Molecular Basis Of Inheritance - Class 12 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
What is the function of the codon AUG?
Differentiate between the genetic codes :
Degenerate and Initiator
Protein sequences are encoded in ..........
Explain the following: Degenerate code, Unambiguous code, Universal code, Initiator code.
Match the names of triplet codons with the amino acids given under columns. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabets of the two columns.
(a) A- s, B- t, C- q, D- r
(b) A- t, B- s, C- r, D- q
(c) A- p, B- r, C- s, D- t
(d) A- q, B- r, C- s, D- t
What is a genetic code?
Following a severe accident, many charred-disfigured bodies are recovered from the site making the identification of the dead very difficult. Name and explain the technique that would help the authorities to establish the identity of the dead to be able to hand over the dead to their respective relatives.
Explain the significance of satellite DNA in DNA fingerprinting technique.
State the difference between the structural gene in a transcription unit of prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Name the transcriptionally active region of chromatin in a nucleus.
(a) Construct a complete transcription unit with promoter and terminator on the basis of the hypothetical template strand given below:
(b) Write the RNA strand transcribed from the above transcription unit along with its polarity.
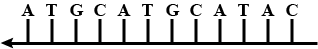
Name the scientist who suggested that the genetic code should be made of a combination of three molecules.
What would be the molar concentration of human DNA in a human cell? Consult your teacher.
Name the enzyme and state its property that is responsible for continuous and discontinuous replication of the two strands of a DNA molecule.
Why is the Human Genome project called a mega project?
Briefly describe the following:
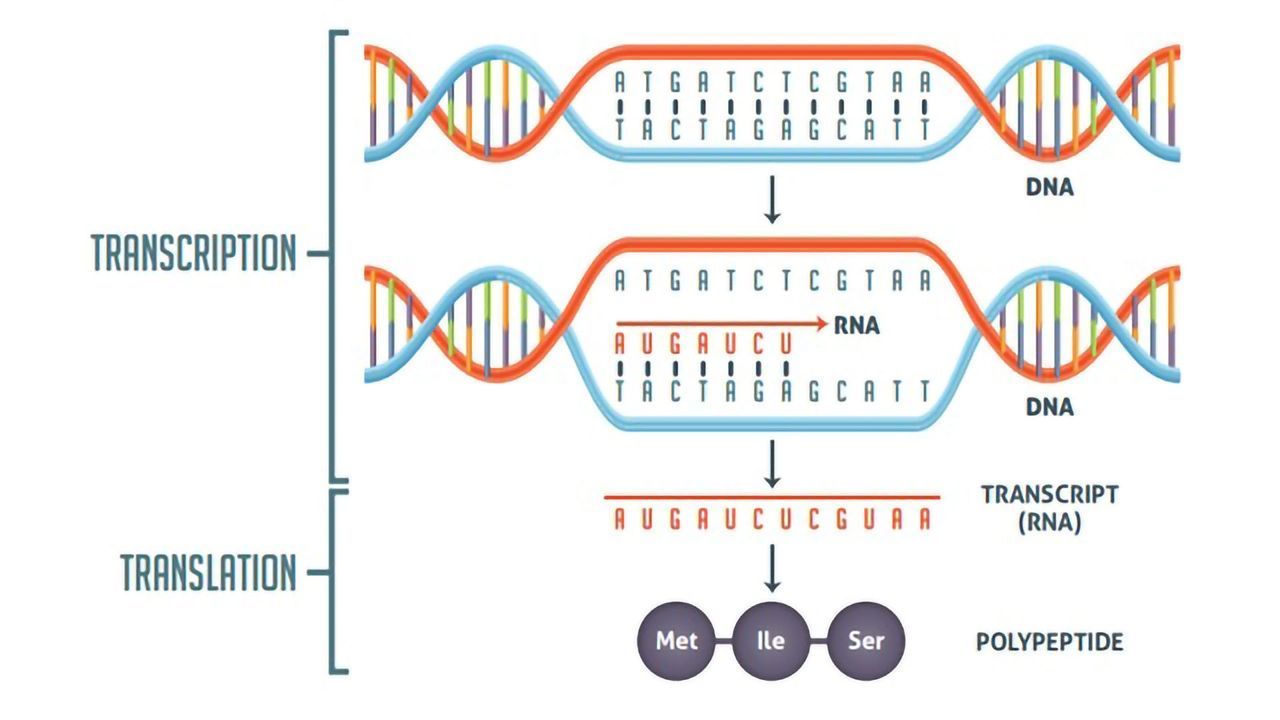
(a) Transcription
(b) Polymorphism
(c) Translation
(d) Bioinformatics
Depending upon the chemical nature of the template (DNA or RNA) and the nature of nucleic acids synthesised from it (DNA or RNA), list the types of nucleic acid polymerases.
Which property of DNA double helix led Watson and Crick to hypothesise semi-conservative mode of DNA replication? Explain.
Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides:
Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine.
Collect 5 examples of palindromic sequence by consulting your teacher. Better try to create a palindromic sequence by following base-pair rules.
What is complementary base pairing?
