Equilibrium - Class 11 Medical Chemistry - Extra Questions
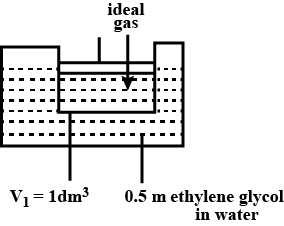
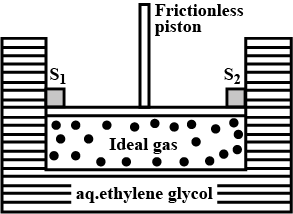
A cylinder containing an ideal gas $$(0.1\ mol$$ of $$1.0\ dm^3$$) is in thermal equilibrium with a large volume of $$0.5$$ molal aqueous solution of ethylene glycol at its freezing point. If the stoppers $$S_1$$ and $$S_2$$ ( as shown in the figure) are suddenly withdrawn , the volume of the gas in litres after equilibrium is achieved will be ________.
(Given, $$K_f(water)=2.0\ K\ kg\ mol^{-1},R=0.08\ dm^3\ atm\ K^{-1}\ mol^{-1}$$)
What is a buffer solution?
You have been provided with three test tubes, one of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper; how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Arrange the following in order (ascending) of their pH values.
NaOH solution, Blood, lemon Juice
What is rock salt? Why is it brown in colour?
Silver ______ is stored in dark coloured bottle.
Dissociation constant of an acid $$HA$$ is $$X \times {10}^{-3}$$ so that it will be $$1$$% dissociated in a solution having $$[{H}_{3}{O}^{+}]$$ fixed at $$0.1M$$. Value of $$X$$ is:
Give three factors on which solubility of solids depends.
Match the following in column A with the correct answer from the choices given in column B:
The ionisation constant of ammonia and ammonium hydroxide is same. If true write 1, else write 0.
The dissociation of $${NH}_{4}OH$$ decreases on addition of $${NH}_{4}Cl$$. If true write 1, else write 0.
Acetic acid is less acidic in sodium acetate solution than in $$NaCl$$ solution. If true write 1, else write 0.
Addition of $${NH}_{4}Cl$$ does not effect the $$pH$$ of solution of $${NH}_{4}OH$$. If true write 1, else write 0.
An .......... is a substance that tastes sour.
Fill in the blank with the correct word from the given set:(chemical, electrons, acid, physical, positive, neutrons, nucleus, atom, atomic, molecule)
(chemical, electrons, acid, physical, positive, neutrons, nucleus, atom, atomic, molecule)
The $$\displaystyle pH$$ of 0.005 M codeine ($$\displaystyle { C }_{ 18 }{ H }_{ 21 }{ NO }_{ 3 }$$) solution is 9.Calculate its ionization constant and $$\displaystyle { pK }_{ b }$$.
Acetic acid is a weak acid whereas $$HCl$$ is a strong acid. Give reasons.
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
A student add a spoon full of powdered sodium hydrogen carbonate to a flask containing ethanoic acid. List two main observations he must note in his note book about the reaction that takes place. Also write chemical equation for the reaction.
In mouth, tooth decay occurs when $$pH$$ is less than _______ .
Give the molecular formula for bleaching powder.
State what would you observe when :
(i) Washing soda crystals are exposed to the atmosphere.
(ii) The salt ferric chloride is exposed to the atmosphere.
The pH of rain water is $$7$$. Is it true or false?
State your observation in each of the following cases:
When calcium hydroxide is heated with ammonium chloride crystals.
What is buffer solution? Give an example.
If the ionization (dissociation) constant of acetic acid is $$k_a$$, what will be the pH of a solution containing equal concentrations of acetic acid and sodium acetate?
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(increases, decreases, positive, efficient, 68, non-efficient, no $$\alpha$$-hydrogen, $$\alpha$$-hydrogen, negative, Rosenmund's, greater, Cannizzaro, 74, common-ion effect, lesser, buffer action, diamagnetic, paramagnetic)
Solubility of silver chloride ............... in the presence of sodium chloride because of ............... .
A solution of $$NH_{4}Cl$$ and $$NH_{4}OH$$ acts as a buffer.
What is $$pH$$ Scale? Explain that $$pH$$ change of the mouth is the cause of tooth decay.
What is the effect of temperature on the ionic product of water? How will it change the pH value of a neutral solution?
What is a buffer solution? How is it prepared? Explain the buffer action of a basic buffer with a suitable example.
Explain most important buffer in blood plasma.
Why the soil of agriculture lands get tested for $$pH$$?
The $$pH$$ values of certain familiar substances are given below:
Substance
$$pH$$ value
Blood
7.4
Baking Soda
8.2
Vinegar
2.5
Household ammonia
12
Analyse the data in the table and answer the following questions
i) Which substances are acidic in nature?
ii) Which substances are basic in nature?
| Substance | $$pH$$ value |
| Blood | 7.4 |
| Baking Soda | 8.2 |
| Vinegar | 2.5 |
| Household ammonia | 12 |
Analyse the data in the table and answer the following questions
i) Which substances are acidic in nature?
ii) Which substances are basic in nature?
The solubility product of lead iodide is $$1.4\times { 10 }^{ -8 }$$. Calculate its molar solubility in $$0.1M$$ $$KI$$ solution.
