac{3}{2}$$ and $$\cfrac{4}{3}$$ respectively)
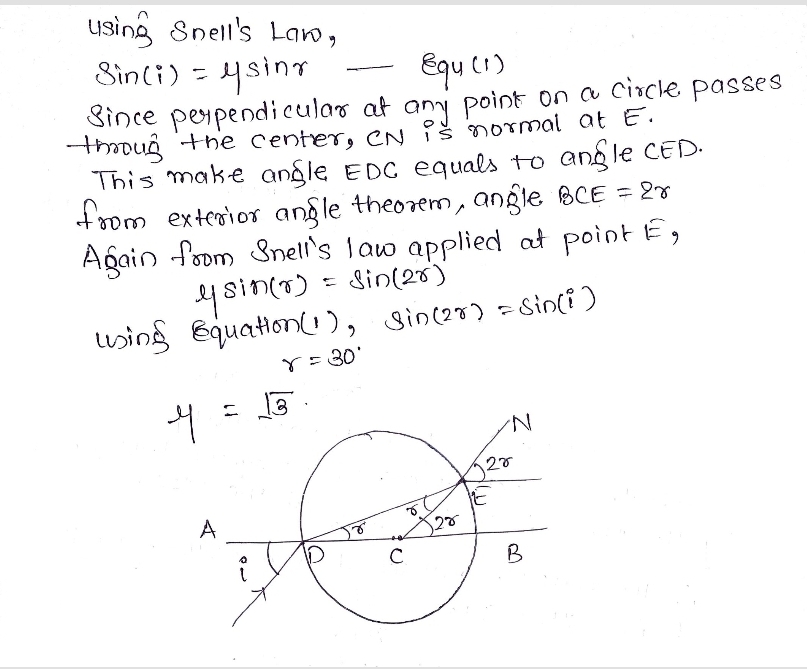
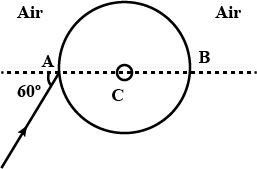
A ray of light falls on transparent sphere with centre $$C$$ as shown in figure. The ray emerges from the sphere parallel to the line $$AB.$$ Find the angle of refraction at $$A$$ if refractive index of the material of the sphere is $$\sqrt { 3 } .$$
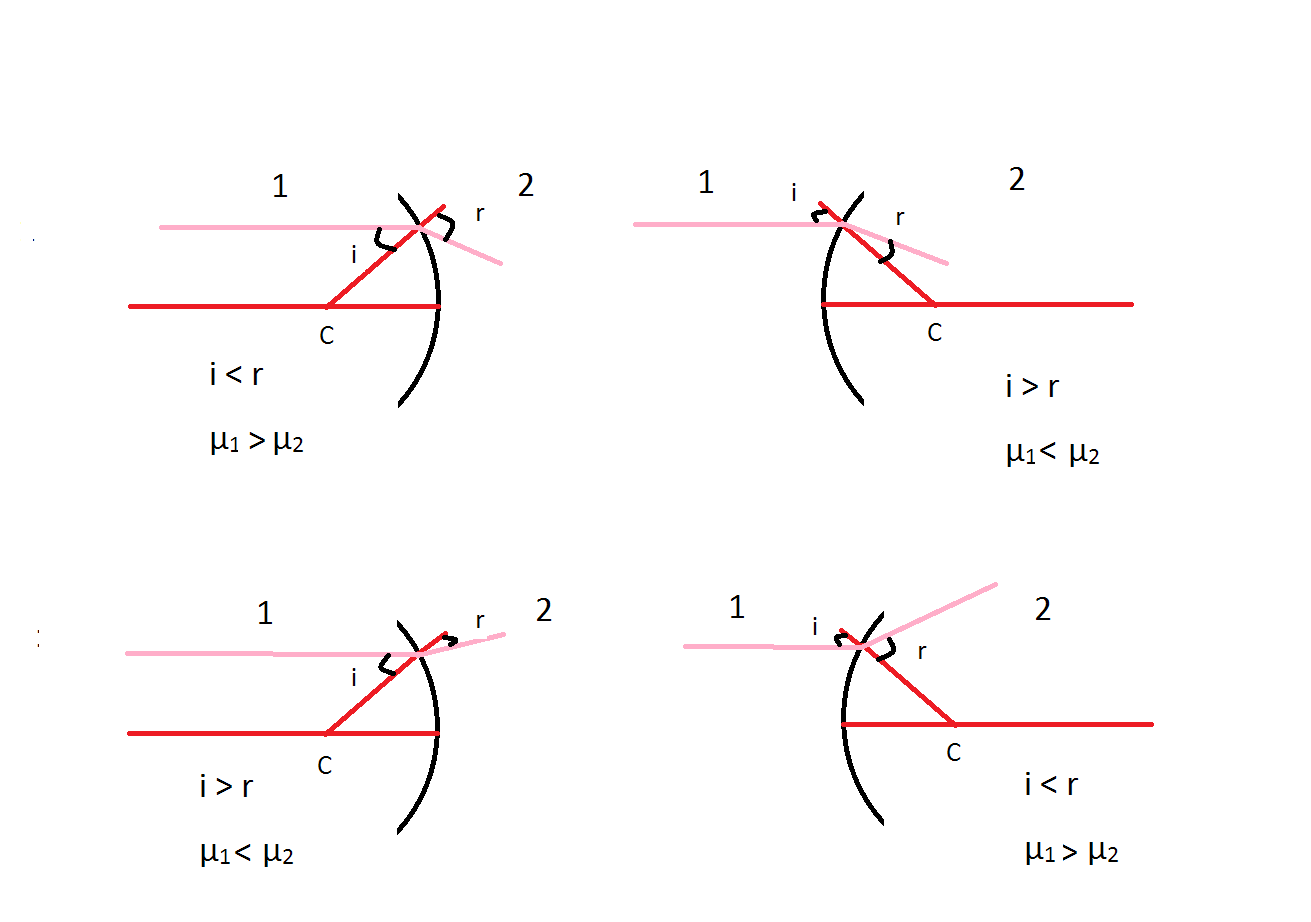
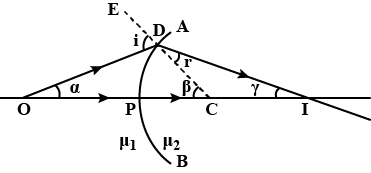
What is the relation between the refractive indices $$ \mu_1 and\ \mu_2 $$, if the behaviour of light rays is as shown in the figure.
