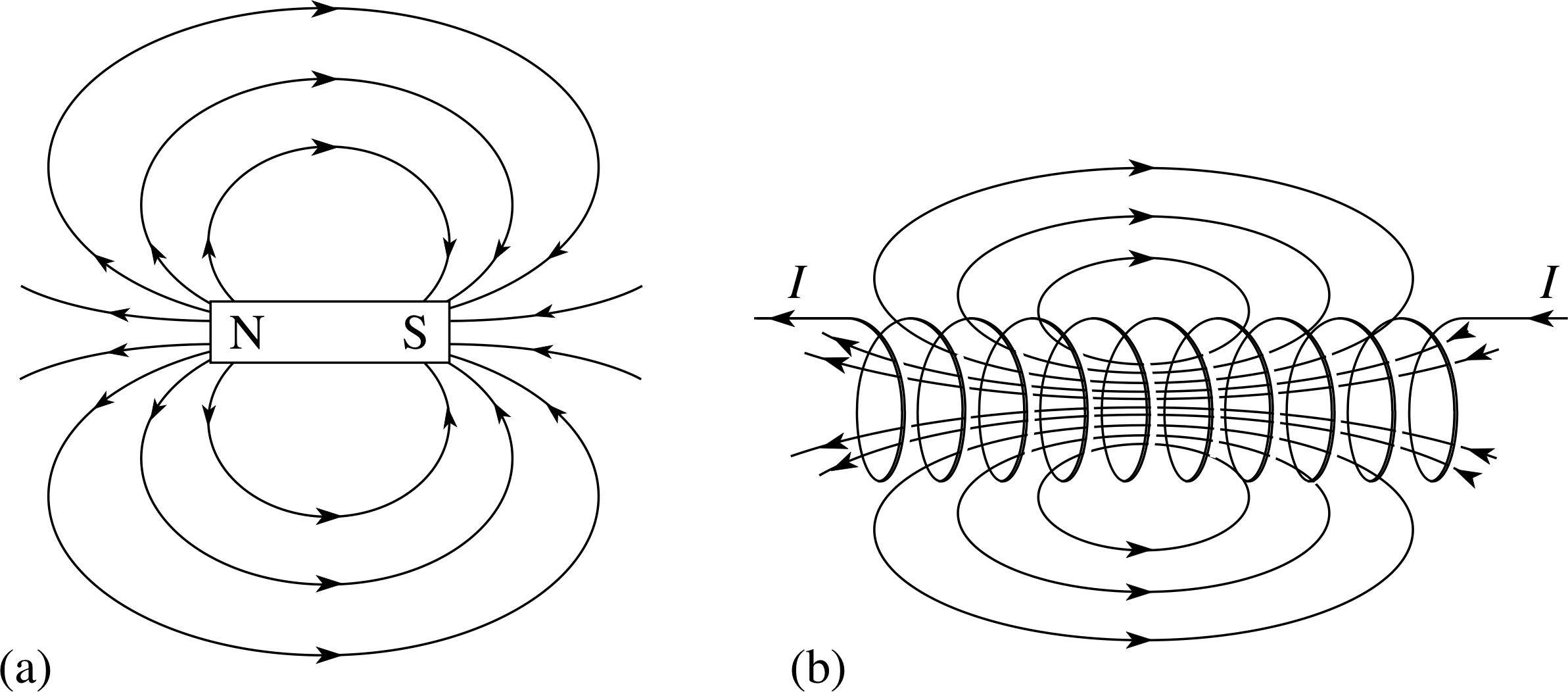
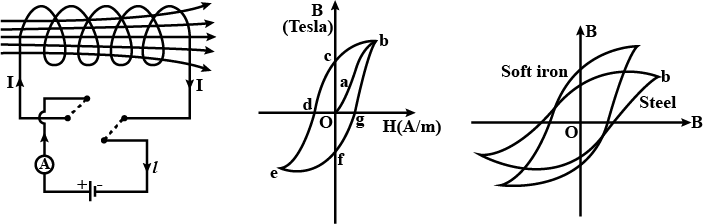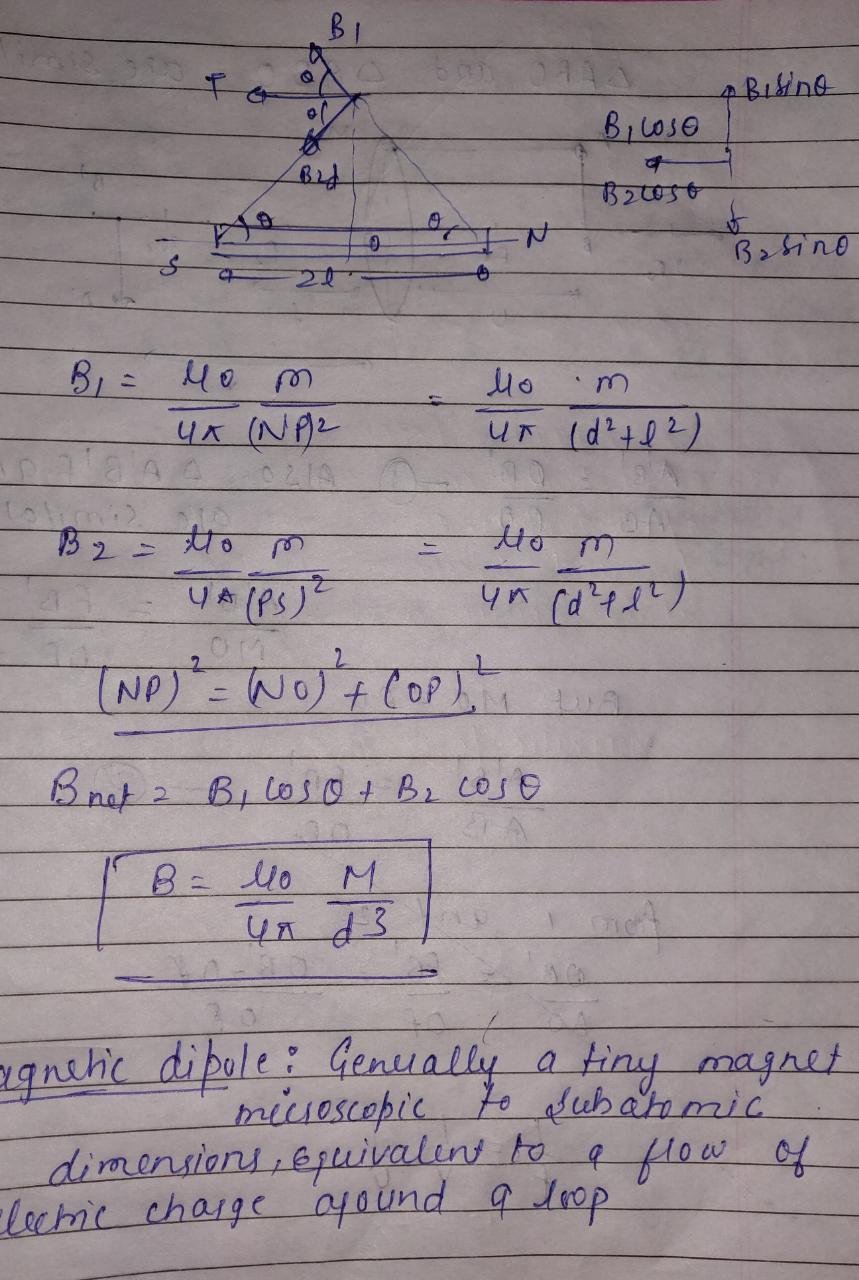Magnetism And Matter - Class 12 Medical Physics - Extra Questions
State any two properties of magnetic lines of force.
