Biotechnology: Principles And Processes - Class 12 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
Answer in 3 to 5 sentences:
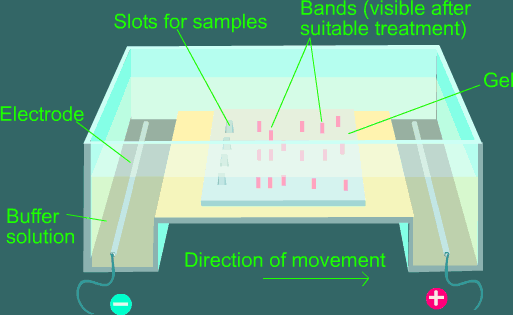
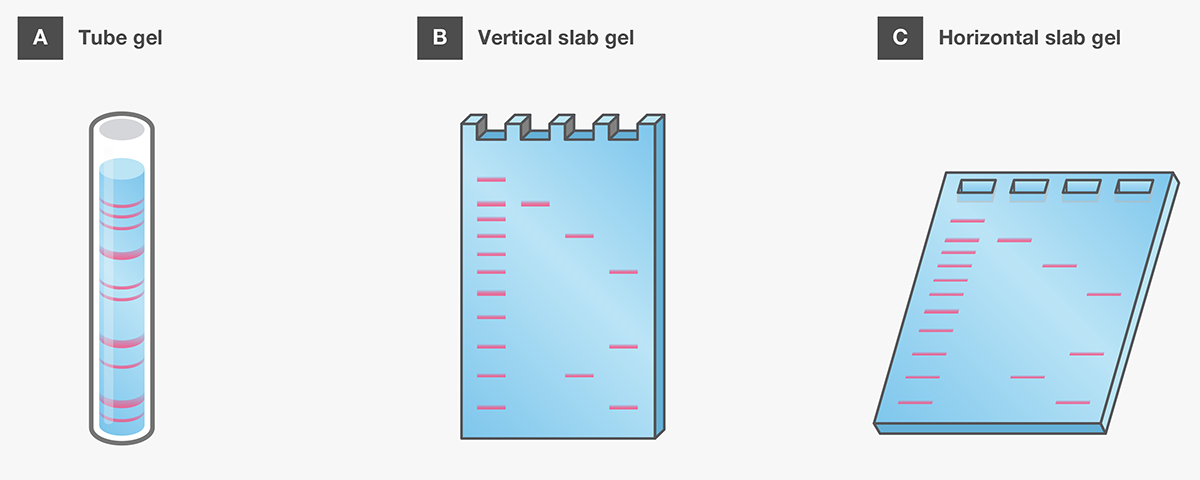
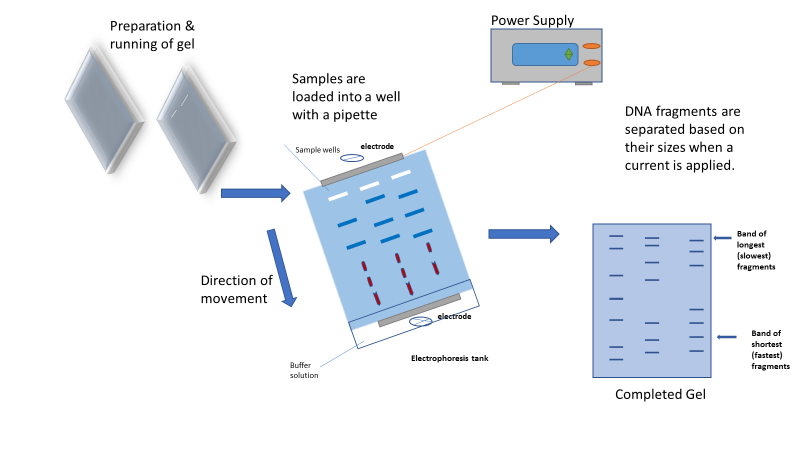
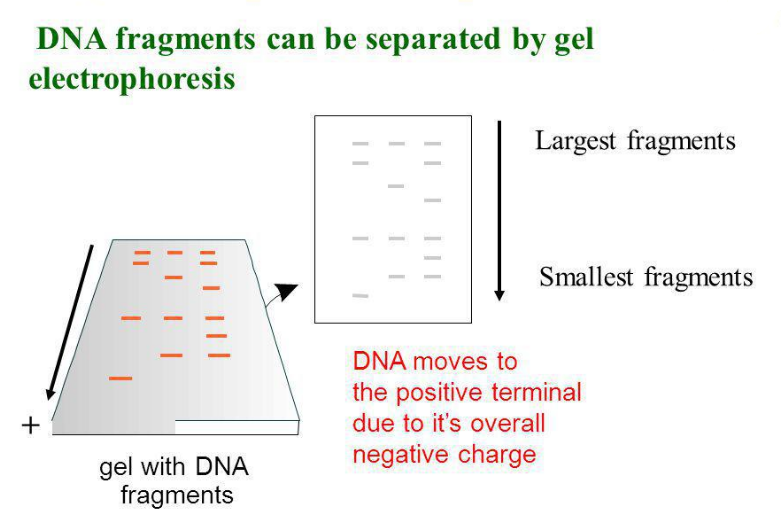
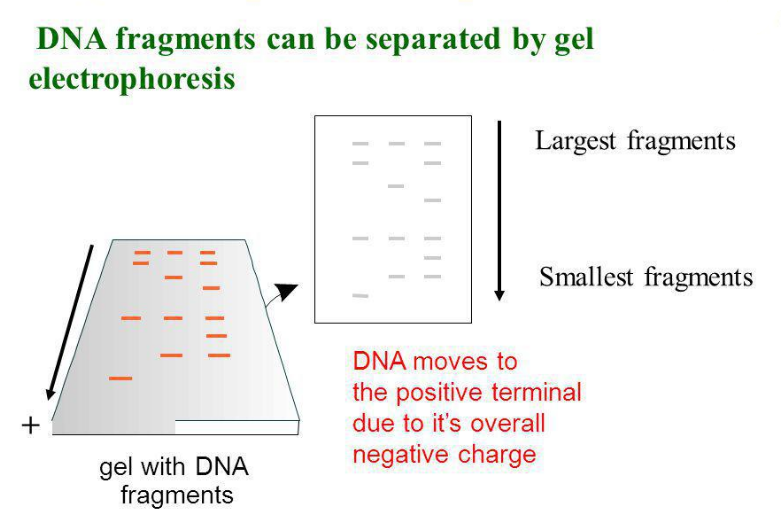
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a typical agarose gel electrophoresis.
Manipulating with nucleic acid is a trend in biotechnology.
(a) Name any one organism used as vector.
(b) What are DNA polymerase ?
How will you transfer a whole chromosome into a fertilized egg?
Name the bacterium that yields a thermostable DNA polymerase.
What is main function of gel electrophoresis?
