Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices And Simple Circuits - Class 12 Medical Physics - Extra Questions
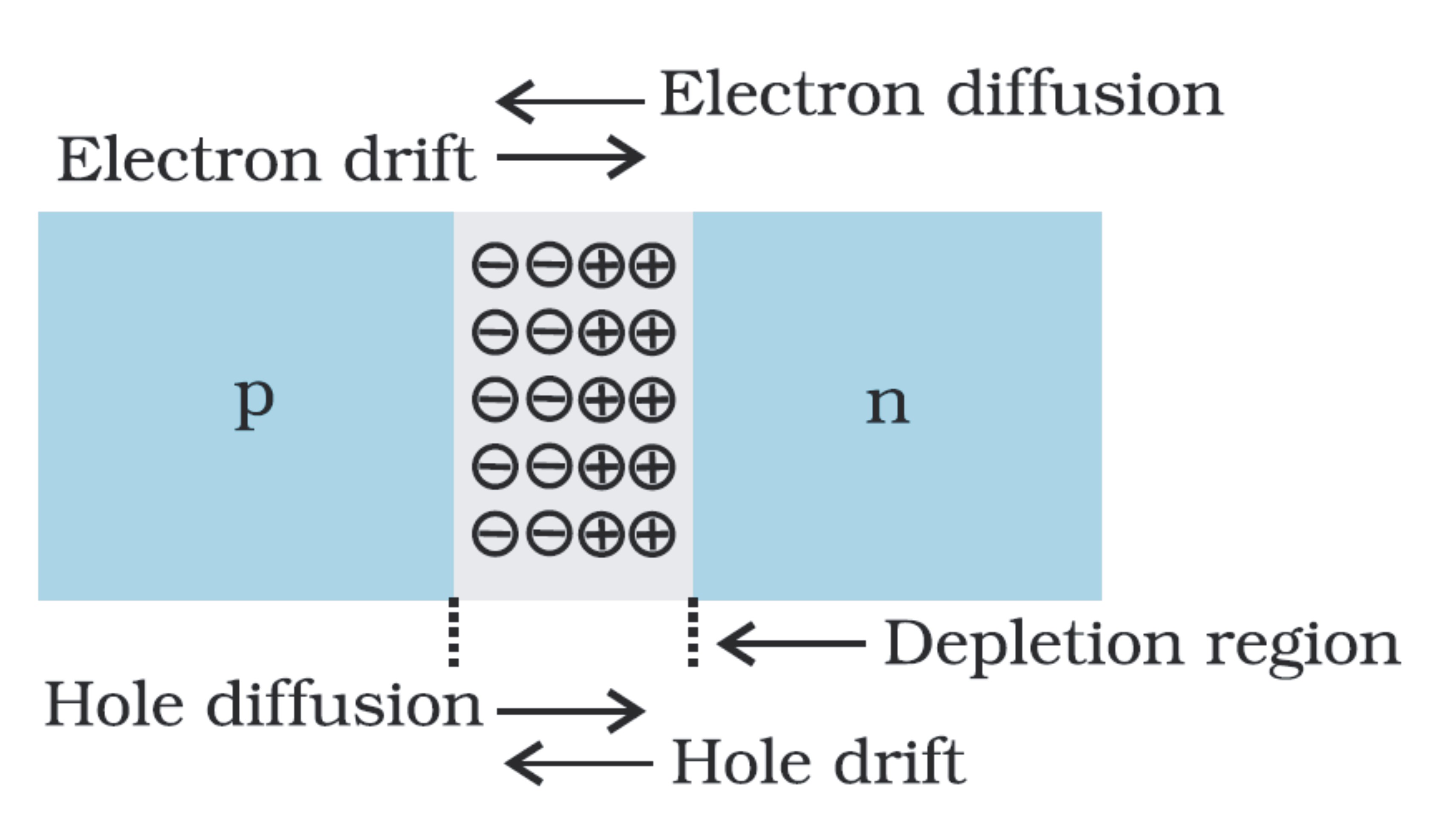
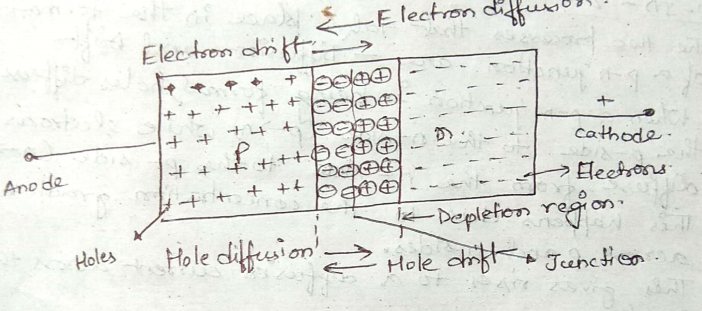
Describe briefly , with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a pn junction.
Write he name of any one doped semiconductor used for making light emitting diode (LED)
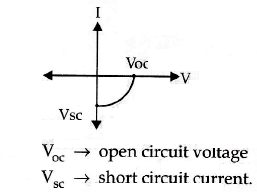
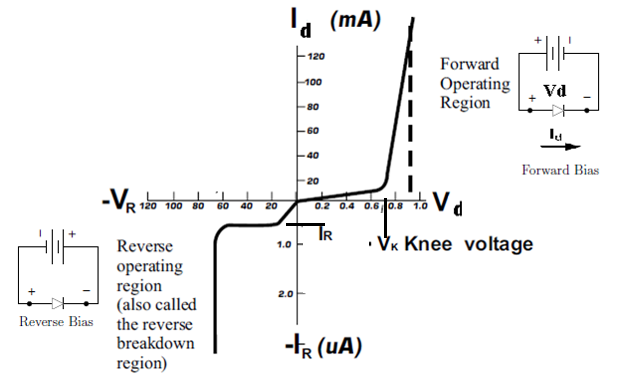
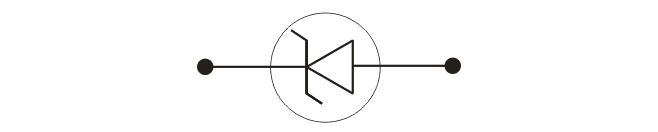
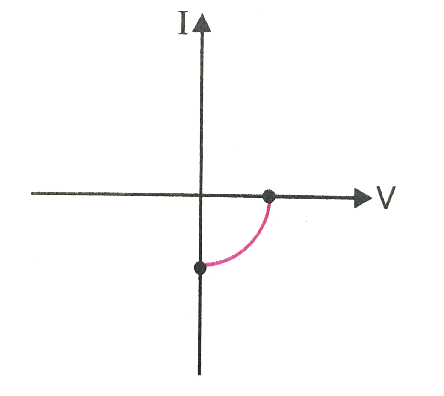
Name the junction diode whose I−V characteristics are drawn below :
A Zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
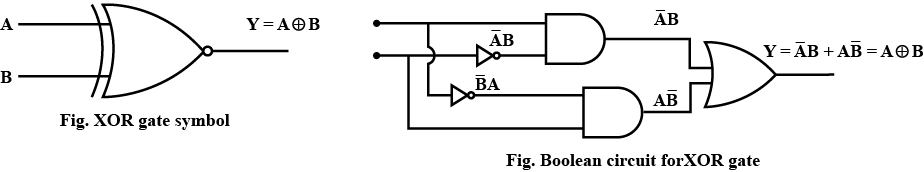
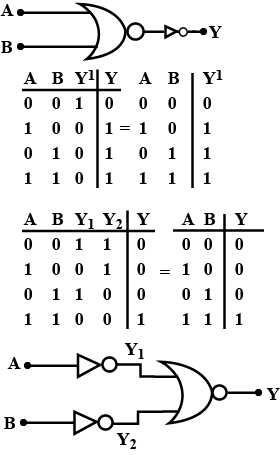
What do you understand by the logic gate? Draw the symbol for XOR gate and also the truth table.
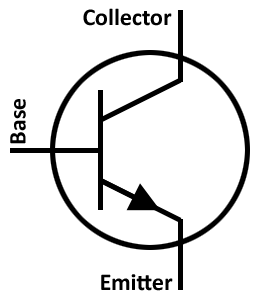
In a transistor why is the base made thin in comparison to the emitter and collector?
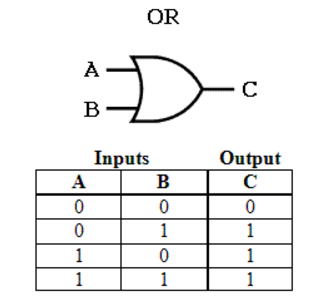
Make truth table for OR gate.