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of $$0.48 J T^{-1}$$ . Give the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance of 10 cm from the centre of the magnet on (a) the axis, (b) the equatorial lines (normal bisector) of the magnet.
(a) An iron ring of relative permeability $$\mu_{r}$$ has windings of insulated copper wire of $$n$$ turns per metre. When the current in the windings is $$I$$, find the expression for the magnetic field in the ring.
(b) The susceptibility of a magnetic material is $$0.9853$$. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field.
Answer the question in at least $$50$$ words.
Give the characteristic of magnetic field lines.
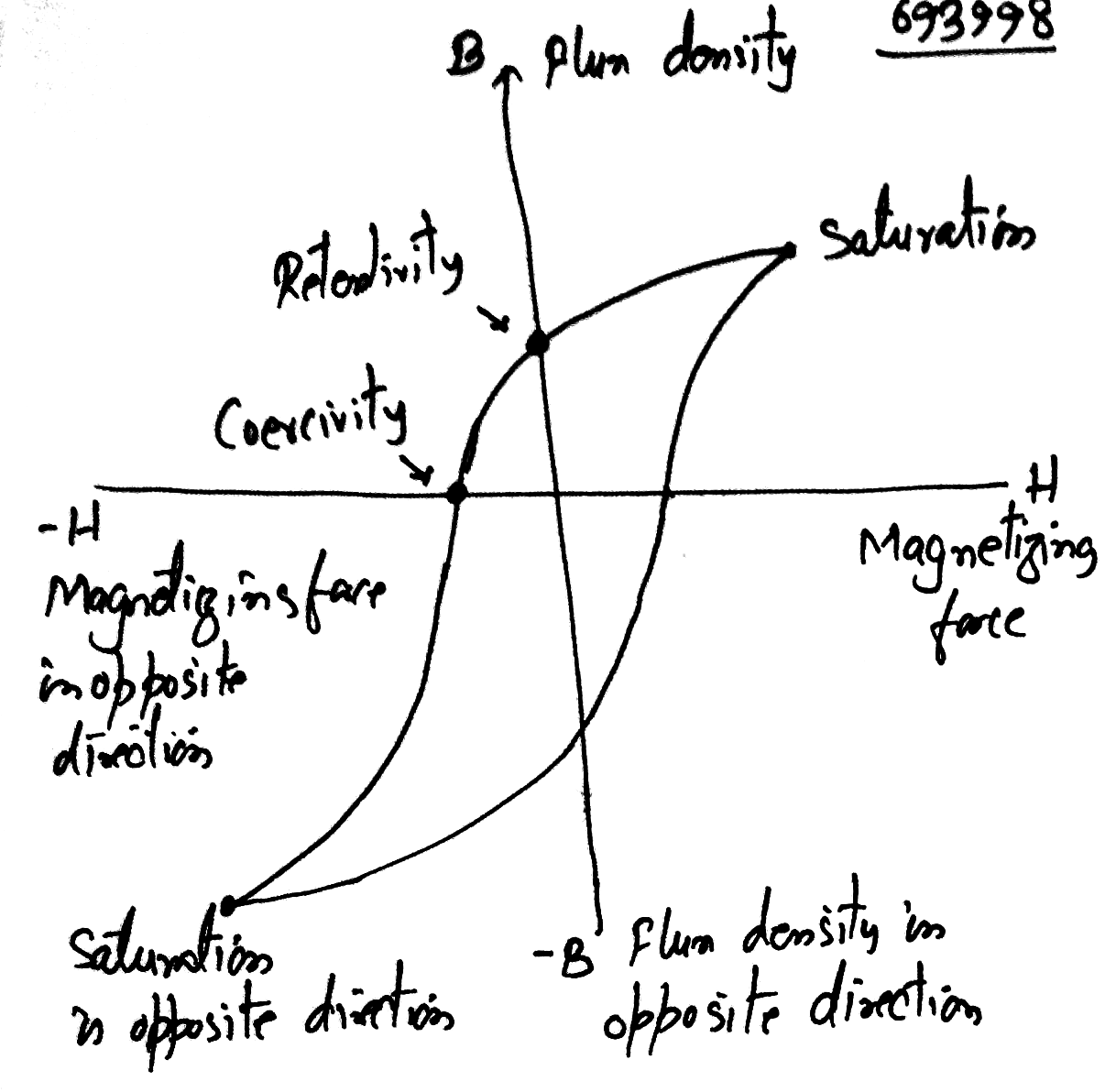
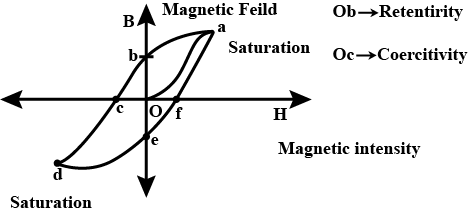
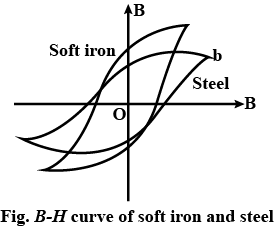
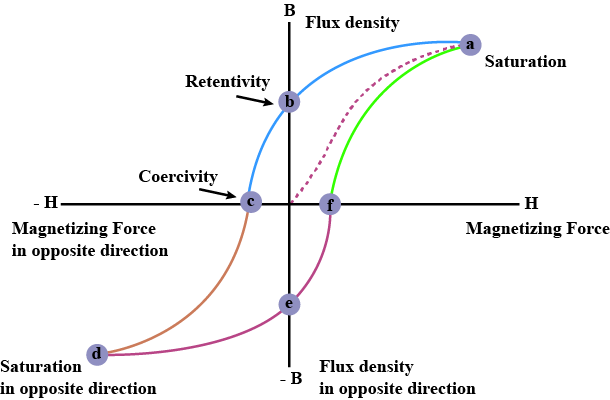
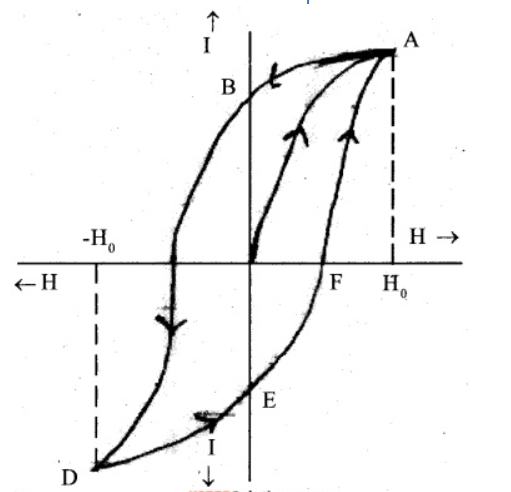
What is hysteresis? Define the terms 'coercivity' and 'retentivity' of a ferromagnetic material.