State the best known contribution of:
(i) Alec Jeffery
(ii) P.K. Sethi
(iii) Hugo de Vries
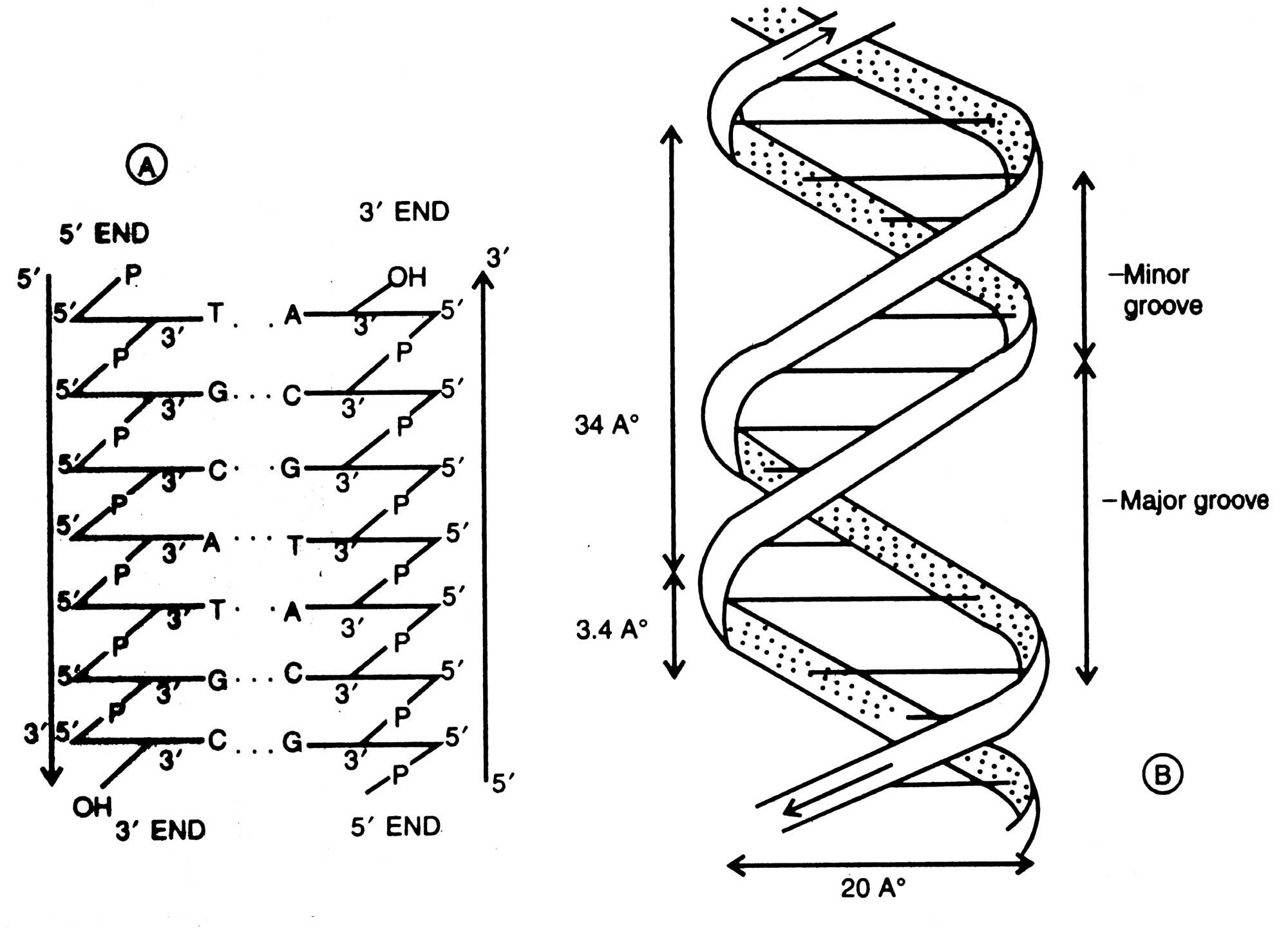
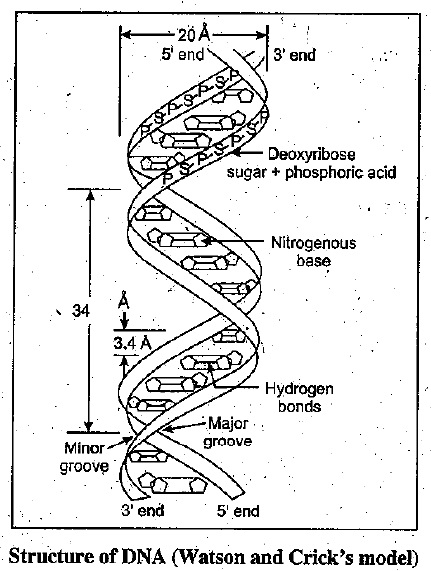
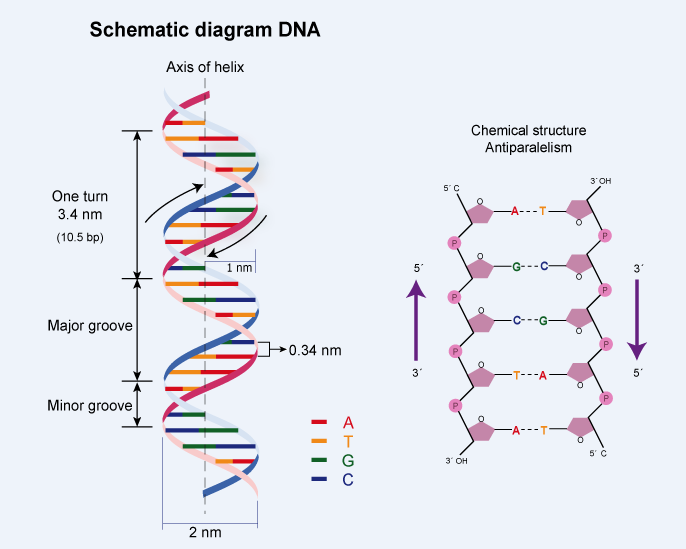
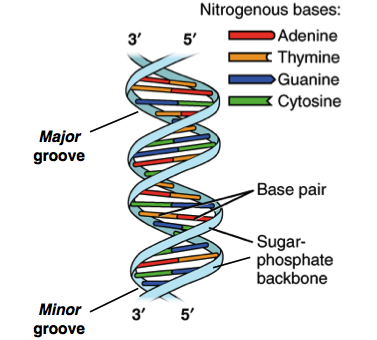
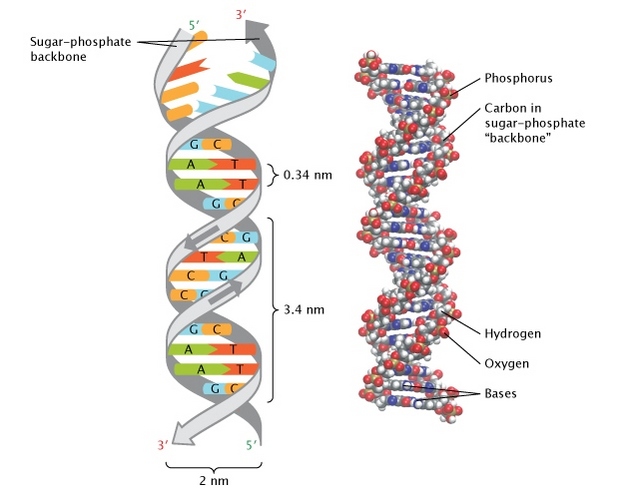
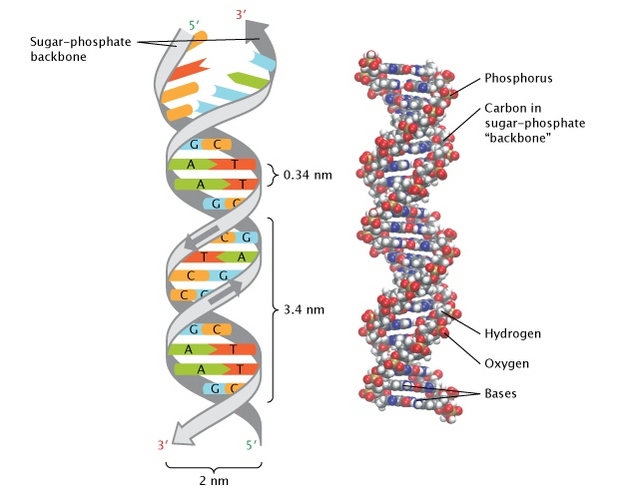
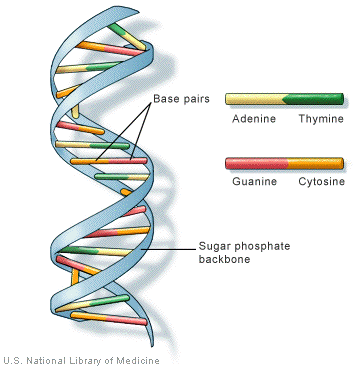
With the help of a neat and labeled diagram describe Waston and Crick's model of DNA.
Describe Watson and Crick's model of DNA.