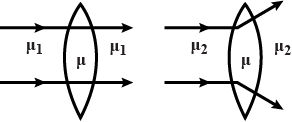
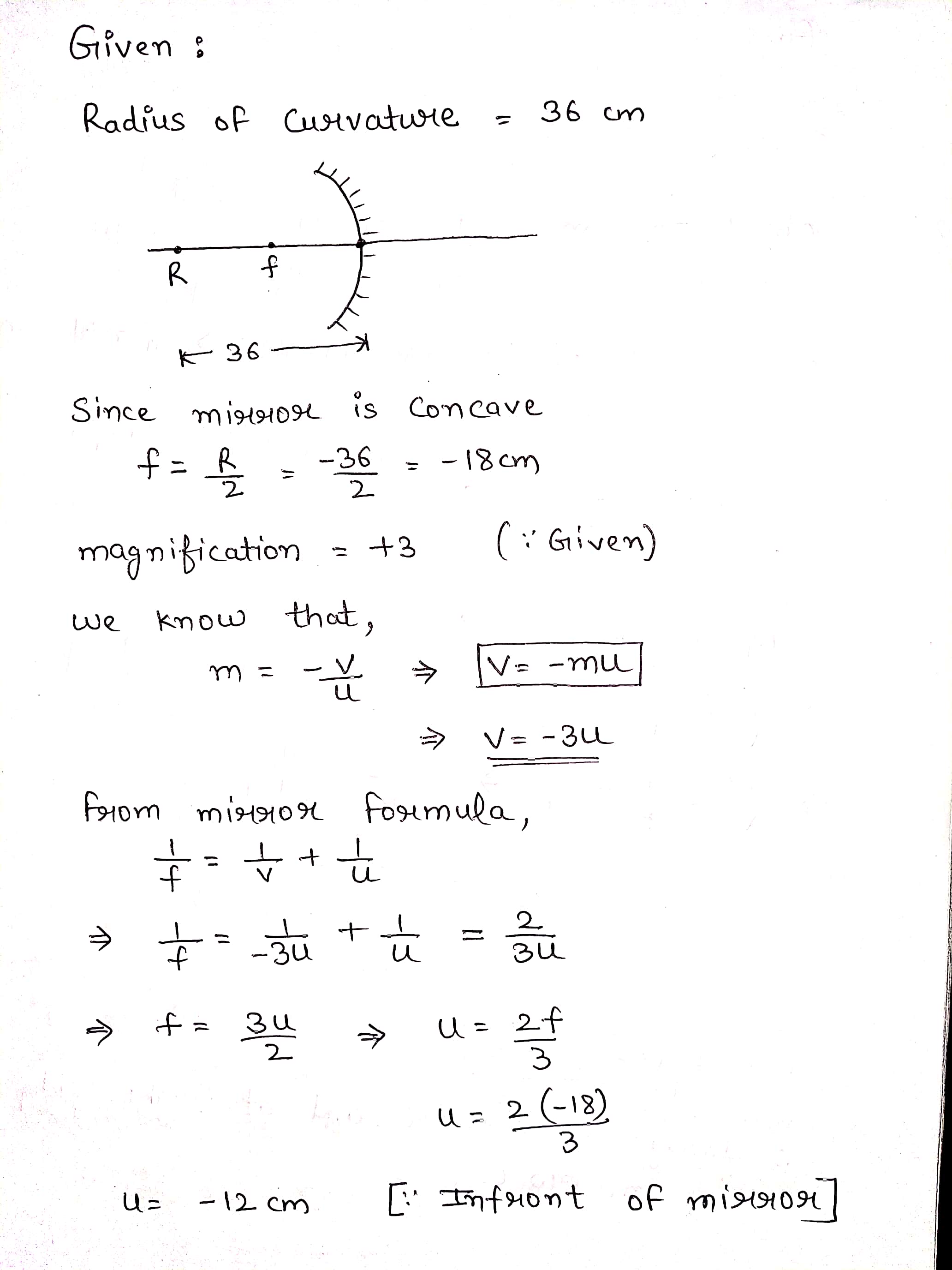
An erect image $$3$$ times the size of the object is obtained with a concave mirror of radius of curvature $$36\ cm$$. What is the position of the object?
Write the spherical mirror's formula and explain the meaning of each symbol used in it.
You are given the following three lenses. Which two lenses will you use as an eyepiece and as an objective to construct an astronomical telescope ? Give reason.
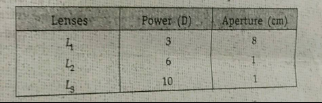
The object distance of a lens is $$30$$ cm and the image distance is $$10$$ cm.Find the magnificence of the lens with the help of this decide whether the size of the image is small or big than the size of the object ?
A light of wavelength $$6000\ \mathring{A}$$ in air centre a medium of refractive index $$1.5$$. What will be the frequency and wavelength of length in the medium?
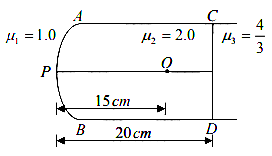
A slab of a material of refractive index $$2$$ shown in the figure, has a curved surface $$APB$$ of radius of curvature $$10\ cm$$ and a plane surface $$CD$$. On the left of $$APB$$ is air and on the right of $$CD$$ is water with refractive indices as given in the figure. An object $$O$$ is placed at a distance of $$15\ cm$$ from the pole $$P$$ as shown. The distance of the final image of $$O$$ from $$P$$, as viewed from the left is _______.
Who Invented the Microscope?
An isosceles right-angled prism and a convex lens (focal length $$= 40 cm$$) are placed as shown in the above figure, and a 5 cm wide strip with the letter 'LIGHT' written on it placed as indicated. What is the nature and position of the image formed after refraction through the prism and the lens?[Given the critical angle of the glass used for the prism and the lens is $$42 ^{\circ}$$.]

Two transparent media of refractive indices $$\mu_{1}$$ and $$\mu_{3}$$ have a solid lens shaped transparent material of refractive index $$\mu_{2}$$ between them as shown in figures in ListA ray traversing these media is also shown in the figures. In List 1 different relationships between $$\mu_{1},\ \mu_{2}$$ and $$\mu_{3}$$ are given. Match them to the ray diagram shown in List 2.
A simple telescope used to view distant objects has eyepiece and objective lens of focal lengths $$\mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{e}}$$ and $$\mathrm{f}_{0}$$, respectively. Then
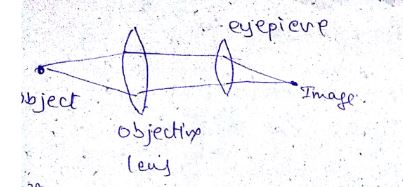
Explain the basic differences between the construction and working of a telescope and a microscope.
Fill in the blanks.
The first telescope was designed by ________.
Fill in the blanks.
Name of an optical instrument which is used to see erect image of distant object is _______.
Give the scientific reason for the following.
a) The focal length of the eyepiece of a compound microscope is larger.
b) A telescope of a binocular has two total internal reflecting prisms.
Mention any two uses of a simple microscope.
Name the two types of microscopes.
Mention any two uses of a binocular.
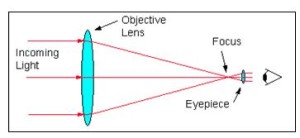
What is a telescope?
Why eyepiece of a telescope is of short focal length while objective is of large focal length ?
Which mirror gives rectifiable whatever the distance between the object and mirror is i. Plane mirror.
ii. Convex mirror.
iii. Concave mirror.
iv. Plane or convex mirror.
ii. Convex mirror.
iii. Concave mirror.
iv. Plane or convex mirror.
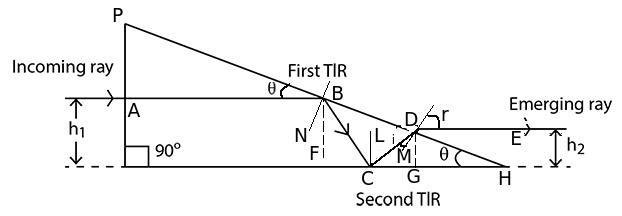
How will you use two identical prisms so that a ray of white light incident on one prism emerges out of the second prism as white light? Draw the diagram.
Match the entries in column A with appropriate one from column B.
Two transparent media of refractive indices $$\mu_{1}$$ and $$\mu_{3}$$ have a solid lens shaped transparent material of refractive index $$\mu_{2}$$ between them as shown in figures in Column II. A ray traversing these media is also shown in the figures. In Column I different relationship between $$\mu_{1}, \mu_{2}$$ and $$\mu_{3}$$ are given. Match them to the ray diagram shown in Column II.
A simple telescope used to view distant objects has eyepiece and objective lens of focal lengths $$f_{e}$$ and $$f$$, respectively. Then,
State whether the given statement is True or False.
In a telescope the focal length of eye lens is greater than objective lens.