A small rod of bismuth is suspended freely between the poles of a strong magnet. It is found to arrange itself at right angles to the magnetic field. What is established by the observation?
A magnet has coercivity of $$3\times 10^3$$ $$Am^{-1}$$. It is kept in a $$10$$cm long solenoid with a total of $$50$$ turns. How much current has to be passed through the solenoid to demagnetize it?
In the Bohr model of hydrogen atom, the electron circulates around the nucleus in a path of radius $$5.1\times{10}^{-11}\ m$$ at a frequency $$6.8\times{10}^{15}\ {s}^{-1}$$. Find the magnetic field set up at the centre of the orbit.
A magnetising field of $$1600\dfrac{A}{m}$$produces a magnetic flux $$2.4 X 10^{-5} Wb$$ in a bar of iron of cross section $$0.2 cm^2$$ .Calculate permeability and susceptibility of the bar:
Ferrimagnetic those expected to have large magnetism but actually have small net magnetic moment e.g., magnetic $$(Fe_{3}O_{4})$$, ferrites $$(M^{2}+Fe_{2}O_{4})$$. This is because of unequal number of domains in opposite direction.
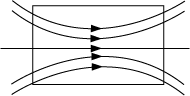
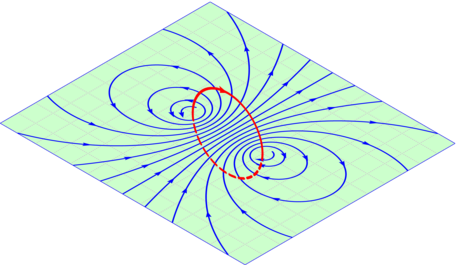
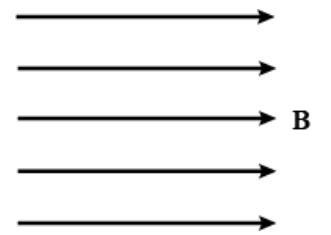
Draw diagram to represent a uniform magnetic field in a given region.
If a particle of charge q is moving with velocity v along the z - axis and the magnetic field B is acting along x - axis, use the expression $$\vec{F} = q (\vec{v} \times \vec{B} )$$ to find the direction of the force F acting on it.
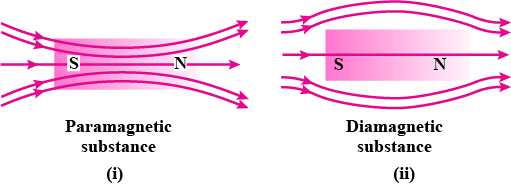
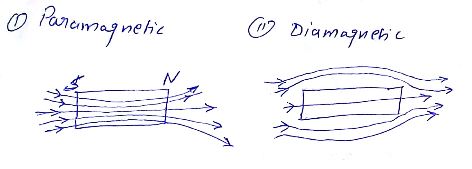
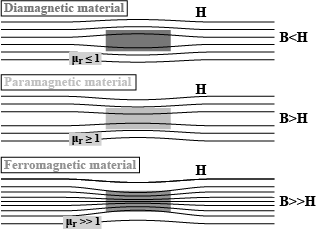
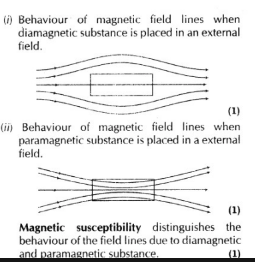
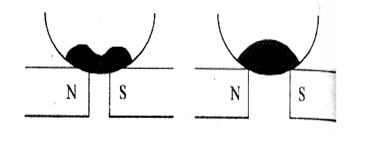
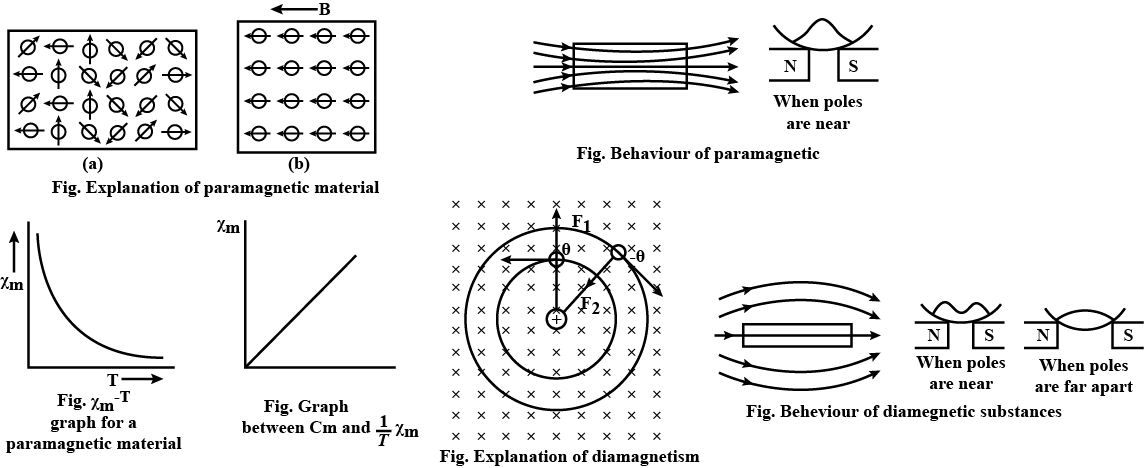
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence
of (i) paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this
distinguishing feature?
OR
Draw the magnetic field lines distinguishing between diamagnetic and paramagnetic materials.
Give a simple explanation to account for the difference in the magnetic behaviour
of these materials.
A sample of the paramagnetic salt to which the magnetization
curve of Fig. applies is held at room temperature $$(300 K)$$.
At what applied magnetic field will the degree of magnetic saturation of the sample be (a) $$50\%$$ and (b) $$90\%$$ ? (c) Are these fields
attainable in the laboratory?
A sample of the paramagnetic salt to which the magnetization
curve of Figure applies is to be tested to see whether it obeys
Curies law. The sample is placed in a uniform $$0.50$$ T magnetic field
that remains constant throughout the experiment. The magnetization M is then measured at temperatures ranging from $$10$$ to $$300$$ K.
Will it be found that Curies law is valid under these conditions?
Answer the following question
Name the properties of a magnetic material that make it suitable for making
(a) a permanent magnetic and (b) a core of an electromagnetic.
Answer the following question
What happens when a diamagnetic substance is placed in a varying magnetic
field?
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law in magnetism. How is it different from Gauss's law in
electrostatic and why?
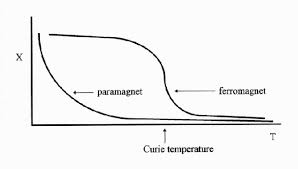
Measurements in mines and boreholes indicate that Earth’s interior temperature increases with depth at the average rate of $$30 C°/km$$. Assuming a surface temperature of $$10°C$$, at what depth does iron cease to be ferromagnetic? (The Curie temperature of iron varies very little with pressure.)
In Figure, a bar magnet lies near a paper cylinder.
(a) Sketch the magnetic field lines that pass through the surface of
the cylinder. (b) What is the sign of for every area on the
surface? (c) Does this contradict Gauss law for magnetism?