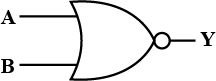
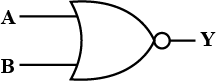
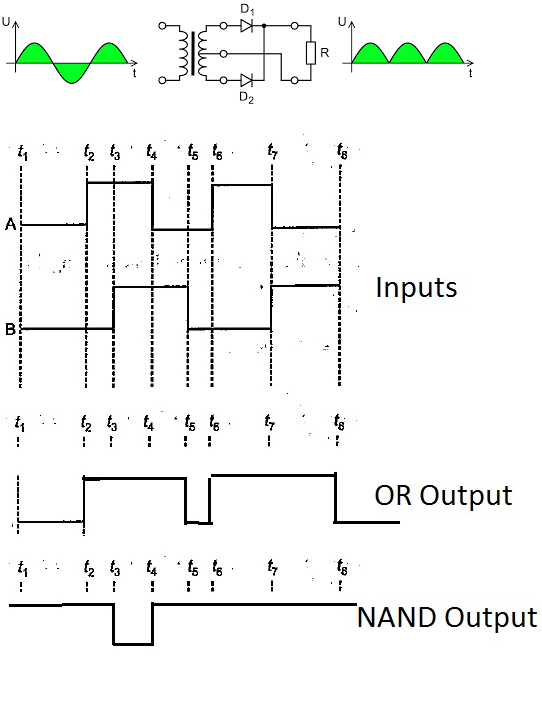
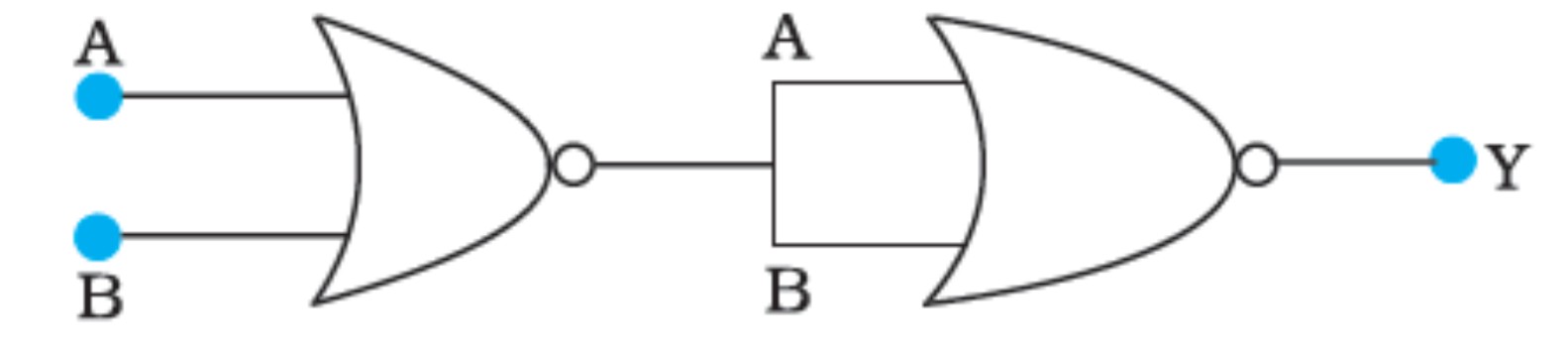
Write the truth table for circuit given in the figure, consisting of NOR gates and identify the logic operation (OR, AND, NOT) which this circuit is performing.
(Hint: A = 0, B = 1 then A and B inputs of second NOR gate will be 0 and hence Y=Similarly work out the values of Y for other combinations of A and B. Compare with the truth table of OR, AND, NOT gates and find the correct one).
Eg(T)=Eg(m)−αT2T+β is the Varshni's empirical expression,then the value of m is
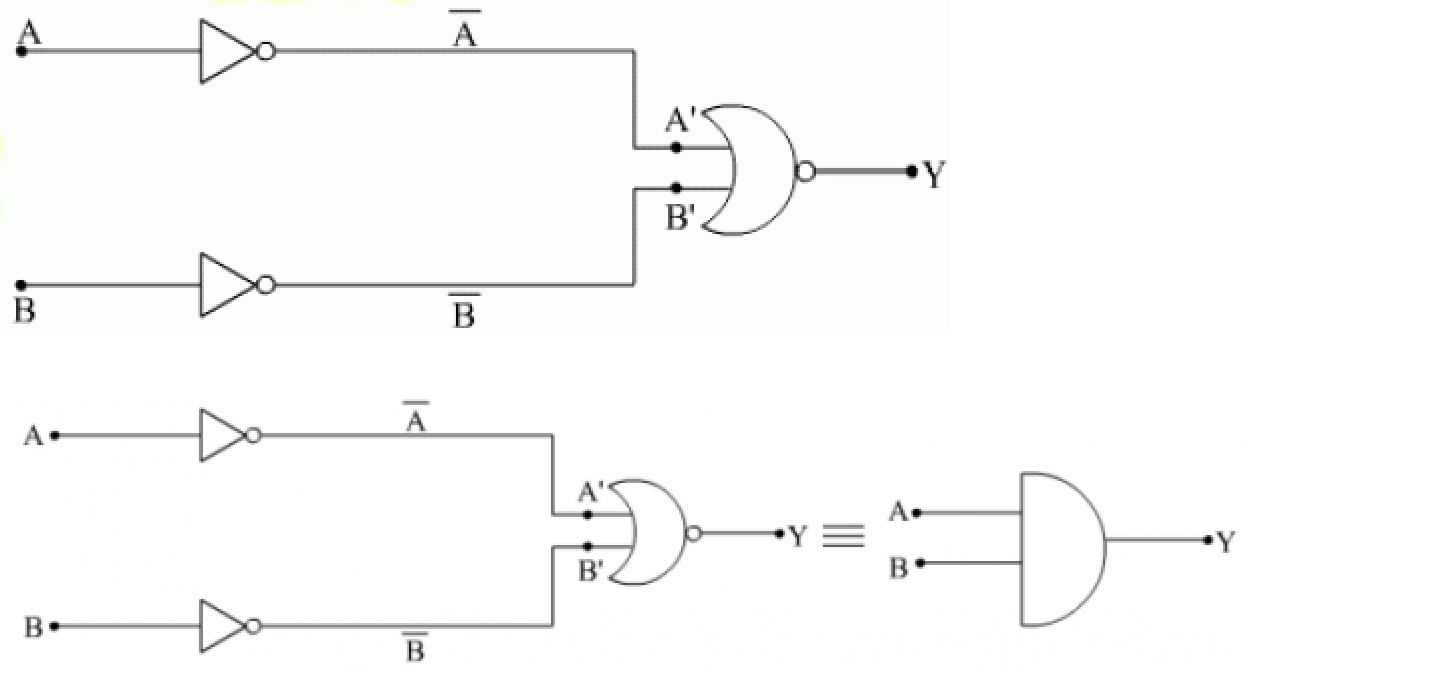
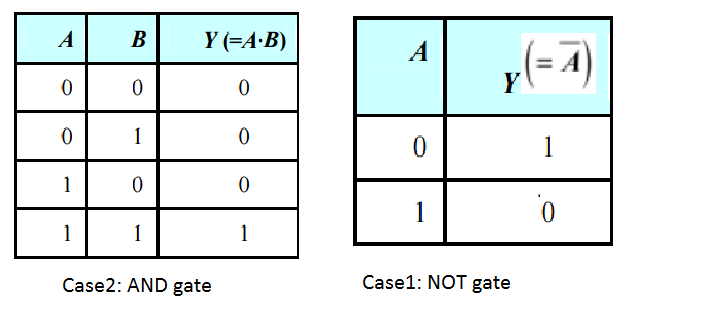
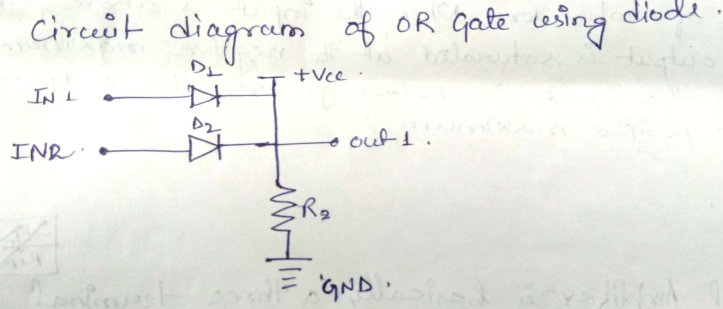
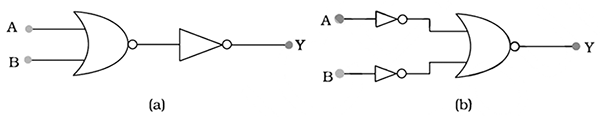
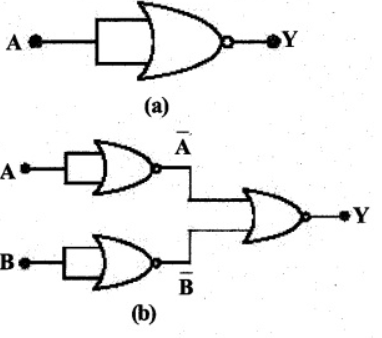
You are given the two circuits as shown in fig . show that circuit (a) acts as OR gate while the circuit (b) act as AND gate.
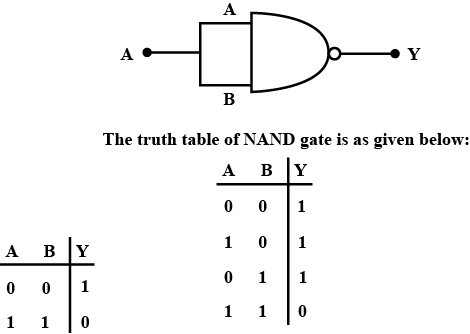
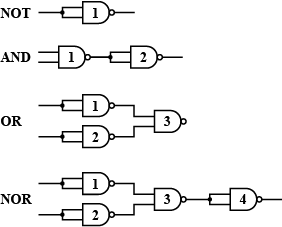
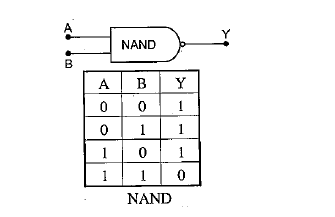
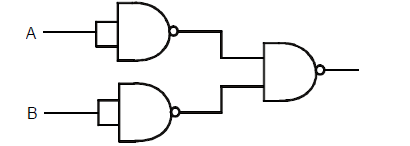
Write the truth table for a NAND gate connected as given in fig.
