Human Reproduction - Class 12 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
Write two major functions of testis.
What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
The female is in the reproductive phase between menarche and_________
Name the body part in which the embryo develops.
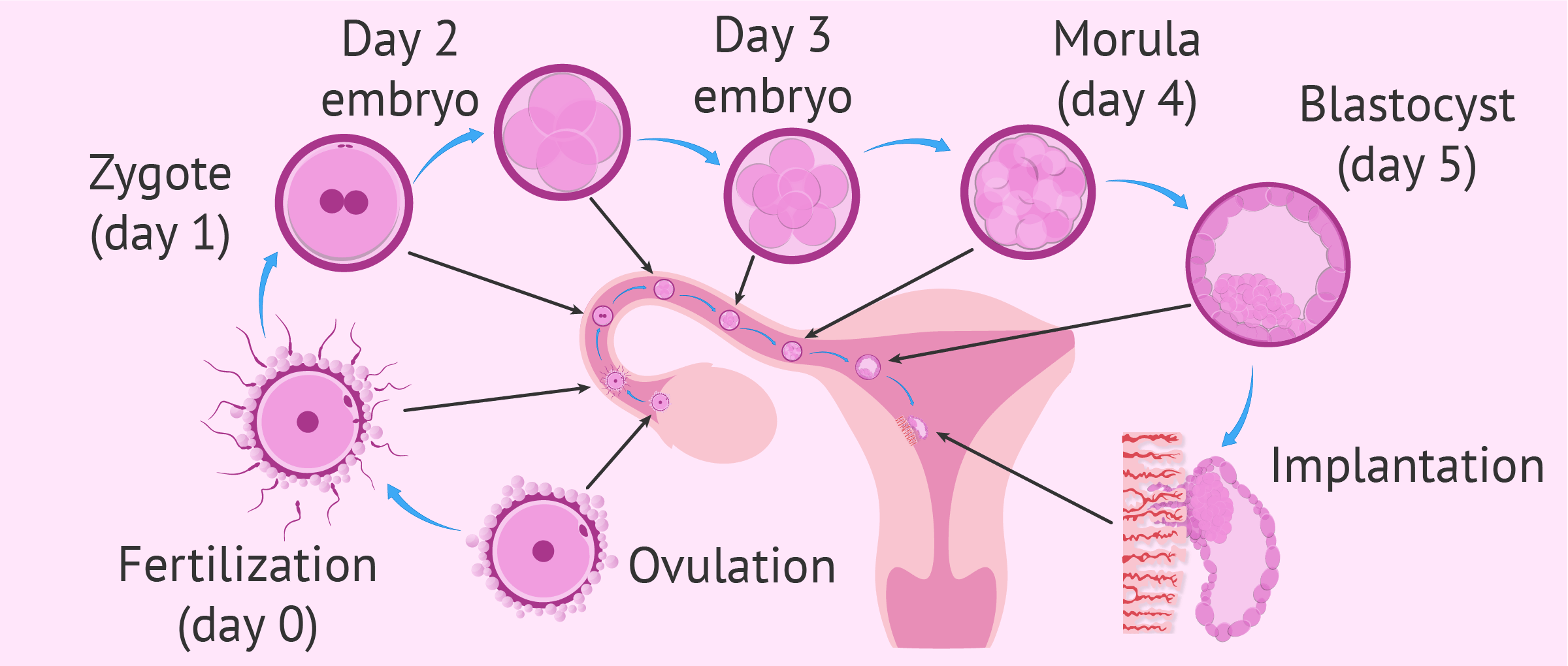
Define zygote.
Seminal vesicles are located near the ampullae of the vasa deferentia. They do not store sperms. They contribute yellowish, slightly alkaline, a viscous seminal fluid that contains the sugar fructose, a coagulating enzyme, ascorbic acid, and hormone-like prostaglandins. Type 1 for true and 0 for flase
Each question contains statements given in two columns which have to be matched. Statements in column have to be matched with statements in column II.
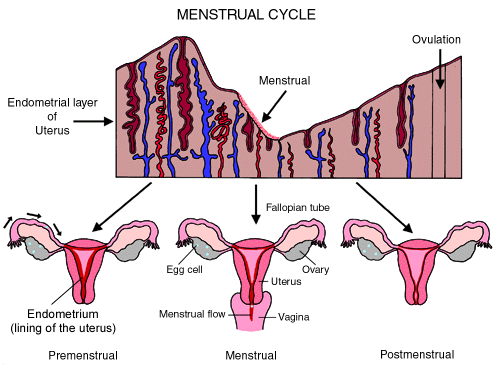
What is a menstrual cycle?
What is menopause?