Explain.

A sample of the paramagnetic salt to which the magnetization
curve of Fig. applies is immersed in a uniform magnetic field
of $$2.0$$ T. At what temperature will the degree of magnetic saturation of the sample be (a) $$50%$$ and (b)$$90%$$?
The magnetic properties of the different materials A,B and C are shown in the following table:
| Material | Permeability | Susceptibility | Temperature dependence of susceptibility |
| A | Low positive | Small but negative | Independent of temperature |
| B | high | Vert high $$1$$ | Susceptibility decreases with temperature |
| C | Grater than $$1$$ | Small but positive | Decreases with temperature |
Which of the above three materials should be used for making an electromagnet and why?
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is $$2.6\times 10^{-5}$$. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
Write any three characteristics, a ferromagnetic substance should possess if it is to be used to make a permanent magnet. Give one example of such a material.
What is Curie law in magnetism?
The susceptibility of a magnetic materials $$-4.2\times 10^{-6}$$. Name the type of magnetic material it represents.
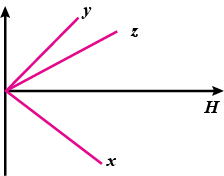
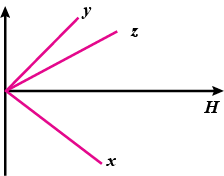
The variation of intensity of magnetisation $$I$$ and the applied magnetic field intensity $$H$$ for three magnetic materials $$X,\ Y$$ and $$Z$$ are as shown in the given graphs.
Identify the materials $$X,\ Y$$ and $$Z$$.
A magnetic needle free to rotate in a vertical plane parallel to the magnetic meridian has its north tip down at $$60^{o}$$ with the horizontal. The horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field at the place is known at to be $$0.4\ G$$. Determine the magnitude of the earth's magnetic field at the place.
Which of the following substances are diamagnetic? $$Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca$$ and $$Ni$$
The variation of intensity of magnetisation $$I$$ and the applied magnetic field intensity $$H$$ for three magnetic materials $$X,\ Y$$ and $$Z$$ are as shown in the given graphs
Shows graphically the variation of susceptibility with temperature for $$X$$.
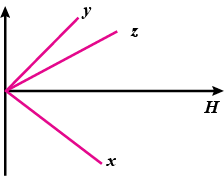
The variation of intensity of magnetisation $$I$$ and the applied magnetic field intensity $$H$$ for three magnetic materials $$X,\ Y$$ and $$Z$$ are as shown in the given graphs
Put of $$Y$$ and $$Z$$, which of the material will you prefer for making transformer cores and why?
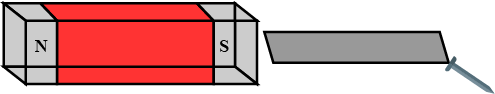
Why is the core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic materials?
In what ways is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material different from that of a paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
What is the basic difference between the atom and molecule of a diamagnetic and a paramagnetic material? Why are elements with even atomic number more likely to be diamagnetic?
The magnetic field lines prefer to pass through iron than air. Explain why?
What kind of ferromagnetic material is used for coating magnetic tapes in a cassette player or for building memory stores in a modern computer?
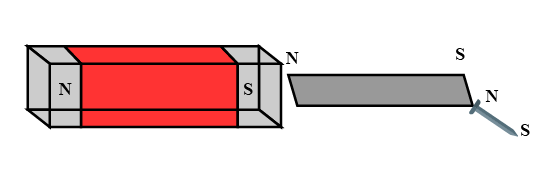
Boojho kept a magnet close to an ordinary iron bar. He observed that the iron bar attracts a pin as shown in the figure.
What inference could he draw from this observation? Explain.
State with reason, whether the following statement is true or false? The product of magnetic susceptibility and absolute temperature $$XT$$ is constant for a paramagnetic material.
From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of susceptibility for diamagnetism, Para magnetism and ferromagnetism.
Fill in the blanks
In a magnet, __________ have the maximum attractive property.
Two magnetic lines of force never intersect each other. True/False?
State whether the following statement is True or False.
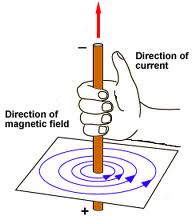
Ampere's swimming rule describes the direction of magnetic lines of force in a straight conductor.
A small magnet is suspended by a silk thread from a rigid support such that the magnet can freely swing. Describe its behaviour.
Sketch magnetic lines of force around a current carrying coil.
State the characteristics of magnetic lines of force.
List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Which of the following substances are para-magnetic?
$$Bi, Al, Cu, Ca, Pb, Ni$$
The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is $$800$$. Identify the nature of magnetic material and state its own properties.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is $$-2.6 \times {10}^{-5}$$. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
What are permanent magnets? Give one example.
A ________ is a region around a magnet where magnetic lines of force act.
Classify the following materials with regard to magnetism:
Manganese, Cobalt, Bismuth, Copper
What are diamagnetic substances? Give one example
Why do magnetic field lines not intersect each other?
Write any three properties of magnetic lines of force.
State True or False.Magnetic lines of force are closed continuous curves.
Compare paramagnetism and ferro magnetism. Give examples of each.
State and explain Curie's law.
What is Curie temperature?
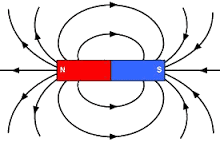
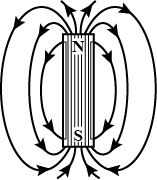
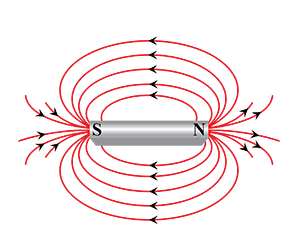
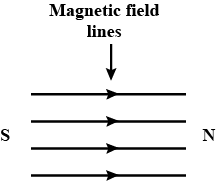
Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines for a bar magnet.
Classify the following materials with regard to magnetism:
Manganese, Cobalt, Nickel, Bismuth, Oxygen and Copper
Distinguish between Para, Ferro and Diamagnetism.
Write two properties of magnetic lines of force.
Define Curie temperature in magnetism.
Out of the two magnetic materials, 'A' has relative permeability slightly greater than unity while 'B' has less than unity. Identify the nature of the materials 'A' and 'B'. Will their susceptibilities be positive or negative?
A rectangle has sides of lengths $$6 cm$$ and $$8 cm$$. Two magnetic poles each of pole strength '$$m$$' are placed at the ends of one side of smaller length and magnetic force acting between them is '$$F$$'. If they are moved to new positions of same rectangle so that they are diagonally opposite. Find the final force acting on each pole.
Conductivity of metal decreases with temperature while conductivity of electrolytic conductors increases with temperature. Why ?
Write the causes of energy loss and ways to reduce them in transformer (any four).
State the characteristics of magnetic field lines.
Define magnetic lines of force and state its two properties.
Few iron nails and screws got mixed with wood shavings while a carpenter was working with them. How can you help him in getting the nails and screws back from the scrap without wasting his time by searching with his hands?
