Reproduction In Organisms - Class 12 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
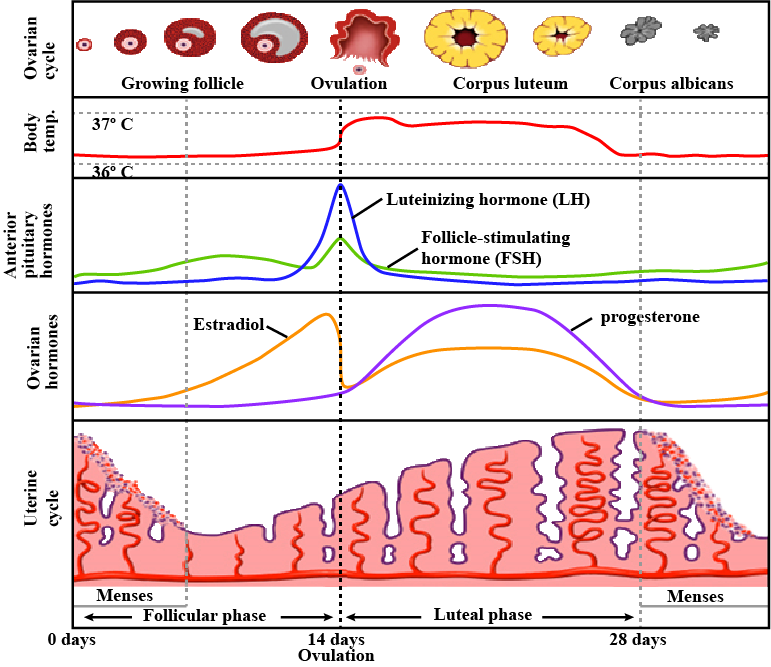
Give appropriate terms for the monthly discharge of blood and disintegrated tissue in the human female.
The transfer of a pollen grain from anther to stigma is called ___________.
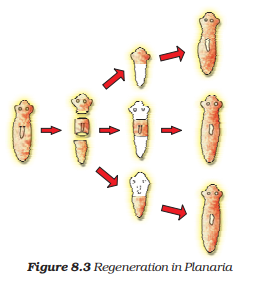
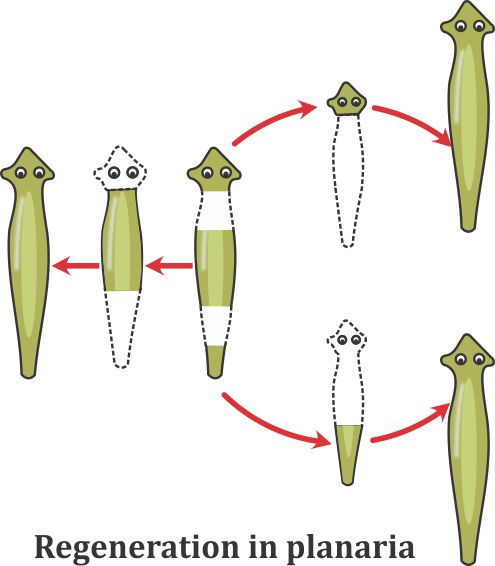
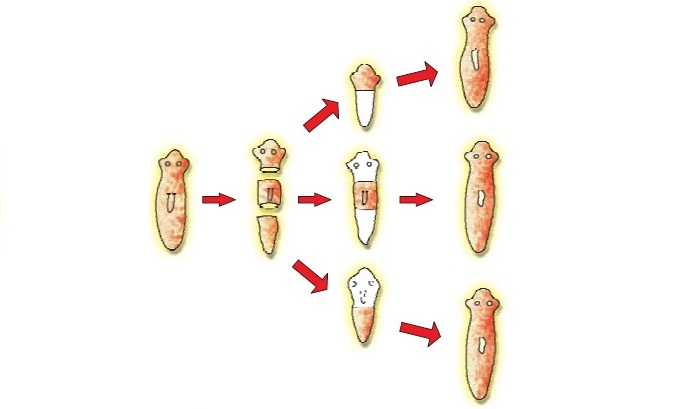
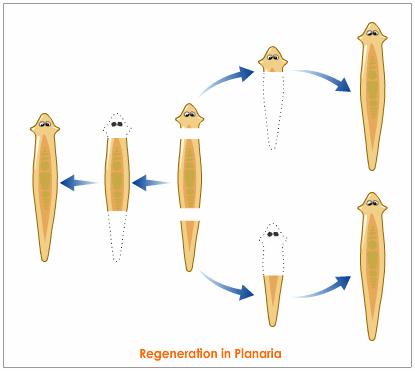
What is regeneration? Describe regeneration in Planaria with the help of a suitable diagram.