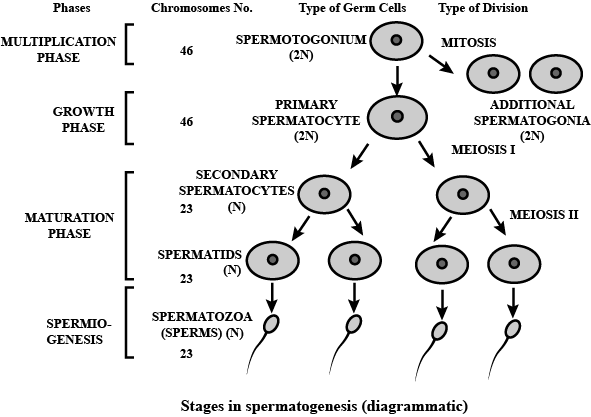
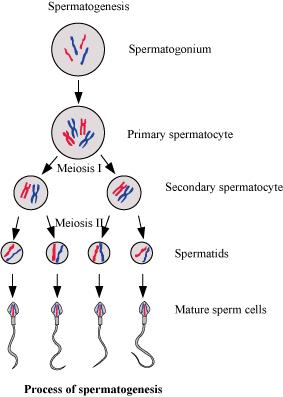
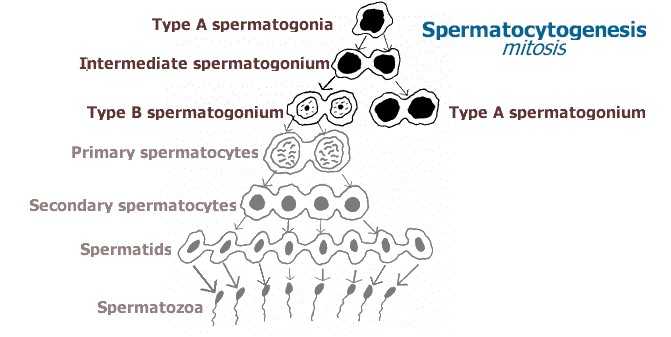
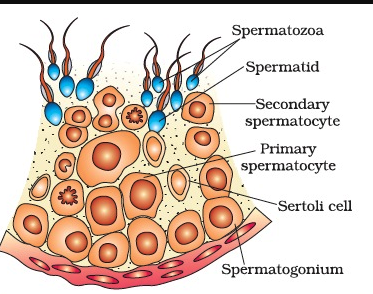
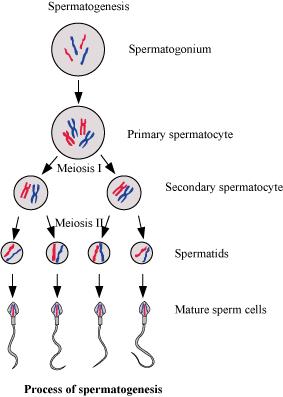
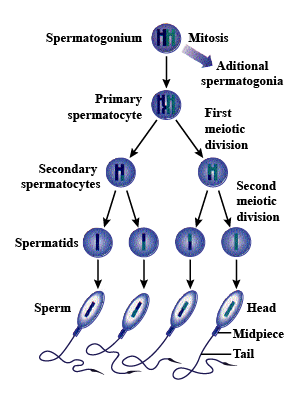
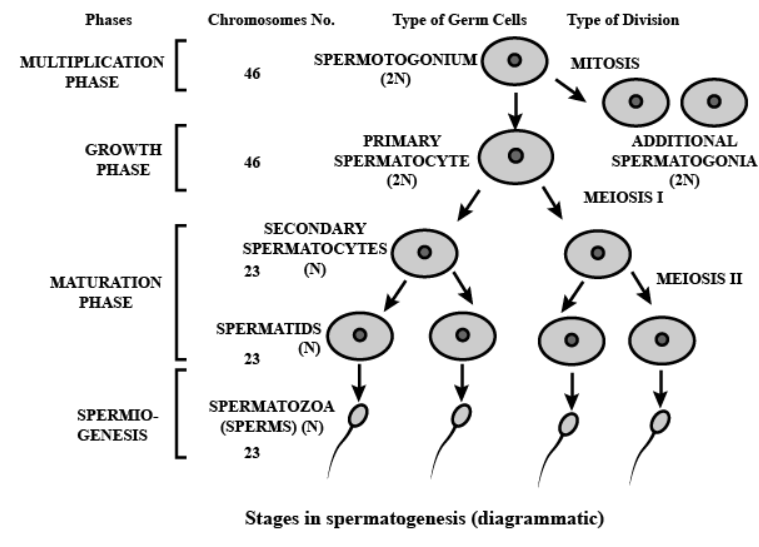
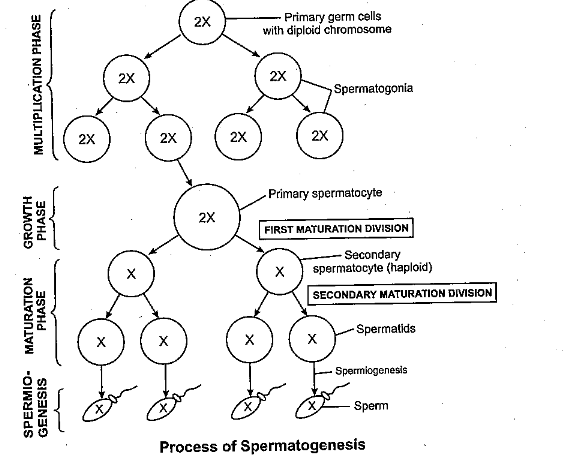
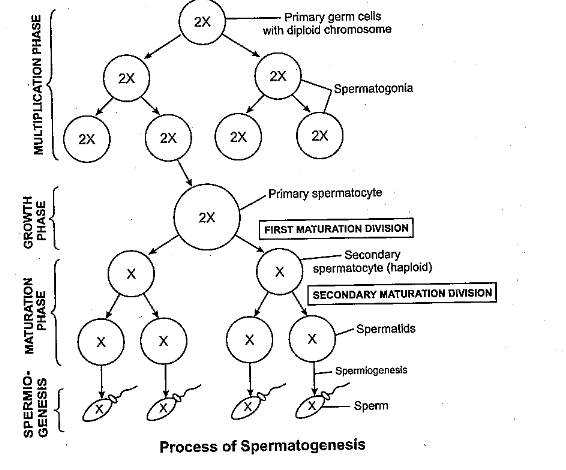
Schematically represent and explain the events of spermatogenesis in humans.
Describe the path that sperm take while leaving the body.
What do the sperms do after being released?
In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
Write the location and function of the following in human testes:
(a) Sertoli cells (b) Leydig cells
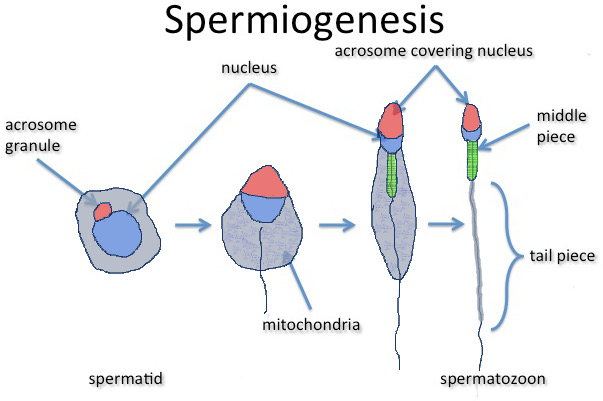
Mention the difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation.