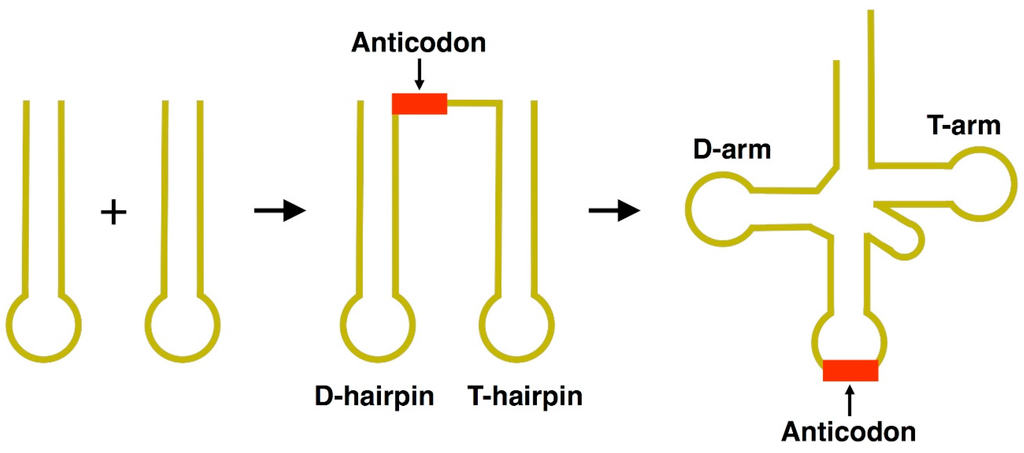
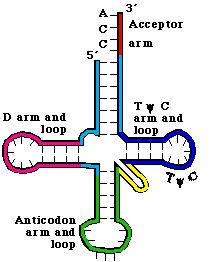
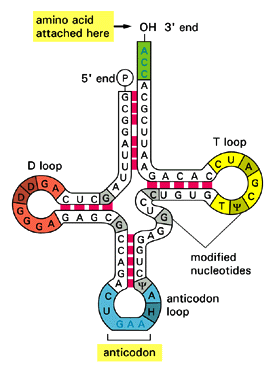
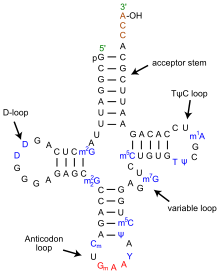
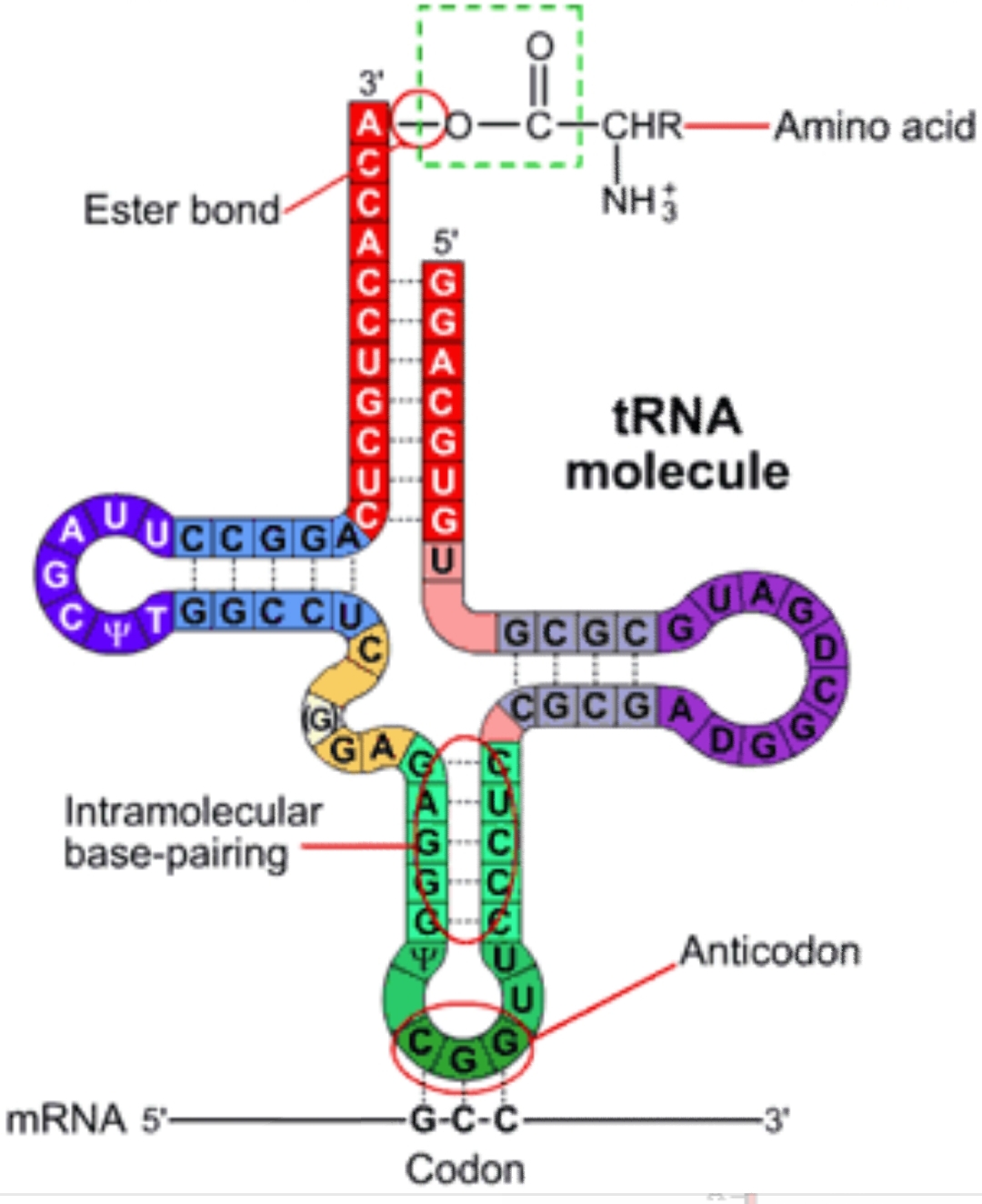
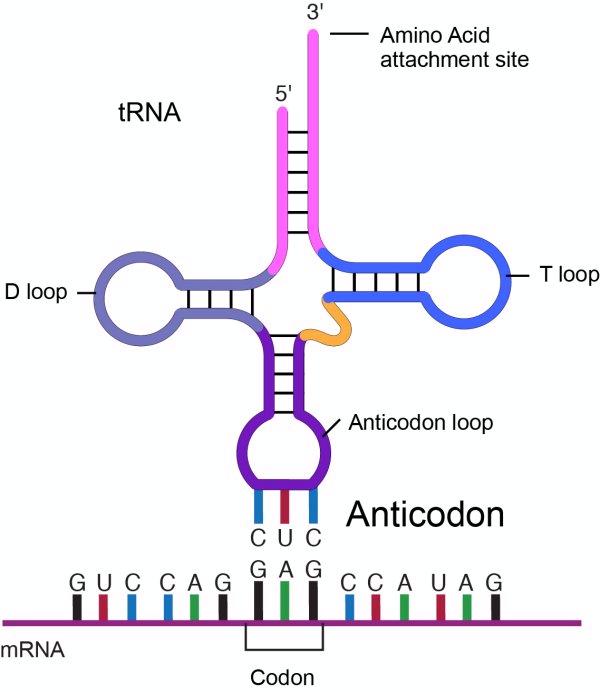
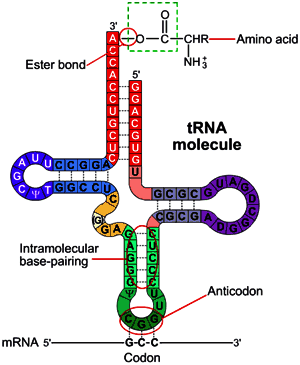
Sketch and label hair- pin model for t-RNA.
What is genetic code? Write its four salient features. Draw a diagram of t-RNA.
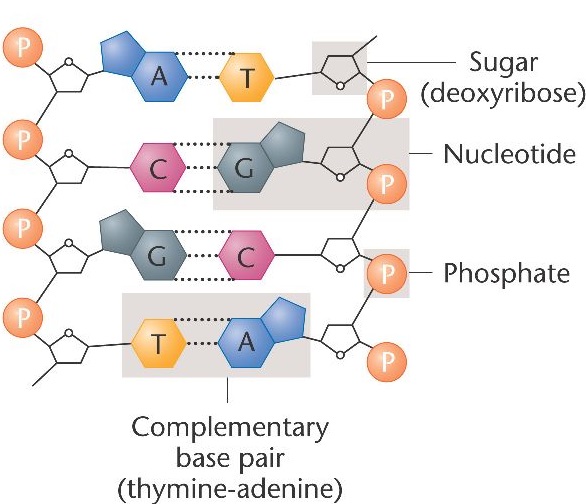
What is nucleosome ? Draw diagram of double stranded polynucleotide chain of DNA and explain its structure.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the hair pin model of t-RNA?
Write down the four salient features of genetic code.
Give the application of DNA fingerprinting technique.
What is human genome project (HGP)?
Write the important features of genetic code.
What is DNA fingerprinting? Write any four applications of DNA fingerprinting.
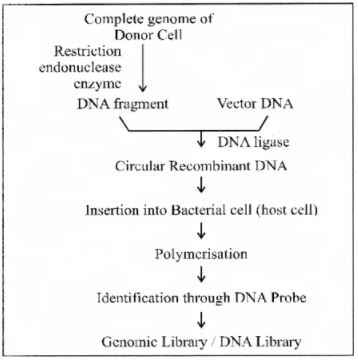
What is DNA Library?