Hence identify the exact logic operation carried out by this circuit.
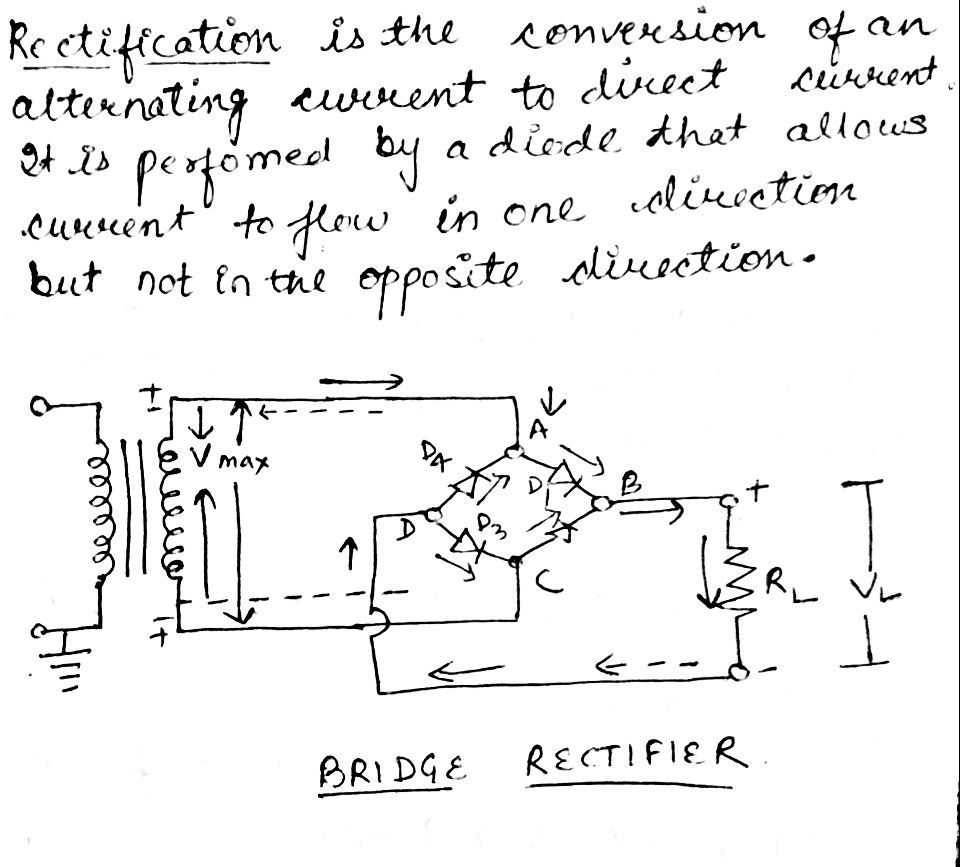
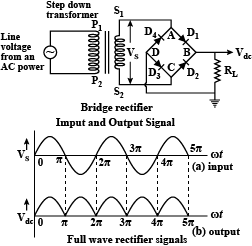
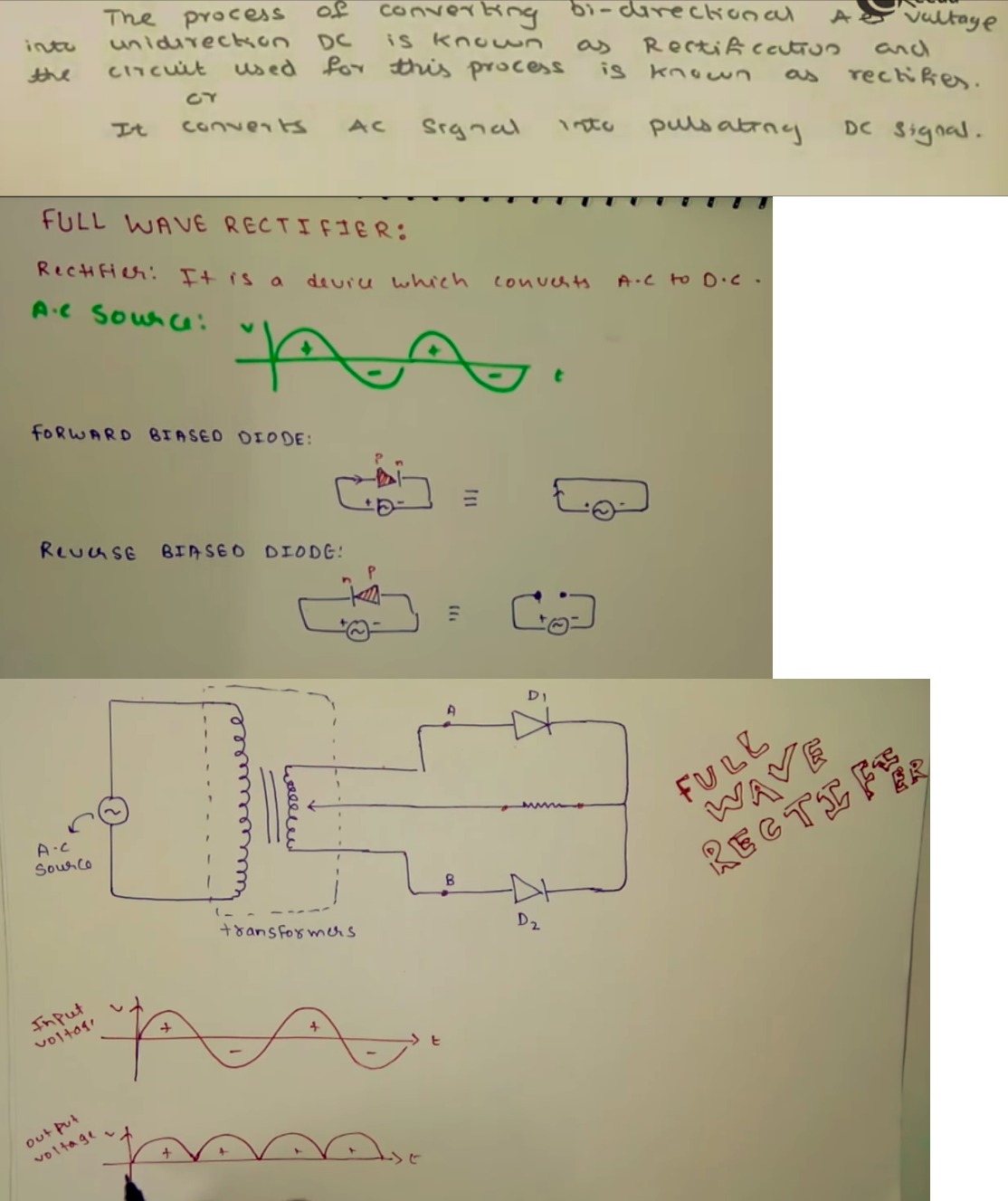
What is rectification? Draw the figure of bridge wave rectifier.
Observe the following figure. Which property of diode is indicated here? Explain that property.
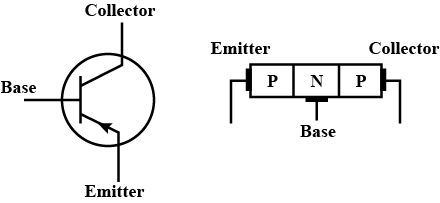
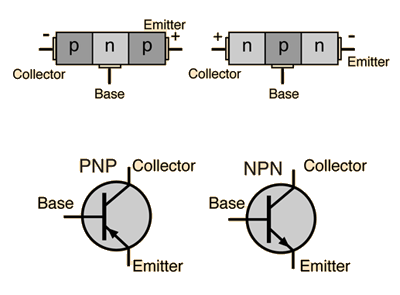
Write the circuit symbol of p−n−p transistor.
Write down the name of that logic gate in which the output is 1 when all the inputs are 1.
What do you mean by a logic gate?
In a p-n-p transistor circuit the collector current is 10mA if 90 % of the holes reach the collector , find emitter and base current.
An ideal diode should pass a current freely in one direction and should stop it completely in the opposite direction. Which is closer to ideal-vacuum diode or a p-n junction diode ?
In a full-wave rectifier, the output is taken across a load resistor of 800 ohm. If the resistance of diode in the forward biased condition is 200 ohm, the efficiency of rectification of ac power into dc power is(in percentage)
A certain computer chip that is about the size of a postage stamp (2.54cm,2.22cm) contains about 3.5 million transistors. If the transistors are square, what must be their maximum dimension? (Note: Devices other than transistors are also on the chip,and there must be room for the interconnections among the circuit elements. Transistors smaller than 0.7 mm are now commonly and inexpensively fabricated.)
Even though the p-type and n-type semiconductors have holes and electrons respectively as majority charge carries, why are they electrically neutral? Explain.
The source of electric current for a hand held transistor is _____ .
Write any two distinguishing features between conductors, semiconductors and insulators on the basis of energy band diagrams.
Match the following:
Left column lists the level of integration and right column lists the number of circuit components.