The solubility product of $$Ba{SO}_{4}$$ is $$1.5\times { 10 }^{ -9 }$$. Find out the solubility in (i) pure water and (ii) $$0.1M$$ $$Ba{Cl}_{2}$$ solution.
What is the hydrogen ion concentration of $$0.1N$$ $${ CH }_{ 3 }COOH$$ solution. The ionisation constant of $${ CH }_{ 3 }COOH$$ is $$1.8\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$. What is the pH of the solution?
A solution has $$0.05M$$ $${Mg}^{2+}$$ and $$0.05M$$ $${NH}_{3}$$. Calculate the concentration of $${ NH }_{ 4 }Cl$$ required to prevent the formation of $$Mg{ \left( OH \right) }_{ 2 }$$ in this solution. $${ K }_{ sp }$$ of $$Mg{ \left( OH \right) }_{ 2 }=9.0\times { 10 }^{ -12 }$$ and ionisation constant of $${ NH }_{ 3 }=1.8\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$
The pH of $$0.1M$$ hydrocyanic acid solution is $$5.2$$. What is the value of $${K}_{a}$$ for hydrocyanic acid?
The dissociation constants for $$HCOOH$$ and $${CH}_{3}COOH$$ are $$2.1\times { 10 }^{ -4 }$$ a.nd $$1.8\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$ respectively. Calculate the relative strengths of the acids.
Saccarin ($${ K }_{ a }=2\times { 10 }^{ -12 }$$) is a weak acid represented by formula $$HSac$$. A $$4\times { 10 }^{ -4 }$$ mole amount of saccharin is dissolved in $$200{cm}^{3}$$ water of pH$$=3$$. Assuming no change in volume, calculate the concentration of $${Sac}^{-}$$ ions in the resulting solution at equilibrium.
$$0.02M$$ solution of $${ NH }_{ 4 }OH$$ is $$3$$% dissociated. Calculate the dissociation constant of $${ NH }_{ 4 }OH$$.
At $${ 15 }^{ o }C,0.05N$$ solution of a weak monobasic acid is $$3.5$$% ionised. Calculate the ionisation constant of acid.
$$0.16g$$ of $${ N }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 4 }$$ are dissolved in water and the total volume made up to $$500mL$$. Calculate the percentage of $${ N }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 4 }$$ that has reached with water at this dilution. The $${K}_{b}$$ for $${ N }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 4 }$$ is $$4.0\times { 10 }^{ -6 }M$$.
The degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte in $$0.1M$$ aqueous solution is $$0.0114$$ at $$298K$$. Calculate the degree of dissociation of the same electrolyte at $$298K$$ in $$0.001M$$ solution.
The degree of dissociation of water is $$1.8\times { 10 }^{ -9 }$$ at $$298K$$. Calculate the ionisation constant and ionic product of water at $$298K$$.
Calculate the degree of ionisation of $$01.M$$ acetic acid. the dissociation constant of acetic acid is $$1.8\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$.
Calculate the degree of ionisation and hydroxyl ion concentration in $$0.2M$$ $${ NH }_{ 3 }$$ solution.($${ K }_{ b }=1.85\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$ for $$298K$$)
Calculate $${K}_{b}$$ for a base whose $$0.1M$$ solution has pH of $$10.5$$.
Calculate the concentration of $${ OH }^{ - }$$ ions of $$0.01M$$ $${ NH }_{ 4 }OH$$ solution. The equilibrium constant of $${ NH }_{ 4 }OH$$ is $$1.8\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$.
Calculate the simultaneous solubilities cations of $$Ca{ F }_{ 2 }$$ and $$Sr{ F }_{ 2 }$$. $${K}_{sp}$$ for the two salts are $$4\times { 10 }^{ -11 }$$ and $$2.8\times { 10 }^{ -9 }$$ respectively.
The dissociation constants of m-nitrobenzoic acid and acetic acid are $$36.0\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$ and $$1.8\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$ respectively. What are their relative strengths?
Which of the two solutions $$0.1M$$ $$HCN$$ $$\left( { K }_{ a }=4\times { 10 }^{ -10 } \right) $$ and $$0.1M$$ $$HF$$ $$\left( { K }_{ a }=6.7\times { 10 }^{ -4 } \right) $$ will have greater degree of ionisation and to what extent?
A sample of $$AgCl$$ was treated with $$5\ mL$$ of $$1.5\ M$$ $${ Na }_{ 2 }{ CO }_{ 3 }$$ solution to give $${ Ag }_{ 2 }{ CO }_{ 3 }$$. The remaining solution contained $$0.0026 \ g\ { Cl }^{ - }$$ per litre. Calculate the solubility product of $$AgCl$$.
$$\left( { K }_{ sp }({ Ag }_{ 2 }{ CO }_{ 3 })=8.2\times { 10 }^{ -12 } \right) $$
Explain the following:
(i) Hydrolysis of ester (ethyl acetate) begins slowly but becomes fast after sometime.
(ii) The pH value of acetic acid increases on addition of a few drops of sodium acetate.
Answer the following:
(1) What is the effect of temperature on ionic product of water $$\left(Kw\right)$$?
(2) What happen to the ionic product of water $$\left(Kw\right)$$ if some acid is added to it?
Write a balanced chemical equation for the following.
Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on magnesium sulphate.
Write a balanced chemical equation for the following :
Reaction of sodium hydroxide solution with iron(III) chloride solution.