With the help of a diagram only show regeneration in Planaria. Regeneration is not possible in all types of animals. Why?
Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
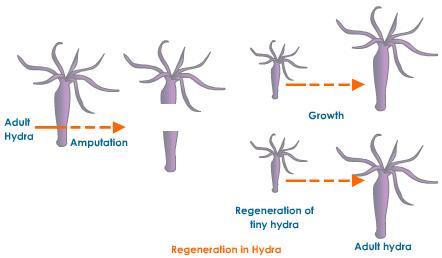
Explain the term "regeneration" as used in relation to reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra.
Draw diagrams to explain the regeneration that takes place in each of the body parts of planaria when its body is cut into three pieces. Name any other organism in which a similar process can be observed.
Choose the most appropriate answer.
(a) Internal fertilization occurs
(i) in female body.
(ii) outside female body.
(iii) in male body.
(iv) outside male body.
(b) A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of
(i) fertilization (ii) metamorphosis (iii) embedding (iv) budding
(c) The number of nuclei present in a zygote is
(i) none (ii) one (iii) two (iv) four
(b) A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of
(i) fertilization (ii) metamorphosis (iii) embedding (iv) budding
(c) The number of nuclei present in a zygote is
(i) none (ii) one (iii) two (iv) four
Name the phenomenon and one bird where the female gamete directly develops into a new organism
What is tissue culture? What are its advantages?
(a) Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
(b) How is regeneration different from reproduction?
Give reasons for the following:
(a) The human testes are located outside the abdominal cavity.
(b) Some organisms like honeybees are called parthenogenetic animals.
Define parthenogenesis.
Write a short note on regeneration.
Answer in 40 to 80 words:
What is parthenogenesis? Give two examples.
What is regeneration? Describe the process of regeneration in Planaria.
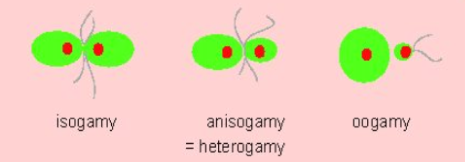
Define isogamy / heterogamy/ anisogamy/ oogamy.
Write the definition and any one significance of parthenogenesis.
Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called _________.
State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction
Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Answer the following question briefly and to the point.
Give a significant point of difference between oestrous and menstrual cycle.
Differentiate between.
Hologamy and autogamy
What is vegetative reproduction?
Explain the importance of syngamy and meiosis in a sexual life cycle of an organism.
Define parthenogenesis. Give two examples.
Differentiate between internal fertilization and external fertilization.
"A fertilized egg is the blue print of future development". Explain.
Explain the following terms : parthenogenesis
Differentiate between internal fertilisation and external fertilisation.
Give appropriate terms for the process of fusion of ovum and sperm.
How many types of fertilization are there? What are they?
What is isogamous, anisogamous and oogamous reproduction?
Differentiate between external and internal fertilization with an example for each.
Why is the period between 10 and 17 days of menstrual cycle called fertile period?
Production of plant without fertilization is done by?
Why is reproduction important?
Write about Menstrual Cycle.
Name the reproductive cycle that occur in seasonal breeders. Give an example.
What is meant by tissue culture? How this technique is performed? In which area is this technique finding its application?
One morning, as Paheli strolled in her garden, she noticed many small plants which were not there a week ago. She wondered where they had come from as nobody had planted them there. Explain the reason for the growth of these plants.
Hens and frogs are both oviparous exhibiting different types of fertilization. Explain.
How do the ornamental plants propagate? Mention the method of propagation for the following:
(i) Jasmine
(ii) Rose
(iii) Bougainvillea
(iv) Hibiscus
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Menstrual cycle
Menstrual cycle
What happens during this process and what is formed?
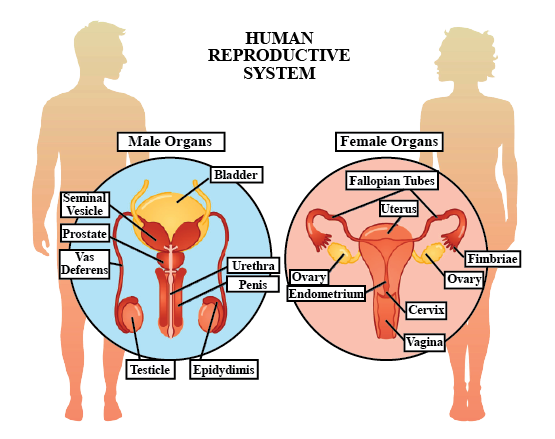
Describe the reproductive organs of human with the help of a labelled diagram ?