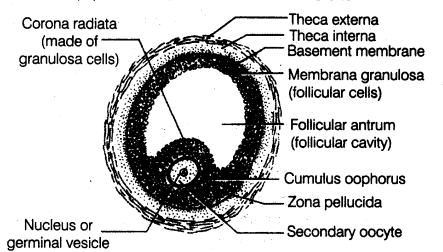
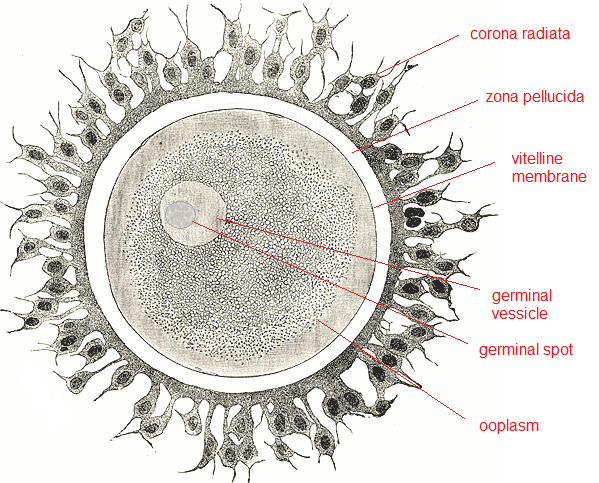
(a) Draw a diagram of the structure of a human ovum surrounded by corona radiata. Label the following parts:
(i) Ovum (ii) Plasma Membrane (iii) Zona Pellucida
(b) State the function of Zona Pellucida.
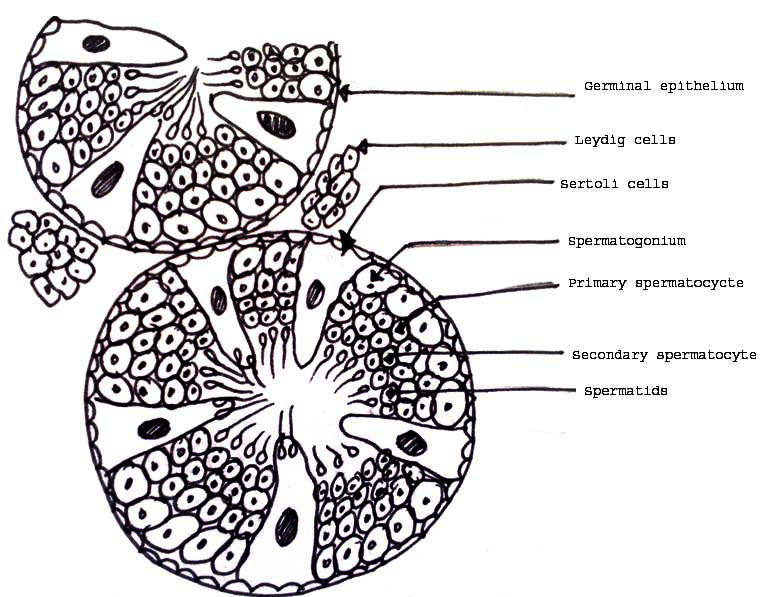
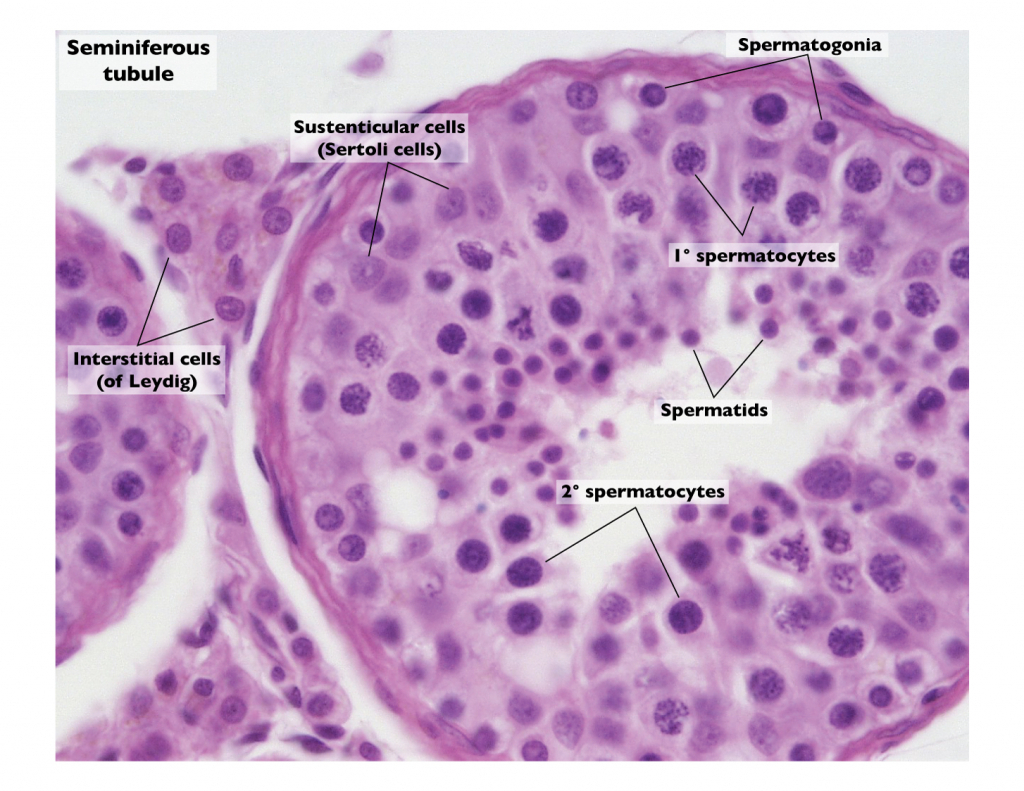
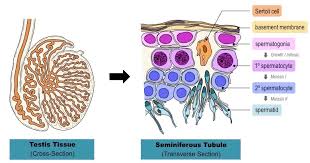
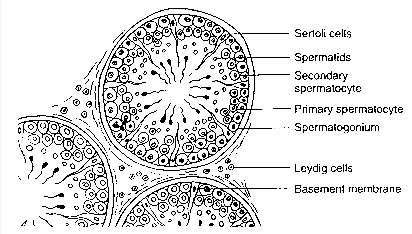
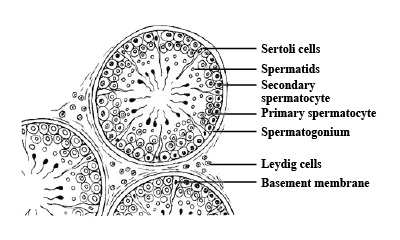
Draw a labelled diagram of the sectional view of a human seminiferous tubule. (six parts to be labelled)
What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
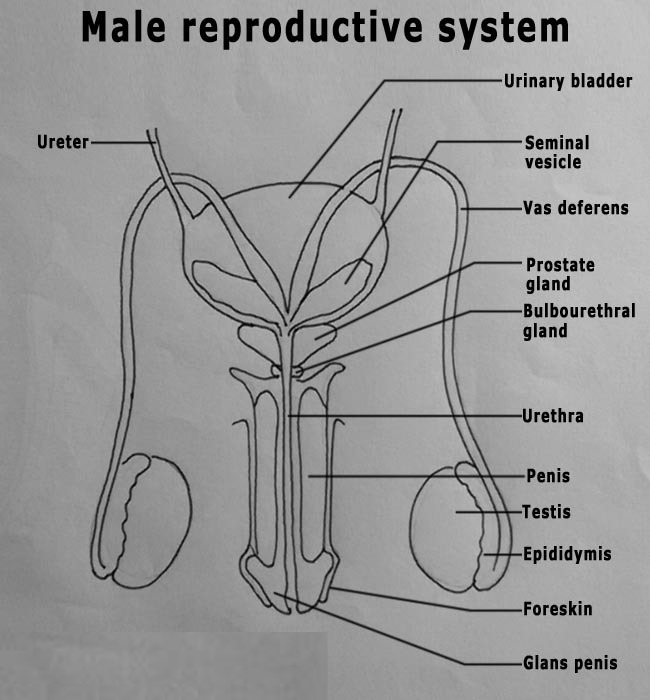
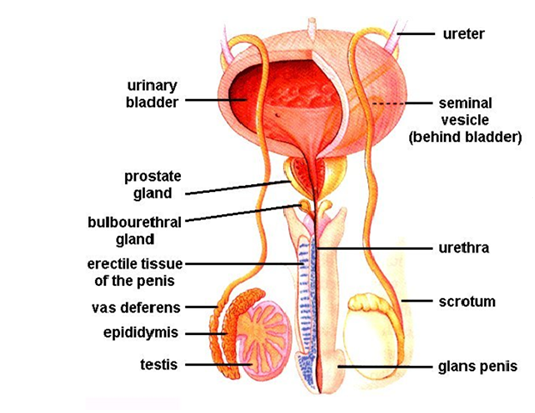
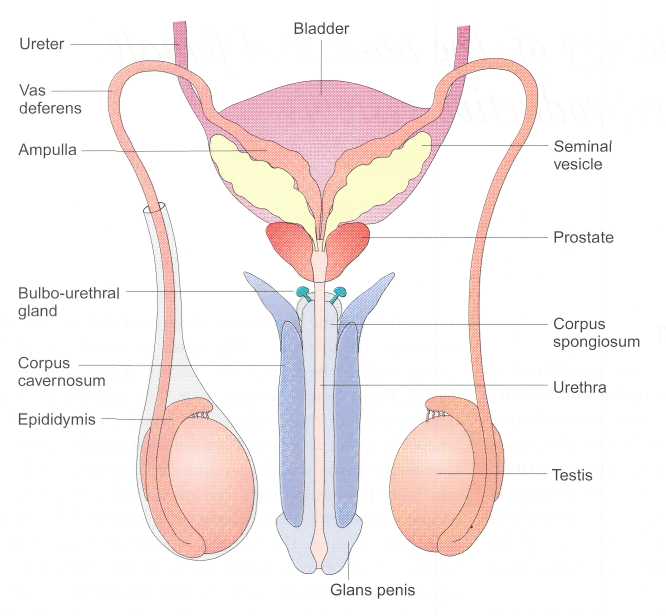
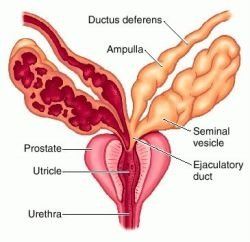
Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
(a) Draw a labelled diagrammatic view of human male reproductive system.
(b) Differentiate between:
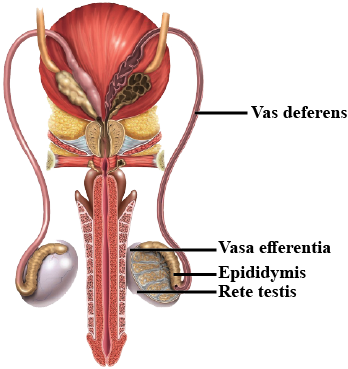
(i) Vas deferens and vasa efferentia
(ii) Spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis
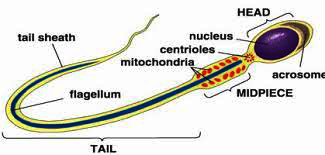
Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
What are the major components of seminal plasma?
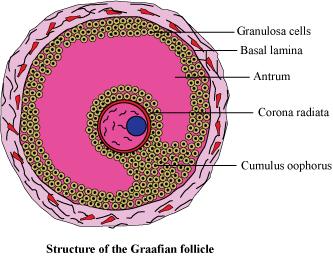
Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian follicle.
Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true.
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. (True/False)
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. (True/False)
(c) Leydig cells are found in ovary. (True/False)
(d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens. (True/False)
(e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (True/False)
(f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True/False)
(g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience. (True/False)
Why do fish and frog produce a huge number of eggs each year?
What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
When an ovum gets fertilized, menstrual cycle stop temporarily in a woman. Give reason.
Give the exact location of the prostate gland.
Find the odd one out and write it:
Vagina, Uterus, Vas deferens, Ovary.
Give the biological technical term for complete stoppage of menstrual cycle in females.
Explain the process of spermatogenesis in humans.
Explain the process of spermatogenesis in detail.