Reaction of sodium hydroxide solution with iron(III) chloride solution.
State one relevant observation for the following.
Barium chloride solution is slowly added to sodium sulphate solution.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of chemicals.
(i) Lead nitrate solution and Zinc nitrate solution.
(ii) Sodium chloride solution and Sodium nitrate solution.
$$1\ M$$ benzoic acid $$(pK_{a} = 4.2)$$ and $$1M\ C_{6}H_{5}\ COONa$$ solutions are given separately. What is the volume of benzoic acid required to prepare a $$93\ mL$$ buffer solution of $$pH = 4.5$$?
(i) What is the type of salt formed when the reactants are heated at a suitable temperature for the preparation of nitric acid?
(ii) State why for the preparation of nitric acid, the complete apparatus is made up of glass.
Write a balanced equation for the preparation of the following salts.
(i) Copper sulphate from Copper carbonate.
(ii) Zinc carbonate from zinc sulphate.
A recent investigation of the complexation of $$SCN^-$$ with $$Fe^{3+}$$ led of $$130, 16$$ and $$1.0$$ for $$K_1, K_2$$ and $$K_3$$, respectively. What is the overall formation constant of $$Fe(SCN)_3$$ from its component ions, and what is the dissociation constant of $$Fe(SCN)_3$$ into its simplest ions on the basis of these data?
An acid $$HA$$ ionises as
$$HA\rightleftharpoons H^++A^-$$
The pH of $$1.0$$M solution is $$5$$. Its dissociation constant would be:
Percentage ionisation of water as follows at certain temperature is $$3.6 \times 10^{-7}%$$. Calculate $$K_w$$ and $$pH$$ of water this temperature. $$2H_2O \rightleftharpoons H_3O^+ + OH^-$$.
$$K_{w}$$ for $$H_{2}O$$ is $$9 \times 10^{-14}$$ at $$60^{o}\ C$$. What is $$pH$$ of water at $$60^{o}\ C$$? $$ (log 3=0.47)$$
Ionisation constant of $${ CH }_{ 3 }COOH$$ is $$1.7\times { 10 }^{ -5 }$$ and concentration of $${ H }^{ + }$$ ions is $$3.4\times { 10 }^{ -4 }$$. Then find out initial concentration of $${ CH }_{ 3 }COOH$$ molecules:
Write the nature of the ionic solids.
Answer the following question relating your answers only -to salts in the list given below: Anhydrous $${ CaCl }_{ 2 },{ CuSO }_{ 4 }.5{ H }_{ 2 }{ O,Na }_{ 2 }{ CO }_{ 3 }.{ 10H }_{ 2 }O$$
What would be seen on mixing the solution of calcium chloride with the solution of sodium carbonate?
What would be seen on mixing the solution of calcium chloride with the solution of sodium carbonate?
Why is the electrolytic dissociation represented by a reversible $$(\rightleftharpoons )$$ sign?
Name the following:
Name two bases which are not alkalis i.e insoluble bases
Do basic solutions also have H+ ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Define common ion effect.
In a coagulation experiment, 5ml $${ As }_{ 2 }{ S }_{ 3 }$$ is mixed with distilled water and 0.1M solution of an electrolyte AB so that the total volume is 10ml. It was found that all solutions containing more than 4.6ml of AB coagulate within 5min. What is the flocculation value of AB for $${ As }_{ 2 }{ S }_{ 3 }$$ solution?
What would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte in the electrolytic refining of a metal M?
Arrange the following in increasing order of their $$pH$$ values:NaOH solution, Blood, Lemon juice.
Give a balanced equation for the following type of reaction :
A decomposition reaction of a salt which leaves behind a silvery metal.
How is tooth decay related to $$pH$$? How can it be prevented?
Fresh milk has a pH of $$6$$. When it changes into curd (yogurt), will its pH value increase or decrease?Why?
A certain compound (X) shows the following reactions.
i) When the paste of (X) in water is heated with ethyl alcohol, a product of anaesthetic use is obtained.
Identify (X) and write down chemical equations for reaction.
Answer the following:
What is the percentage of available chlorine in a good sample of bleaching powder?
What is the percentage of available chlorine in a good sample of bleaching powder?
The hydronium ion concentration (in millimole per litre) in a solution containing $$1.8 g$$ $$NaHSO_{4}$$ per $$100 ml$$ is $$x$$. Write the value of $$x^2$$. ($$K_{a}$$ for $$HSO_{4}^{-}$$ is $$4.0 \times 10^{-2}$$)
An aqueous solution contains $$10$$% ammonia by mass and has a density of $$0.99 g/ml$$. If $$[OH^{-}]$$ in this solution is '$$x$$' M, then the value of '$$x \times 10^{2}$$' is ($$K_{a}$$ for $$NH_{4}^{+} = 5.0 \times 10^{-10} M$$)
The soil in a field is highly acidic. Name two materials that can be added to this soil to reduce its acidity. Give the reason for your choice.
With which substance should chlorine be treated to get bleaching powder?
Potatoes grow well on Anhad's farm which has soil with a pH of 5.Anhad decides to add lot of lime to soil so that he can grow broccoli in the same farm:
(a) Do potatoes grow better in acidic or alkaline soil?
(b) Does broccoli grow better in acidic or alkaline soil?
a) What happens during a bee sting? What is its remedy?b)What happens during a wasp sting? What is its remedy?