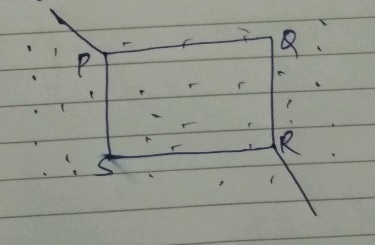
A square frame $$PQRS$$ of side $$20\ cm$$, made up of a conducting wire is placed in a magnetic field of $$1$$ tesla as shown. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the frame directed upwards. An electric current of $$2A$$ enters at the edge $$P$$ of the frame and exist from the edge $$R$$. Find out the magnetic forces acting on the sides of the frame.
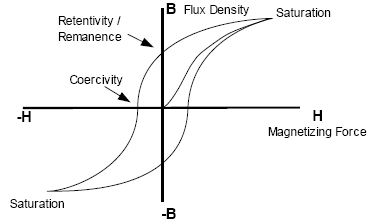
Draw the hysteresis curve for ferromagnetic substance. Show coercivity and retentivity on the curve.
Explain Curie's law for a paramagnetic substance.
Write whether the given statement is true or false : The magnetic susceptibility $$(X_m)$$ of a paramagnetic substance has a small negative value.
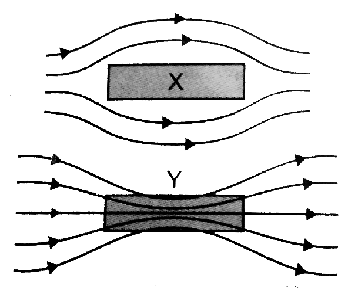
A uniform magnetic field gets modifies as shown in Figure below , when two speciments X and Y are placed in it . Identyfy wether speciment X and Y are diagramatic , paramagnetic or ferromagnetic .
The susceptibility of magnesium at $$300 \,K$$ is $$1.2 \times 10^5$$. What will be its susceptibility at $$200 \,K$$?
Write definition of Curie temperature for ferromagnetic substance.
Draw hysteresis curve (B-H curve) for a ferromagnetic substance
When a electric current is passed through ant wire, a magnetic filed is produced around it. Then why an electric iron connecting cable does not attract nearby iron objects when electric current is switched on through it?
In New Hampshire, the average horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field in $$1912$$ was $$16 \mu T$$, and the average inclination or “dip” was $$73°$$. What was the corresponding magnitude of Earth’s magnetic field?
How can you distinguish between diamagnetic and paramagnetic rods?
Define retentivity.
Give two examples of paramagnetic substances.
What are the behaviour of diamagnetic, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances in non-uniform magnetic field?
The Curie temperature for a ferromagnetic substance is $$300 K$$. If magnetic susceptibility of the substance is $$0.6$$ at $$450 K$$ temperature, then find out Curie constant.
At which place on a magnet, its magnetic force is maximum ?
In an exhibition, a plastic car with an iron piece fixed inside it is made to run on a wooden table by sliding a strong magnet below it. The experiment failed when a steel table was used instead.Explain the reason.
A physics teacher suspends two pointers in a magnetic field. One pointer is made of brass and the other is a magnet.
She holds the pointers in the initial positions shown in the two upper circle of figure. She then releases the pointers.
In the lower circles of figure, draw the settles final positions of the two pointers.

What are the difference in the magnetic properties of iron and steel?
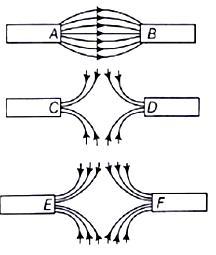
Three diagrams in the following figures show the magnetic field lines between the poles of the magnets. Identify the poles between $$A, B, C, D, E,$$ and $$F$$.
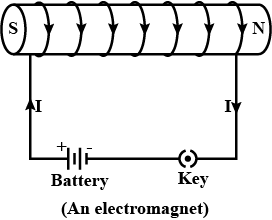
Distinguish between a bar magnet and an electromagnet.
Explain why, two magnetic lines of force do not intersect.
Magnetic field lines of two magnets are shown in fig. A and fig. B.
Select the figure that represents the correct pattern of field lines. Give reasons for your answer. Also name the poles of the magnets facing each other.
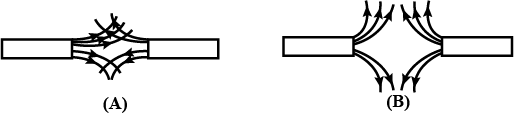
(a) Draw a diagram to represent a uniform magnetic field in a given region.
(b) List two properties of magnetic field lines.
$$N = 300$$ turns of this wire are uniformly wound on a permanent magnet shaped as a cylinder whose length is equal to $$l = 15\ cm$$. When a current $$I = 3.0\ A$$ was passed through the wiring the field outside the magnet disappeared. Find the coercive force $$H_{c}$$ of the material from which the magnet was manufactured.
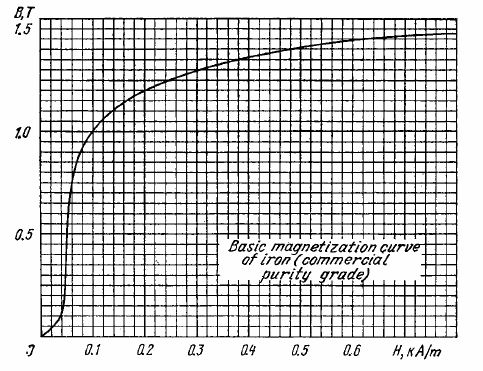
A thin iron ring with mean diameter $$d = 50\ cm$$ supports a winding consisting of $$N = 800$$ turns carrying current $$I = 3.0\ A$$. The ring has a cross-cut of width $$b = 2.0\ mm$$. Neglecting the scattering of the magnetic flux at the gap edges, and using the plot shown in Fig., find the permeability of iron under these conditions.