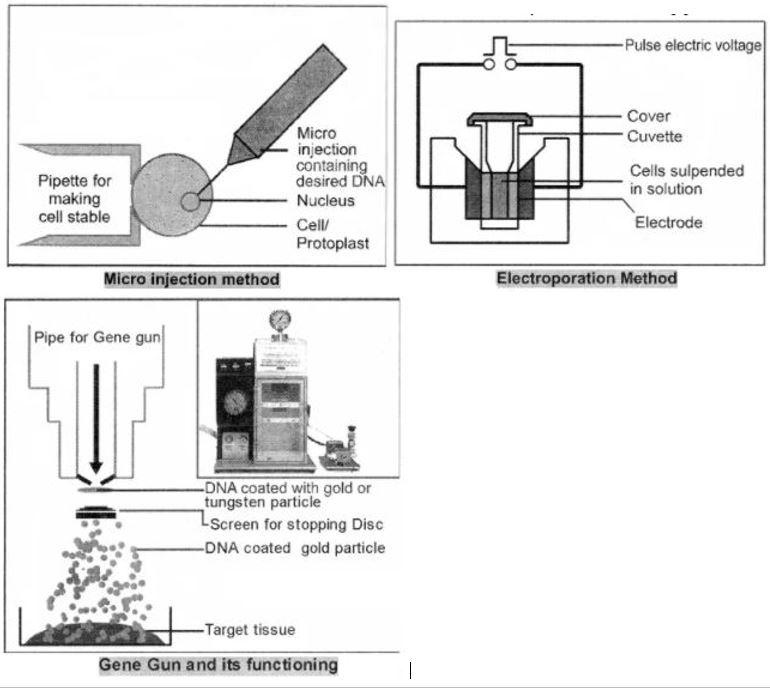
What is particle gun?
What chemical is used in vectorless gene transfer?
Which cloning vector was discovered for the first time?
Name an eukaryotic organism that has plasmids, and can be used as a host in gene cloning experiments.
What was the first recombinant DNA based product, produced and marketed in India?
What is called a 'probe'?
Name the compound used for staining the isolated DNA in the gel.
(a) Why must a cell be made 'competent' in biotechnology experiments? How does calcium ion help in doing so?
(b) State the role of biolistic gun in biotechnology experiments.
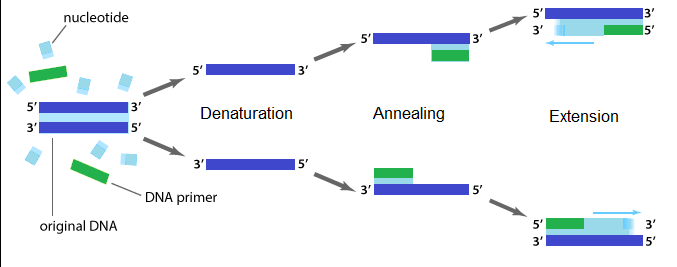