Mention important characteristics and applications of a diode.
How many electrons are there is the outermost shell of silicon atom?
What is called a hole?
What is a semi conductor diode or junction diode?
What are conductors and insulators? Give examples.
Suggest any two situations in which photocells can be used as automatic switches.
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by a rectifier?
Silicon nitride has band gap energy of _______________eV.
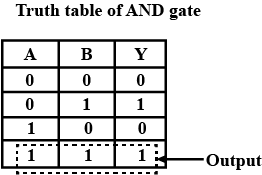
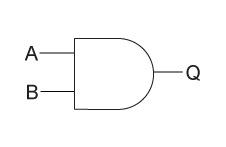
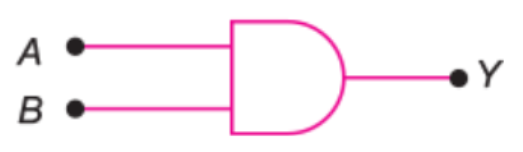
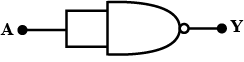
Draw the logic symbol of AND gate.
State the difference between laser light and ordinary light
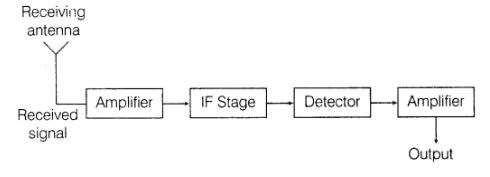
Draw a block diagram of a simple radio receiver
In a radio receiver, the device that separates AF signals from RF signals is ___________.
The more doped region in the transistor is ...........................
Draw the circuit symbol of n−p−n transistor.
Zener diode is used as ......................
Identify the gate.
Draw the logic symbol of the gate.
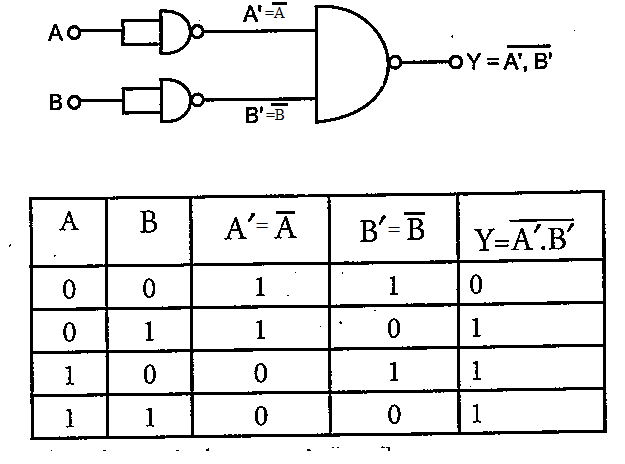
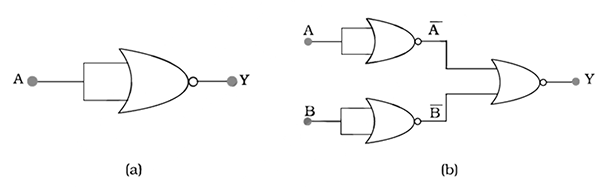
Explain why NAND gate is known as universal gate.
What type of gate is this,
Whats the difference between
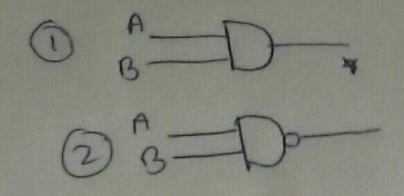
Carbon, Silicone, and Germanium all have the same number of electrons in an outer most shell. Explain?
The outputs of two NOT gates are fed to a NOR gate. Draw the logic circuit of the combination of gates. Give its truth table. Identify the gate represented by this combination.
In what respect is an LED different from an ordinary PN - junction diode? Where should we prefer LEDs over ordinary incandescent lamps? Why?
What is a transistor? Why is it so called? What are the advantages of transistors over vacuum tubes?
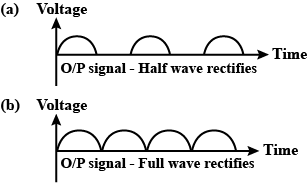
In half-wave rectification, what is the output frequency if the input frequency is 50 Hz
What is the output frequency of a full-wave rectifier for the same input frequency.
Write the truth table for the circuits given in figure. consisting of NOR gates only. Identify the logic operations (OR, AND, NOT) performed by the two circuits.
You are given the two circuits as shown in Fig. Show that circuit (a) acts as OR gate while the circuit (b) acts as AND gate.
Draw a circuit diagram of n-p-n transistor amplifier in CE configuration. Under what condition does the transistor act as an amplifier?
Write the truth table for the combination of the gates shown. Name the gates used.
A graph of the output from an A.C. generator is given. This is given as:
(a) an input to a half wave rectifier
(b) an input to a full wave rectifier
Give graphic representations of the outputs in the cases (a) and (b).

Write the truth table of logic OR gate.
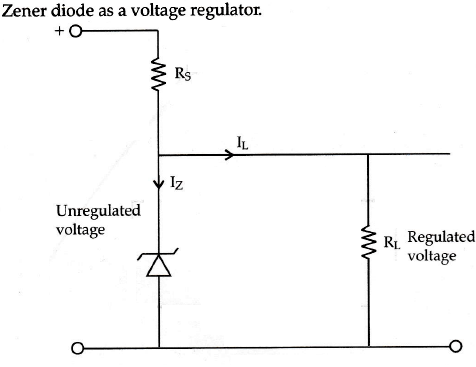
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode. What is the use of a Zener diode?
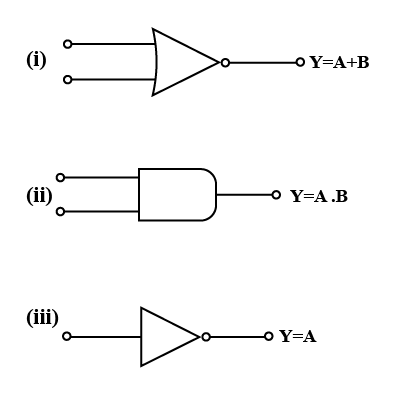
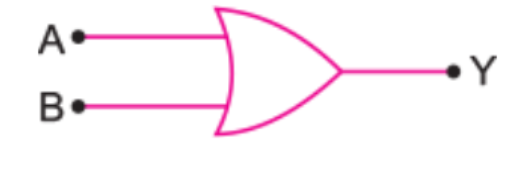
Construct the logic symbol, Boolean expression, circuit diagram and truth table for an OR gate.
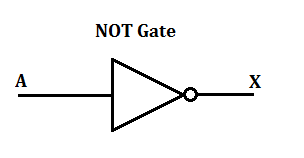
Make logic symbol and write Boolean expression of NOT gate.
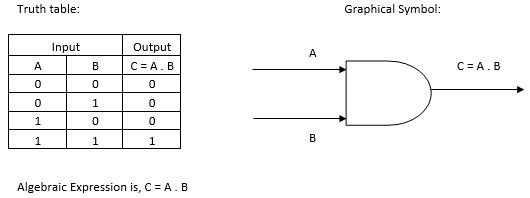
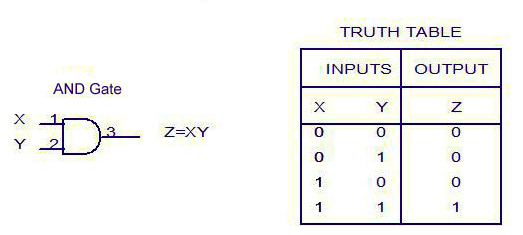
Construct the logic symbol, Boolean expression and truth table for an AND gate.
For a common emitter amplifier. dc(direct current) current gain is 100. If the base current is 20\muA, calculate the collector and emitter current.
The arrangement given represents a logic gate.
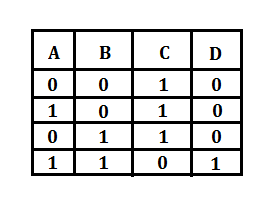
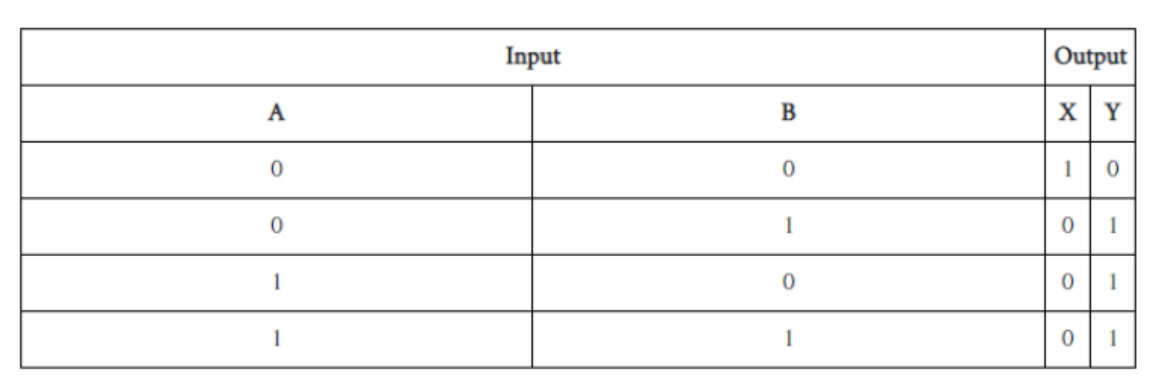
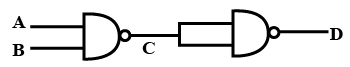
Copy the following truth table and complete it showing outputs at C and D.
| A | B | C | D |
| 0 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 |
Transistors used for making NOT gate.why?