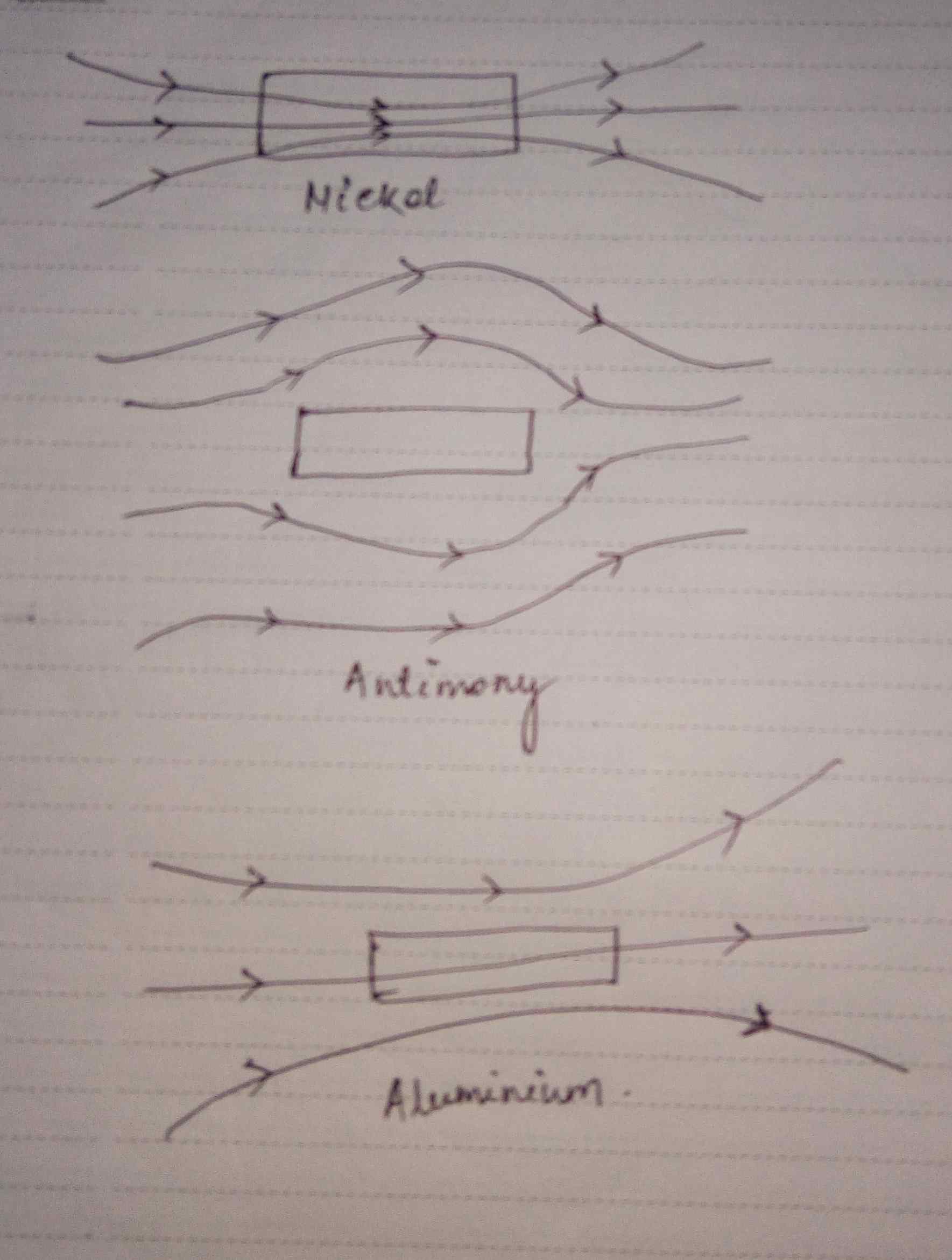
Three identical specimens of a magnetic materials nickel, antimony and aluminium are kept in a non-uniform magnetic field. Draw the modification in the field line in each case. Justify your answer.
Discuss the special properties of ferromagnetic materials.
Write two examples of ferromagnetic substance.
What happens to ferromagnetic substance heated above Curie temperature?
What is the unit of ratio $$\dfrac {E}{H}$$?
Draw neat labelled diagrams of showing magnetic field with pencil only:
The individual plates composing the earth's crust are called________.
Column II gives approximate values of magnetic field due to source given in column I
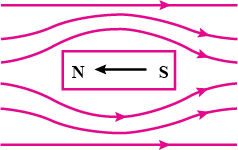
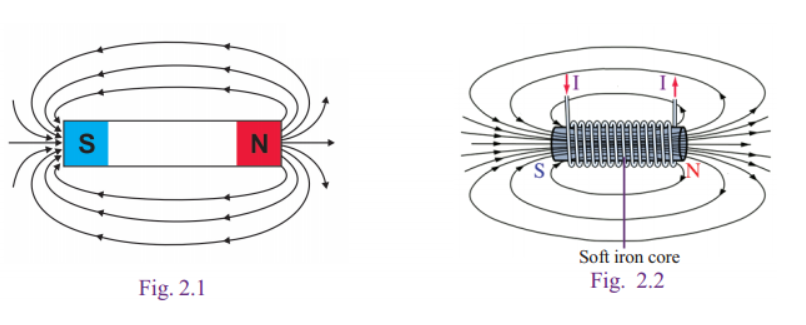
Why does a magnetic compass needle pointing North and South in the absence of a nearby magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of force concept :
State two differences between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet.
A short bar magnet placed in a horizontal plane has its axis aligned along the magnetic north-south direction. Null points are found on the axis of the magnet at 14 cm from the centre of the magnet. The earth's magnetic field at the place is 0.36 G and the angle of dip is zero. What is the total magnetic field on the normal bisector of the magnet at the same distance as the null-point (i.e., 14 cm) from the centre of the magnet? (At null points, field due to a magnet is equal and opposite to the horizontal component of earth's magnetic field.)
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetising field) when cooled?
(b) Why is diamagnetism, in contrast, almost independent of temperature?
(c) If a toroid uses bismuth for its core, will the field in the core be (slightly) greater or (slightly) less than when the core is empty?
(d) Is the permeability of a ferromagnetic material independent of the magnetic field? If not, is it more for lower or higher fields?
(e) Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
(f) Would the maximum possible magnetisation of a paramagnetic sample be of the same order of magnitude as the magnetisation of a ferromagnet?
Answer the following questions:
(a) Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
(b) The hysteresis loop of a soft iron piece has a much smaller area than that of a carbon steel piece. If the material is to go through repeated cycles of magnetisation, which piece will dissipate greater heat energy?
(c) 'A system displaying a hysteresis loop such as a ferromagnet, is a device for storing memory? Explain the meaning of this statement.
(d) What kind of ferromagnetic material is used for coating magnetic tapes in a cassette player, or for building 'memory stores' in a modern computer?
(e) A certain region of space is to be shielded from magnetic fields. Suggest a method.
If the bar magnet is turned around by $$180^{o}$$, where will the new null points be located?
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of
(i) paramagnetic and
(ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature?
Show diagramatically the behavior of magnetic field lines in the presence of (i) paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature.
Distinguish between 'paramagnetic' and 'ferromagnetic' substances.
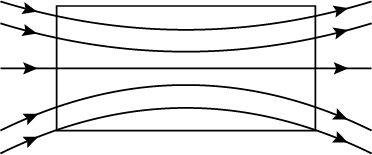
The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
At a certain temperature, a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic. What is this temperature called?
State the characteristics of the magnetic lines of force.
Explain the term hysteresis.
What are the changes observed at the transition temperature in superconductors?
Draw the variation of magnetic field (B) with magnetic intensity (H) when a ferromagnetic material is subjected to a cycle of magnetisation.
Write three properties of ferromagnetic materials.
Write two properties of a material suitable for making (a) a permanent magnet, and (b) an electromagnet.
Define transition temperature.
Write three difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substances.
Why do the lines of the magnetic field not cross each other?
Depending on the magnetic property, the materials are classified in to diamagnetic, paramagnetic and ferro magnetic. The behaviour of magnetic field lines near a magnetic substance is shown in the figure. Which material corresponds to the figure.
Compare the magnetic properties of diamagnetic ,paramagnetic and ferro magnetic substance.
What we have learnt about heating effect of electric current. In studied about magnets and magnetic lines of force .
Give the characteristics of magnetic field lines.
Explain ferromagnetism on the basis of domain theory?
Why don't two magnetic lines of force intersect with each other?
Mention the desired properties of magnetic materials used in making electromagnets.
List the factors on which the strength of magnetic field produced by
(a) a current-carrying straight conductor
(b) current carrying solenoid depends.