What is compaction in the human development?
Define:
1) Reparative regeneration 2) Capacitation 3) Menarche
What is corpus luteum and what is its function?
Name the cells that secrete androgens.
Sketch the label 'human male reproductive system'.
Answer in one sentences:
What is Menarche?
Explain the phases of spermatogenesis in humans with the help of a diagram.
Draw only ray-diagram of spermatogenesis.
What is spermatogenesis? Explain with the help of diagram.
Why testis are found outside the abdominal cavity in males?
Write only the name of different stages of human reproduction.
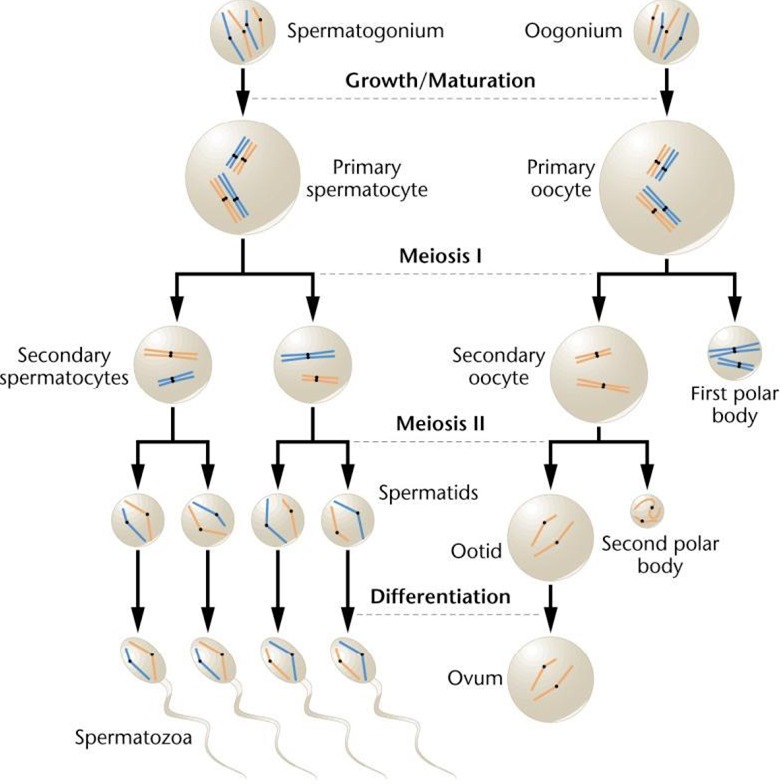
Write four differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
The study of physical abnormalities of embryo is called as
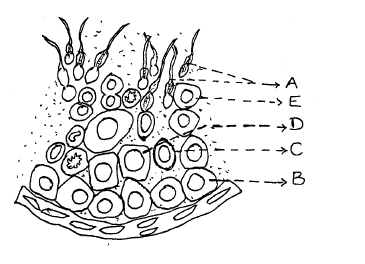
Observe the diagram, and answer the question:
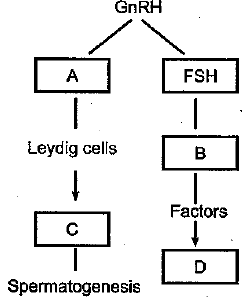
(a) Identify A and B.
(b) What is the function of C?
(c) In which of the marked part reduction division takes place? What is the significance of it?
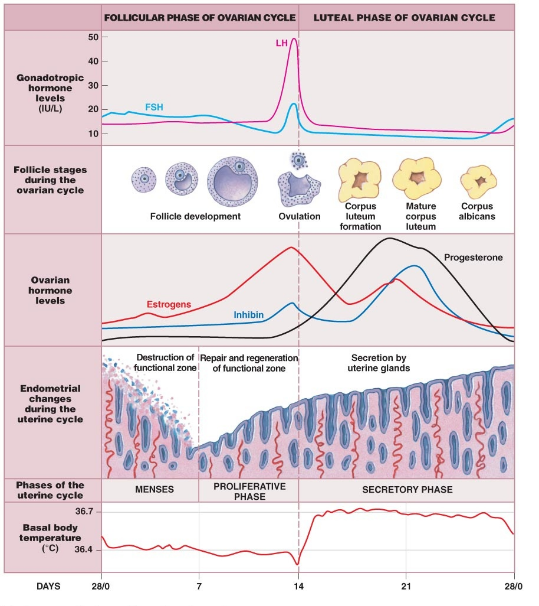
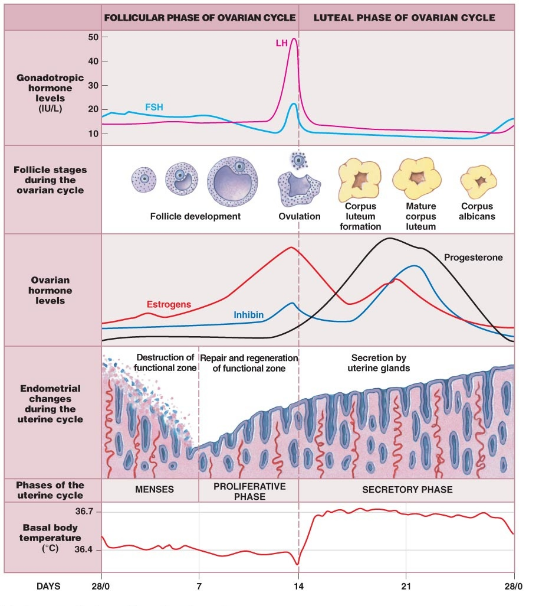
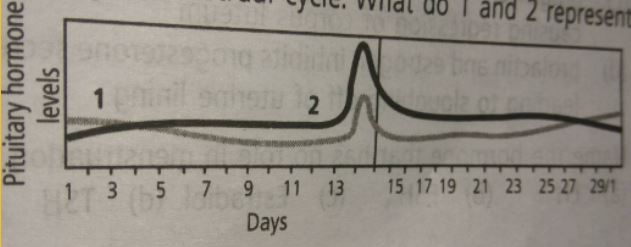
The following graph shows the levels of pituitary hormones during a menstrual cycle. What do 1 and 2 represent?