State whether the following statement is True or False.
In a telescope the focal length of eye lens is always more than the objective lens.
Telescopes are used to obtain an .................. image of a ........... object.
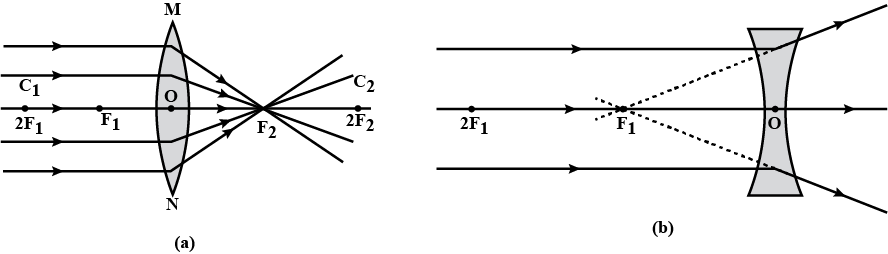
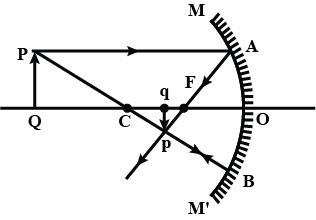
Which lens has the greater in the focal plane of which lens ?
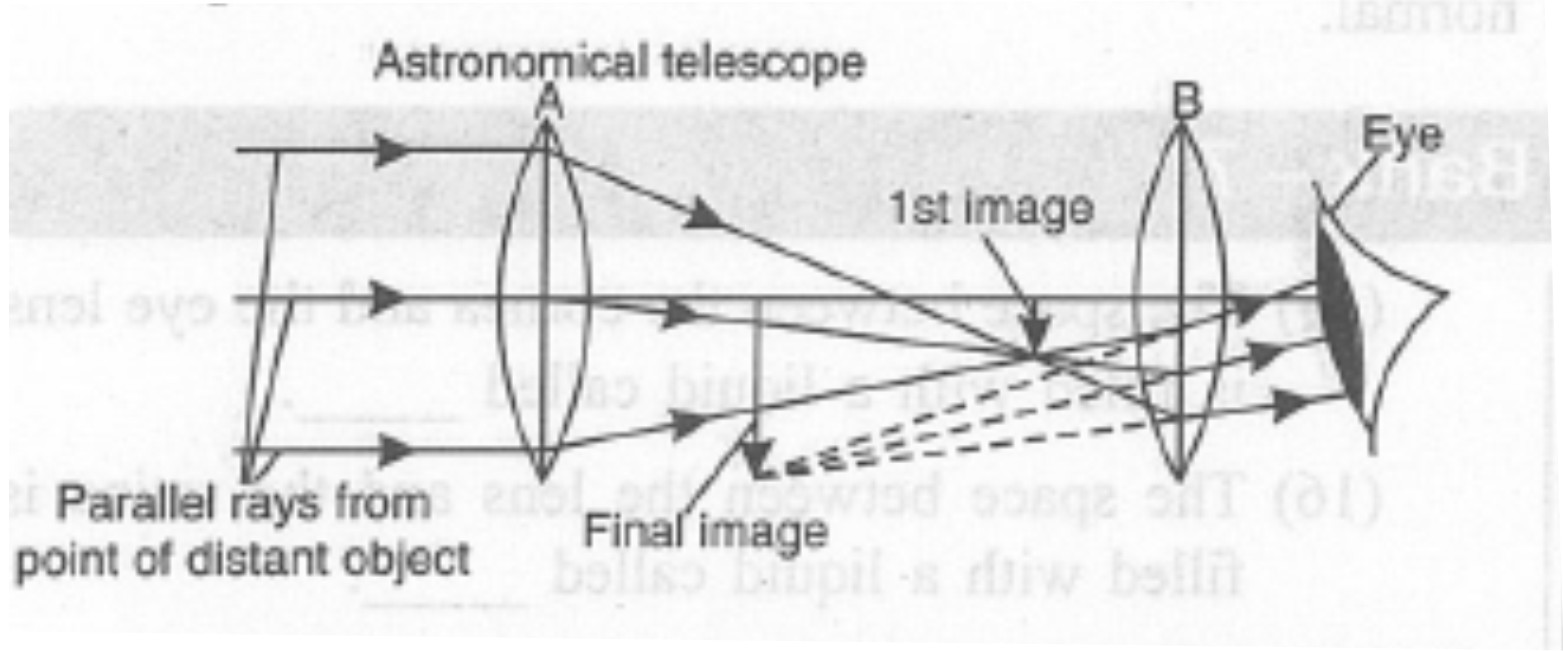
What is lens $$B$$ called ?

You are given two convex lenses of focal lengths 5 cm and 25 cm. Which one of these would you like to use as an objective in a telescope? Give reasons for your answer.
What is the name of the convex lens at $$A$$?

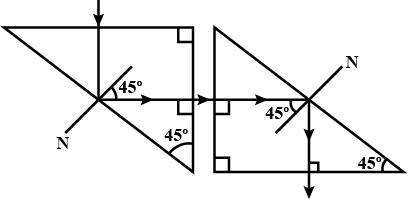
Two isosceles right angled glass prism are placed near each other as shown in the figure. Complete the path of the light ray entering the first isosceles right angled glass prism till it emerges from the second identical prism.
What are the characteristics of the final image formed by a magnifying glass ?
What are the characteristics of the final image formed by a telescope ?
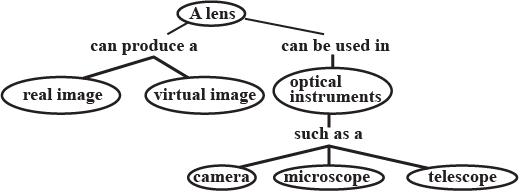
Draw a concept map using the following terms.
(lens, real image, virtual image, optical instrument, camera, microscope, telescope)
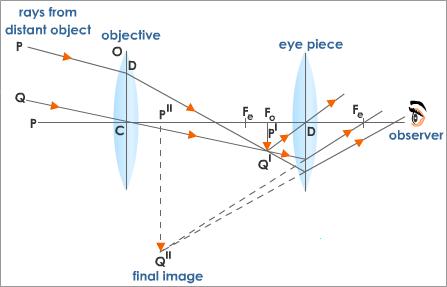
Describe the astronomical telescope on the basis of the following points:
(i) Labelled Ray diagram.
(ii) Derivation of formula for magnifying power, when final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
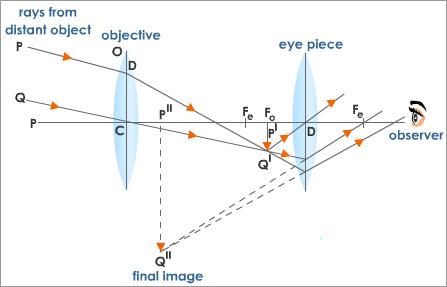
Describe the astronomical telescope on the basis of the following points:
(i) Labelled ray diagram.
(ii) Derivation of formula for magnifying power, when final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
Explain the refraction at a spherical surface using a schematic diagram.
Establish the formula $$\cfrac { 1 }{ f } =\cfrac { 1 }{ u } +\cfrac { 1 }{ v } $$ for a concave mirror, where symbols have their usual meanings.