(a) Why is it wrong to treat a bee sting with vinegar?(b) Why is it wrong to treat a wasp sting with a baking soda solution?
(a) What is the chemical name of bleaching powder?
(b) What is the chemical formula of bleaching powder?
(c) What are the materials used for the preparation of bleaching powder?
(d) State one use of bleaching powder (other than bleaching).
The electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride gives us three products. Name them.
Name three chemicals made from common salt (or sodium chloride).
A first-aid manual suggests that vinegar should be used to treat wasp stings and baking soda for bee stings. What does this information tell you about the chemical nature of:(a) wasp stings?(b) bee stings?
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
(a) What is bleaching powder? How is bleaching powder prepared? Write chemical equation of the reaction involved in the preparation of bleaching powder.(b) What happens when bleaching powder reacts with dilute sulphuric acid? Give equation of the reaction involved.(c) State two important uses of bleaching powder.
(a) What is "baking powder"? How does it make the cake soft and spongy?(b) In addition to sodium hydrogencarbonate, baking powders contain a substance X. Name the substance X. What is the role of substance X in the baking powder?
Consider the following substances:
$$NaCl, Ca(OH)_2, NaHCO_3, NH_3, Na_2CO_3, H_2O, Cl_2, CO_2, CaSO_4.2H_2O$$ $$2CaSO_4H_2O, CaOCl_2.$$
(a) Which two substance combine to form bleaching powder?(b) Which four substances are utilised in the production of washing soda?(c) Which compound represents plaster of Paris?(d) Which compound is a part of baking powder?(e) Which compound is used as an antacid?
When chlorine and sodium hydroxide being produced during the electrolysis of brine are allowed to mix, a new chemical is formed. Name the chemical and write its uses.
A white powdery substance having strong smell of chlorine is used for disinfecting drinking water supply at waterworks. Identify the substance. Give its chemical name and write the chemical reaction for its preparation.
Name a salt whose solubility decreases with temperature.
Farmers are using a large number of pesticides and fertilizers in their fields to increase crop production and to enhance their profits. But by doing so, they are causing damage to the soil as well as to the environment.
Answer the following questions based on the above situation:
(i) Do you agree with this statement?
(ii) Why should we avoid eating fruits and vegetables without washing them properly
(iii) What values are neglected by the farmers?
Two salts whose solubility increases with temperature,
Nishant is a lazy boy. He doesn't like to brush his teeth instead he rinses his mouth with water. His mother makes sure that he brushes his teeth twice a day.
Answer the following questions based on the above situation:
(i) Why does Nishant's mother insist on brushing teeth twice a day?
(ii) How is toothpaste better than just water, for cleaning teeth?
(iii) What values are promoted by Nishant's mother?
Give reason:Table salt becomes moist during rainy season.
Name the acid present in an ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also give the common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
How can a farmer convert acidic soil to neutral soil?
Identify the odd one out and justify.
Crystalline blue vitriol, crystalline common salt, crystalline ferrous sulphate, crystalline sodium carbonate.
What is meant by ionic product of water $$(K_a)$$?
Define ionic equilibrium.
What is buffer solution?
Why do lemons, tamarind and oranges taste sour?
Match the pairs
Design an activity to prove that acids show acidic behaviour only when dissolved in water.
Write the properties of salt.
What is the significance of $$pH$$ in everyday life?
Why slats are neutral in nature?
Write two chemical properties of salt.
Conduct an activity to find the $$pH$$ value of the soil related to different crops. Identify the $$pH$$ values of soil samples collected from different places.
Prepare a list of the crops that are suitable for the soil of each area on the basis of its $$pH$$ value.
List the acids that are present in lime juice, curd, tamarind, vinegar.
Which component is responsible for the common properties of acids?
Mention the types of buffer solution.
It is better to determine the $$pH$$ of soil before farming? Why?
Complete the chemical equations for the following ionization equations.
$$KCl \rightarrow K^{+} + .......$$
$$HNO_{3} \rightarrow H^{+} + ......$$
$$Mg(OH)_{3} \rightarrow ...... + 2OH$$
$$H_{2}SO_{4} \rightarrow 2H^{+} + .....$$
$$NH_{4}Cl \rightarrow NH_{4}^{+} + .....$$
$$CuSO_{4} \rightarrow ..... + SO_{4}^{2-}$$.
Explain the Mechanism or working of basic buffer.
What is buffer solution ? Write any two properties of buffer solution. Derive the formula for calculating the pH for acidic buffer. Write any two examples of simple buffer.
A first aid manual suggests that vinegar should be used to treat wasp stings and baking soda for bee stings.
(i) What does this information tell you about the chemical nature of the wasp stings
(ii) If there were no baking soda in the house, what other household substance could you use to treat bee stings?
The equilibrium $$H_2O(l) \rightleftharpoons H_2O(v)$$ is attained in a closed container at $$40^oC$$. The aqueous tension of water at $$40^oC$$ is $$23\ mm$$. What is $$K_p$$ for the said equilibrium?
Fill in the blanks:
A compound whose aqueous solution or melt conducts electricity called __________.
What is the function of adding $$NH_{4}OH $$ in group V ?
Fill in the blank:
The word acid comes from the Latin word _______.
What happens to ionic product of water if some acid id added into water ?