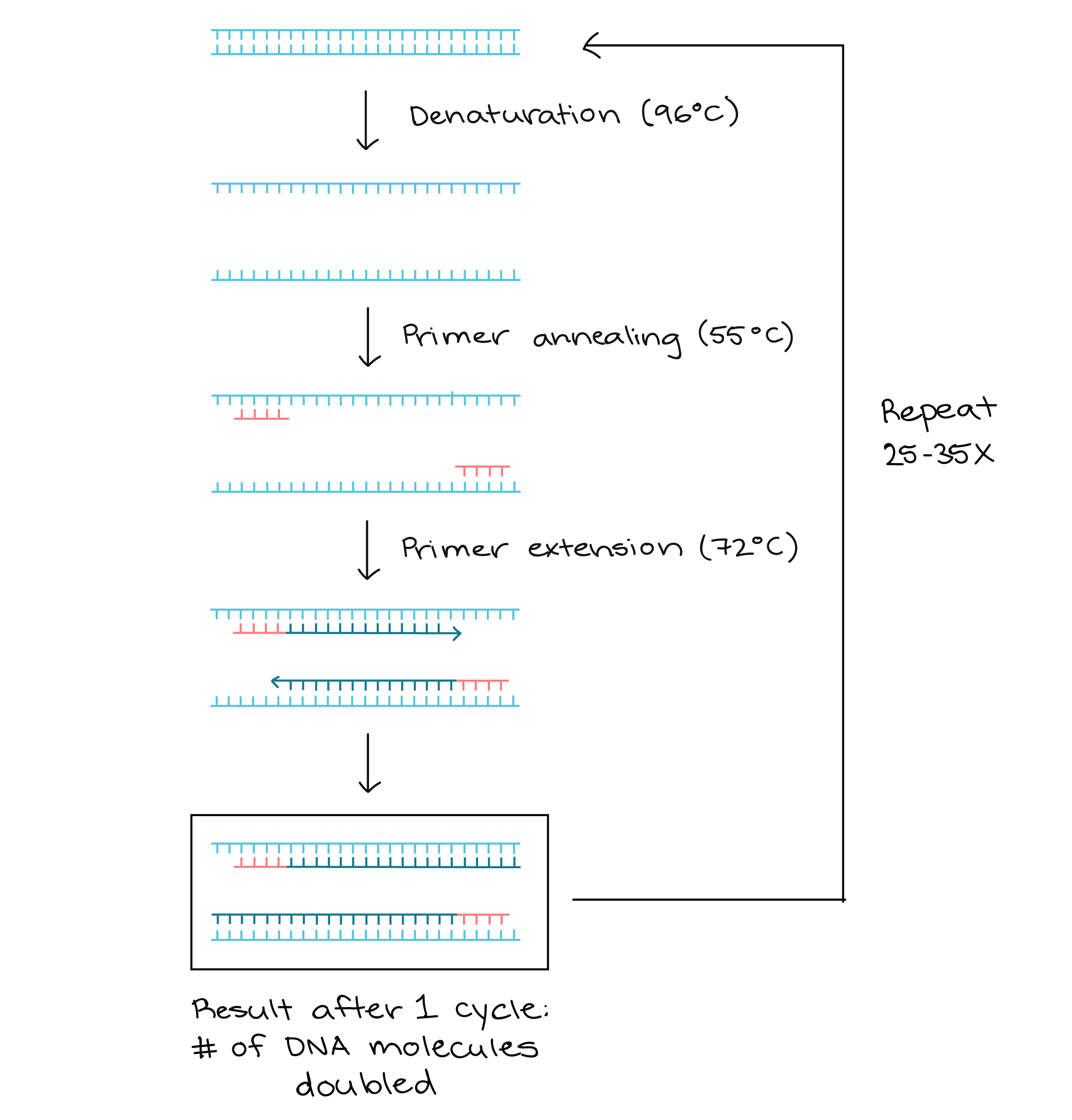
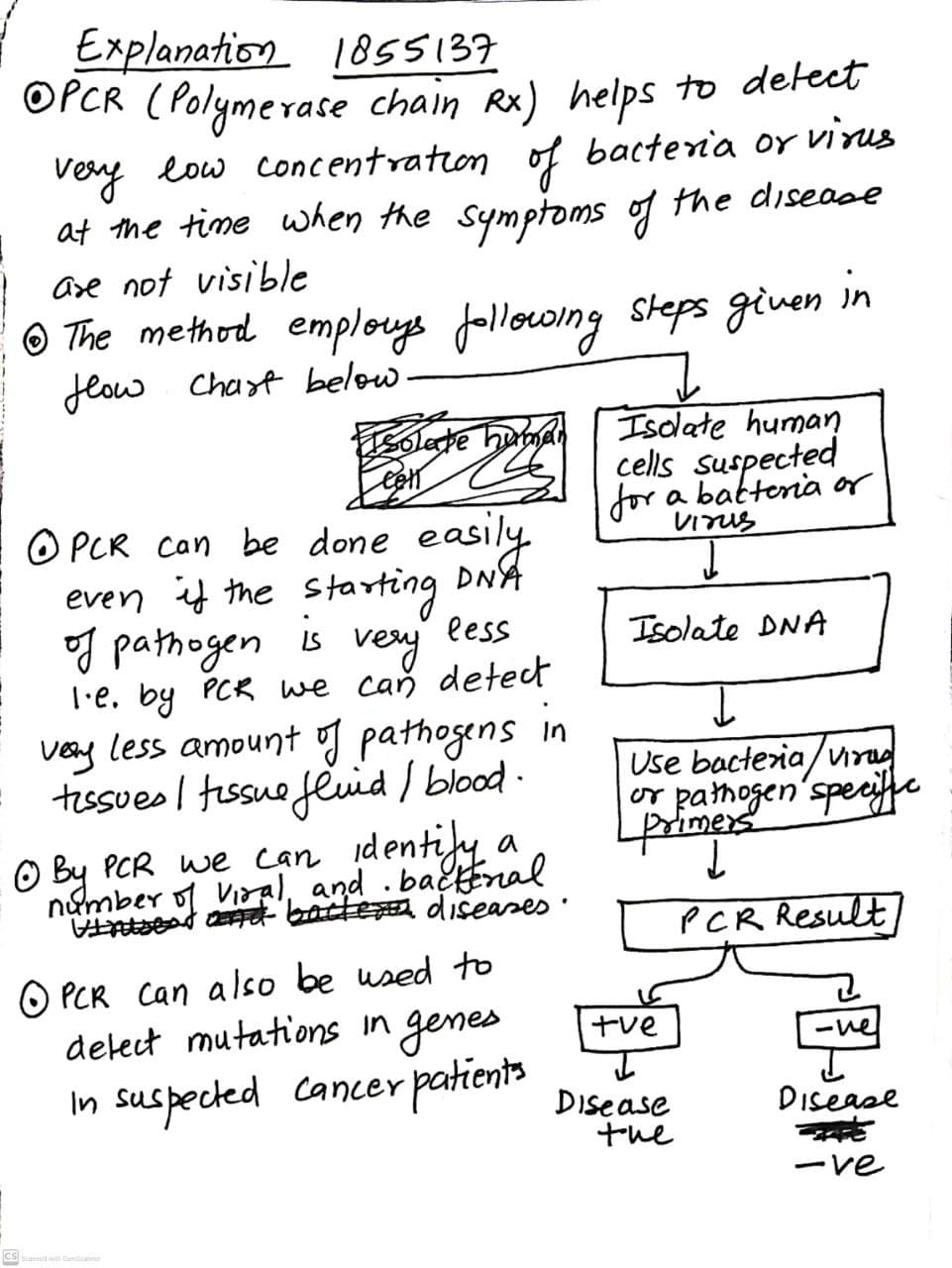
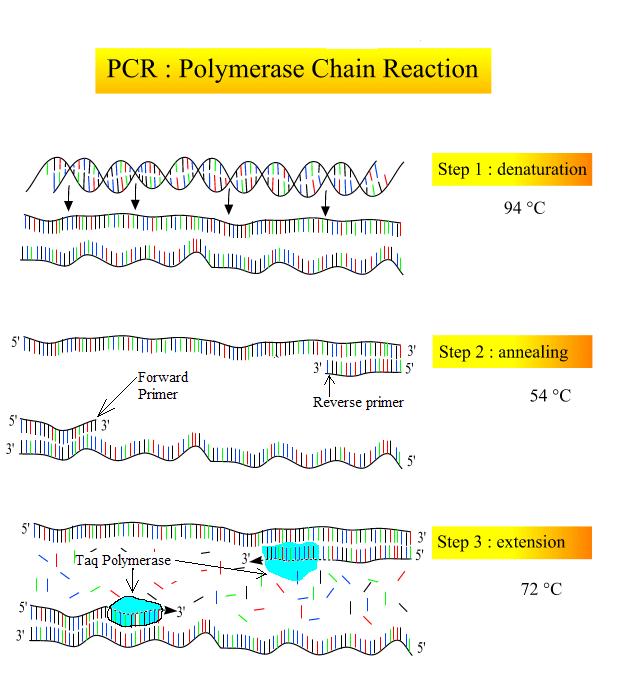
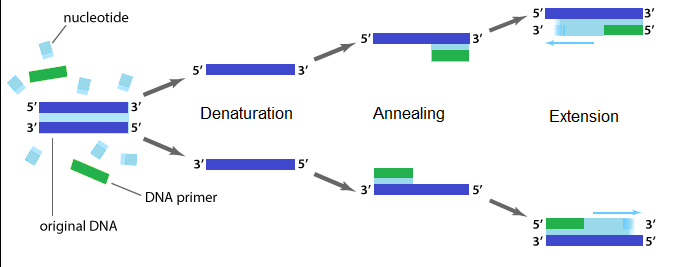
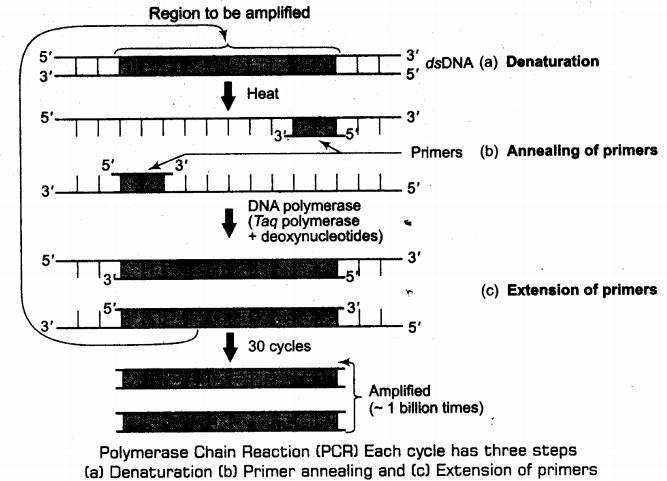
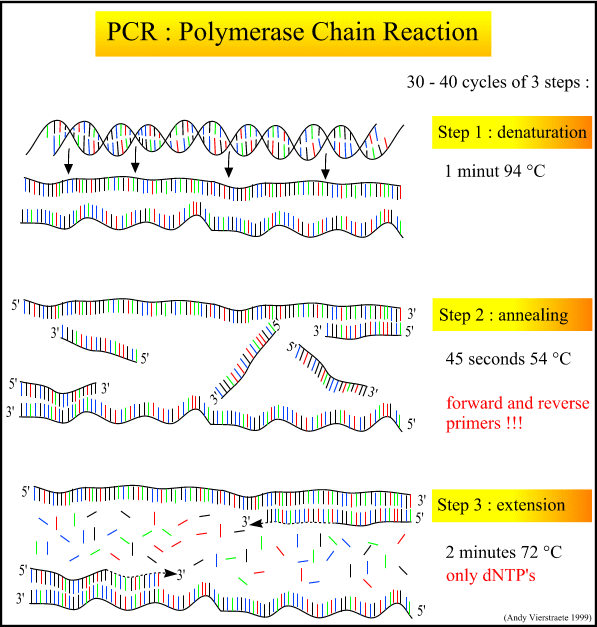
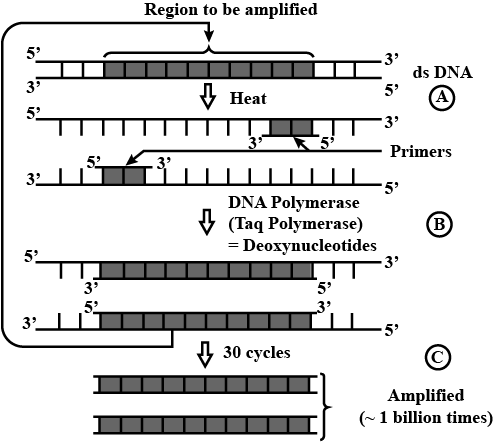
How is the amplification of a gene sample of interest carried out using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
Name the source organism that possesses Taq polymerase. What is so special about the function of this enzyme?
How does a restriction nucleases function? Explain.
Why is the enzyme cellulase needed for isolating genetic material from plant cells and not from the animal cells?