In a typical DNA molecule, the proportion of thymine is 20% of the N bases. Find out the percentages of other N bases.
In a typical DNA molecule, the proportion of thymine is 30% of the N bases. Find out the percentage of other N bases.
List the salient features of human genome project.
Define stop codon. Write the codons.
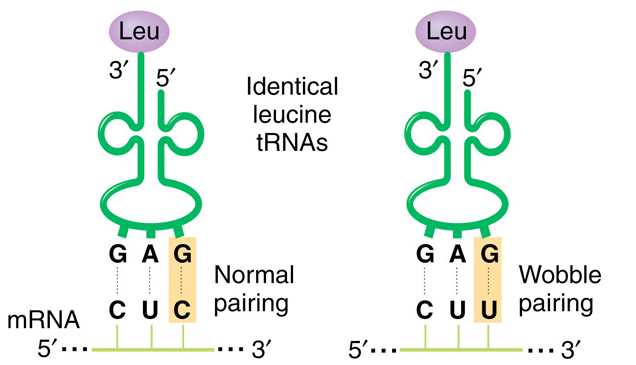
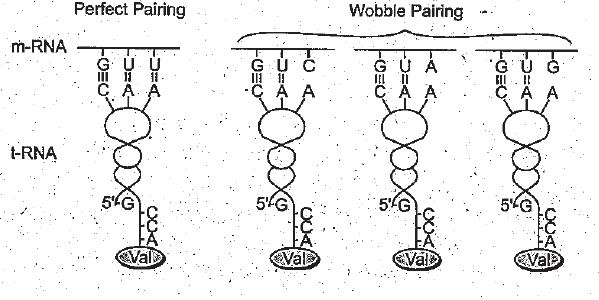
Explain 'Wobble hypothesis' with the help of a suitable diagram.
Answer in 200 to 250 words:
Enumerate the salient features of Human Genome Project (HGP).
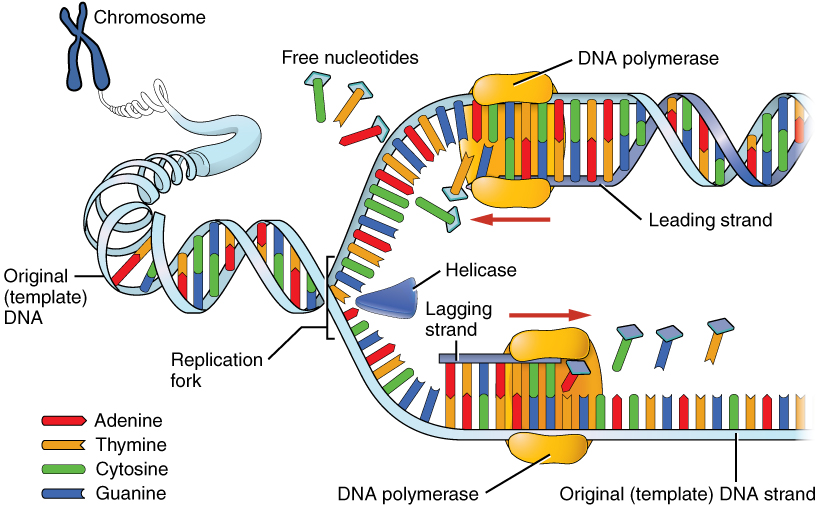
Describe the process of DNA replication with the help of a diagram.
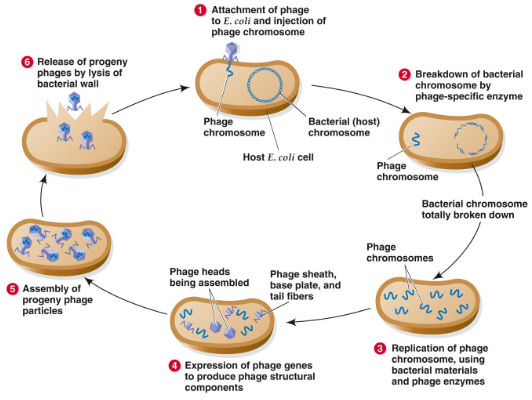
Explain replication of bacteriophage with the help of a suitable diagram.
Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times. Gives one reason.
What is DNA replication? Write the chemical composition of DNA.
Differentiate between the genetic codes:
Unambiguous and Universal
Rearrange B and C according to the data given in A.
| A | B | C |
| Nucleic Acids | Sugar | Nitrogen Base |
| DNA | a) Ribosome | x) Uracil |
| RNA | b) Deoxyribose | y) Adenine |
| c) Ribose | z) Thymine |
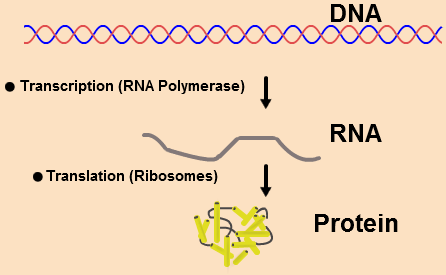
Diagrammatic representation of 'central dogma' is given below :
Observe the diagram carefully and redraw it making appropriate corrections.
↺DNAtranslation→mRNAtranscription→Protein
Find the odd one. Write down the common features of others.
Adenine, Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil.
"Prediction of the sequence of amino acids from the nucleotide sequence in mRNA is very easy, but the exact prediction of the nucleotide sequence in mRNA from the sequence of amino acids coded by mRNA is difficult". Which properties of the genetic code is the reason for the above condition? Explain.
List the two methodologies which were involved in human genome project. Mention how they were used.
Given below is the transcribed strand of the DNA duplex :3'-TACCGATCCGAGCTG-5'
(a)Draw the complementary DNA polynucleotide chain
(b)Construct the RNA molecule, which will'be transcribed.
Briefly discuss the structure and functions of DNA.
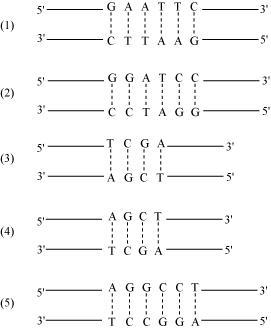
What do you understand by the antiparallel arrangement of DNA strands?