A semiconductor doped with a donor impurity is.
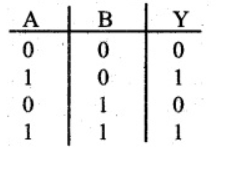
Write down output Y in terms of inputs A and B.
In a zener -regulated power supply a zener diode with V_z=6 volt is used for regulation. The load current is to be 4mA and the unregulated input is 10 volt. What should be he value of series resistor R_s.if the current through diode is five time the load current ?
what is the PN junction diode?
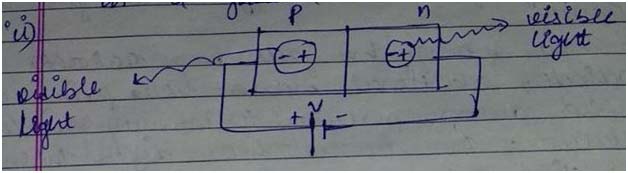
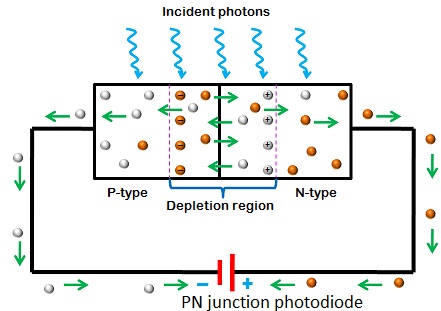
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of a photo-diode. Write briefly how it is used to detect the optical signals.
OR
Mention the important considerations required while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
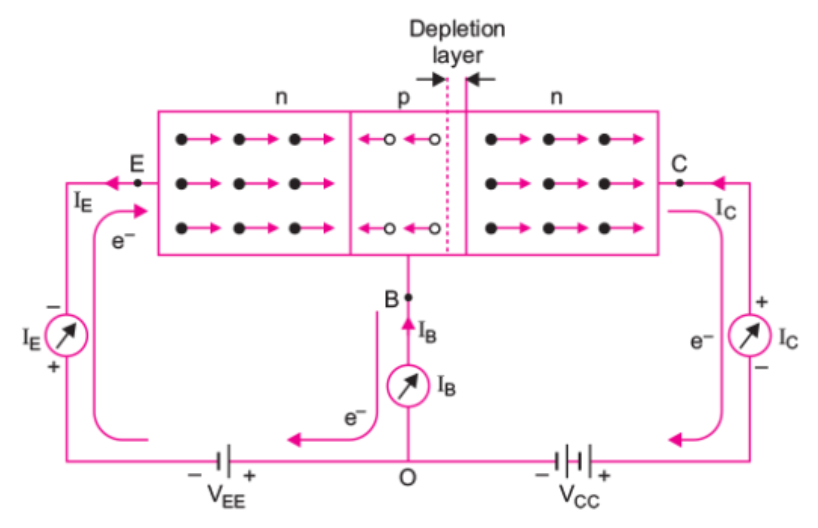
When is a transistor said to be in active state? Draw a circuit diagram of a p-n-p transistor and explain how it works as a transistor amplifier. Write clearly, why in the case of a transistor (i) the base is thin and lightly doped and (ii) the emitter is heavily doped.
(i) Distinguish between a conductor and a semi conductor on the basis of energy band diagram
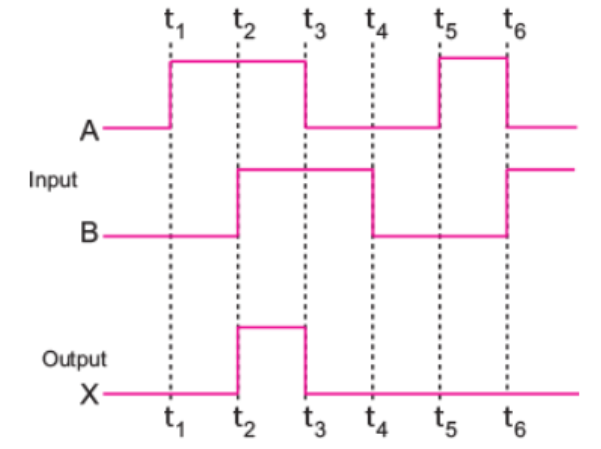
(ii) The following figure shows the input waveforms (A, B) and the output waveform (Y) of a gate. Identify the gate, write its truth table and draw its logic symbol.
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
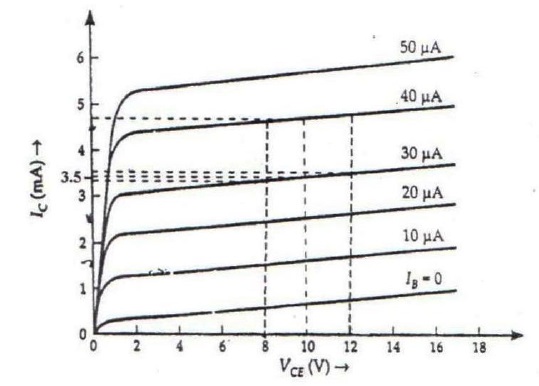
Output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration is shown in the figure. Determine:
(i) dynamic output resistance
(ii) dc current gain and
(iii) ac current gain at an operating point {V}_{CE}=10 V, when {I}_{B}=30 \mu A.
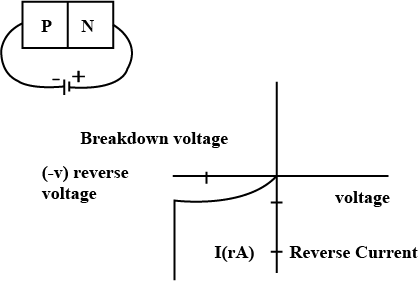
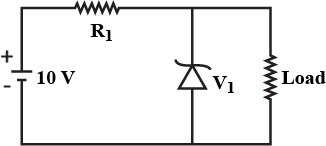
How is a Zener diode fabricated? What causes the setting up of high electric field even for small reverse bias voltage across the diode?
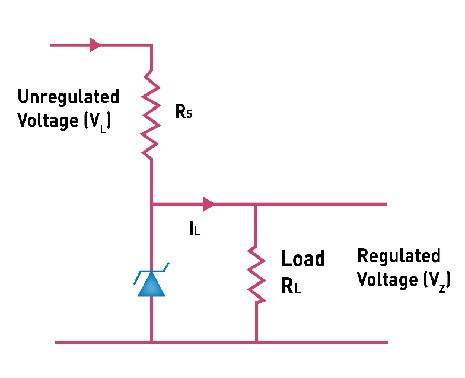
Describe, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of Zener diode as a voltage regulator.
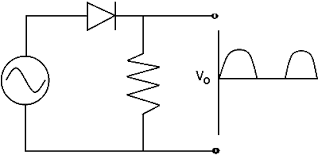
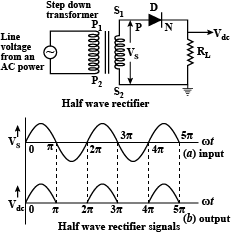
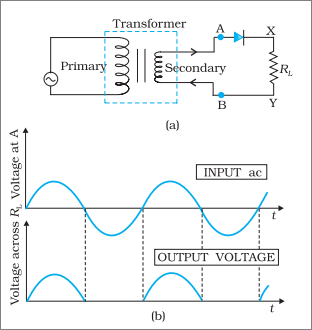
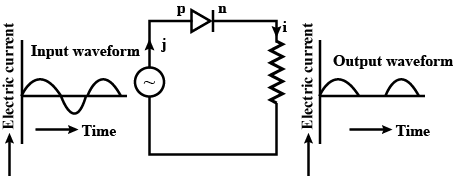
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of a p-n junction diode as a half-wave rectifier.
(a) State briefly the processes involved in the formation of p-n junction explaining clearly how the depletion region is formed.