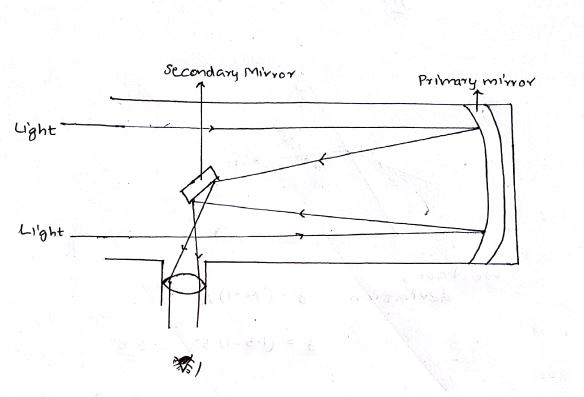
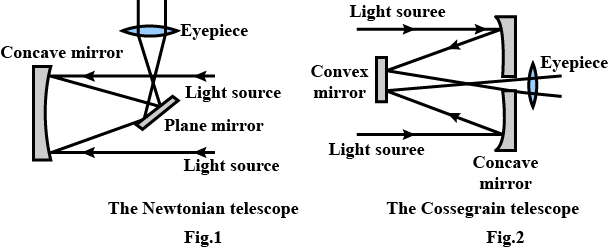
Draw ray diagram of reflecting telescope for image formation. How can we increase its resolving power?
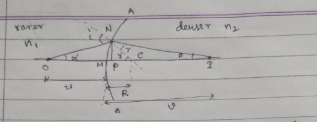
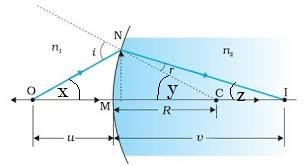
Prove that $$\cfrac { { n }_{ 2 } }{ v } - \cfrac { { n }_{ 1 } }{ u } =\cfrac { { n }_{ 2 }-{ n }_{ 1 } }{ R } $$
When refraction occurs of a convex spherical refracting surface and the ray travels from rearer to denser medium
A magnified, inverted image is located a distance of 32.0 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 12.0 cm. Determine the object distance and tell whether the image is real or virtual.
An object of 2 cm height is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the image distance, height and magnification.
A lens made with $$R_2 = 2R_1 $$ . Find its refractive index of lens.
Can a microscope function as a telescope by inverting it?Can a telescope function as a microscope?
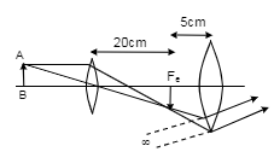
Find the position of the image formed by the lens combination given in the figure
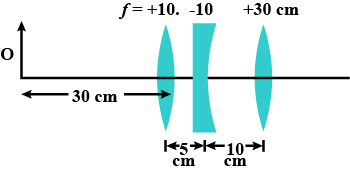
What is the formula for refraction through spherical Lens when the refractive index of the medium on two sides of lens are different ?
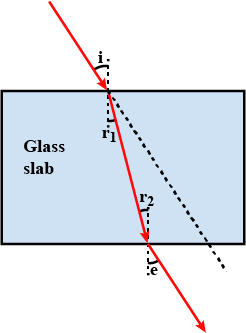
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate how a ray of light incident obliquely on one face of a rectangular glass slab of uniform thickness emerges.
A glass sphere of radius $$15\ cm$$ has a small bubble $$6\ cm$$ from it centre. The bubble is viewed along a diameter of the sphere from the side o which it lies. How far from the surface will it appear to be if the refractive index of glass is $$1.5$$?
A convex lens made up of glass of refractive index $$1.5$$ is dipped, in turn in
(i) a medium of refractive index $$1.6$$
(ii) a medium of refractive index $$1.33$$
Will it behave as a converging or a diverging lens in the two cases?
How will it focal length change in the two cases?
Which type of telescope can be made using a concave mirror, convex mirror, plane mirror and a lens? Draw diagrams of these telescopes.
A concave lens has a focal length of $$20\ cm$$. At what distance from a lens a $$5\ cm$$ tall object should be placed, so that it forms an image at $$15\ cm$$ from the lens? Also, calculate the size of the image formed.
A ray of light passing from air through an equilateral glass prism undergoes minimum deviation when the angle of incidence is $$3/4$$ of the angle of prism. Calculate the aped of light in the prism.
The focal length of an equiconcave lens is $$\dfrac{3}{4}$$ times of radius of curvature of its surfaces. Find the refractive index of the material of the lens. Under what condition will this lens behave as a converging lens ?
An optical instrument used for angular magnification has a $$25$$ D objective and a $$20$$ D eyepiece. The tube length is $$25$$ cm when the eye is least strained. Whether it is a microscope or a telescope?
If a concave mirror has a focal length of 10cm, find the two positions where an object can be placed to give, in each case, an image twice the height of the object.
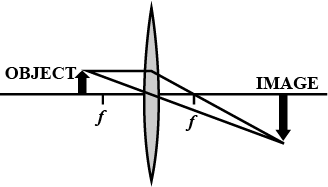
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length ?
If the angular magnification of an astronomical telescope is $$36$$ and the diameter of the objective is $$75$$ mm, what is the minimum diameter of the eyepiece required to collect all the light entering the objective from a distant point source on the telescope axis?
A concave mirror of focal length $$1.5\ m$$ forms an image of an object placed at a distance of $$40\ cm$$. Find the position and nature of the image.
Give the SI unit of power of lens. State whether the power of a converging lens is positive or negative.
Name the phenomena on which the working of a lens is based.
A man is holding a lighted cand le in front of a thick glass mirror and on viewing it obliquely he noticed a number of images of the cand le why
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a (i) convex lens, (ii) concave lens . Draw a diagram in each case to show the refraction of light through the lens.
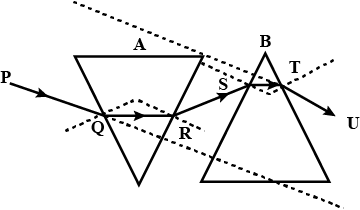
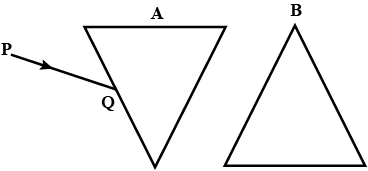
The diagram above shows two identical prisms $$A$$ and $$B$$ placed with their faces parallel to each other. A ray of light of single colour $$PQ$$ is incident at the face of the prism $$A$$. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray till it emerges out of the prism $$B$$. [Hint: The emergent ray of the prism $$B$$ will be parallel to the incident ray $$PQ$$]
A ray of light after refraction through a lens emerges parallel to the principal axis of the lens. The incident ray either passes through or appears to meet at :
(a) optical center
(b) first focus
(c) Second focus
(d) center of curvature of the first surface.
If a convex lens is used to focus sunlight on a paper, where should the paper be placed so that it catches fire.
Give scientific reason :
Astronauts on the moon can not hear each other directly
Write nature, position and relative size of the image form by concave lens
Simple microscope is used for watch repairs.
Imagine that a spherical mirror gives an image magnified 5 times at a distance 5 m. If so determine whether the mirror is concave or convex. How much will be the focal length of the mirror?
Write a note on astronomical telescope.
Using local resources and with the help of your teacher and friend, make telescope. Write the method, instruments, procedure to make telescope.
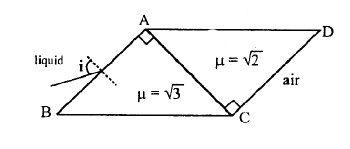
A ray of light from a liquid $$\left ( \mu =\sqrt{3} \right )$$ is incident on a system of two right angled prism of refractive indices $$\sqrt{3} and \sqrt{2}$$ as shown in the figure. The light suffers zero net deviation when it emerges into air from surface CD. If the angle of incidence (in degrees) is $$5{n}$$. Find n ?
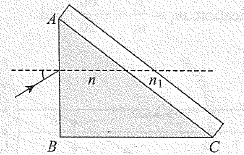
A right angles prism $$(45^o, 90^o, 45^o)$$ of refractive index n has a plate of refractive index $$(n_1 < n)$$ cemented to its diagonal face. The assembly is in air. A ray is incident on AB.