Expand the following and mention one application of each:
(i) PCR (ii) ELISA
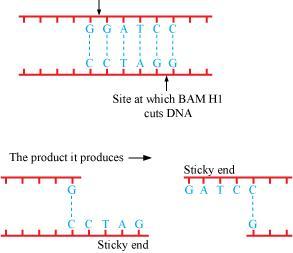
How are 'sticky ends' formed on a DNA strand? Why are they so called?
Explain with the help of a suitable example the naming of a restriction endonuclease.
Mention the type of host cells suitable for the gene guns to introduce an alien DNA.
Name and describe the technique that helps in separating the DNA fragments formed by the use of restriction endonuclease.
State the role of DNA ligase in biotechnology.
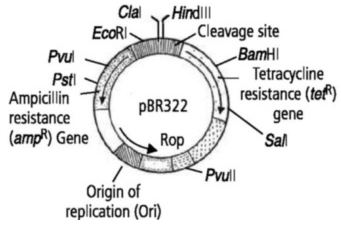
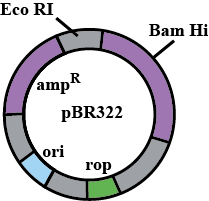
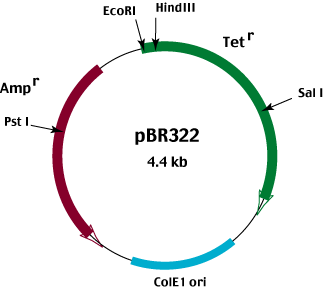
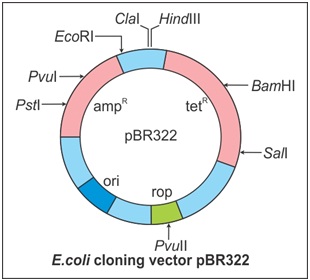
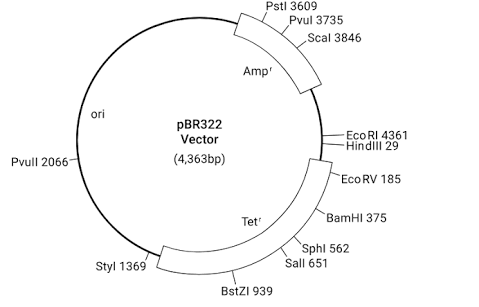
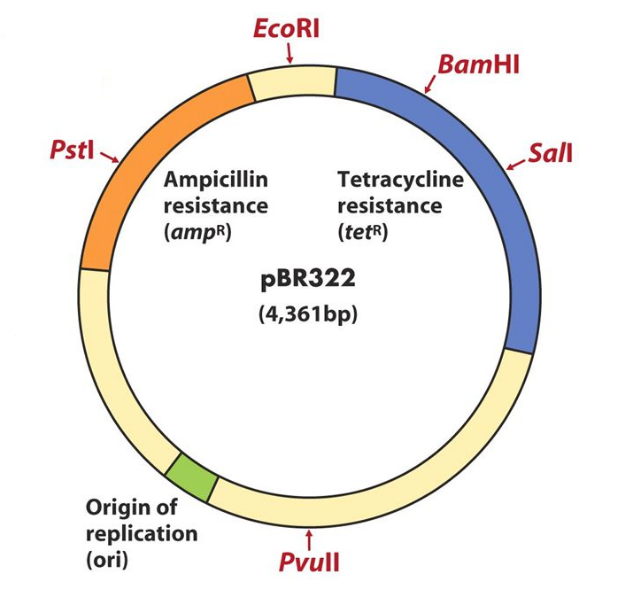
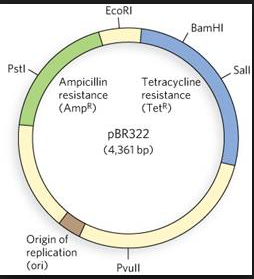
Draw a schematic sketch of pBR 322 plasmid and label the following in it.
(a) Any two restriction sites
(b) Ori and rop genes
(c) An antibiotic resistant gene
Make a chart(with diagrammatic representation) showing a restriction enzyme, the substrate DNA on which it acts, the site at which it cuts DNA and the product it produces.
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
Explain briefy.
(a) PCR
(b) Restriction enzymes and DNA
(c) Chitinase
Explain the use of Agrobacterium tumifaciens in gene cloning.
Give a brief account of the tools of recombinant DNA technology.
What is the name of the sequence of base pairs which reads same on the two strands of DNA when orientation of reading is kept same?
What is downstream processing?
How to produce viruses as effective vectors?
What is palindrome in DNA?
How does one visualize DNA on an agar gel?
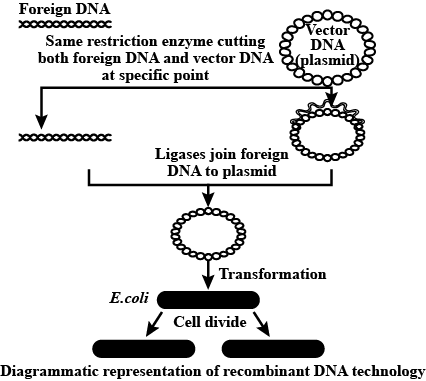
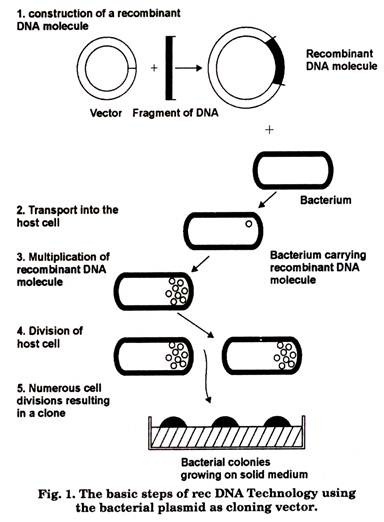
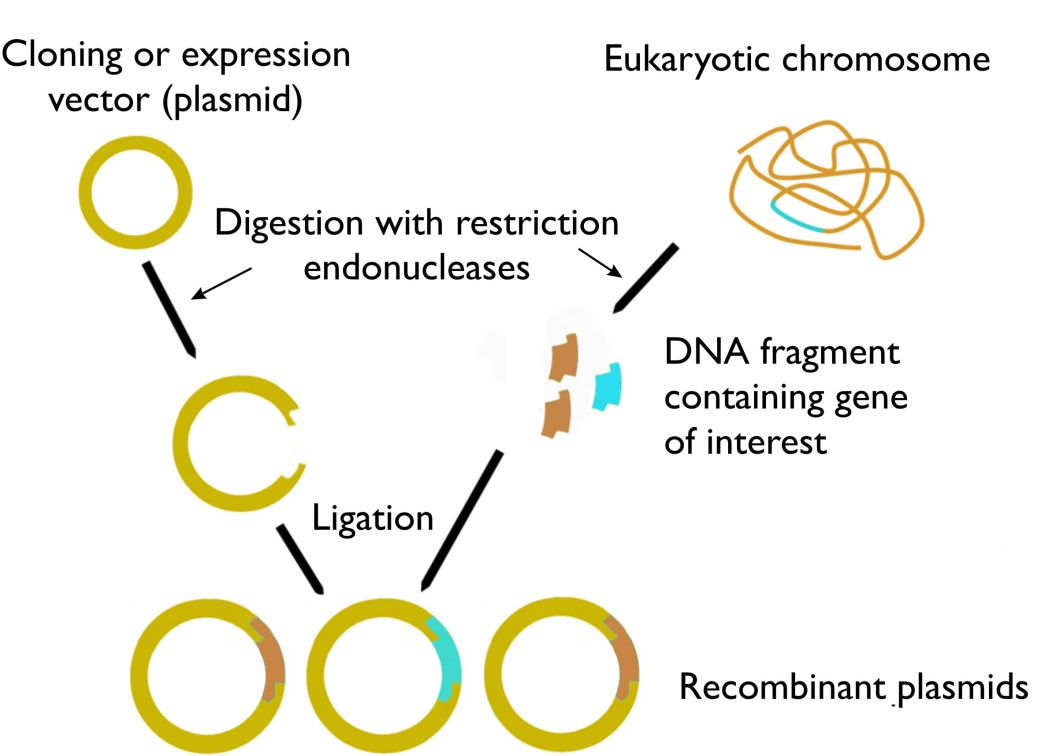
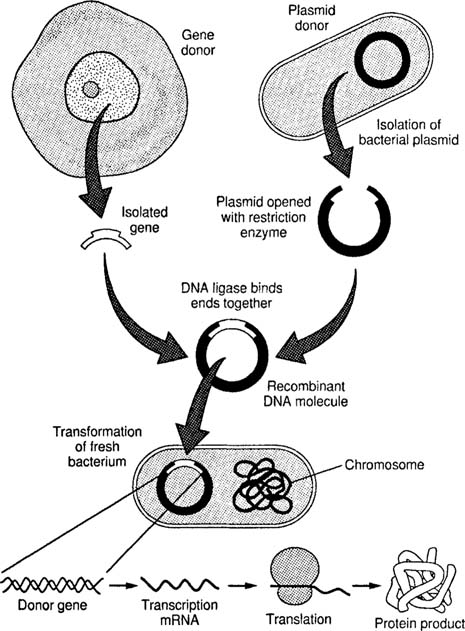
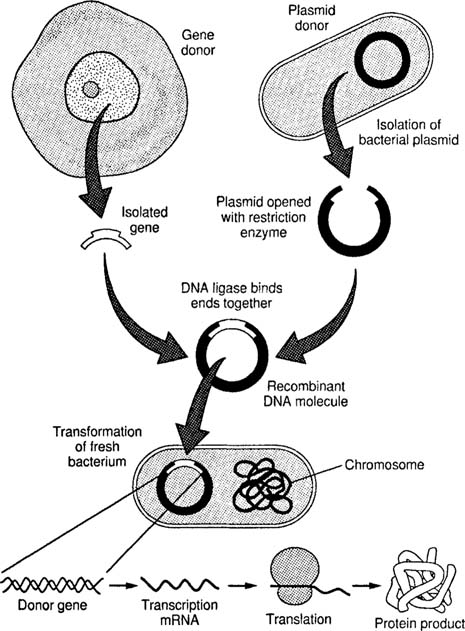
With the help of a neat and labelled diagram describe steps in recombinant DNA technology.
Explain the significance of 'palindromic nucleotide sequence' in the formation of recombinant DNA.
Expand 'YAC' and mention what was it used for.
Write the use of restriction endonuclease in the above process.
Figure representing the reactions associated with Polymer Chain Reaction (PCR).
Name the steps A, B, C in the progress.
Answer in 40 to 80 words:
Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA fragments.
Given an example of the source of thermostable enzyme DNA polymerase.
Use of a thermostable DNA polymerase from the bacterium, Thermus aquatics, made it possible to generate a billion copies of DNA in a very short time using a process. Name the process.
Define polymerase chain reaction.
Match the lists and find the correct option.
Name two commonly used vectors in genetic engineering.
Describe the steps of PCR technique.
Enlist the basic steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
List the key tools used in recombinant DNA technology.
Differentiate between-: Gene cloning and cell cloning
Very short answer type.
Selfing is a kind of inbreeding.