Write ionic equations to show the presence of ions in aqueous
solutions of:
(i) Sodium hydroxide
(ii) Barium hydroxide
(iii) Ammonium hydroxide
Salt A commonly used in bakery products on heating gets converted into another salt B which itself is used for removal of hardness of water and a gas C is evolved. The gas C, when passed through lime water, turns it milky. Identify A, B and C and hence write the molecular masses of B
A $$0.01M$$ aqueous solution of weak acid $$HA$$ has an osmotic pressure $$0.293$$ atm at $${25}^{o}C$$. Another $$0.01M$$ aqueous solution of other weak acid $$HB$$ has an osmotic pressure of $$0.345$$ atm under the same conditions. Equilibrium constants of second acid for their dissociation is $$X\times {10}^{-3}$$, nearest integer to X is:
$$X \times 100$$ mL water must be added to $$300$$ mL of $$0.2M$$ solution of $${CH}_{3}COOH$$ for the degree of dissociation of the acid to double? The value of X is ____.
$$[{K}_{a}$$ for acetic acid $$=1.8\times {10}^{-5}]$$
$$[{K}_{a}$$ for acetic acid $$=1.8\times {10}^{-5}]$$
For an organic monoprotic acid solution of concentration $$C_o$$ $$mol$$ $${litre}^{-1}$$, if $${K}_{a}$$ has a value comparable to $${K}_{w}$$, show that the hydronium ion concentration is given by:
$$[{H}^{+}]==\left[ \cfrac { { K }_{ w } }{ \left[ { H }^{ + } \right] } +\cfrac { { K }_{ a }\cdot Co }{ \left[ { K }_{ a }+{ H }^{ + } \right] } \right] $$
If $$[{H}^{+}]={10}^{-3}M$$ and $$C_o={10}^{-1}M$$ in a solution of some organic monoportic acid. According to the above equation, the order of magnitude of $${K}_{a}$$ must be $${10}^{-X}$$, the value of $$X$$ should be:
List I and List II contains four entries each. Entries of List I are to be matched with some entries of List II. One or more than one entries of List I may have the matching with the same entries of List II
When we Titrate sodium carbonate solution (in beaker) with hydrochloric acid
$$0.16\ g\space N_2H_4(K_b = 4\times10^{-6})$$ are dissolved in water and the total volume made up to $$500\space mL$$. Calculate the percentage of $$N_2H_4$$ that has reacted to water in this solution.
Two weak acids $$HA$$ and $$HB$$ have same $$pH$$ when their concentration ratio is $$3:1$$. The ratio of the dissociation constants of $$HB$$ and $$HA$$ is ________.
A buffer solution has unlimited capacity to absorb $${H}^{+}$$ or $${OH}^{-}$$ ion. If true write 1, else write 0.
A $$0.1$$ M solution of weak acid $$HA$$ is 1% dissociated at 298 K. The new $$pH$$ when $$0.2$$ M of $$NaA$$ is added to it is $$530\times10^{-x}$$, then what is the value of $$x$$?
Which one of the following metallic hydroxides does not dissolve in sodium hydroxide solution?
$$Zn(OH)_2$$$$Fe(OH)_3$$
Calculate the weight of $$(NH_4)_2SO_4$$ which must be added to 500 mL of 0.2 M $$NH_3$$ to yield a solution of pH = 9.35, $$K_b$$ for $$NH_3 = 1.78\times 10^{-5}$$ (in gm)(Write answer nearest integer)
$${K}_{a}$$ for $${H}_{2}O; ({K}_{w}={10}^{-14})$$ is $$1.8\times {10}^{-x}$$.
Then find the value of x. (Moar conc. of pure water is 55.55)
When we add titrate sodium carbonate solution (in beaker) with hydrochloric acid, we observe various results. Match list I with list II.
$${K_a}$$ for an acid, $$HA$$ is $${1\times 10^{-6}}$$ and $${K_b}$$ for $${A^{-}}$$ is $${10^{-x}}$$. Here, the value of $$x$$ is:
The ionization constant of phenol is $$\displaystyle 1.0\times { 10 }^{ -10 }$$. What is the concentration of phenolate ion in $$0.05\ M$$ solution of phenol? What will be its degree of ionization if the solution is also $$0.01\ M$$ in sodium phenolate?
A buffer is a solution of weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. It resists the change in $$pH$$ , when small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions have wide applications.
$$20.0 mL$$ of $$0.10 M$$ of 1-aminopropane is titrated with $$0.10 M$$ of $$HCl$$ . The $$pH$$ at the equivalence point is $$ p \simeq 6 $$ and the appropriate acid-base indicator. is Methyl red. (4.2-6.2) wright the right answer
Table 1.
Table 1: List of acid/base indicators
Common name Transition range, $$pH$$ Color change Methyl orange 3.2 - 4.4 red-orange Methyl red 4.2 - 6.2 red-yellow Phenol red 6.8 - 8.2 yellow-red Phenolphthalein 8.0 - 9.8 colorless-red Thymolphthalein 9.3 - 10.5 colorless-blue
Table 1.