If the angle of incidence at AB for which the ray strikes the diagonal face at the critical angle is X in degrees. Find X?
A ray of light is falling on a glass sphere of $$\mu = \sqrt {3}$$ such that the incident ray and the emergent ray, when produced, intersect at a point on the surface of the sphere. Find the value of angle of incidence in degrees.
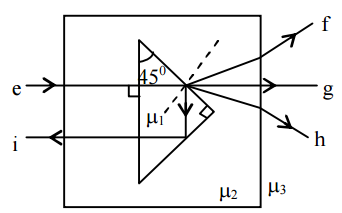
A right angled prism of refractive index $$\mu_1$$ is placed in a rectangular block of refractive index $$\mu_2$$, which is surrounded by a medium of refractive index $$\mu_3$$, as shown in the figure. A ray of light e enters the rectangular block at normal incidence. Depending upon the relationships between $$\mu_1, \mu_2$$ and $$\mu_3$$ it takes one of the four possible paths ef, eg, eh, or ei.
Match the paths in List I with conditions of refractive indices in List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists
A parallel beam of light travelling in water (refractive index $$=4/3$$) is refracted by a spherical air bubble of radius 2 mm situated in water. Assuming the light rays to be paraxial, Find out the distance between a final image from the centre of the bubble in mm.
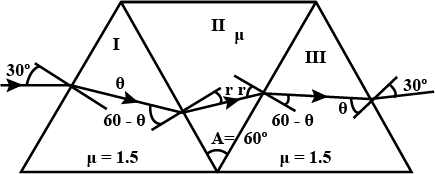
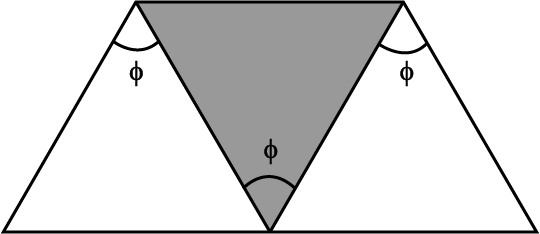
A direct-vision prism is made out of three prisms, each with a refracting angle of $$\phi = 60^{\circ}$$, attached to each other as shown in Fig. Light of a certain wavelength is incident on the first prism. The angle of incidence is $$30^{\circ}$$ and the ray leaves the third prism parallel to the direction of incidence. The refractive index of the glass of the first and third prisms is $$1.5$$. Find the refractive index of the material of the middle prism. $$(\sqrt {6} = 2.45)$$.
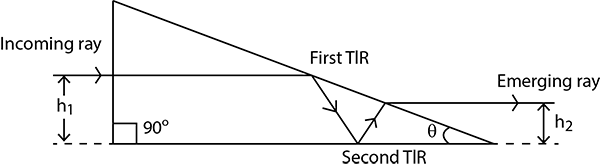
the incoming ray suffers total internal reflection (TIR) times as shown. The prism mhas reflective index $$\mu$$ and top angle $$\theta$$. The emerging ray propagates horizontally. The refrative index $$\mu = \frac{cos\, \theta}{cos\, n\theta}$$. Find n
Define refraction of light waves.
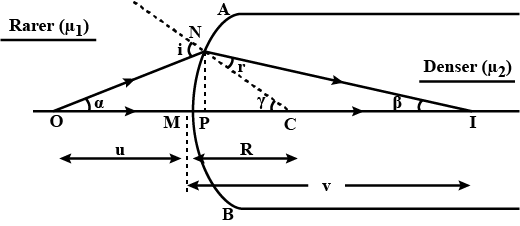
Draw a ray diagram for refraction at a spherical separating two media. For refraction at a spherical surface, derive the relation $$\cfrac { { n }_{ 2 } }{ v } -\cfrac { { n }_{ 1 } }{ u } =\cfrac { { n }_{ 2 }-{ n }_{ 1 } }{ R } $$ in object distance $$(u)$$, image distance $$(v)$$, refractive index of media $$({ n }_{ 1 },{ n }_{ 2 })$$ and radius of curvature $$(R)$$.
Explain simple microscope on the basis of the following points:
(a) Ray diagram for the formation of image;
(b) Expression for magnifying power when the final image is formed:
(i) At the least distance of distinct vision;
(ii) At infinity.
Derive an expression:
$$\dfrac { \mu }{ v } -\dfrac { 1 }{ u } =\dfrac { \mu -1 }{ R } $$
for refraction of light at spherical surface.
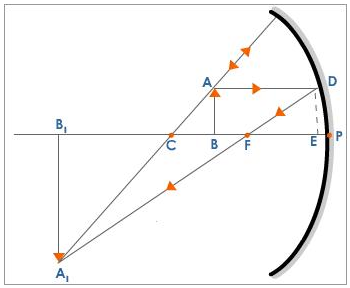
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show image formation when the concave mirror produces a real, inverted and magnified image of the object.
(b) Obtain the mirror formula and write the expression for the linear magnification.
(c) Explain two advantages of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope.
A prism of refractive index $$n_{1}$$ and another prism of refractive index $$n_{2}$$ are struck together without a gap as shown, $$n_{1}$$ and $$n_{2}$$ depend upon $$\lambda$$ the wave length of light according to$$n_{1}=1.2+\dfrac {10.8 \times 10^{4}}{\lambda^{2}}$$ and $$ n_{2}=1.45+\dfrac {1.8 \times 10^{4}}{\lambda^{2}}$$, where $$\lambda$$ is in nanometer.
(a)Calculate the wave length $$\lambda_{0}$$ for which rays incident at any angle on the interface pass through without bending a the interface.
(b)For light of wave length $$\lambda_{0}$$ for which rays incident on the face $$A\ C$$ such that the deviated produced by the combination of the prism is minimum.
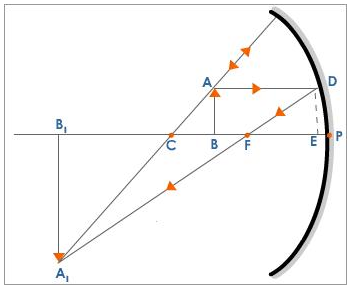
The convex surface of a thin concavo-convex lens of glass of $$R.l$$. $$1.5$$ has a radius curvature $$20\ cm$$. The concave surface has a radius of curvature $$60\ cm$$. The convex side is silvered and placed horizontally.
(a)Where should a pin be placed on the axis such that its image is formed at the same place.
(b)If the concave part is filled with water of refractive index $$4/3$$, find the distance through which the pin should be moved so that the image of the pin again coincided with the pin?
The distance between a convex lens and a plane mirror is $$10\ cm$$. The parallel rays incident on the convex lens, after reflection from the mirror, form image at the optical centre of the lens. Draw ray-diagram and find out the focal length of the lens.
A soap film of thikness 0.0011 mm appears dark when seen by the reflated light of wavelength 580 nm. What is the index of refraction of the soap solution, if it is known to be between 1.2 and 1.5 ?