What are molecular scissors ? Give one example. Explain their role in recombinant DNA technology.
Do you know what palindromes are?
Write the methods to introduce foreign DNA into the host cells.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of PBR322.
"A very small sample of tissue or even a drop of blood can help determine paternity." Provide scientific explanation to substantiate the statement.
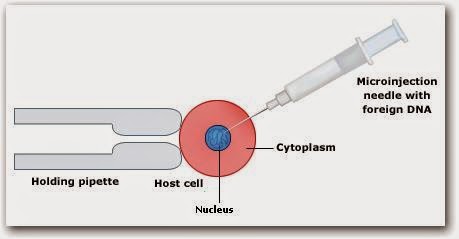
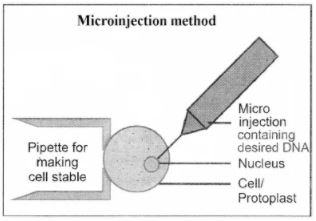
What is micro-injection?
Why is the enzyme cellulase used for isolating genetic material from plant cells but not for animal cells?
Describe briefly Chitinase.
Collect five examples of palindromic DNA sequences by consulting your teacher. Better try to create a palindromic sequence by following base pair rules.
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Why?
Distinguish between plasmid DNA and chromosomal DNA.
Explain briefly Restriction enzymes and DNA.
Draw a schematic sketch of pBR 322 plasmid and label Ori and rop genes.
What are palindromic nucleotide sequences?
Why is a thermostable DNA polymerase needed in amplification/genetic engineering?
What is elution in the process of separation of DNA fragments?
Who discovered enzyme DNA polymerase?
Which enzymes are used for releasing macromolecules (DNA) from cell envelope?
What are the two sets of primers needed for amplification of gene?
Draw a schematic sketch of pBR322 plasmid and label any two restriction sites.
What is the best method for separation of DNA fragments?
Name the scientists who generated first recombinant DNA molecules.
Expand PCR. Mention its importance in biotechnology.
How are restriction enzymes different from the topoisomerases functionally?
What were the two main discoveries that led to the birth of genetic engineering?
How does restriction endonuclease function.
Why must a cell be made 'competent' in biotechnology experiments? How does calcium ion help in doing so?
How is the amplification of gene sample of interest carried out using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) ?
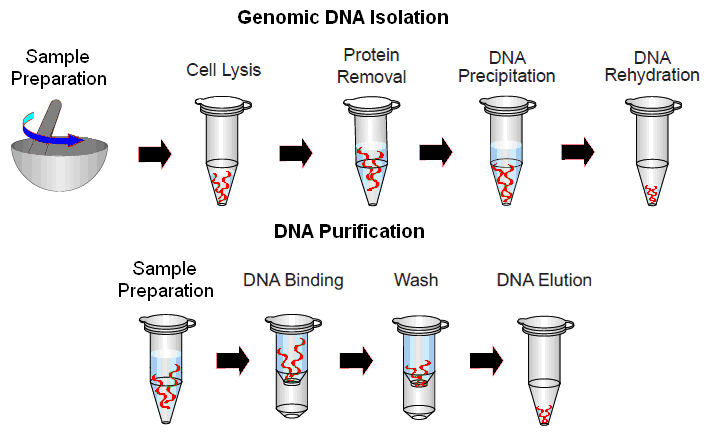
How is DNA isolated from prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
What are the functions of the enzymes isolated by Stewart Linn and Werner Arber?
State the role of 'biolistic gun' in biotechnology experiments.
Draw a schematic sketch of pBR 322 plasmid and label an antibiotic-resistant gene.
What is PCR?
Pathogen of which disease is best detected by PCR?
What are the molecular scissors?
Why DNA cannot pass through the cell membrane? Explain. How is a bacterial cell made "competent" to take up recombinant DNA from the medium?
Who invented it?
Name the technique used for separation of DNA fragments.
What are the properties of ideal cloning vectors?
PCR Machine/thermal cycler for PCR
In rDNA technology restriction endonucleases play a very important role. Give in brief its role in r- DNA technology.
What is DNA libraries?
How does one visualise DNA on an agarose gel?
Explain the isolation of genomic (chromosomal) DNA (from bacteria/plant cell/ animal cell, by cell lysis).