Mention the exact location of the following:
Prostate gland.
The diagram shown below is the longitudinal section of a testis of man. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow:
State the functions of the parts labelled $$1$$ and $$3$$ in the diagram.
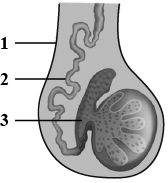
Given appropriate biological/ technical terms for the following:
The accessory gland in human males whose secretion activates the sperms.
The diagram shown below is the longitudinal section of the testis of man. Study it carefully and answer the following questions.
a. Label the parts numbered $$1$$ to $$3$$ in the diagram.b. In which part of the testis sperms are produced?
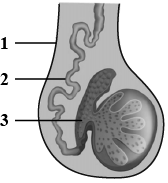
a. Label the parts numbered $$1$$ to $$3$$ in the diagram.
The diagram shown below is the longitudinal section of a testis of man. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow:
In which part of the testis are the sperms produced?
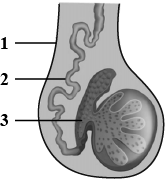
Define spermiogenesis.
Mention the exact location of the following:a. Epididymis
b. Lacrimal glandc. Malleusd. Hydathodese. Pulmonary semilunar valve
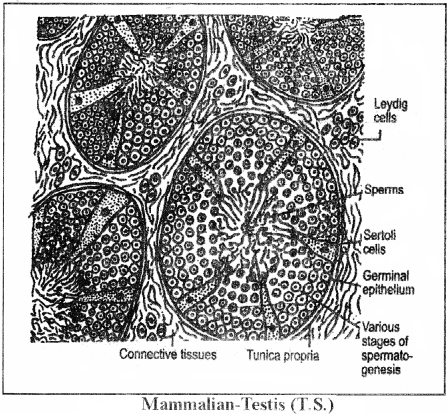
Draw a labelled diagram of L.S. of human testis.
Give appropriate biological or technical terms for the following.
The onset of menstruation in a young girl.
Choose the ODD one out from the following terms given and name the CATEGORY to which the others belong.
Example: Nose, Tongue, Arm, Eye
Answer: Odd Term- Arm, Category- Sense organs
Prostate gland, Cowper's gland, seminal vesicle, seminiferous tubules.
Define the following term:
Implantation
Describe the histology of human testis. Write a note on human sperm.
State the functions of the following:
Seminal vesicles
Why is it important that a very large number of sperms should be present in the semen?
Very short answer type.
Give the scientific term for the animals which gave birth to young ones.
Application Based Questions :
Lack of menstruation is an indication of pregnancy.
Differentiate between :
Menarche and menopause
Give basic difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Very short answer type.
Mention the most significant function/role of acrosome:
Short / Long Answer question Type :
Write short notes on Menarche
Very short answer type.
When and where does spermatogenesis occur in .a human male?
Very short answer type.
Define the term spermiogenesis
Application Based Questions :
In humans, the testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity. Why?
Very short answer type.
What is the proliferative phase in the menstrual cycle? For how many days does it last?
Differentiate between :
Vas deferens and vasa efferentia
Fill in the blanks:
Zygote is ______ (diploid/haploid)
What is implantation?
Name the functions of Endometrium.
Humans are ______ as they undergo internal fertilization to give birth to newborns.
What is Periodic abstinence?
Enumerate the events in the ovary of a human female during follicular phase of menstrual cycle.
What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
Explain the steps in the formation of an ovum from an oogonium in humans.
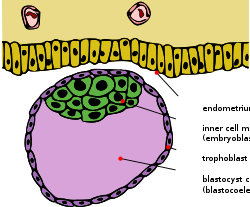
Mention the function of trophoblast in human embryo.
Give a schematic representation of spermatogenesis in humans.
When and how does placenta develop in human female?
Draw a labelled diagram of a sectional view of human seminiferous tubule.
Enumerate the events in the ovary of a human female during Luteal phase of menstrual cycle.
Explain the hormonal regulation of the process of spermatogenesis in humans.
Draw a diagrammatic sectional view of a human seminiferous tubule, and label Sertoli cells, primary spermatocyte, spermatogonium and spermatozoa in it.
What is Menstrual cycle? Describe it in brief.
Which cell organelles are found in the formation of middle part of sperm?
Describe the functions of seminal vesicles.
Write a brief note on hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis.
Rewrite the terms in the correct order so as to be in a logical sequence.
Puberty, menopause, menstruals, menarche, reproductive age.
Differentiate oviparous and viviparous organisms. Also, give examples.
Name the fluid surrounding the developing embryo.
Give appropriate terms for the fixing of developing zygote (blastocyst) on the uterine wall.
Name the part where the where the sperms are produced in the testes.
Name the tubular knot fitting like a cup on the upper side of the testis.
Give appropriate terms for the onset of reproduction phase in a female.
Name the accessory gland in human males whose secretion activates the sperms.
Why more spermatozoa are formed as compared to ova?
What is implantation ? When does this process begin?
Explain with a neat labelled diagram the T.S. of mammalian testis.
What is menopause and menarche?
Write note on : Implantation
Differentiate between male and female gametes.
Write note on : Spermatogenesis
What is menstrual cycle? When does it begins? What happens during this period?
Is there an age limit to male fertility?
Label the parts A to D of the diagram.
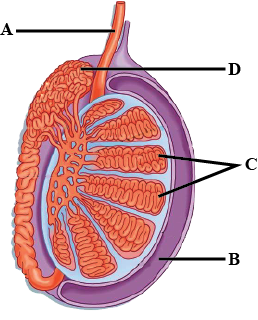
Define fertilisation and implantation?
Give one significant difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
What are oviparous and viviparous animals?
Give functions of :
(a) Epididymis
(b) Seminiferous tubule
Give one significant difference between puberty and menarche.
Ovulation takes place on the $$14^{th}$$ day of menstrual cycle. Why?
Name an animal that stays in water like fish but has no gills to breathe in water. It gives birth to babies like the tiger does, but does not live in the forest.
What is Zygote?
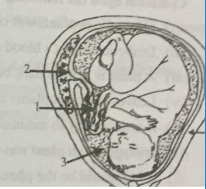
The diagram given alongside is that of a developing human foetus in the womb. Study the same and answer the following question.