Table 1: List of acid/base indicators
| Common name | Transition range, $$pH$$ | Color change |
| Methyl orange | 3.2 - 4.4 | red-orange |
| Methyl red | 4.2 - 6.2 | red-yellow |
| Phenol red | 6.8 - 8.2 | yellow-red |
| Phenolphthalein | 8.0 - 9.8 | colorless-red |
| Thymolphthalein | 9.3 - 10.5 | colorless-blue |
The degree of ionization of a $$0.1\ M$$ bromoacetic acid solution is $$0.132$$. Calculate the $$pH$$ of the solution and the $$pK_{a}$$ of bromoacetic acid.
What is the $$\displaystyle pH$$ of 0.001 M aniline solution ? The ionization constant of aniline can be taken from Table 7.Calculate the degree of ionization of aniline in the solution. Also calculate the ionization constant of the conjugate acid of aniline.
It has been found that the $$pH$$ of a $$0.01\ M$$ solution of an organic acid is $$4.15$$. Calculate the concentration of the anion, the ionization constant of the acid and its $$\displaystyle { pK }_{ a }$$.
Calculate the degree of ionization of 0.05 M acetic acid if its $$\displaystyle { PK }_{ a }$$ value is 4.How is the degree of dissociation affected when its solution also contains (a) 0.01M (b) 0.1M in $$\displaystyle HCl$$ ?
The ionization constant of dimethylamine is $$\displaystyle 5.4\times { 10 }^{ -4 }$$. Calculate its degree of ionization in its 0.02 M solution. What percentage of dimethylamine is ionized if the solution is also 0.1M in $$\displaystyle NaOH$$?
Equal volumes of 0.002 M solutions of sodium iodate and cupric chlorate are mixed together. Will it lead to precipitation of copper iodate? (For cupric iodate, $$\displaystyle { K }_{ sp }=7.4\times { 10 }^{ -8 }$$ ).
What is common ion effect? Give an example.
(a) Describe the action of an acid buffer solution with an example.
(b) Write any five common terms in Cell Terminology.
A solution contains $$0.01mol\ { L }^{ -1 } $$ of each $${ Pb }^{ 2+ }$$ and $${ Zn }^{ 2+ }$$ ions. The solution is saturated with $${ H }_{ 2 }S$$ when $$\left[ { S }^{ 2- } \right] $$ is $$1.0\times { 10 }^{ -14 }mol\quad { L }^{ -1 }$$. Predict which one of the two ions will be precipitated from the solution? ($${ K }_{ sp }: \ PbS=2.4\times { 10 }^{ -27 }$$ and $$ { K }_{ sp }: \ ZnS=1.0\times { 10 }^{ -21 }$$)
Calculate simultaneous solubility of $$AgCNS$$ and $$AgBr$$ in a solution of water.
[Given: $${ K }_{ sp }$$ of $$AgCNS=1\times { 10 }^{ -12 }$$, $${ K }_{ sp }$$ of $$AgBr=5\times { 10 }^{ -13 }]$$.
The solubility of silver acetate in pure water at $${ 25 }^{ o }C$$ $$8.35g. { litre }^{ -1 }$$ and $$61.8g. { litre }^{ -1 }$$ in an acid solution of $$pH=3$$. Calculate:
(i) $${K}_{sp}$$ of silver acetate and
(ii) dissociation constant of acetic acid.
In $$1\ L$$ saturated solution of $$AgCl\left[ { K }_{ sp }(AgCl)=1.6\times { 10 }^{ -10 } \right] $$, $$0.1\ mol$$ of $$CuCl\left[ { K }_{ sp }(CuCl)=1\times { 10 }^{ -6 } \right]$$ is added. The resultant concentration of $${ Ag }^{ + }$$ in the solution is $$1.6\times { 10 }^{ -x }$$. The value of $$x$$ is:
Given $$Ag{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 2 }^{ + }\rightleftharpoons { Ag }^{ + }+2{ NH }_{ 3 }$$, $${ K }_{ c }=6.2\times { 10 }^{ -8 }$$ and $${ K }_{ sp }$$ of $$AgCl$$ is $$1.8\times { 10 }^{ -10 }$$ at $$298K$$. Calculate concentration of the complex in $$1M$$ aqueous ammonia.
Maximum $$pH$$ that must be maintained in a saturated $${ H }_{ 2 }S$$ (0.1 M) to precipitate $$CdS$$ but not $$ZnS$$ is $$x$$ and concentration of $$C{ d }^{ 2+ }$$ ion at that $$pH$$ is $$y\times { 10 }^{ -7 }$$ then $$x+y=$$
Given $$\left[ C{ d }^{ 2+ } \right] =\left[ { Zn }^{ 2+ } \right] =0.1\ M$$ initially
$${ K }_{ sp }\left( CdS \right) \ =\ 8\ \times \ { 10 }^{ -27 }$$
$${ K }_{ sp }\left( ZnS \right) \ =\ 1\ \times \ { 10 }^{ -21 }$$
$${ K }_{ a1 }\left( { H }_{ 2 }S \right) \ =\ 1.0\ \times \ { 10 }^{ -8 }$$
$${ K }_{ a2 }\left( { H }_{ 2 }S \right) \ =\ 1.0\ \times \ { 10 }^{ -13 }$$
$$K_{a_{1}}, K_{a_{2}}$$ and $$K_{a_{3}}$$ values of $$H_{3}PO_{4}$$ are $$10^{-3}, 10^{-6}$$ and $$10^{-12}$$ respectively. If $$K_{w}(H_{2}O) = 10^{-14}$$, then:
What is $$K_{b}$$ is $$HPO_{4}{^-}$$?