A plasmid without a selectable marker was chosen as vector for cloning a gene. How does this affect the experiment?
Explain the vector pBR 322 with neat labelled diagram.
A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in an agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed. What could be the reason?
Explain the isolation of gene of interest(by electrophoresis).
What is gel electrophoresis?
Describe selection and selfing of superior recombinants.
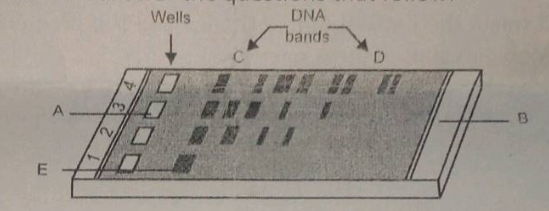
Why DNA has fragments in band 'D' moved farther away in comparison to those in band 'C'?
Explain the three steps involved in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction.
Name the substance used as the medium / matrix in gel electrophoresis. Mention its source.
With help of diagram explain plasmid BR322.
What is gel electrophoresis ? Explain how DNA fragments are separated and detected using this.
___________ is the revolutionary event in biotechnology after cloning.
Write the two components of the first artificial recombinant DNA molecule constructed by Cohen and Boyer.
What are plasmids ? Mention any two features of an ideal plasmid.
What is meant by gene gun method?
Give reasons for the following:
Restriction enzymes are called chemical scalpels.
Describe the steps in rDNA technology.
Write any four ways used to introduce a desired DNA segment into a bacterial cell in recombined technology experiments.
Which of the following is not component of yeast artificial chromosome?
A. What is the role of Cry I Ac, Cry IIAb and Cry I Ab?
B. (i) Write the sequence of restriction site of EcoRI and give the sequence of sticky ends after EcoRI digestion (ii) Name the source of EcoRI restriction enzyme
Given is the diagram of agarose gel kept under UV light.
How are the separated DNA fragments finally isolated?
Explain how rDNA gets introduced into a plant cell.
Mention two uses of cloning vectors.
Mention the significance of Gel-electrophoresis in r-DNA technology.
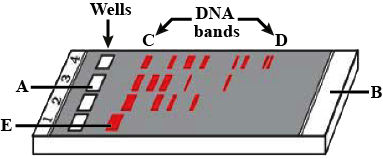
Study the diagram given and answer the question.
What does E represent in the diagram?
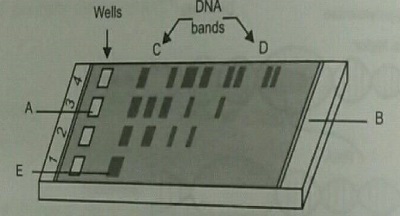
Name two commonly used vectors in rDNA technology.
Study the diagram given and answer the question.
Why have DNA fragments in band 'D' moved farther away in comparison to those in band 'C'.
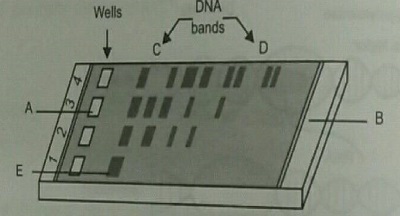
Study the diagram given and answer the question.
Identify the anode end in the diagram.
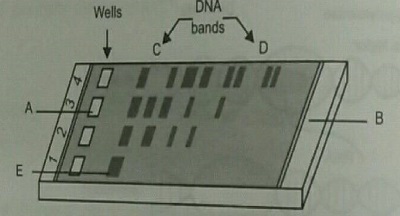
Restriction enzymes are considered as a type of endonuclease. Why?
REN are called as molecular scissors. Why?
Give brief account of replication of bacteriophages.
What are molecular scissors? Where are they obtained from?
Describe the steps that constitute one cycle of reactions in PCR.
Define PCR.
Expand PCR. How it helps in amplification of gene of interest ?
Name the vectors which can be used for transfer of genes to plant and animal cell?
Explain any two methods for introduction of recombinant DNA into host cell.
'The basis of genetic engineering is the discovery of the fact that genes can be cut and joined with the help of enzymes."
a. Name the enzyme used for cutting genes.
b. Name the enzyme used for joining the genes.
Describe the process of amplification of ''gene of interest '' using PCR technique.
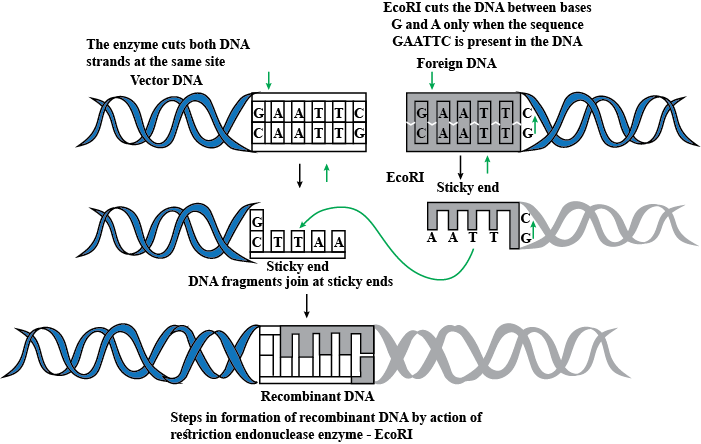
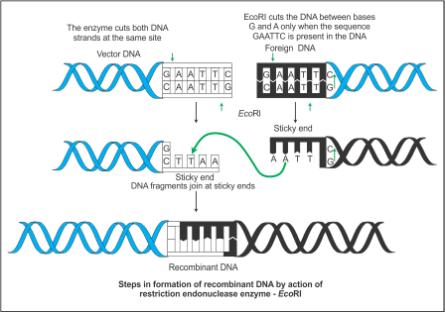
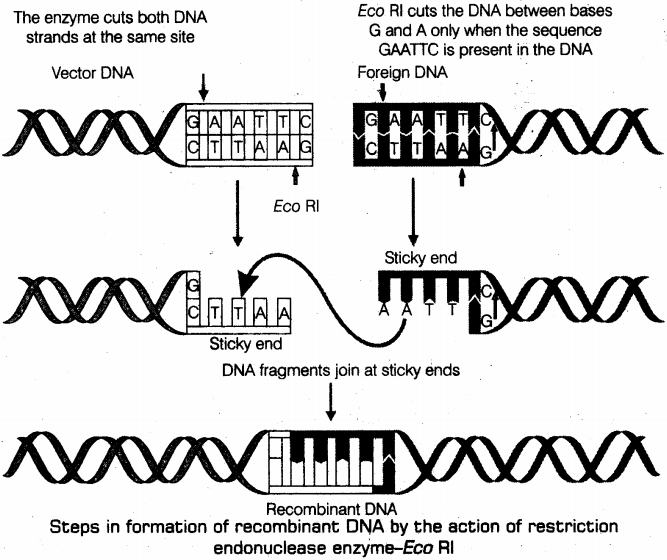
Describe the formation of recombinant DNA by the action of EcoRI.
Mention application of PCR in the field of Biotechnology
Write the palindromic nucleotide sequence EcoRI recognises.
Observe the table in which size of different DNA fragments are given and answer the questions:
| DNA fragments | A | B | C |
| Size (in Base Pairs) | 700 | 1500 | 3000 |
"DNA copies generated will be similar, but may not be identical to the original." Explain.
Observe the table in which size of different DNA fragments are given and answer the questions:
| DNA fragments | A | B | C |
| Size (in Base Pairs) | 700 | 1500 | 3000 |
Mention application of PCR in the field of Diagnostics
All cloning vectors do have a 'selectable marker'. Describe its role in recombinant DNA-technology.