List the properties of magnetic lines of force
Explain the following:
(i) Why do magnetic lines of force form continuous closed loops?
(ii) Why are the field lines repelled (expelled) when a diamagnetic material is placed in an external uniform magnetic field?
Draw the diagram for the diamagnetic liquid kept in watch glass shows a rise in the middle..
Write SI unit of magnetic dipole moment.
What are diamagnetic substances?
Suppose we want to verify the analogy between electrostatic and magnetostatic by an explicit experiment. Consider the motion of
(i) electric dipole $$ \underset{p}{\rightarrow } $$ in an electrostatic field $$ \underset{E}{\rightarrow } $$ and (iii) magnetic dipole $$ \underset{m}{\rightarrow } $$ in a magnetic field. $$ \underset{B}{\rightarrow } $$. Write down a set of conditions on $$ \underset{E}{\rightarrow } $$, $$ \underset{B}{\rightarrow } $$, $$ \underset{p}{\rightarrow } $$, $$ \underset{m}{\rightarrow } $$ so that the two motions are verified to be identical. (Assume identical initial conditions. )
Describe an experiment to show that the maximum attractive property is at the poles of a magnet.
What is meant by the directional property of magnets?
Fill in the blanks
Rough handling destroys the ______ properties of a magnet.
The perpendicular bisector of the line joining the two poles of a magnet is called ________.
The north pole of the imaginary magnet of the earth is near the geographic ________ pole.
State three ways of demagnetizing a magnet.
You are provided with two similar bars, one is a magnet and the other is a soft iron bar. How will you distinguish between them without the use of any other magnet or bar?
[Hint: A magnet when suspended freely will rest only in north-south direction, but soft iron bar will rest in any direction]
Explain: When two pins are hung by their heads from the same pole of a magnet, their pointed ends move apart.
Mention two properties of magnetic field lines.
Explain: Several soft iron pins can cling, one below the other, from the pole of a magnet.
Can two magnetic field lines intersect each other? Give reason to your answer.
Sketch four magnetic field lines as obtained in a limited space on a horizontal plane in the earths magnetic field alone.
Name the magnetic substance whose nature does not change by changing the normal temperature.
What is magnetic hysteresis?
The magnetic susceptibility of substance is $$-0.085.$$What type of substance this is?
Write Curie-Weiss law and what is Curie temperature for iron?
Why soft iron is used in making electromagnet?
What do you mean by magnetic hysteresis curve ? Draw hysteresis curve and define terms related to it.
How will you select materials for making electromagnets and permanent magnets ? Write the uses also.
What is Gauss's law in magnetism? What does it represent?
What are the uses of hysteresis curve?
Explain paramagnetism and specify its characteristics. Write five differences between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substance.
What is Curie temperature ? How magnetic susceptibility of dia, para and ferro magnetic substances depend on temperature ? Explain and write essential law for it.
Magnetic lines of force form closed curve. Why?
Answer the following :
The earth's field departs from its dipole shape substantially at large distances (greater than about 30,000 km). What agencies may be responsible for this distortion?
What does the hysteresis loop represent?
Discuss the Curie law for paramagnetic material.
What does the paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation ( for the same magnetising field ) when cooled ?
Which property of soft iron makes it useful for preparing electromagnet?
The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is $$ X $$ at $$ 27^o C $$. At what temperature is susceptibility be $$ X/3 $$?
What happens to a ferromagnetic material when its temperature increases above curie temperature?
Write any two properties of a magnet .
Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
Why is diamagnetism, in contrast, almost independent of temperature?
Is the permeability of a ferromagnetic material independent of the magnetic field? If not, is it more for lower or higher fields?
Observe the depiction of magnetic fields of two types of magnets.
How can you find out the polarity of these magnets using a magnetic compass ?
Would the maximum possible magnetisation of a paramagnetic sample be of the same order of magnitude as the magnetisation of a ferromagnet?
In which direction does a suspended magnet come to rest ?
Two short bar magnets with magnetic moments 400 ab-amp $$cm^2$$ and 800 ab-amp $$cm^2$$ are placed with their axis in the same straight line with similar poles facing each other and with their centres at 20 cm from each other. Find the force of repulsion.
State any two advantages of electromagnets over permanent magnets.
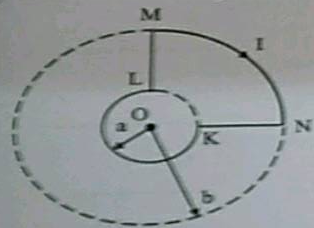
Calculate the magnetic field at the point O of a loop with current $$i$$ whose shape is as shown in the figure.
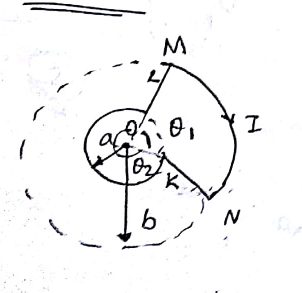
A short bar magnet of magnetic moment $$5.5\times 10^{-2}JT^{-1}$$ is placed with its axis perpendicular to the earth's field direction. At what distance from the centre of the magnet, the resultant field is inclined at $$45^0$$ with earth's field on (a) its normal bisector and (b) its axis. Magnitude of the earth's field at the place is given to be $$0.42G$$. Ignore the length of the magnet in comparison to the distance involved.
A telephone cable at a place has four long straight horizontal wires carrying a current of 1.0 A in the same direction east to west. The earth's magnetic field at the place is 0.39 G, and the angle of dip is 35∘35∘ .The magnetic declination is nearly zero. What are the resultant magnetic fields at points 4.0 cm below the cable?
The susceptibility of magnetic material is $$ - 4.2 \times 10^{-6} $$ . Name the type of magnetic material it represents.
How does the magnetic energy resembles with the electrostatic energy stored in a capacitor?
What are magnetic field lines? How is the direction of magnetic field at a point in a magnetic field determined using field lines?
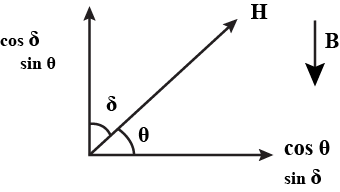
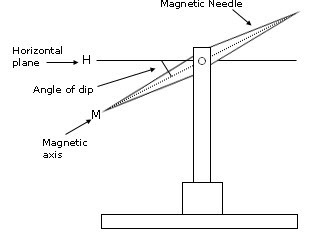
Explain the magnetic elements of the earth's magnetic field.
Write on expression for vector from of magnetic force on a moving charge.
Explain an analogy between magnetic dipole moment $$M$$ of circular current loop and electric dipole moment $$P$$ of electric dipole.
What is magnetic dipole? Derive an expression for magnetic field intensity at a point on the equatorial tine of a bur magnet.
What is the value of magnetic field within a hollow sphere made of ferromagnetic substance? Hence explain magneto static shielding..
The figure gives the magnetization curve for a paramagnetic material. The vertical axis scale is set by $$a = 0.15$$, and the horizontal axis scale is set by $$b = 0.2$$ T/K. Let $$\mu_{sam}$$ be the measured net magnetic moment of a sample of the material and $$\mu_{max}$$ be the maximum possible net magnetic moment of that sample.According to Curie’s law, what would be the ratio $$\mu_{sam}/\mu_{max}$$ were the sample placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude $$0.800$$ T, at a temperature of $$2.00$$ K?