Match the triplet codons mentioned in list I with their amino acids mentioned in listcolumn II and select the correct option from the given codes.
'Genetic code is unambiguous and specific.' Explain.
The double helix model for DNA was proposed by .......... and ..........
Chemical analysis has shown that the number of adenine molecules in a DNA sample is always the same as the number of molecules of ..........
Very short answer type.
Name two scientists who were awarded Nobel Prize for deciphering DNA structure.
Write the importance of DNA.
Double-helical structure is found in ..........
Differentiate between nucleoside and nucleotide.
What name is applied to the model for the molecular structure of DNA?
Why is the Human Genome Project called a mega project?
What is transformation?
Give reasons Genetic code is universal.
The genetic code is said to be a triplet code. What does this mean and why is it important?
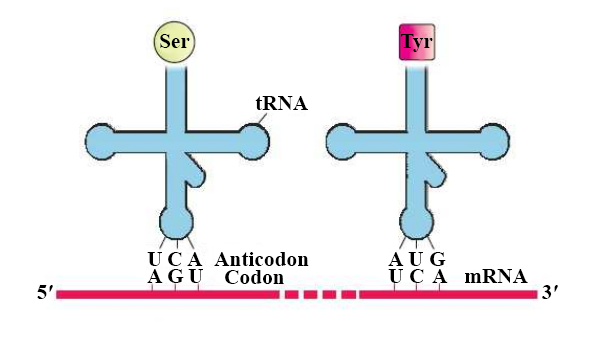
How do a code, codon, and anticodon differ?
(a) In an experiment Griffith introduced heat-killed S-strain bacteria Streptococcus into a mouse along with live R-strain bacteria. The mouse died but the scientist recovered living S-strain bacteria from the dead mouse. Explain the conclusion Griffith arrived at after the experiment.
(b) Explain MacLeod, McCarty and Averys work that followed Griffith's experiment. State the conclusion they arrived at.
(a) Explain the experiment performed by Griffith on Streptococcus pneumoniae. What did he conclude from this experiment?
(b) Name the three scientists who followed up Griffiths experiments.
(c) What did they conclude and how?
(a) How many codons code for amino acids and how many do not?
(b) Explain the following giving one example of each
(i) Unambiguous and specific codon
(ii) Degenerate codon
(iii) Universal codon
(iv) Initiator codon.
What is amplification with reference to DNA fingerprinting?
Describe the experiment performed by Griffith. What conclusions did he infer from his observations?
What is genetic code? Mention the essential qualities for a universal genetic code.
Why are there 64 different codons for 20 different amino acids?
Codon AUG has dual function. Justify.
List the salient features of human genome.
What is the diagram representing?
Mention the DNA sequence coding for serine and the anticodon to tRNA for the same amino acid.
Name the parts a, b and c.
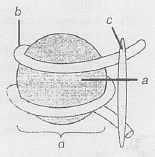
Mention the contribution of genetic maps in human genome project.
How do histones acquire positive charge?
Give salient features of human genome.
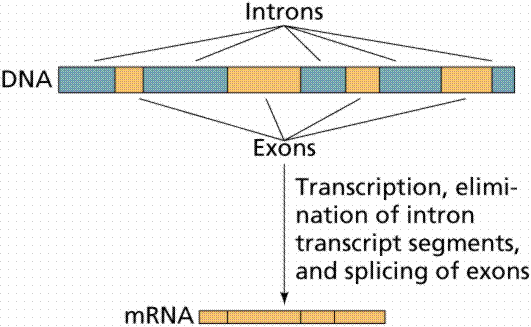
Why are some untranslated sequences of bases seen in mRNA coding for polypeptide? Where exactly are they present on mRNA?
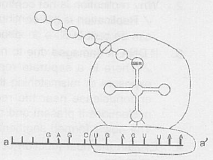
Explain the mechanism of DNA replication. Highlight the role of enzymes in the process.
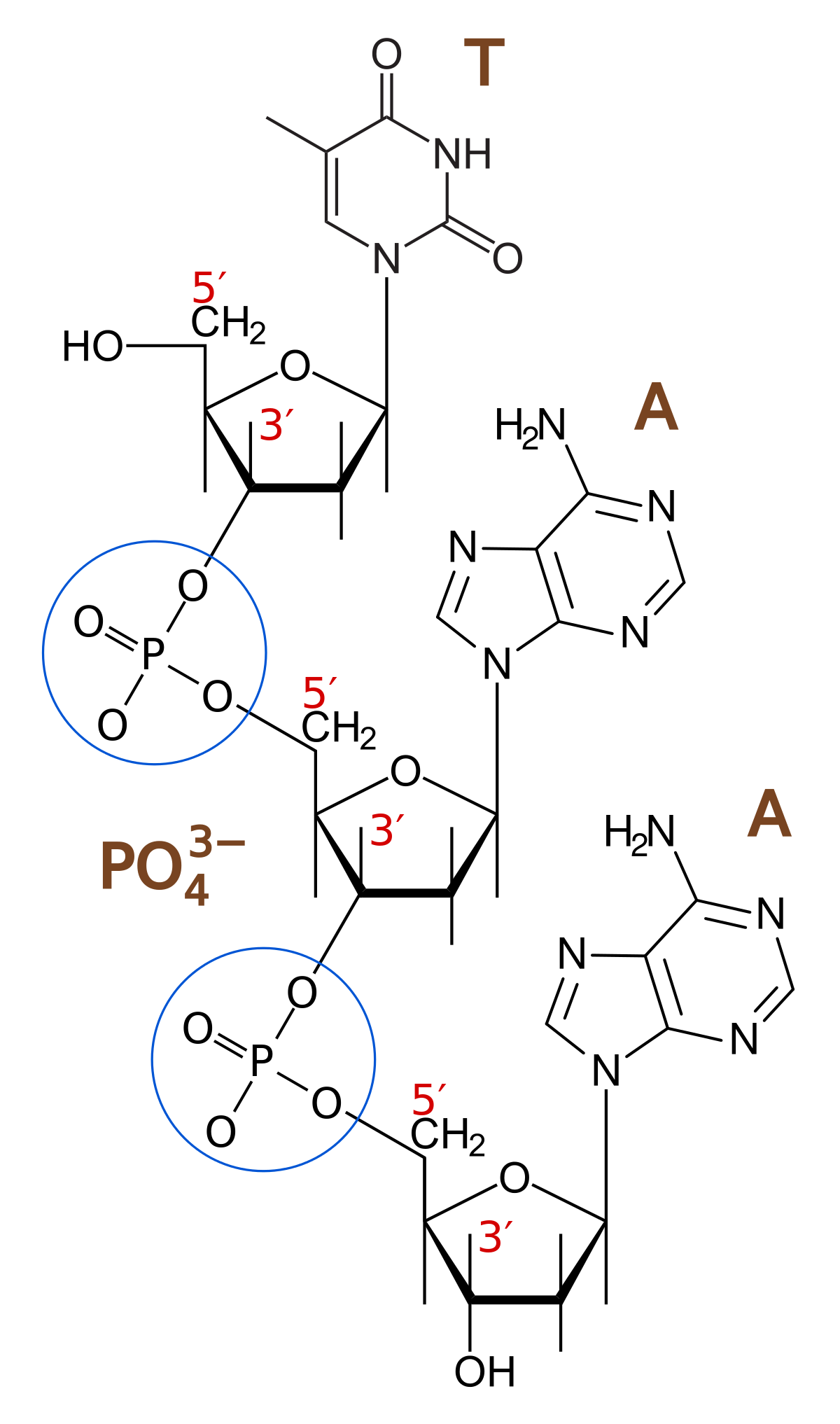
Two nucleotide are linked through 3′−5′ phosphodiester linkage to from dinucleotide. Explain.