Draw the vector DNA and a foreign DNA showing the sites where EcoRI has acted to form the sticky ends.
What is the source organism for EcoR1, restriction endonuclease?
What does 'competent' refer to in competent cells used in transformation experiments?
While doing a PCR, 'denaturation' step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
What is the significance of adding proteases at the time of isolation of genetic material (DNA).
Restriction enzymes should not have more than one site of action in the cloning site of a vector. Comment.
A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in an agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed. What could be the reason?
Restriction enzymes that are used in the construction of recombinant DNA are endonucleases which cut the DNA at 'specific-recognition sequence'. What would be the disadvantage if they do not cut the DNA at specific-recognition sequence?
Taking examples under each category, discuss upstream and downstream processing.
When a foreign DNA is introduced into an organism, how is it maintained in the host and how is it transferred to the progeny of the organism?
Who is credited for developing the recombinant DNA Technique (RDT)?
How does one visualise DNA on an agarose gel?
What is meant by gene cloning?
A plasmid without a selectable marker was chosen as vector for cloning a gene. How does this affect the experiment?
Describe the role CaCl2 of in the preparation of competent cells?
PCR is a useful tool for early diagnosis of an infectious disease. Elaborate.
What are Cosmids?
What do you understand by molecular probes? Explain its utility.
What are cloning vectors?
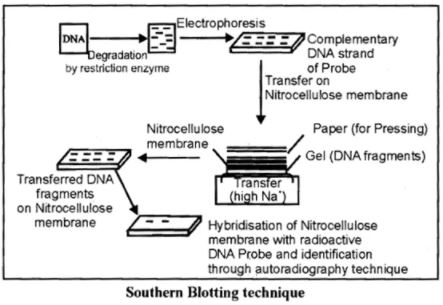
Describe different blotting techniques in detail.
Define the restriction endonuclease enzyme.
Write the names of any three methods of direct gene transfer.
Write a short note on the importance of Bacteriophage as a clonal vector.
Name the gels used in the gel electrophoresis technique.
Define recombinant DNA technology?
What do you understand by indirect gene transfer?
Explain the microinjection technique of gene transfer.
Write an illustrated account of physical methods of gene transfer.
What is accomplished during PCR amplification?
These are important set of enzymes used in biotechnology. Match them with their exact role.
(a) Tobacco plants are damaged severely when infested with Meloidogyne incognita. Name and explain the strategy that is adopted to stop this infestation.
(b) Name the vector used for introducing the nematode specific gene in the tobacco plant.
Rearrange the following in the current sequences to accomplish an important biotechnological reaction.
(a) In vitro synthesis of copies of DNA of interest
(b) Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides
(c) Enzyme DNA-polymerase
(d) Complementary region of DNA
(e) Genomic DNA template
(f) Nucleotides provided
(g) Primers
(h) Thermostable DNA-polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus)
(i) Denaturation of ds-DNA
Can you think and answer how a reporter enzyme can be used to monitor transformation of host cells by foreign DNA in addition to a selectable marker?
Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Explain in detail the role of restriction endonuclease in formation of recombinant DNA. Draw a labelled diagram of E.Coli cloning vector pBR 322.
What do you mean by fermentors?
Write the name of the technique, by which DNA fragments can be separated.
Given an account of artificial chromosomes in transfer of genetic material.
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II and choose the correct answer.
Define r-DNA technology. Give the basic steps in r-DNA technology and give any three examples of the therapeutic products produced by r-DNA technology.
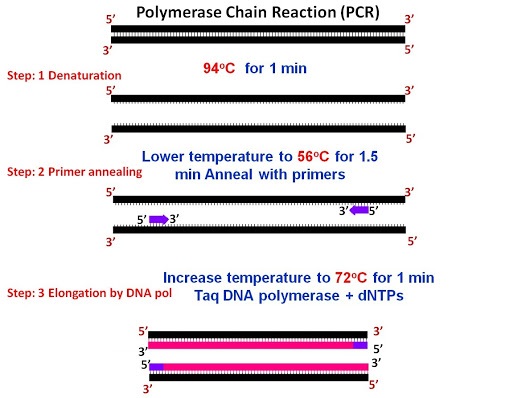
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing steps of PCR?
What is Recombinant D.N.A. ? Explain the process of separation and isolation of D.N.A fragment by gel electrophoresis technique.
Write the steps in specific sequence of recombinant DNA technology. Describe the method of isolation of the genetic material (DNA).
Explain briefly the various processes of recombinant DNA technology.
Name the three important steps involved in PCR process.
Mention the different steps of process of recombinant DNA technology.
Write the names of two antibiotic resistant genes found in plasmid PBR322.
What is the full form of PCR? How is it useful in biotechnology?
Match the columns and choose the right option.
How is the amplification of gene done using the technique of PCR? Explain with the help of diagram.
What does PCR stand for? Describe the different steps of PCR.
Match the columns and choose the right option.
Explain the role of restriction endonucleases in recombinant DNA technology. Name the endonuclease that was first discovered.
Mention the role of molecular scissors in recombinant DNA technology.
Give an account of the Blue-White Method of selection of recombinants.
How and why is bacterium Thermus aquaticus employed in recombinant DNA technology? Explain.
Mention the three steps involved in each cycle of Polymerase-chain Reaction (PCR). How is repeated amplification of DNA made possible during PCR
What is recombinant DNA technology called popularly ? Name the vectors and enzymes used in this technique.
Name and explain the techniques used in the separation and isolation of DNA fragments to be used in recombinant DNA technology.
Explain the contribution of Thermus aquaticus in the amplification of a gene of interest.
(a) Why are restriction endonucleases so called ? (b) What is a palindromic nucleotide sequence ? How do restriction endonucleases act on palindromic sites to create sticky ends ?
(a) With the help of diagrams show the different steps in the formation of
recombinant DNA by action of restriction endonuclease enzyme Eco RI (b) Name the technique that is used for separating the fragments of DNA cut by restriction endonucleases.
(a)EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease. How is it named so? Explain (b) Write the sequence of DNA bases that the enzyme recognises. Mention the point at which the enzyme makes a cut in the DNA segment.
Any recombinant DNA with a desired gene is required in billion copies for commercial use. How is the amplification done? Explain.
(a) Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of polymerase chain
reaction (PCR). Write the role of primers and DNA polymerase in PCR., (b) Give the characteristic feature and source organism of the DNA polymerase in PCR.
(a) Illustrate the recognition sequence of Eco RI and mention what such sequences are called (b) How does restriction endonuclease act on a DNA molecule?
Describe the process of gene amplification for rDNA technology experiments.
Why is the enzyme cellulase used for isolating genetic material from plant cells but not for animal cells?
How is the action of exonuclease different from that of endonuclease?
Eco RI is used to cut a segment of foreign DNA and that of a vector DNA to form a recombinant DNA. Show with the help of schematic diagrams.(i)
The set of palindromic nucleotide sequence of base pairs the Eco RI-will
recognise in both the DNA segments. mark the site at which Eco RI will act and-cut both the segments., (ii) Sticky ends formed on both the segments where the two DNA segments will join later to forma recombinant DNA.
How are the following used in biotechnology ? (a) plasmid DNA (b) recognition sequence (c) gel electrophoresis
Match column I with column II with respect to the nomenclature of restriction enzyme EcoRI and select the correct answer from the given codes.
List the key tools used in recombinant DNA technology.
Name the source of the DNA polymerase used in PCR technique. Mention why it is used.
Explain briefly PCR.
Expand and mention one application of PCR.
Match the scientists in column I with their related discoveries in column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
Write any four ways used to introduce a desired DNA segment into a bacterial cell in recombinant technology experiments.
Describe the characteristics a cloning vector must possess.