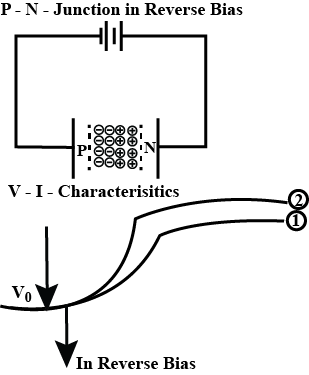
(b) Using the necessary circuit diagram, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
(i) Forward biasing
(ii) Reverse biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
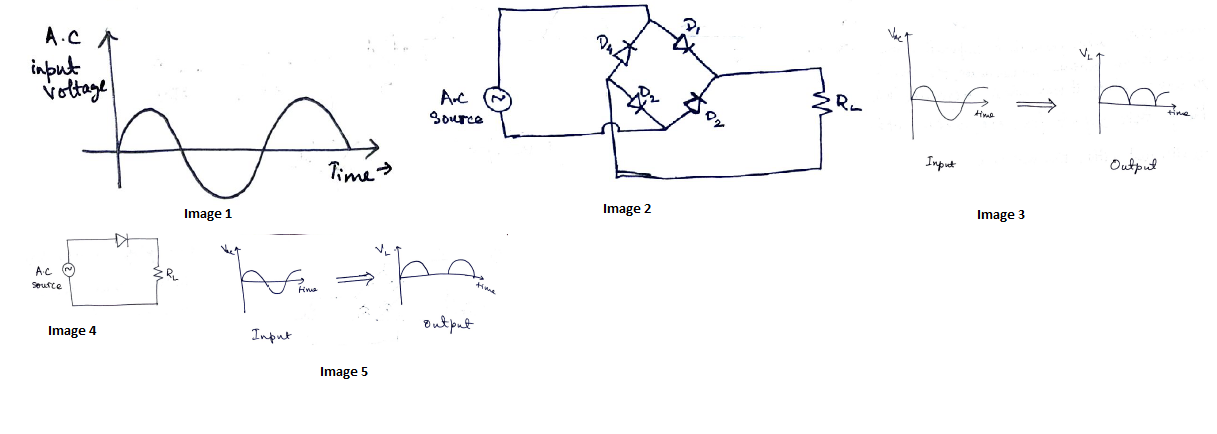
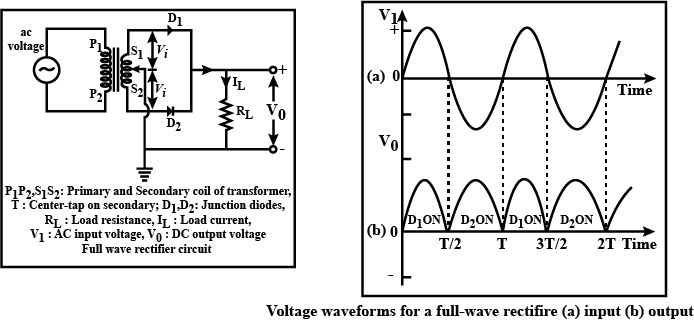
(a) Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier using p-n junction diode.
Explain its working and show the output, input waveforms.
(b) Show the output waveforms (Y) for the following inputs A and B of
(i) OR gate (ii) NAND gate
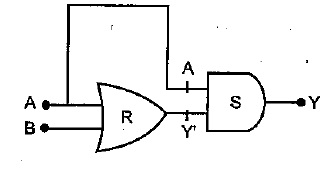
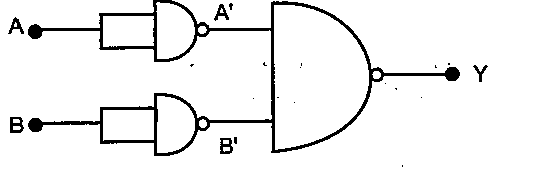
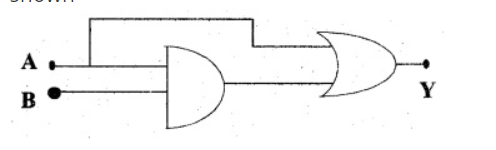
In the circuit shown in the figure identify the equivalent gate of the circuit and make its truth table .
How does a diode acts as a rectifier.
Give the circuit symbol of a diode.
Fill in the blanks.
In an npn transistor p type semi conduct is sandwiched between ___________.
What are semiconductors? Give examples.
Mention the applications of a transistor.
Match the items in List 1 with items in list 2
Match the items in List 1 with items in List 2
State one important use of a Zener diode.
Prepare a truth table for the combination of gates shown in figure.
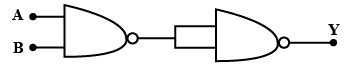
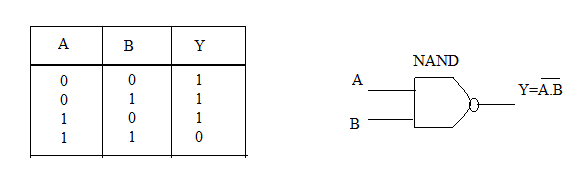
What is NAND gate? Write its truth table.
Write the function of the three segment of a transistor.
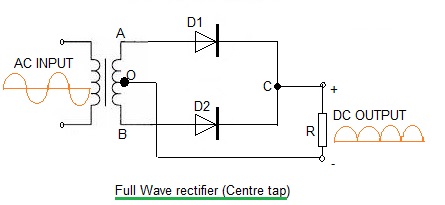
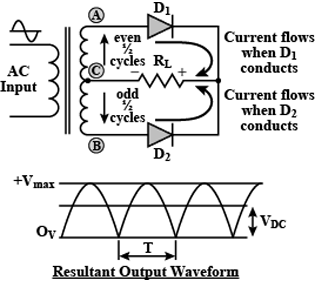
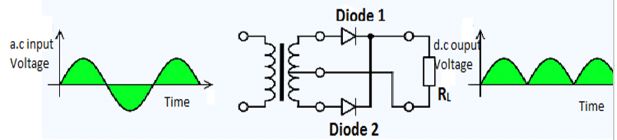
What is rectifier? Explain with neat circuit diagram the action of semiconductor diode as a full wave rectifier.
Figure shows the circuit of an electronic device.
(i) Which electronic device: a rectifier, an amplifier or an oscillator does the circuit represent?
(ii) State where the input voltage is applied and where the output voltage is available.
(iii) Compare the output voltage of this circuit with its input voltage.
What are the advantages of Integrated Circuits (IC)
State the properties and uses of a Junction Diode.
State the properties and uses of a Junction transistor.
Explain the working of a diode as half wave rectifier.
Show the output waveform of OR gate for the following input waveforms of A and B
What is extrinsic semiconductor? How many types of these are? Write their names. Explain the processes which are occurred during the formation of a P-N junction. Determine the electric field produced at a P-N junction when width of depletion layer is 1 micrometer and barrier potential is 0.7 volt.
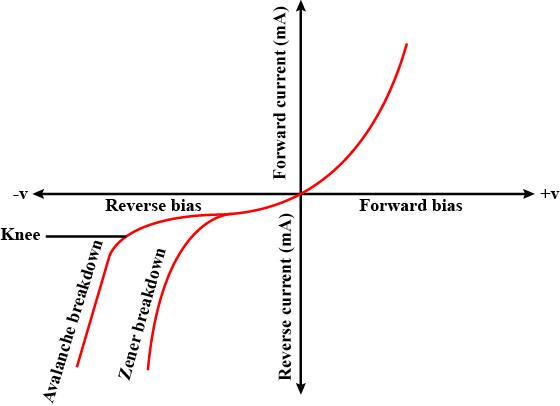
Distinguish between Avalanche breakdown and Zener breakdown.
Draw the circuit diagram of AND gate using diodes.
What is rectification? Explain the working of a fullwave rectifier. Draw necessary circuit diagram.
What is rectification? With relevant circuit diagram and waveforms explain the working of a P-N junction diode as a full-wave rectifier.
Answer the following question :
(i) Write the functions of the three segments of a transistor.
(ii) The figure shows the input wave forms A and B for 'AND' gate . Draw the output wave form and write the truth table for this logic gate.
Explain avalanche breakdown in a diode and zener breakdown in a zener diode.
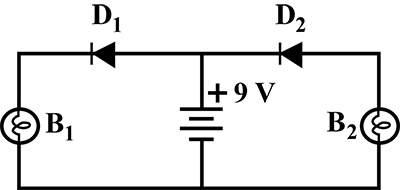
(a) In the following diagram, which bulb out of B_1 and B_2 will glow and why?
(b) Draw a diagram of an illuminated p-n junction solar cell.
(c) Explain briefly the three processes due to which generation of emf takes place in a solar cell.
What is rectification? Explain the working of a full wave rectifier.
What is a Fermi energy level? What is its position in case of an intrinsic semiconductor?
What is rectification? Explain the working of a full-wave rectifier with a diagram. What is a zener diode? How will a zener diode be connected in a circuit generally?
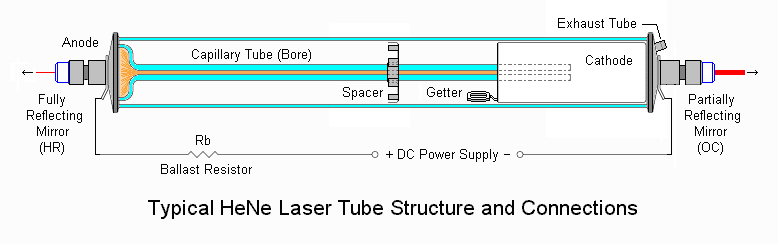
Draw the diagram of a Helium-Neon laser tube and label the parts.
Write the logic symbols and prepare the truth tables of the following gates.
(i) AND
(ii) NOR.
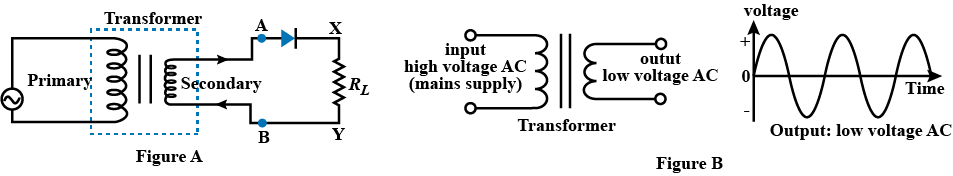
A diode is connected to the output of a transformer as shown in the figure given below. Analyse the figure.
a) Draw a time-voltage graph for the current obtained across AB.
b) What is the function of the diode in the circuit?
(A) What do you mean by barrier potential of diode?
(B) With help of a diagram explain the working of a full wave rectifier.