How many days does the foetus take to be fully developed?

Mr. X is diagnosed for failure of spermiogenesis. Give a brief account on spermiogenesis.
Write about Zygote.
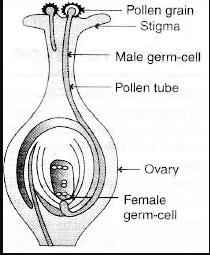
Draw the diagram showing the germination of pollen on stigma and label the following parts (i) stigma (ii) pollen tube
How do the characteristics of mother and father get transmitted in a human embryo?
Why there is pain when a woman is in a periods?
Where are sperms stored and ejaculated from ?
Where Barr body is found?
What is endometrium and what happens to it during the menstural cycle
Which part of the sperm head part comes in contact with the egg at the time of fertilization?
The onset of menstruation is termed as ____________Loss of reproductive capacity in women after age of 45-50 years, is termed as_______________.
Draw the structure of human male reproductive system.
The cells of the testes that produce male hormones are known as __________
How much chromosomes do the drones of honeybees have? Name the type of cell division that occurs during the formation of spermatozoa in them.
Explain the terms
a) Implantation
b) Placenta
b) Placenta
Explain the terms :
(a) Implantation
(b) Placenta
(b) Placenta
Differentiate between menarche and menopause.
Define ''Spermiation '' and ''Spermiogenesis''.
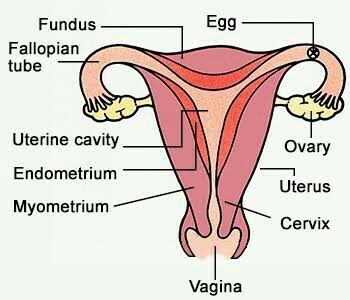
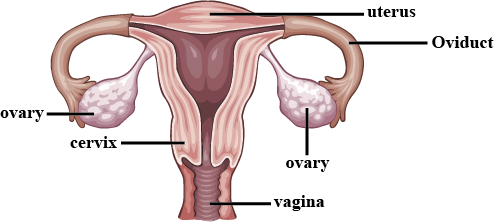
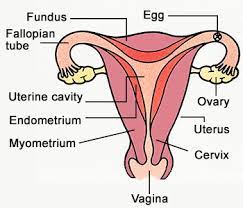
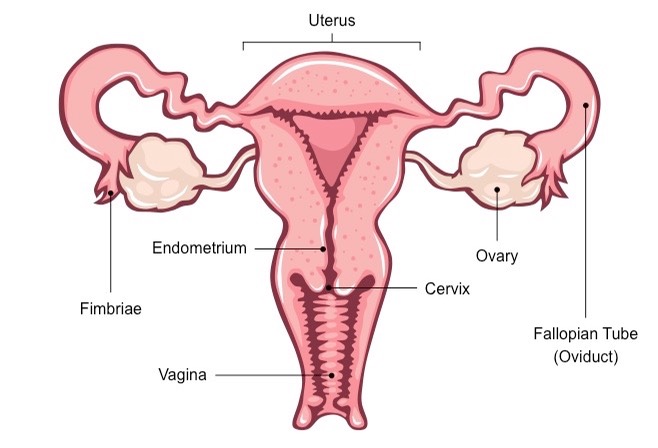
Explain the female reproductive organ with diagram.
Explain the term:-
Implantation
What is Menarche?
What are the two main functions of the fluid secreted by seminal vesicles and the prostate gland in human male reproductive system?
Draw a labelled diagram to show interrelationship of accessory ducts in a human male reproductive system.
Name the largest cell in human body.
The figure shows a foetus in the uterus. Define implantation.
Differentiate between spermatogenesis and oogenesis on the basis of
(i) Time of initiation of the process
(ii) Site of completion of the process
(iii) Nature of meiotic division undergone by gamete mother cells
In human females, an event that reflects onset of reproductive phase is :
A. Growth of body
B. Changes in hair pattern
C. Changes in voice
D. Menstruation
What is the function of prostate glands and seminal vesicles
Name the homones and state their role involved in controlling spermatogensis in humans.
Fill in the blank.
In male and female reproductive system of human, _______ gland is same.
In male and female reproductive system of human, _______ gland is same.
Fill in the blank.
Implantation of embryo occurs in _____
Implantation of embryo occurs in _____
Answer the following question is short.
What is menstrual cycle? Describe it in brief.
What is menstrual cycle? Describe it in brief.
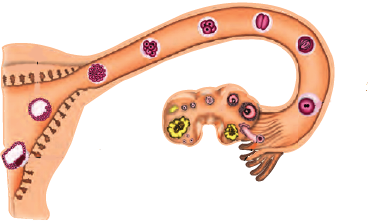
After observing figure answer the following.
Read the following statements and label them in the figure:
(i) The part which produces female gametes.
(ii) The part where development of the baby takes place.
(iii) The part through which the developing embryo passes to reach the uterus.
Unscramble the underlined words in the following sentences.
Reproductive life of a woman lasts from hacreemn to spauoemen.
Where does implantation of embryo take place in mother?
What is the role of cervix in the human female reproductive system?
Write a short note on cleavage and implantation.
What is gametogenesis?
What is the role of vas deferens?
What is zygote?
Why are menstrual cydes absent during pregnancy.
Female reproductive organs and associated functions are given below in column A and B. Fill the blank boxes.
Column A Column B Ovaries Ovulation Oviduct (a) (b) Pregnancy Vagina Birth
| Column A | Column B |
| Ovaries | Ovulation |
| Oviduct | (a) |
| (b) | Pregnancy |
| Vagina | Birth |
What is the significance of epididymis in male fertility?
Which type of cell division forms spermatids from the secondary spermatocytes?
(a) How many spermatozoa are formed from one secondary spermatocyte?
(b) Where does the first cleavage division of zygote take place?
Meiotic division during oogenesis is different from that in spermatogenesis. Explain how and why?
What role does pituitary gonadotropins play during follicular and ovulatory phases of menstrual cycle? Explain the shifts in steroidal secretions.