Any recombinant DNA with a desired gene is required in billion copies for commercial use. How is the amplification done? Explain.
Identify A and B illustrations in the following
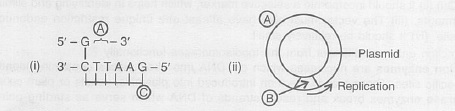
Explain the role of molecular scissors in recombinant DNA technology.
Explain the role of Ti plasmids in biotechnology.
What does PCR stand for? What is the principle of PCR? Name the different steps in PCR reaction.
How does restriction endonuclease act on a DNA molecule?
With the help of diagrams show the different steps in the formation of recombinant DNA by action of restriction endonuclease enzymes EcoR1.
Name the selectable markers in the cloning vector pBR322? Mention the role they play.
Name the technique that is used for separating the fragments of DNA cut by restriction endonucleases.
How is the separated DNA visualised and extracted for use in recombinant technology ?
How are the DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis is visualized and separated for use in constructing recombinant DNA?
Write the type of matrix used in the technique for the separation of DNA fragments.
What would happen when one grows a recombinant bacterium in a bioreactor but forget to add antibiotic to the medium in which the recombinant is growing?
While cloning vectors, which of the two will be performed by biotechnologists bacteriophages or plasmids. Justify with reason.
How does the wells gets charged in the Gel electrophoresis?
What are vectors?
Restriction enzymes that are used in the construction of recombinant DNA are endonucleases which cut the DNA at 'specific-recognition sequence'. What would be the disadvantage if they do not cut the DNA at specific-recognition sequence?
Mention four features of pBR322.
Define Insertional inactivation.
a) Why have DNA fragments in band 'D' moved farther away in comparison to those in band 'C'
b) Identify the anode end in the diagram.
c) What does E represent in the above diagram?
What are restriction enzymes? Mention any two restriction enzymes and their source.
Given is the diagram of agarose gel kept under UV light.
Mention the positive and negative terminals.
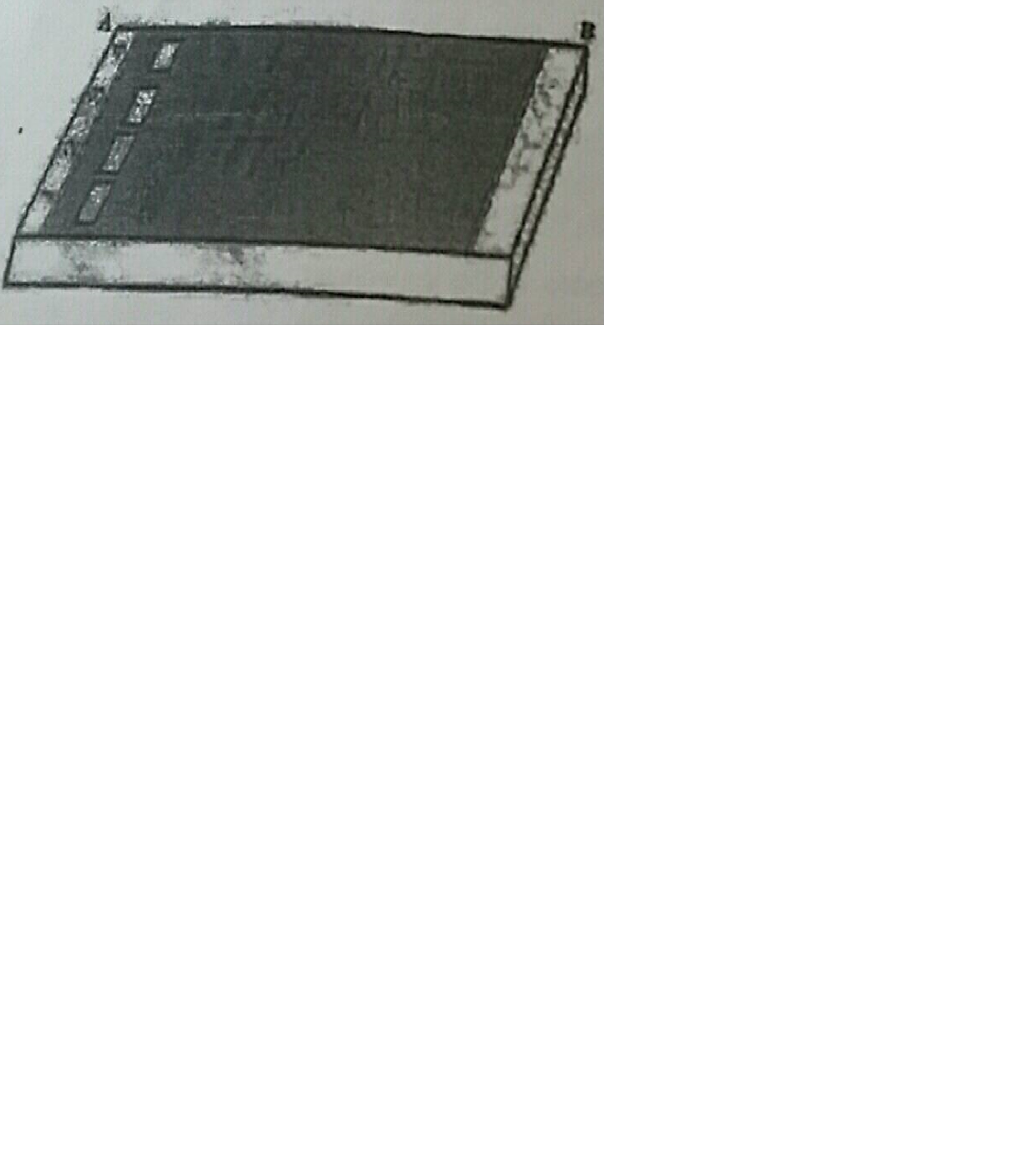
a) How do DNA fragments migrate and resolve in a Gel electrophoresis?
b) How lane one is different from lane 2,3 and 4 in the Gel electrophoresis set up?
c) How pure DNA fragments are made observable in the visible light?

What modification is done on the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to convert it into a cloning vector?
What is DNA probe?
Would you choose an exonuclease while producing a recombinant DNA molecule?
How is copy number of the plasmid vector related to yield of recombinant protein?
A recombinant DNA molecule was created by ligating a gene to a plasmid vector. By mistake, an exonuclease was added to the tube containing the recombinant DNA. How does this affect the next step in the experiment i.e. bacterial transformation?
Write the types of restriction enzyme. "Synthesis of recominant DNA molecule is possible only when the vectors and source DNA is cut by the same restriction enzyme" explain reason.
A person wanted to isolate DNA from cells of a human to perform his experiment on recombinant DNA technology. He used RBC cells and WBC cells for the same and loaded well 1 (sample from RBC) and well 2 (sample from WBC). After performing gel electrophoresis he found the following patterns of fragments in the gel. Why do you think Well 1 has no fragments? Note: No DNase was used.

A plasmid DNA and a linear DNA (both are of the same size) have one site for a restriction endonuclease. When cut and separated on agarose gel electrophoresis, plasmid shows one DNA band while linear DNA shows two fragments. Explain.
Class 12 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Biodiversity And Its Conservation Extra Questions
- Biotechnology And Its Applications Extra Questions
- Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Extra Questions
- Ecosystem Extra Questions
- Environmental Issues Extra Questions
- Evolution Extra Questions
- Human Health And Disease Extra Questions
- Human Reproduction Extra Questions
- Microbes In Human Welfare Extra Questions
- Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Extra Questions
- Organisms And Population Extra Questions
- Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Extra Questions
- Reproduction In Organisms Extra Questions
- Reproductive Health Extra Questions
- Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Extra Questions