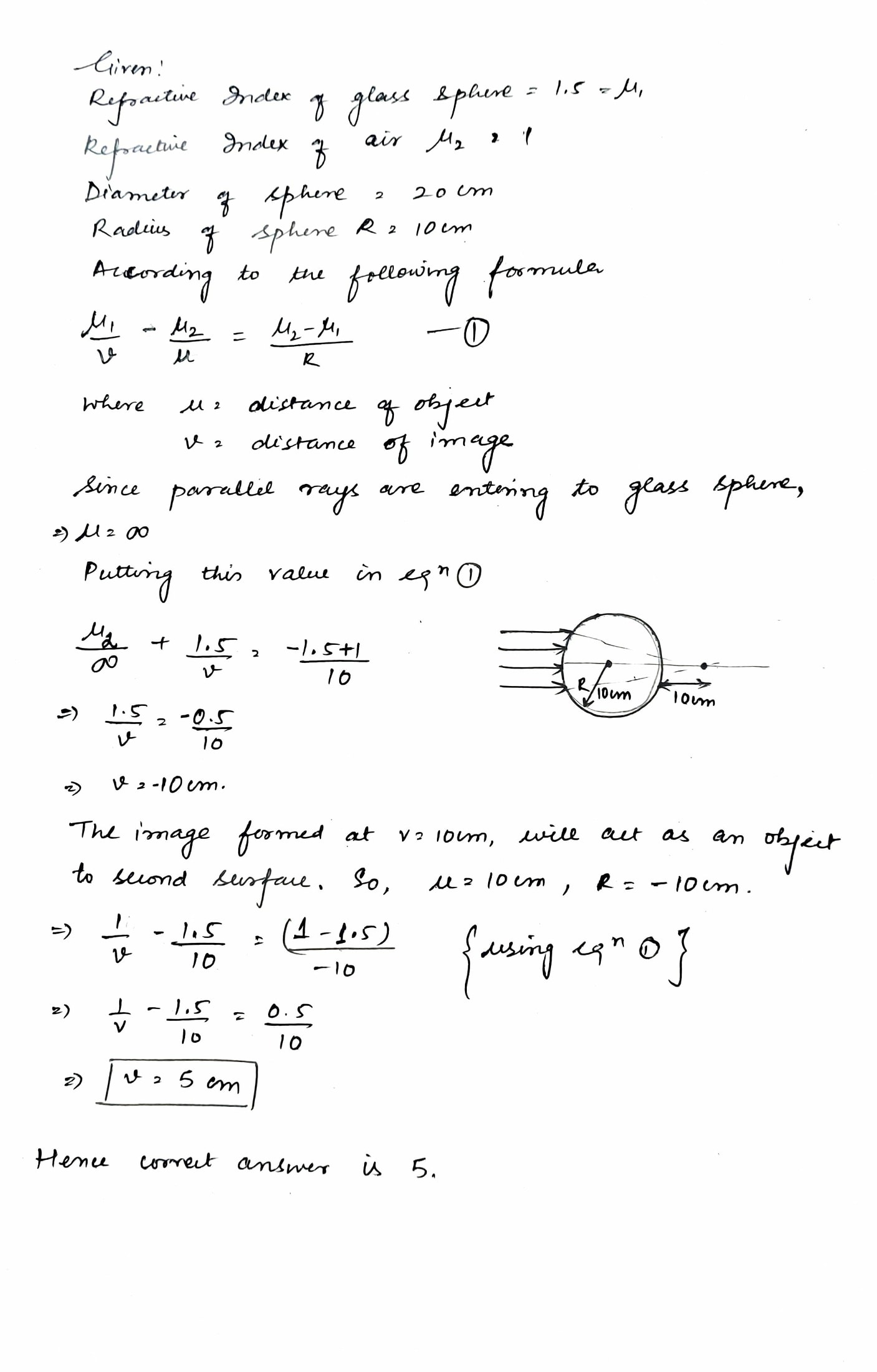
A sphere of glass $$(\mu = 1.5)$$ is of $$20\ cm$$ diameter. A parallel beam enters it from one side. Where will it get focused on the other side $$(in\ cm)$$.
A ray of light passing through an equilateral glass prism from air undergoes minimum duration when angle of incidence is $$\dfrac{3}{4}^{th}$$ the angle of prism, calculate the speed of light in prism.
The image of an object, formed by plano-convex lens at a distance of 8 m behind the lens, is real and is one-third the size of the object. The wavelength of light. inside the lens is $$\dfrac{2}{3}$$ times the wavelength in free space. The radius of the curved surface of the lens is :
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image - distance (v) with object - distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations: (a) what is the focal length of the convex lease? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No.Also the approximate value of magnification.
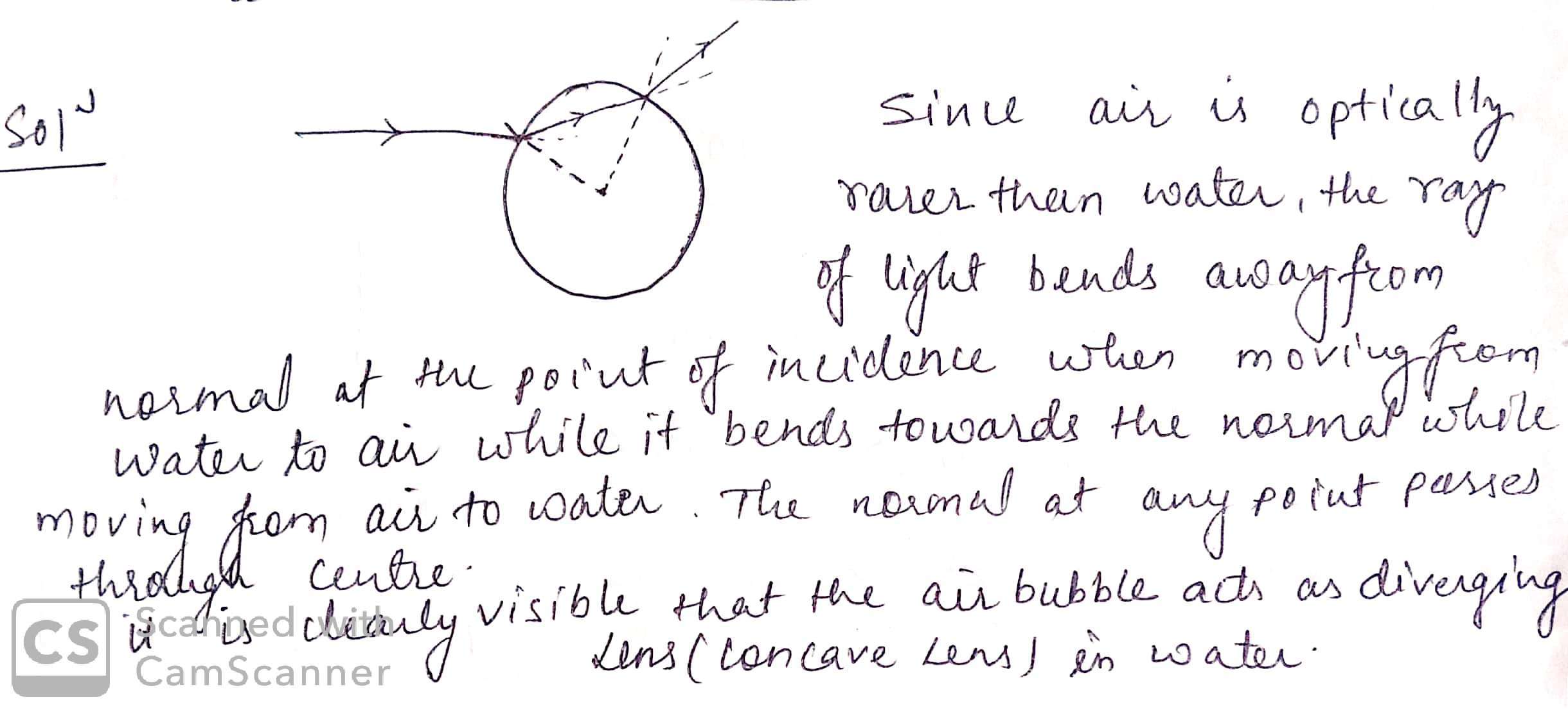
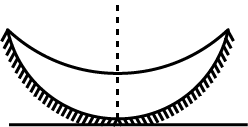
why an air bubble in water act as lens
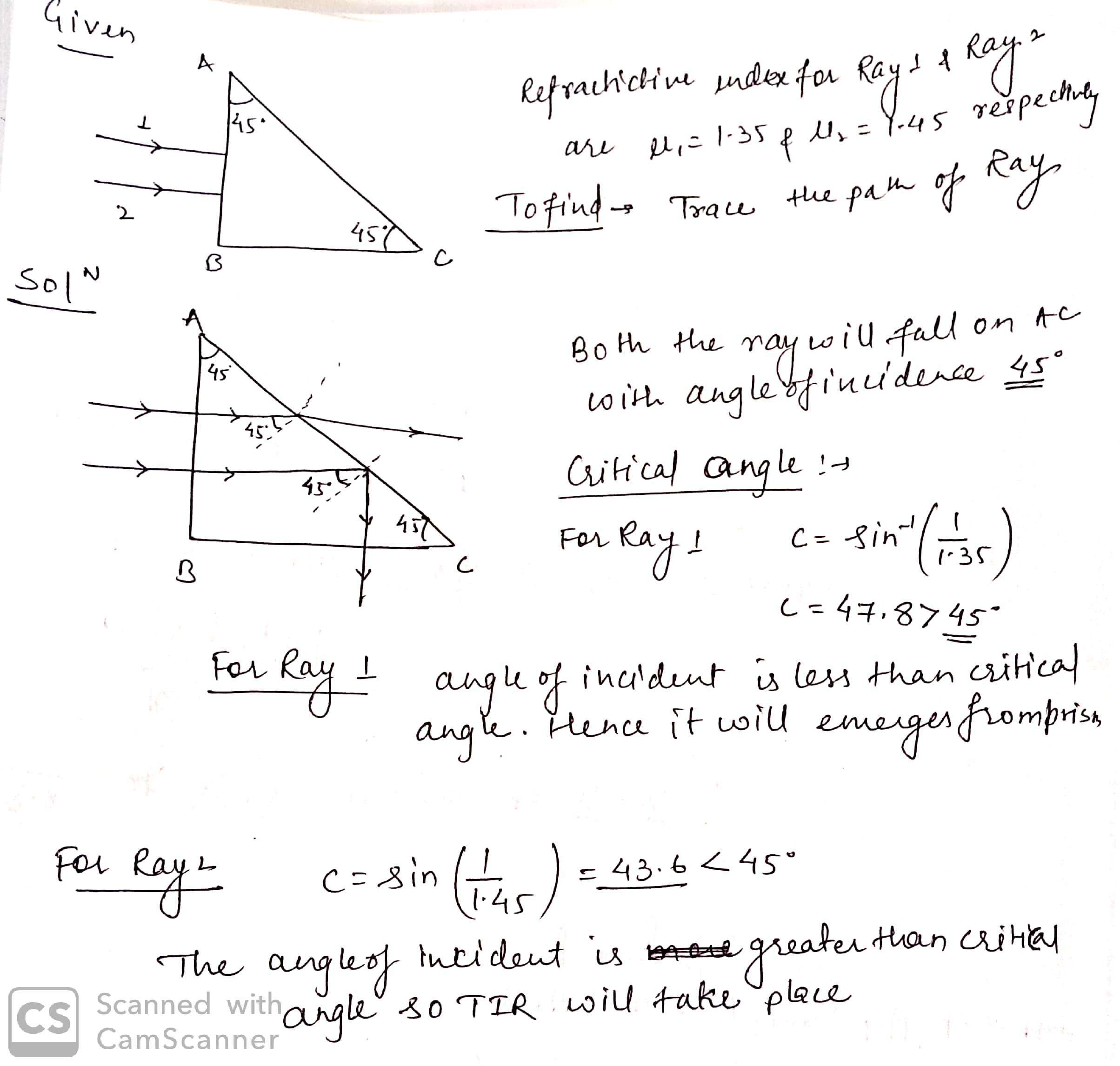
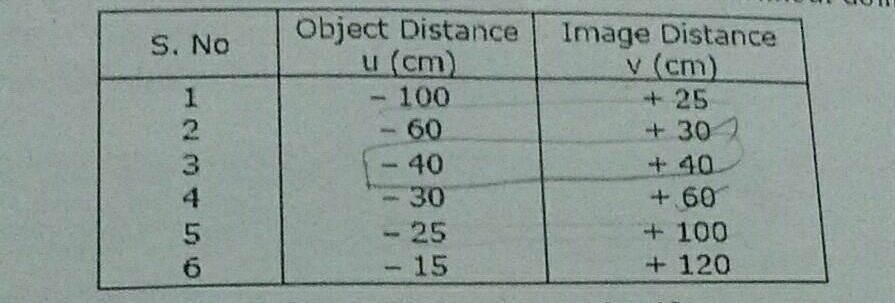
Two
monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an
isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for
the two rays $$'1'$$ and $$'2'$$ are respectively $$1.35$$ and $$1.45$$. Trace the path of
these rays after entering through the prism.
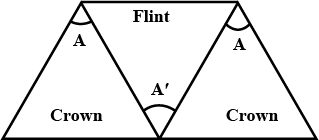
Three thin prism are combined as shown in figure .The refractive indices of the crown glass for red.yellow and violet rays are $$ \mu_r , \mu_y $$ and $$\mu_v$$ respectively and those the flint.glass are $$ \mu_r , \mu'_y $$ and $$\mu_v$$ respectively. Find the ratio $$A'/A$$ for which (a) there is not net angular dispersion, and (b) there is no net deviation in the yellow ray.