What is fertilization?
Short Answer.
Is there a relationship between the size of an organism and its life span ? Give two examples in support of your answer.
What do spores look like?
Write the importance of vegetative reproduction.
Fill in the blanks by selecting suitable words given below: (unisexual, fertilisation, fruit, stamen, anther, bisexual, pollination, seed, ovary)
(a) A flower that bears both the male and the female parts is known as ____ flower.(b) A flower-bearing either male or female part is known as _______ flower.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as _______.
(d) The fusion of a male cell with a female cell is called ________.
(e) The ovule develops into a _______.
(f) The ovary of the flower develops into a _______.
(a) A flower that bears both the male and the female parts is known as ____ flower.
(b) A flower-bearing either male or female part is known as _______ flower.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as _______.
(d) The fusion of a male cell with a female cell is called ________.
(e) The ovule develops into a _______.
(f) The ovary of the flower develops into a _______.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as _______.
(d) The fusion of a male cell with a female cell is called ________.
(e) The ovule develops into a _______.
(f) The ovary of the flower develops into a _______.
Briefly explain why a gardener prefers to grow certain plants vegetatively.
In how many days one menstrual cycle completes?
Underground stems of some plants such as grass and strawberry, etc., spread to new niches and when older parts die new plants are formed. In plants like mint and jasmine a slender lateral branch arises from the base of the main axis and after growing aerially for some time arch downwards to touch the ground. A lateral branch with short internodes and each node bearing a rosette of leaves and a tuft of roots is found in aquatic plants like Pistia and Eichhornia.
Underground stems of some plants such as grass and strawberry, etc., spread to new niches and when older parts die new plants are formed. In plants like mint and jasmine a slender lateral branch arises from the base of the main axis and after growing aerially for some time arch downwards to touch the ground. A lateral branch with short internodes and each node bearing a rosette of leaves and a tuft of roots is found in aquatic plants like Pistia and Eichhornia. In banana, pineapple and Chrysanthemum, the lateral branches originate from the basal and underground portion of the main stem, grow horizontally beneath the soil and then come out obliquely upward giving rise to leafy shoots.
What is parthenogenesis?
Give two advantages why plants like banana and grapes are grown by vegetative propagation.
Write a short note on Adrenal gland.
No. | Characteristics | Parental Care Type | Mating System |
| 1. | Large investment required for incubating and feeding the young for a prolonged time | ||
| 2. | Lactating females, internal fertilization | ||
| 3. | External fertilization, females exhibit territorial behaviour |
a. Male parental care
b. Female parental care
c. Biparental care
d. No parental care
Options for Mating System:
I. Monogamy
II. Polyandry
III. Polygyny
IV. Promiscuity
There are basic differences in the physiology and life histories such as mode of fertilization, bearing and rearing the young, etc in different groups of animals. These can account for the differences in parental care as well as mating systems in these groups. For each of the following life-history characteristics, assign the most probable mating system and parental care type. Choose from the options given above and fill in the table with the appropriate alphabets and numbers.
(a) State the difference between meiocyte and gamete with respect to chromosome number.
(b) Why is a whiptail lizard referred to as partheno-genetic?
Name and describe the method of artificial vegetative propagation employed by gardeners and farmers for the following (i) Lemon, (ii) Litchi, (iii) Jasmine, (iv) China rose.
Short / Long Answer question Type :
What does each accessory sex gland contribute to semen?
Short / Long Answer question Type :
Where is this ovum fertilized under normal conditions?
Difference b/w internal and External fertilization?
Fertilisation is a physio-chemical process. Explain.
What is vegetative propagation ? List with brief explanation three advantages of practising this process for growing some types of plants. Select two plants from the following, which are grown by this process: banana, wheat, mustard, jasmine, gram.
Long Answer.
Rose plants produce large, attractive bisexual flowers but they seldom produce fruits. On the other hand, a tomato plant produces plenty of fruits though they have small flowers. Analyse the reasons for the failure of fruit formation in rose plants.
Class 12 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Biodiversity And Its Conservation Extra Questions
- Biotechnology And Its Applications Extra Questions
- Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Extra Questions
- Ecosystem Extra Questions
- Environmental Issues Extra Questions
- Evolution Extra Questions
- Human Health And Disease Extra Questions
- Human Reproduction Extra Questions
- Microbes In Human Welfare Extra Questions
- Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Extra Questions
- Organisms And Population Extra Questions
- Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Extra Questions
- Reproduction In Organisms Extra Questions
- Reproductive Health Extra Questions
- Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Extra Questions