What are the events that take place in the ovary and uterus during follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
Give the names and functions of the hormones Involved In the process of spermatogenesis. Write the names of the endocrine glands from where they are released.
What is the significance of ampullary-isthmic Junction in the female reproductive tract?
The zygote passes through several developmental stages till implantation. Describe each stage briefly with suitable diagrams.
Mention the importance of LH surge during menstrual cycle.
A human female experiences two major changes, menarche and menopause during her life. Mention the significance of both the events.
Explain the structure of ovary.
What kind of cell divisions take place during cleavage?
State the functions of the following:
(a) Ovary
(b) Testes
(c) Fallopian tubes
(d) Seminal vesicle
(e) Uterus
Which of the cells function as endocrine gland in the testes? Write the name of the hormone secreted by these cells.
Write a brief note on three stages of gametogenesis.
Describe two structural differences between a mature sperm and a mature egg.
(a) Explain the menstrual phase in a human female. State the levels of ovarian and pituitary hormones during this phase.
(b) Why is the follicular phase in the menstrual cycle also referred as a proliferative phase? Explain.
(c) Explain the events that occur in a Graafian follicle at the time of ovulation and thereafter.
(d) Draw a Graafian follicle and label antrum and secondary oocyte.
Give the functions of the following:
(a) Corpus luteum (b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome (d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae
Implantation, Parturition, Ovulation, Gestation, Fertilisation (Stages leading to formation of foetus and birth)
Define menstrual cycle and explain its various phases with diagram.
Write an essay on menstrual cycle.
Short / Long Answer question Type :
At what stage does the developing human embryo get attached to the inner lining of the mothers uterus? Explain the developmental changes the embryo undergoes till the establishment of three germinal layers .
Application Based Questions :
Why not all copulations lead to fertilization and pregnancy?
Short / Long Answer question Type :
Tell the functions of each part of a sperm cell.
Application Based Questions :
Identify A, B, C and D with reference to gametogenesis in humans, in the flow chart given below
Differentiate between seminiferous tubules and Leydig cells.
Very short answer type.
To which structures do the mesovarium, ovarian ligament, and suspensory ligament anchor the ovary?
Differentiate between :
Spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis
Define spermiation?
A woman can give birth to how many children in her lifetime?
Define gametogenesis. Name two types of gametogenesis. Give a Schematic represenation of spermatogenesis in humans.
Draw a diagram of the sectional view of human seminiferous tubule and label its parts.
Write a short note on ovum and sperm.
What happens when the egg is not fertilised?
Where do the following functions occur in humans?
Production of egg
Fertilization
Implantation of zygote
Fertilization
Implantation of zygote
State the difference between sperm and egg in a tabulas form with the diagram.
Write the name of those parts of a flower with serve the same function as the following do in the animals. (i) Testis (ii) Sperm (iii) Ovary (iv) Egg.
In human body what is the role of (i) Seminal vesicles
(ii) Prostate glands
Corpus luteum gets converted into corpus albicans in absence of fertilization, give reason.
Draw labelled diagram of a transverse section of the testis.
During reproduction, the chromosome number (2n) reduces to half (n) in the gametes and again the original number (2n) is restored In the offspring, What are the processes through which these events take place?
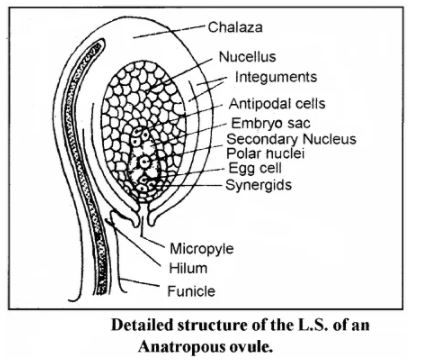
Draw a well-labelled diagram of a typical ovule.
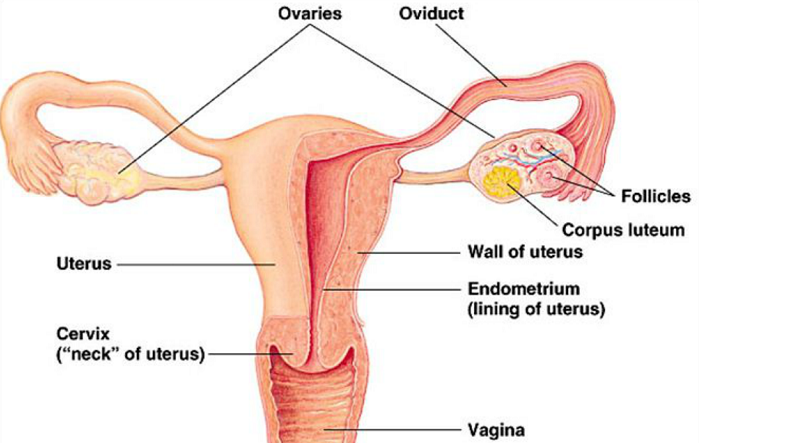
(a) Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the parts where:
(i) eggs develop.
(ii) fertilization takes place
(iii) fertilized egg gets implanted.
(b) Describe, in brief, the changes that the uterus undergoes:
(i) to receive the zygote
(ii) if zygote is not formed.
Draw the diagram of Human female reproductive system and label the following:
(a) Site of production of egg (b) Site of fertilization (c) Site of zygote implantation
Draw a neat diagram of the female reproductive system and label the parts associated with the following (a) production of gamete. (b) site of fertilisation (c) site of implantation and. (d) birth canal.
Describe spermatogenesis with the help of a diagram.
Draw line diagrams of spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Class 12 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Biodiversity And Its Conservation Extra Questions
- Biotechnology And Its Applications Extra Questions
- Biotechnology: Principles And Processes Extra Questions
- Ecosystem Extra Questions
- Environmental Issues Extra Questions
- Evolution Extra Questions
- Human Health And Disease Extra Questions
- Human Reproduction Extra Questions
- Microbes In Human Welfare Extra Questions
- Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Extra Questions
- Organisms And Population Extra Questions
- Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Extra Questions
- Reproduction In Organisms Extra Questions
- Reproductive Health Extra Questions
- Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Extra Questions


.jpg)