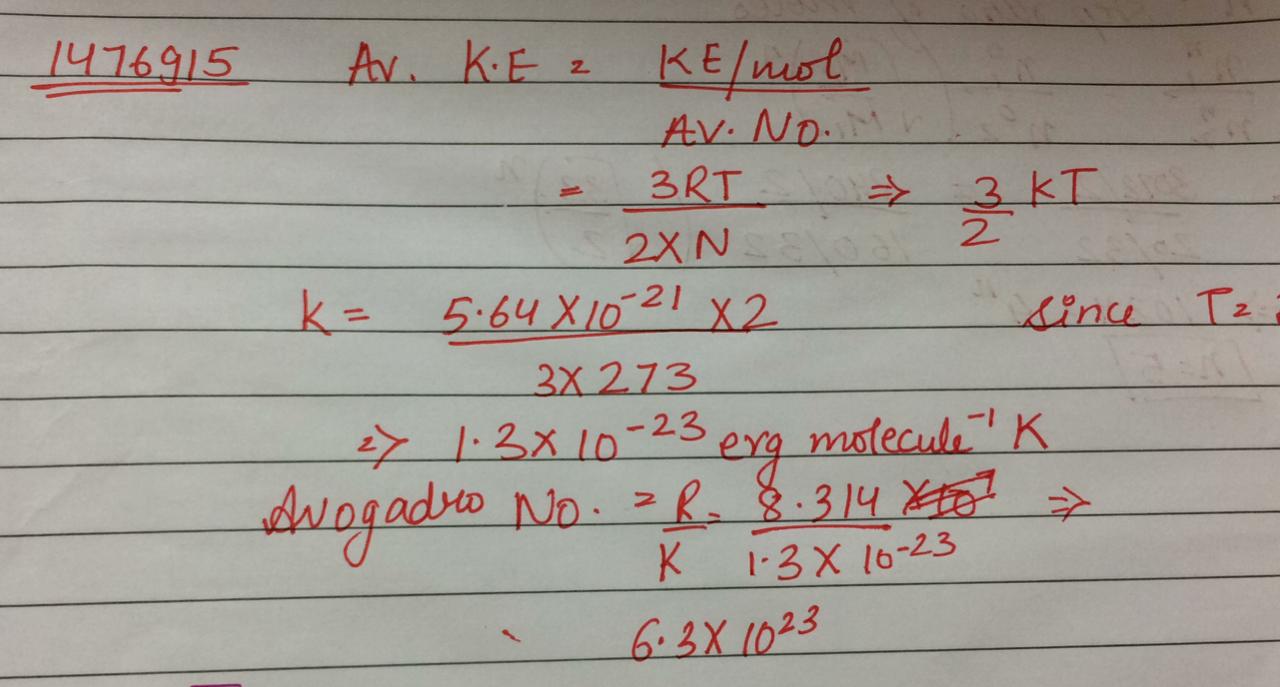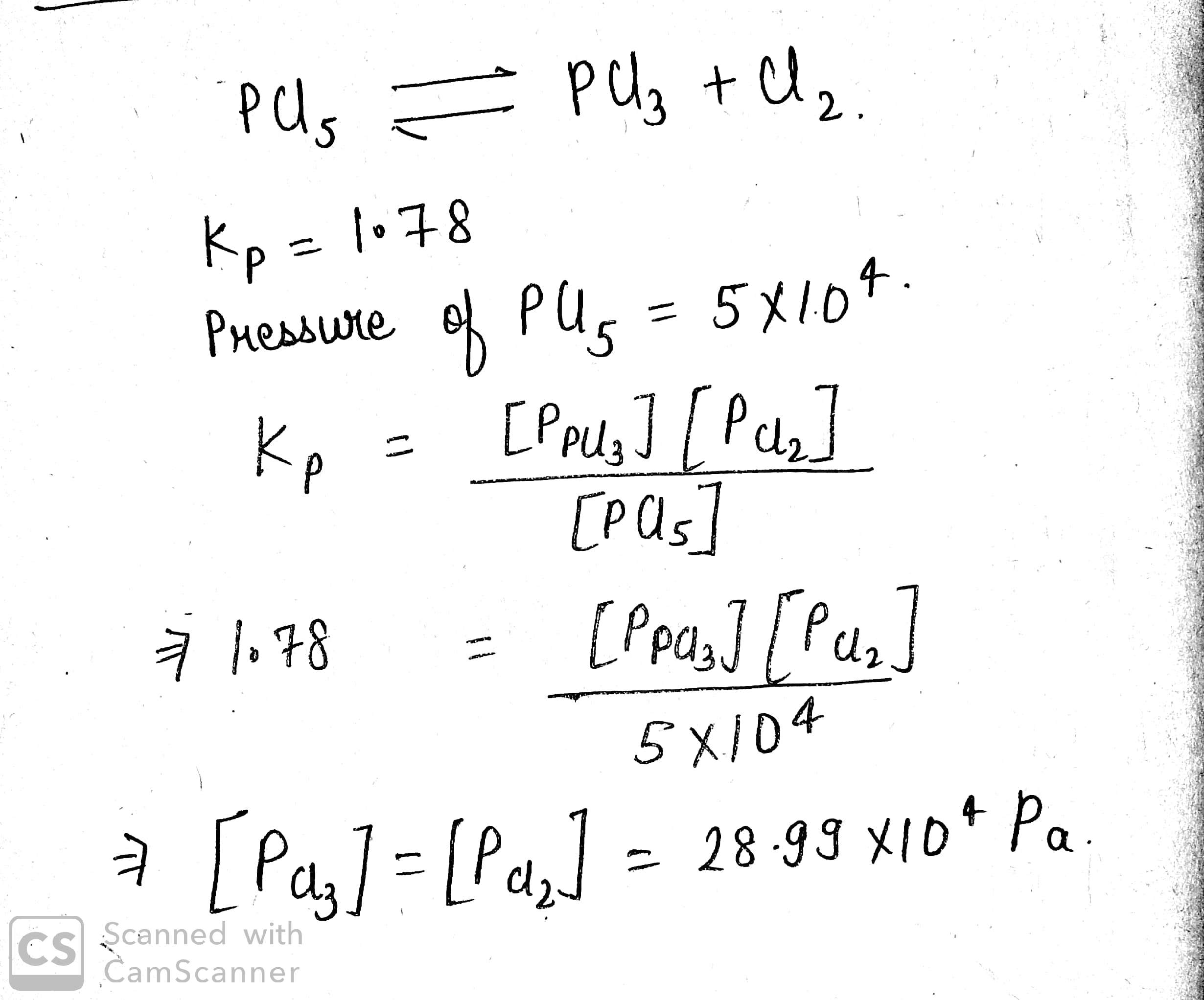States Of Matter Gases And Liquids - Class 11 Medical Chemistry - Extra Questions
Explain, why Dalton's law of partial pressure can be applied only to a mixture of non-reacting gases.
Equal volumes of all gases contain equal number of molecules under similar conditions of temperature and pressure.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
One of the assumptions of kinetic theory of gases is that there is no force of attraction between the
molecules of a gas.
What are the assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory?
The volume occupied by the molecules of an ideal gas is :
Water vapours have more energy than water at same temperature.
Molarity of a substance ______ with increase in temperature.
The units of molarity is ______.