Draw and explain the clover leaf life structure of nucleic acid molecule
What is the importance of copying of DNA during reproduction?
Write the important features of genetic code.
What are satellites in a genome? Explain their role in DNA fingerprinting.
Write about the methodologies of human genome project.
Explain Watson and Crick's model of DNA.
What should be the nature of genetic code if there would have been 65 amino acids?
In DNA you find which type(s) of bond?
A DNA molecules measuring 680Ao contains ______
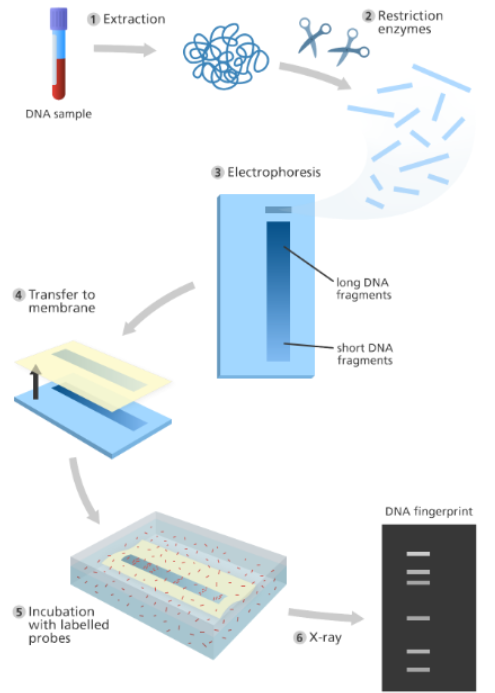
What is DNA fingerprinting ? Describe various steps involved in the same.
What are termination codons?
Define transcription.
Give one significant contribution of each of the following scientists:
Alec Jeffery
The discovery of such a weird phenomenon certainly raises questions about how genomes evolve, and what could have been missed from existing genome sequencing projects. Perhaps we need to go back and take a closer look.
How does a degenerate code differ form an unambiguous one?
Describe the DNA structure worked by Watson and Crick.
Mention two approaches used while sequencing human genome.
How does a degenerate code differ from an unambiguous one?
Draw and label the secondary structure of tDNA carrying methionine.
The twisted ladder like structure of a double stranded DNA is also called ?
Where codons and anticodons are present?
Summarize the action of the gene introduced.
What is DNA Fingerprinting?
Draw a labelled diagram of t-RNA-the adapter molecule.
The proportion of nucleotides in a given acid are : adenine 18%, Guanine 30%, Cytosine42 % and Uracil 10 %. Name the nucleic acid and mention the number of strands in it.
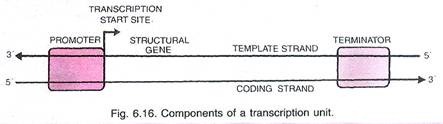
What are the components of a transcription unit?
What are the components of a nucleotide?
What is transcription?
What is Human genome project ? Briefly write about the salient features of Human Genome project.
Stae the importance of a Genetic code in protein biosynthesis.
Write the contribution of the following scientists in deciphering the genetic code.
Georce Gamow; Hargobind Khorana; Marshall Nirenberg; Severo Ochoa
Answer the following question in your own word.
Express your opinion about the use of DNA fingerprinting.
Express your opinion about the use of DNA fingerprinting.
List any four major goals of Human Genome project.
What is the genomic library?
What background information did Watson and Crick have made available for developing a model of DNA? What was their contribution?
Explain the process of forming the Genomic Library.
How has the sequencing of human genome opened new windows for treatment of various genetic disorders. Discuss amongst your classmates.
List the various markers that are used in DNA finger printing.
Who revealed biochemical nature of the transforming principle? Now was it done?
Based on your understanding of genetic code, explain the formation of any abnormal hemoglobin molecule. What are the known consequences of such a change?
Give any six features of the human genome.
The enzyme DNA polymerase in E.coli is a DNA dependent polymerase and also has the ability to proof-read the DNA strand being synthesised. Explain. Discuss the dual polymerase.
Give an account of the methods used in sequencing the human genome.
What 3 codons act as termination signals?
What is the role of the helicase enzyme in DNA replication ?
What is meant by triplet codon ?
How is "DNA fingerprinting" done?
How is the polymerase chain reaction useful in DNA fingerprinting?