A flint prism glass and a crown glass prism are to be combined in such a very that the deviation of the mean ray is zero. The refractive index of flint and crown glaseed for the mean ray are 1.620 and 1.518 respectively.If the refracting angle of the flint prism is $$ 6.0^{\circ}$$ what.would be the refracting angle of the crown prism?
A prism having a $$ 120^{\circ} $$ apex angle is made of glass for which $$ n = 1.53 $$ . (a) Is there any range of angles of incidence $$ i_1 $$ for light rays striking one face of the prism that will result in total reflection at the second face? (b) If so, what is the value of $$ i_1 $$ that corresponds to the critical angle for total reflection?
The refractive index of a material $$M_1$$ changes by 0.014 and that of another material $$M_2$$ changes by 0.024 as colour of the light is changed from red to violet. Two thin prisms, one is made of $$M_1 (A=5.3^o) $$ and another is made of $$ M_2(A=3.7^o) $$ are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. (A) Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination. (B) The prism are now combined with their refracting angles similarly directed.
Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination
A thin prism of angle $$ 6.0^o , \omega = 0.07$$ and $$ \mu_y= 1.50 $$ combined with another thin prism having $$ \omega =0.08 $$ and $$ \mu_y = 1.60 $$ . The combination produces no deviation of the mean ray. (a) Find the angle of the second prism. (b) Find the net angular dispersion produced by the combination when a beam of white light passes through it. (c) If the prisms are similarly directed, what will be the deviation of the mean ray? (d) Find the angular dispersion of the combination described in (c).
A thin prism of crown glass $$ (\mu_r = 1.515, \mu_v = 1.525) $$ and a thin prism of flint glass $$ (\mu_r = 1.612, \mu_v = 1.632) $$ are placed in contact with each other.Their refracting angles are $$ 5.0^o $$ each and are similarly directed. Calculate the angular dispersion produced by the combination.