Why do we add $${ NH }_{ 4 }Cl$$ before adding $${ NH }_{ 4 }OH$$ for precipation of group $$3$$ cations ?
A Student planned an experiment that would use $$0.10\ M$$ propionic acid, $$CH_3CH_2COOH$$. Calculate the value of $$[H^+]$$ and the $$pH$$ for this solution. For propionic acid, $$K_a=1.34\times 10^{-5}$$.
Show that for reaction AB(g)$$\rightleftharpoons$$ A(g) + B(g), the total pressure at which AB is 50% dissociated is numerically equal to three times of $$K_p$$.
$$0.6mL$$ of acetic acid $$(CH_3COOH)$$, having density $$1.06g\ mL^{-1}$$, is dissolved in 1 litre of water. The depression in freezing point observed for this strength of acid was $$0.0205^oC$$. Calculate the van't Hoff factor and the dissociation constant of acid.
Calculate the pH of a $$0.1$$M solution of $$H_2NCH_2CH_2NH_2$$; ethylenediamine(en). Determine the en $$H^{2+}_2$$. Concentration in the solution $$K_{b_1}$$ and $$K_{b_2}$$ values of ethylenediamine are $$9\times 10^{-5}$$ and $$7.1\times 10^{-8}$$ respectively.
Nicotinic acid $$(K_a = 10^{-5})$$ is represented by the formula $$HNiC$$. Calculate percent dissociation in a solution which contains 0.1 mol of nicotinic acid per 2 litre of solution.
What is $$pOH$$ of an aqueous solution with $$[H^+]$$ = $$10^{-2} M$$ $$K_w=2\times10^{-12}$$ ? Report your answer after dividing by 2 and round it off to the nearest whole number.
Percentage ionisation of water as follows at certain temperature is $$3.6$$ $$\times$$ $$10^{-7} $$%. Calculate $$K_w$$ and $$pH$$ of water temperature.
Calculate the simultaneous solubility of AgCNS and AgBr in a solution of water. Ksp of AgCNS=110-, Ksp of AgBr=510-
For a weak electrolyte molar conductance in dilute solution increases sharply as its concentration in solution is decreased. Give reason.
What will be effect on stomach $$pH$$ due to antacids?
Tritium $$_{1}T^{1}$$ (an isotope of $$H$$) combine with fluorine to form a weak acid $$TF$$ which ionises to give $$T^{0}$$. Tritium is radioactive and is a $$\beta-emitter$$. A freshly prepared dilute aqueous solution of $$TF$$ has a $$pT$$ (equivalent of $$pH$$) of $$1.7$$ and freezes at $$0.372^{\circ}C$$. If $$600\ mL$$ of freshly prepared solution were allowed to stand for $$24.8\ years$$, calculate:
(1) Ionisation constant of $$TF$$
(2) Charge carried by $$\beta - particles$$ emitted by tritium in Faraday.
Given : $$K_{f}$$ for $$H_{2}O = 1.86, t_{1/2} (T) = 12.4\ yrs$$.
The self-ionization Constant for pure formic acid, $$K = [HCOOH_{2}^{+}][HCOO^{-}]$$ has been estimated as $$10^{-6} M^{2}$$ and the density of formic acid is $$1.22 g/cm^{3}$$ at room temperature. If 'x %' of formic acid molecules in pure formic acid is converted to formate ions, then the value of '$$1000x$$' is
How many water molecule (s) is/are present in microcosmic salt?
What happens when?
Potassium iodide is added to bleaching powder containing dilute acetic acid
When the first element of the periodic table is treated with dioxygen, it gives a compound whose solid state floats on its liquid state. This compound has an ability to act as an acid as well as a base. What products will be formed when this compound undergoes autoionization?
The pH of a $$0.005M$$ codeine $$({C}_{18}{H}_{21}{NO}_{2})$$ solution is $$9.95$$. Calculate its ionization constant.
The ionization constant of phenol is $$1.0\times {10}^{-10}$$. What is the concentration of phenate ion in $$0.05M$$ solution of phenol? What will be its degree of ionization if the solution is also $$0.01M$$ in sodium phenate?
The ionization constant of formic acid is $$1.8\times {10}^{-4}$$. Around what pH will its mixture with sodium formate give buffer solution of higher capacity. Calculate the ratio of sodium formate and formic acid in a buffer of $$pH$$ $$4.25$$.
$${K}_{SP}$$ of $$Ba{SO}_{4}$$ is $$1.5\times {10}^{-9}$$. Calculate its solubility in:
(i) pure water (ii) $$0.10M$$ $$Ba{Cl}_{2}$$
Saccharin $$(K_a=2\times 10^{-12})$$ is a weak acid represented by the formula HSac. $$4\times 10^{-4}$$ mole saccharin is dissolved in $$200\ cm^3$$ aqueous solution of $$pH\ 3$$. Assuming no change in volume, calculate the concentration of $$Sac^{-1}$$ ions in the resulting solution at equilibrium.
The ionization constant of chloroacetic acid is $$1.35\times {10}^{-3}$$. What will be pH of $$0.1M$$ acid and its $$0.1M$$ sodium salt solution?
The pH of $$0.1M$$ solution of cyanic acid $$(HCNO)$$ is $$2.34$$. Calculate the ionization constant of the acid and its degree of ionization in the solution.