A $$0.50$$ T magnetic field is applied to a paramagnetic gas
whose atoms have an intrinsic magnetic dipole moment of $$1.0 \times 10^{-23} \, J/T$$. At what temperature will the mean kinetic energy of
translation of the atoms equal the energy required to reverse such
a dipole end for end in this magnetic field?
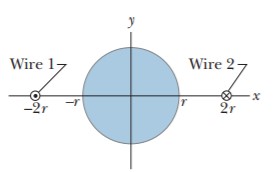
Two wires, parallel to the z-axis and a distance $$4r$$ apart, carry equal currents i in opposite directions, as shown in Figure. A circular cylinder of radius r and length L has its axis on the z-axis, midway between the wires. Use Gauss’ law for magnetism to derive an expression for the net outward magnetic flux through the half of the cylindrical surface above the x-axis. (Hint: Find the flux through the portion of the xz plane that lies within the cylinder.)
What are magnetic field lines? How is the direction of a magnetic field at a point determined? Mention two important properties of magnetic field lines.
The saturation magnetization $$M_{max}$$ of the ferromagnetic metal nickel is $$4.70 \times 10^5\, A/m$$. Calculate the magnetic dipole moment of a single nickel atom. (The density of nickel is $$8.90\, g/cm^3$$ and its molar mass is $$58.71\, g/mol$$.)
The exchange coupling mentioned in Module as being responsible for ferromagnetism is not the mutual magnetic interaction between two elementary magnetic dipoles. To show this, calculate (a) the magnitude of the magnetic field a distance of $$10$$ nm away, along the dipole axis, from an atom with magnetic dipole moment $$1.5 \times 10^{-23} J/T$$ (cobalt), and (b) the minimum energy required to turn a second identical dipole end for end in this field. (c) By comparing the latter with the mean translational the kinetic energy of $$0.040\, eV$$, what can you conclude?
In what way is Gauss's law in magnetism different from that used in
electrostatics? Explain briefly.
The Earth's magnetic field at the Equator is approximately $$0.4\ G$$.Estimate the Earth's magnetic dipole moment. Given: Radius of the Earth$$=6400\ km$$.
What is the circulation of magnetic field? Explain
Ampres Law(30)
Niobium metal becomes a superconductor when cooled below $$9 \,K$$. Its super conductivity is destroyed when the surface magnetic field exceeds $$0.100 \,T$$. In the absence of any external magnetic field, determine the maximum current a $$2.00$$-mm-diameter niobium wire can carry and remain superconducting.
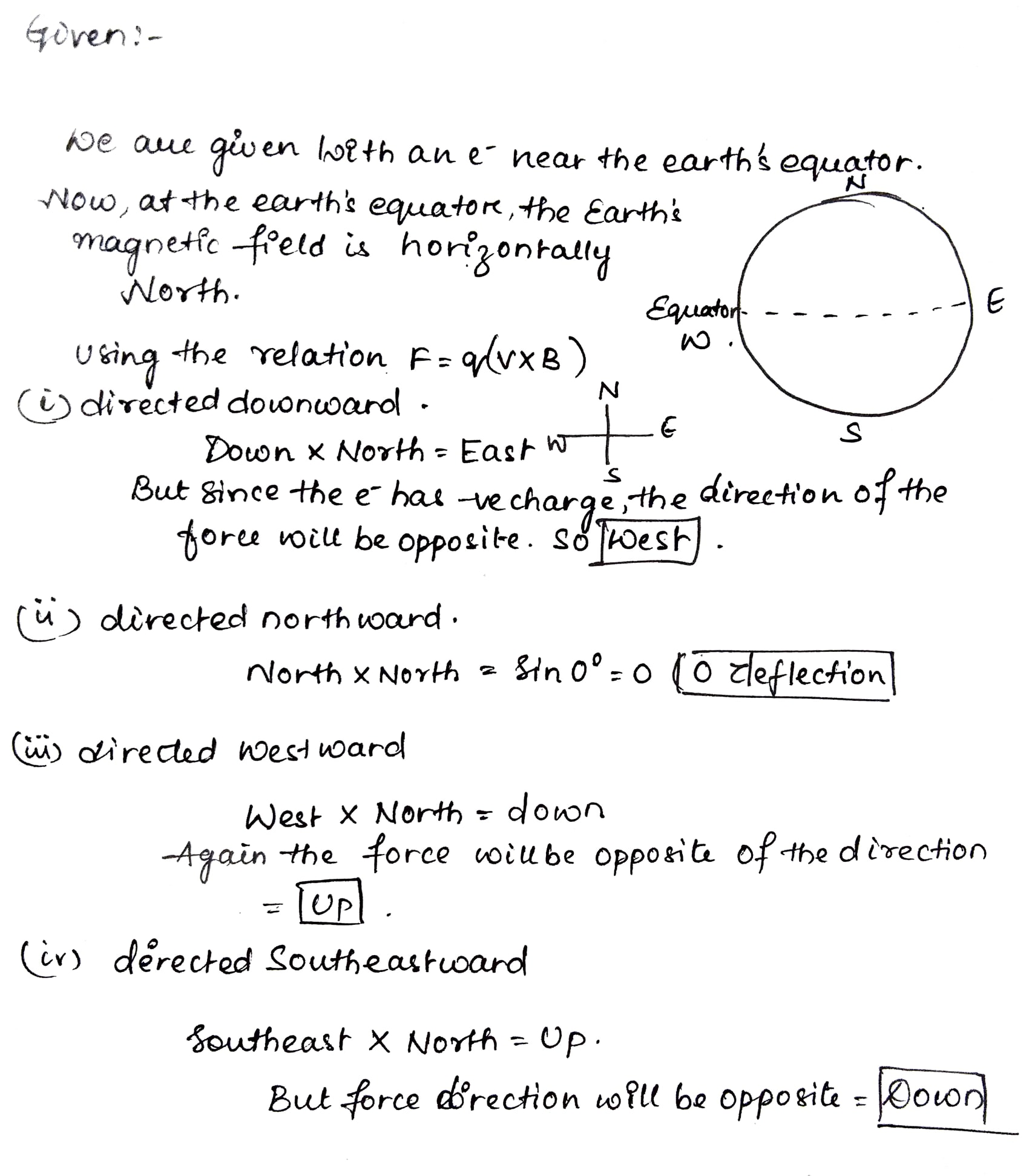
Analysis Model: Particle in a Field (Magnetic)(4)
Consider an electron near the Earths equator. In which direction does it tend to deflect if its velocity is
(a) directed downward?
(b) Directed northward?
(c) Directed westward?
(d) Directed southeastward?
Class 12 Medical Physics Extra Questions
- Alternating Current Extra Questions
- Atoms Extra Questions
- Current Electricity Extra Questions
- Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter Extra Questions
- Electric Charges And Fields Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Induction Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Waves Extra Questions
- Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Extra Questions
- Magnetism And Matter Extra Questions
- Moving Charges And Magnetism Extra Questions
- Nuclei Extra Questions
- Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Extra Questions
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices And Simple Circuits Extra Questions
- Wave Optics Extra Questions