Distinguish between conductor and semiconductor on the basis of band theory of solids.
What is main logic gates? How many types are they? Draw their symbols and Truth Table.
What is an intrinsic semi conductor? Give two examples.
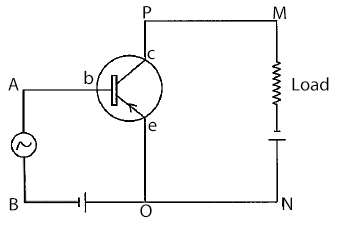
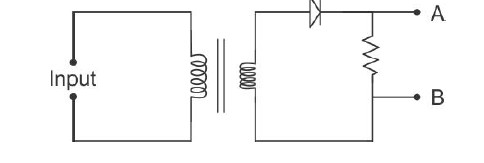
Write the name of device 'X' in the following given diagram. Explain its working making its circuit diagram.
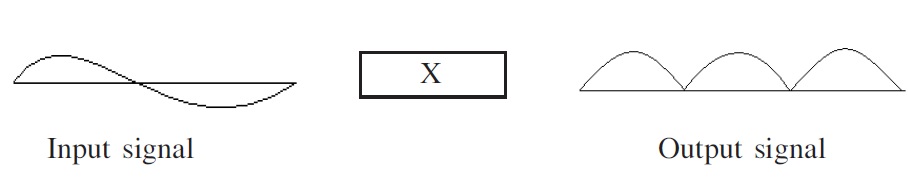
What is a transistor? Mention any two uses of transistor.
What is logic gates? Write two names of universal logic gates.
Explain working of half wave rectifier using p-n junction diode with the help of circuit diagram.
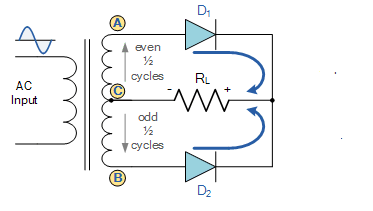
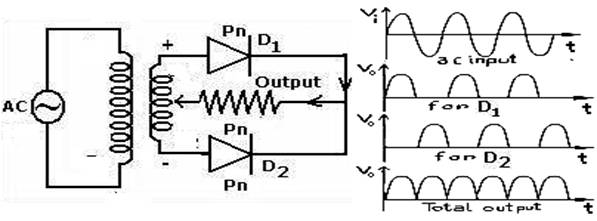
Draw the circuit diagram of full-wave rectifier using two p-n junction diodes and explain its working. Show the input and output waveforms.
Construct the circuit symbol of Zener diode.
How is p-n junction diode used as a half-wave rectifier?
Explain its working, draw a neat circuit diagram. Show the waveforms of input and output voltages.
Write the two processes that take place in the formation of a p-n junction. Explain with the help of a diagram, the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a p-n junction.
A potential barrier V volts exists across a P-N junction. The thickness of the depletion region is 'd'. An electron with velocity 'v' approaches P-N junction from N-side. Find the velocity of the electron crossing the junction.
Why is the base region of the transistor thinly doped?
The input resistance of a transistor is 1000\Omega. On changing the base current by 10\mu A, the collector current increases by 2mA. If a load resistance of 5\ k\Omega is used in the circuit, calculate (i) the current gain, (ii) voltage gain of the amplifier.
What is a rectifier? With a suitable circuit diagram, describe the action of a full wave rectifier by drawing input and output waveforms.
What are n-type and p-type semiconductor?
Draw circuit diagram of common base configuration.
Explain the importance of the PIV rating of a diode.
In the forward bias arrangement of a PN-jucnction diode.
The electric resistance of depletion layer is large bacause
Draw diagram for a P-N junction to obtain reverse bias characteristic curves. Explain the phenomenon of reverse breakdown for a P-N junction in reserve bias state by following processes-
(i) Avalanche breakdown
(ii) Zener breakdown
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED) . What should be the order of band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light, in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain it action.
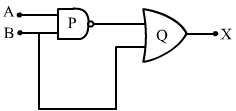
(i) Write the truth tables of the logic gates marked P and Q in the given circuit.
(ii) Write the truth table for the circuit.

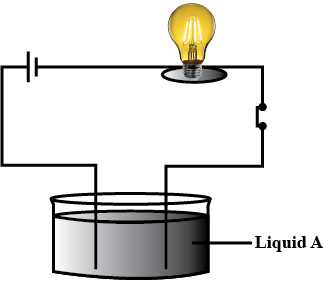
Reashma set up an experiment using liquid 'A' in the beaker as shown in the figure. She observed that the bulb glows. Then she replaced the liquid 'A' by another liquid 'B', this time the bulb did not glow. Rani suggested replacing the bulb by an LED. They observer that the LED glows. Give reason.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying the V_I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in reserve bias. Plot the V-I characteristics in this case.
The potential difference across the collector is a transistor, used in common emitter mode is 1.5 V, with the collector resistance of 3 k\Omega. Find (i) the emitter and (ii) the base current, if the d.c gain of the transistor is 50.
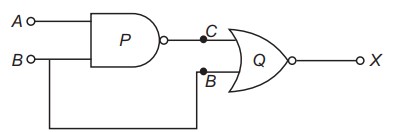
Identify the logic gates marked 'P' and 'Q' in the given circuit. Write the truth table for the combination.
How many minimum NAND GATEs are required for obtaining an output of A.B+C.D?
Answer the following :
(i) Write the truth table of the following gate.
(ii) What will be the values of inputs A and B for the Boolean expression
( A \bar{+} B) . ( \bar {A.B}) = 1
What is a rectifier? With the help of a neat circuit diagram explain the working of a full wave rectifier.
The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor increases when electromagnetic radiation of wavelength shorter than 248\ nm is incident on it. The forbidden band energy for the semiconductor in eV is
What is the resistance of an intrinsic semiconductor at OK ?
Can we measure the potential difference across an unbiased p-n junction by connecting a sensitive voltmeter across it ?
Name fundamental logic gates.
Name two semiconductor materials.
The active volume of a laser constructed of the semi-conductor GaAlAs is only 200 \mu m^3 (smaller than a grain of sand), and yet the laser can continuously deliver 5.0 mW of power at a wavelength of 0.80\mu m. At what rate does it generate photons?
In a transistor , doping level in base is increased slightly. How will it affect base current ?
At what temperature would an intrinsic semiconductor behave like a perfect insulator ?
Name the logic gate marked P and Q in the given logic circuit .
In a transistor , doping level in base is increased slightly. How will it affect collector current ?
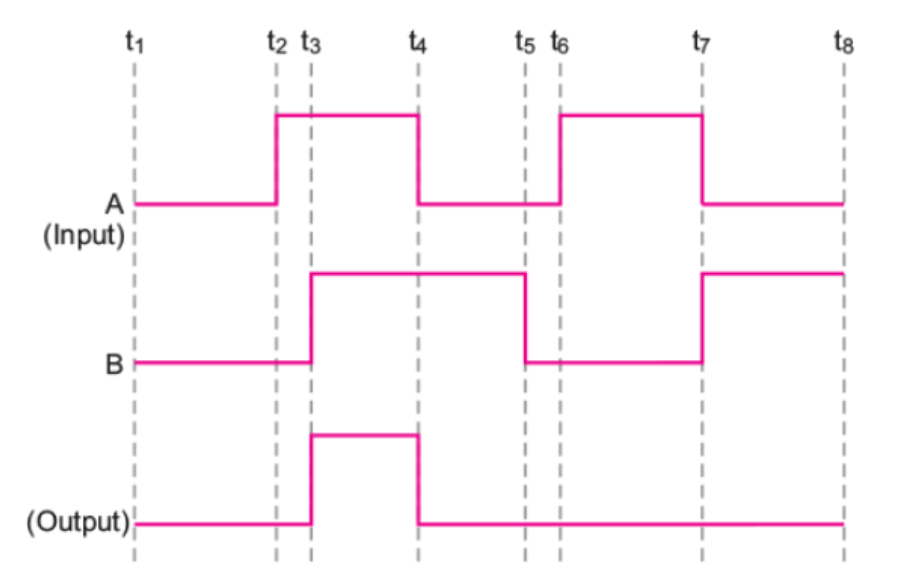
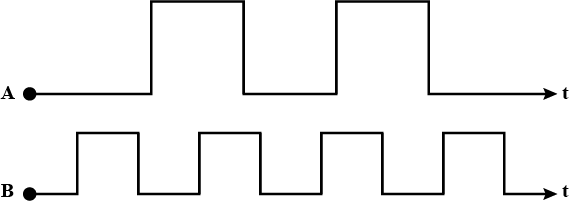
Draw the output waveform at X , using the given inputs A , B for the logic circuit shown alongside . Also identify the gate.
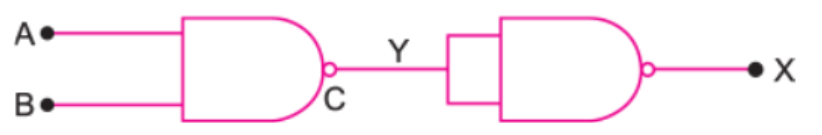
Name the logic gate whose repetitive use can make digital circuits .
What signal voltage is represented for positive logic state 1 ?
(a) Explain briefly the process of emission of light by a Light Emitting diode. (LED).
(b) Which semiconductor are preferred to make LEDs and why ?
(c) Give two advantages of using LEDs over conventional incandescent lamps.