How is "DNA fingerprinting" done?
What are the rungs of the DNA ladder made up of?
Match the names of the scientists with their contributions and choose the correct answer.
Column I - Name of scientists
Column II - Contributions
Identify the correct match between the codons and coding functions.A) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1B) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4C) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1D) A-3, B-2, C-4, D-1
Define a gene?
Match the following in column I with column II and choose the correct combination.
Draw a schematic diagram of a part of double stranded dinucleotide DNA chain having all the four nitrogenous bases and showing the correct polarity.
(a) A DNA segment has a total of 1,500 nucleotides, out of which 410 are guanine containing nucleotides. How many pyrimidine bases this segment possesses?
(b) Draw a diagrammatic sketch of a portion of DNA segment to support your answer.
(a) Write the specific features of the genetic code AUG.
(b) Genetic codes can be universal and degenerative. Write about them, giving one example of each.
(c) Explain aminoacylation of tRNA.
What do 'Y' and 'B' stand for in 'YAC' and 'BAC' used in Human Genome Project (HGP)? Mention their role in the project.
Following are the features of genetic codes. What does each one indicate? __________ Stop codon, Unambiguous codon, Degenerate codon, Universal codon.
Write the percentage of the total human genome that codes for proteins and the percentage of discovered genes whose functions are known as observed during HGP.
Expand 'SNPs' identified by scientists in HGP.
Give any two features of genetic code.
What does abbreviation HGP stand for ?
Sketch and label hair-pin model of t-RNA.
What are introns?
Give diagrammatic representation to show a perfect pairing and any two wobble pairings.
What will be the length of eukaryotic DNA segment having 10 pairs of nucleotides?
State any three goals of the human genome project.
Write four goals of Human Genome project
In a typical DNA molecule, the proportion of thymine is 30% of the N bases. Find out the percentages of other N bases.
What is Human Genome project? Write the salient features of Human genome project. Draw a representative diagram of Human genome project.
Describe the characteristics of genetic code?
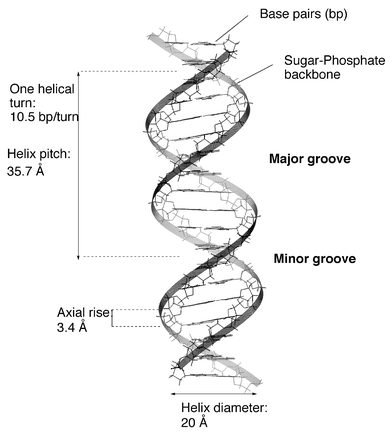
Write any four salient features of the Double helix structure of DNA.
Who discovered the phenomenon of transformation in bacteria and in which year?
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
If the sequences of bases in a segment of a DNA strand were adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, then the sequence in a complementary strand of newly made mRNA would be ..........
In the light of Watson and Cricks model, describe the detailed structure of DNA.
What is transcription? What are the different parts of a DNA transcription unit? What is their role in the process of transcription?
Write a short note on DNA fingerprinting
Write a brief account of the contributions made by J. D. Watson, F.H.C. Crick and M.H.F. Wilkins.
What is DNA fingerprinting? Why is it called finger printing?
Write about the transfer RNAs as follows :
(a) Any two characteristics in their structure. (b) Part of the cell where they are located.
(c) The technical name for the set of bases that are complementary to the triplet code on the mRNA.
Short /Long answer type questions.
State any three goals of the human genome project.
Very short answer type.
What is a gene bank?
Wilkins familiarized the results of high resolution X-ray photographs of crystallized DNA obtained by Franklin to Watson and Crick. What values were shown by him?
Scientists have identified about 1.4 million single nucleotide polymorphs in human genome. How is the information of their existence going to help the scientists?
Name the enzyme involve in the continuous replication of DNA strand. Mention the polarity of the template strand.
Write the function of RNA polymerase II.
Fill the columns and complete the given table. Give explanation for your answer
| Term | Definition | Example | Complementary process/Example | |
| 1 | Transcription | ...... | mRNA | Translation |
| 2 | ...... | Group of organisms that produces fetile individuals | Tiger | .... |
| 3 | Acquired Characters | change in organs/body due to use-disuse during organism's life time | .... | Ancestry of acquired characters |
| 4 | Morphological | Similiarities seen in animals | ..... | Leaf shape |
Explain the double helix structure of DNA with a labelled diagram.
Explain the DNA fingerprinting method of forensic science.
What do you mean by semiconservative method of DNA? Who proved it and how?
Explain the structure of DNA.
Illustrate on Human Genome project (HGP) and the methods used for the study.
Define watson-crick model of DNA
What is degeneracy of genetic code?
There is only one possible sequence of amino acids when deduced from a given nucleotides. But multiple nucleotides sequence can be deduced from a single amino acid sequence. Explain this phenomenon.
During in vitro synthesis of DNA, a researcher used 2', 3'- dideoxy cytidine triphosphate as raw nucleotide in place of 2'-deoxycytidine. What would be the consequence?
Name a few enzymes involved in DNA replication other than DNA polymerase and ligase. Name the key functions for each of them.
Define transformations in Griffith's experiment. Discuss how it helps in the identification of DNA as the genetic material.
Would it be appropriate to use DNA probes such as VNTR in DNA finger printing of a bacteriophage?
Given below is one of the strands of a DNA segment :
3′TACGTACGTACGTACG→5′
(a) Write its complementary strand.
(b) Write a possible RNA strand that can be transcribed from the above DNA molecule formed.
Class 12 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Biodiversity And Its Conservation Extra Questions
- Biotechnology And Its Applications Extra Questions
- Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Extra Questions
- Ecosystem Extra Questions
- Environmental Issues Extra Questions
- Evolution Extra Questions
- Human Health And Disease Extra Questions
- Human Reproduction Extra Questions
- Microbes In Human Welfare Extra Questions
- Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Extra Questions
- Organisms And Population Extra Questions
- Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Extra Questions
- Reproduction In Organisms Extra Questions
- Reproductive Health Extra Questions
- Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Extra Questions