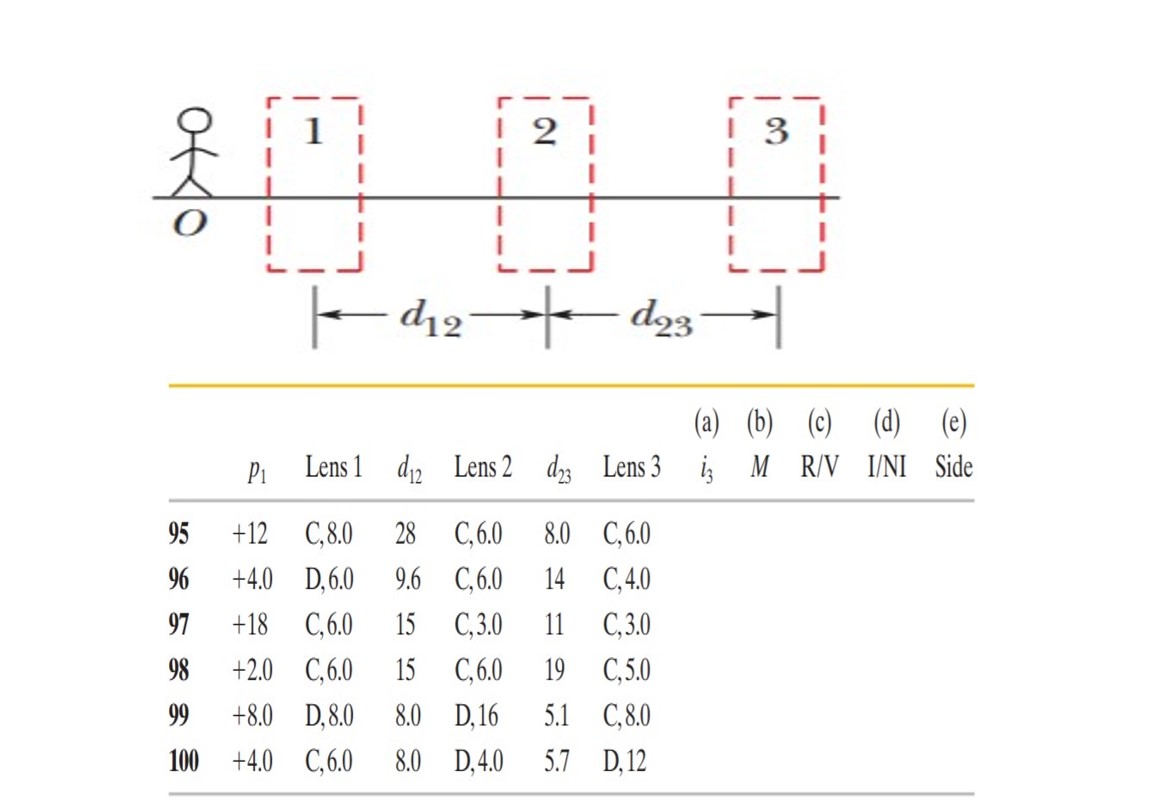
Three-lens systems. In Figure,
stick figure O (the object) stands on the common central axis of
three thin, symmetric lenses, which are mounted in the boxed
regions. Lens 1 is mounted within the boxed region closest to O,
which is at object distance $$p_1$$. Lens 2 is mounted within the middle boxed region, at distance $$d_{12}$$ from lensLens 3 is mounted in
the farthest boxed region, at distance $$d_{23}$$ from lensEach problem in Table refers to a different combination of lenses and
different values for distances, which are given in centimeters. The
type of lens is indicated by C for converging and D for diverging;
the number after C or D is the distance between a lens and either
of the focal points (the proper sign of the focal distance is not
indicated).
Find (a) the image distance $$i_3$$ for the (final) image produced by
lens 3 (the final image produced by
the system) and (b) the overall lateral magnification M for the system,
including signs. Also, determine
whether the final image is (c) real
(R) or virtual (V), (d) inverted (I)
from object O or noninverted (NI), and (e) on the same side of
lens 3 as object O or on the opposite side.
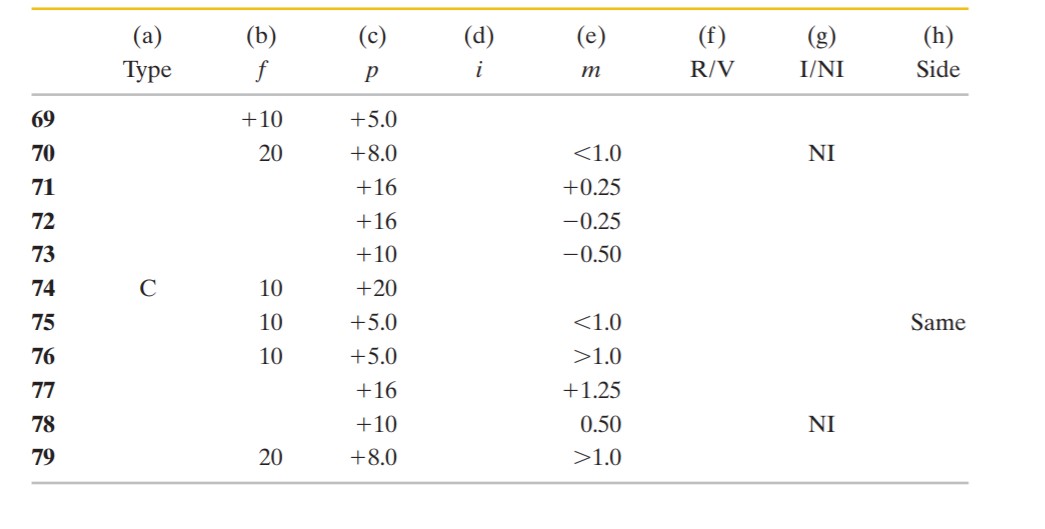
More lenses. Object O stands on the central axis of a thin symmetric lens. For this situation, each problem in Table refers to (a) the lens type, converging (C) or diverging (D), (b) the focal distance f, (c) the object distance p, (d) the image distance i, and (e) the lateral magnification m. (All distances are in centimeters.) It also refers to whether (f) the image is real (R) or virtual (V), (g) inverted (I) or noninverted (NI) from O, and (h) on the same side of the lens as O or on the opposite side. Fill in the missing information, including the value of m when only inequality is given. Where only a sign is missing, answer with the sign.
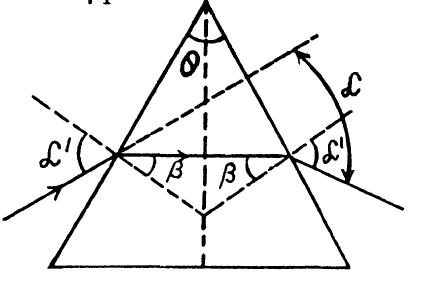
A shaft of light passes through a prism with refracting angle $$ \theta $$ and refractive index $$ n $$. Let $$ \alpha $$ be the diffraction angle of the shaft. Demonstrate that if the shaft of light passes through the prism symmetrically,
(a) the angle $$ \alpha $$ is the least
Derive the formula for spherical mirror
$$\frac{1} {f} = \frac{1} {v} + \frac{1} {u}$$
What happened to the light when it passed through the first prism?
Answer the following question in details.
Derive the formula of relation between radius of curvature ($$R$$), object distance ($$u$$) and image distance ($$v$$) for spherical mirrors.
Class 12 Medical Physics Extra Questions
- Alternating Current Extra Questions
- Atoms Extra Questions
- Current Electricity Extra Questions
- Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter Extra Questions
- Electric Charges And Fields Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Induction Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Waves Extra Questions
- Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Extra Questions
- Magnetism And Matter Extra Questions
- Moving Charges And Magnetism Extra Questions
- Nuclei Extra Questions
- Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Extra Questions
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices And Simple Circuits Extra Questions
- Wave Optics Extra Questions