(a) Suggest a solvent in which aniline acts as strong base
(b) Write equation for the auto ionisation of (i) $$HCOOH$$, (ii) $${NH}_{3}$$
(c) $${ \left[ Al{ \left( { H }_{ 2 }O \right) }_{ 6 } \right] }^{ 3+ }$$ is acid or base and write its conjugate partner and reaction.
(d) Write the order of acidic nature of $$HCl,HCOOH$$ and $${CH}_{3}COOH$$ in (i) $${H}_{2}O$$, (ii) liq. $${NH}_{3}$$
In $$1\ L$$ saturated solution of $$AgCl$$ $$(K_{sp}=1.6\times 10^{-10}), 0.1\ mole$$ of $$CuCl(K_{sp}=1.0\times 10^{-6})$$ is added . The resultant concentration of $$Ag^+$$ is $$1.6 \times 10^{-x}$$. The value of $$x$$ is ....
Liquid ammonia ionises to a slight extent. At $$-{50}^{o}C$$, its self ionisation constant, $${ K }_{ { NH }_{ 3 } }=\left[ { NH }_{ 4 }^{ + } \right] \left[ { NH }_{ 2 }^{ - } \right] ={ 10 }^{ -30 }$$. How many amide ions are present per $${Cm}^{3}$$ of pure liquid ammonia? Assume $$N=6.0\times { 10 }^{ 23 }$$.
Match the effect of addition of 0.1 M KOH to 0.1 M , 50 ml $$ H_3PO_4 $$. $$ Ka_1 , Ka_2 , Ka_3 $$ are the I, II, III ionisation constant of $$ H_3PO_4 $$ :
Give a reason to explain why bleaching powder does not dissolve completely in the water?
Write the name and chemical formula of the calcium compound used for disinfecting drinking water. How is this compound manufactured?
Fill in the missing data in the following table.
$$\begin{array}{|ll|l|l|l|}\hline {\text { Name of the salt }} & & \ {\text { Salt obtained from }} \\\ & & \text { Formula } & \text { Base } & \text { Acid } \\\hline \text { (i) } & \text { Ammonium chloride } & N H_{4} C l & N H_{4} O H & - \\\hline \text { (ii) } & \text { Copper sulphate } & - & - & H_{2} S O_{4} \\\hline \text { (iii) } & \text { Sodium chloride } & N a C l & N a O H & - \\\hline \text { (iv) } & \text { Magnesium nitrate } & M g\left(N O_{3}\right)_{2} & - & H N O_{3} \\\hline \text { (v) } & \text { Potassium sulphate } & K_{2} S O_{4} & - & - \\\hline \text { (vi) } & \text { Calcium nitrate } & C a\left(N O_{3}\right)_{2} & C a(O H)_{2} & - \\\hline\end{array}$$
Ionisation constant of a weak base $$MOH$$, is given by the expression
$$K_{b}=\frac{[M^{+}][OH^{-}]}{[MOH]}$$
Values of ionisation constant of some weak bases at a particular temperature are given below:
| Base | Dimethylamine | Urea | Pyridine | Ammonia |
| $$K_{b}$$ | $$5.4\times10^{-4}$$ | $$1.3\times10^{-14}$$ | $$1.77\times10^{-9}$$ | $$1.77\times10^{-5}$$ |
Arrange the bases in decreasing order of the extent of their ionization at equilibrium. Which of the above base is the strongest?
The skin has and needs natural oils. Why is it advisable to wear gloves while working with strong allkalis ?
Name two sulphates which are insoluble.
Name a chloride which is insoluble.
pH of $$0.08mol$$ $$dm^{-3}$$ $$HOCl$$ solution is $$2.85$$. Calculate its ionisation constant.
Name a chloride which is insoluble in cold water but dissolves in hot water.
Write reaction for autoprotolysis of water. How is ionic product of water related to ionization constant of water ? Derive the relationship.
What is the effect of temperature on ionic product of water and why ?
Explain the term 'ionic product of water'.
Give reasons for the following:
Magnesium is not precipitated from a solution of its salt by $$NH_{4}OH $$ in the presence of $$NH_{4}Cl $$.
Why in Group V of qualitative analysis, sufficient $$NH_{4}OH$$ solution should be added before adding $$(NH_{4})_2CO_{3} $$ solution ?
Give one example of each of the following equilibria:
Liquid-Gas Equilibria
How does $$K_{w}$$ vary with temperature and why ?
What do you understand by the term 'ionic product of water' ? How has this concept been useful in defining the acidity and basicity of a solution ?
Although acetic acid is highly soluble in water but still it is a weak acid. Explain why?
Answer the following question in short:
What is $$pH$$ scale? Why it was needed by S.P.L Sorensen to invent it?
Class 11 Medical Chemistry Extra Questions
- Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Extra Questions
- Classification Of Elements And Periodicity In Properties Extra Questions
- Environmental Chemistry Extra Questions
- Equilibrium Extra Questions
- Hydrocarbons Extra Questions
- Hydrogen Extra Questions
- Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Extra Questions
- Redox Reactions Extra Questions
- Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry Extra Questions
- States Of Matter Gases And Liquids Extra Questions
- Structure Of Atom Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- Thermodynamics Extra Questions
- The S-Block Elements Extra Questions