The output of an OR gate is connected to both the inputs of a NAND gate. Draw the logic circuit of this combination of gates and write its truth table.
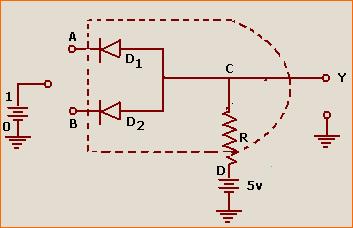
Name the logic gate which can be realised by using p-n junction diode in the given diagram. Give its logic symbol and write the truth table. Name the gate which will be obtained by combining with a NOT gate.
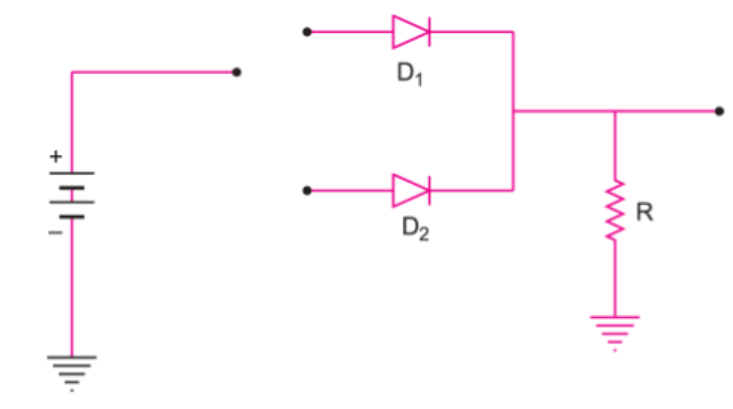
How is a light emitting diode fabricated ? Briefly state is working. Write any two important advantages of LEDs over the conventional incandescent low power lamps.
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams.
In a common emitter mode of a transistor , the d.c current gain is 20 , the emitter is 7 \, mA . Calculate (i) base current and (ii) collector current.
Explain the following :
LEDs are made of compound semiconductor and not by elemental semiconductors.
In the figure given alongside is, (i) the emitter and (ii) the collector forward or reverse biased ? With the help of a circuit diagram explain the action of npn transistor.
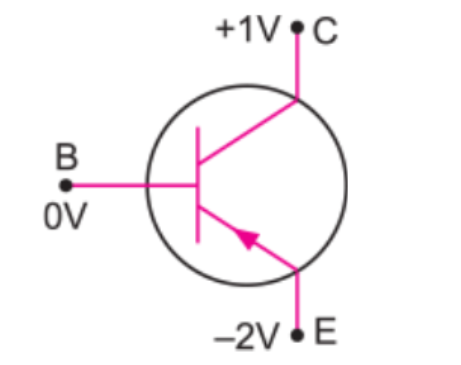
Answer the following questions :
(i) What is an 'Integrated circuit (I.C)' ? Distinguish between (i) linear I.C and (ii) Digital I.C.
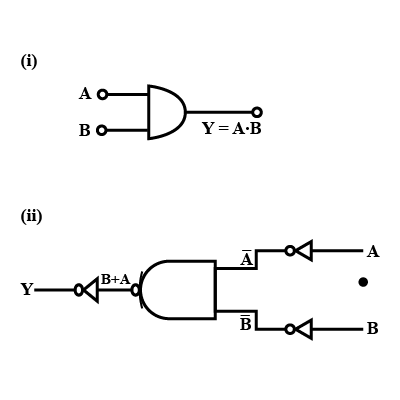
(ii) Identify the equivalent gate for the following circuit and write its truth table.
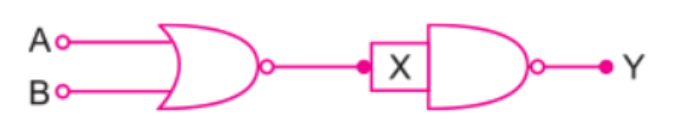
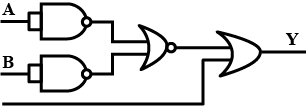
The inputs A and B are inverted by using two NOT gates and their outputs are fed to the NOR gate as shown above .
Analyse the action of the gate (1) and (2) and identify the logic gate of the complete circuit so obtained. Give its symbol and truth table.
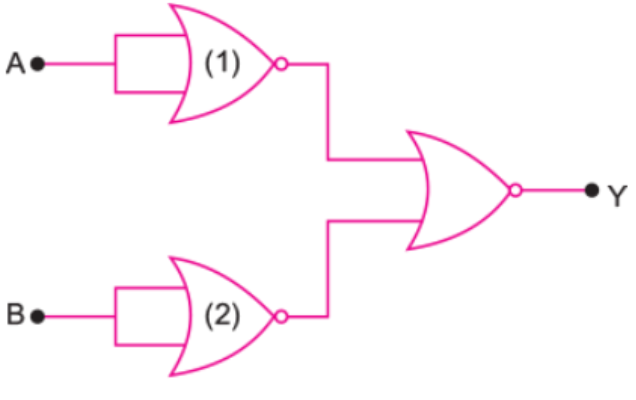
Explain the forward and the reverse characteristic of a Zener diode.
Write the truth table for the circuits given in fig. consisting of NOR gates only. identify the logic operation (OR, AND , NOT) performed by the two circuits.
Draw the circuit diagram of a half-wave rectifier. Explain its working. What is the frequency of ripple in its output?
What do you mean by a truth table?
Why is the base of a transistor made thin and is lightly doped?
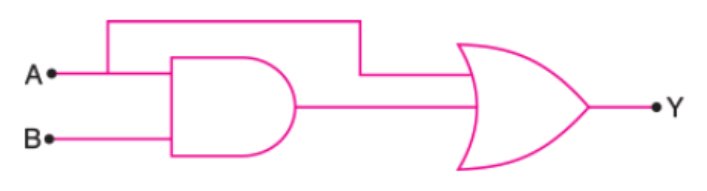
Express by a truth table, the output Y for all possible inputs A and B in the logic as shown
How is a Zener diode different than an ordinary diode?
What is rectification? Draw the circuit diagram of half wave rectifier and explain its working. Show the input ac voltage and output voltage waveforms from the rectifier circuit.
What is rectification? Explain the working of bridge rectifier. Draw the input and output signals.
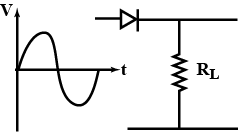
If in a p-n junction diode, a sinusoidal input signal is applied as shown.
Then, the output signal across R_{L} will be:
the intrinsic semiconductor at room temperature is
Suppose a pure Si crystal has 5\times 10^{28} atoms per m^3. It is doped by 1 ppm concentration of pentavalent As. Calculate the number of electrons and holes. Given that n_i=1.5\times 10^{16} per m^3.
Write the truth table of AND gate.
What is rectifier? Explain the working of p-n junction diode as a full-wave rectifier with the help of suitable circuit diagram.
Draw a circuit diagram of an n-p-n transistor with its emitter-base junction foward biased and base-collector junction reverse biased.
Briefly describe its working.
Explain how a transistor in active states exhibits a low resistance at its emitter-base junction and high resistance at its base-collector junction.
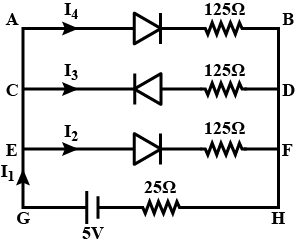
If each diode in figure, has a forward bias resistance of 125\Omega and infinite resistance in reverse bais, what will be the values of the current {I}_{1},{I}_{2},{I}_{3} and {I}_{4}?
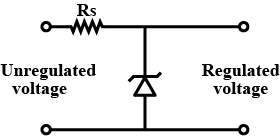
A Zener of power rating 1W is to be used as a voltage regulator. If Zener has a breakdown of 5V and it has to regulate voltage which fluctuated between 3V and 7V, what should be the value of {R}_{s} for safe operation (Figure)?
The current amplification is 0.99 for any transistor in the common-base configuration. Calculate the change in collector current when there is a 5.0 milliampere change in emitter current. What will be the change in base current?
A transistor is connected in common emitter configuration. A power supply of 8 \vee is there in the collector circuit and the potential drop of 0.5 \mathrm{V} is on the resistance of 80012 connected in series with the collector. If current amplification factor is a=0.96 . Then calculate the base current.
When the base current in a transistor is changed from 30 \, \mu\, A to 80 \mu \,A, the collector current is changed from 1.0 \mu \,A to 3\cdot 5\, \mu \,A. Find the current gain \beta
A silicon-based MOSFET has a square gate 0.50 mm on edge. The insulating silicon oxide layer that separates the gate from the p-type substrate is 0.20 mm thick and has a dielectric constant of 4.5. (a) What is the equivalent gate – substrate capacitance (treating the gate as one plate and the substrate as the other plate)? (b) Approximately how many elementary charges e appear in the gate when there is a gate–source potential difference of 1.0 V?
What is the direction of diffusion current in junction diode?
Class 12 Medical Physics Extra Questions
- Alternating Current Extra Questions
- Atoms Extra Questions
- Current Electricity Extra Questions
- Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter Extra Questions
- Electric Charges And Fields Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Induction Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Waves Extra Questions
- Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Extra Questions
- Magnetism And Matter Extra Questions
- Moving Charges And Magnetism Extra Questions
- Nuclei Extra Questions
- Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Extra Questions
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices And Simple Circuits Extra Questions
- Wave Optics Extra Questions