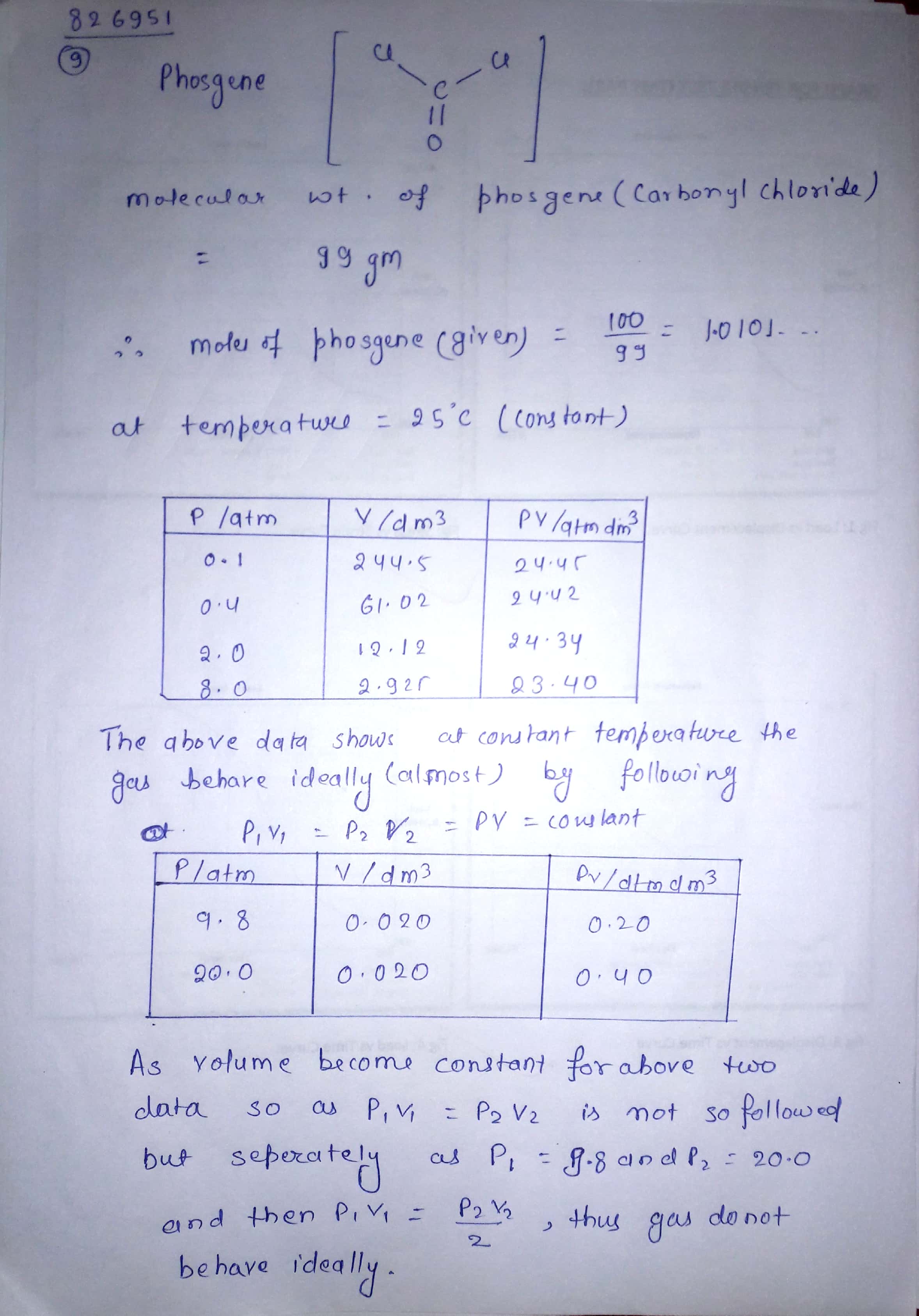
The P, V measurements for 100 g of phosgene gas at 25∘C are given below:
| P/atm | V/dm3 | PV/atm dm3 |
| 0.1 | 244.5 | 24.45 |
| 0.4 | 61.02 | 24.42 |
| 2.0 | 12.17 | 24.34 |
| 8.0 | 2.925 | 23.40 |
| 9.8 | 0.020 | 0.20 |
| 20.0 | 0.020 | 0.40 |
The vapour pressure of water at 80∘C is 355 torr. A 100 ml vessel contained water - saturated oxygen at 80∘C, the total gas pressure being 730 torr. The contents of the vessel were pumped into 50.0 ml, vessel at the same temperature. What were partial pressures of oxygen and of vapour and the total pressure in the final equilibrium state ? Neglect the volume of any water might condense.
Write ideal gas equation for 'n' moles of the gas.
Write any three postulates of Kinetic theory of gases.
What mass of hydrogen peroxide will be present in 2 litres of a 5 molar solution? Calculate the mass of oxygen which will be liberated by decomposition of 200 ml of this solution.
A closed bulb of capacity 200 ml containing CH4,H2 and He at 300K. The ratio of partial pressures of CH4,H2 and He, respectively is 2:3:5. Calculate the ratio of their weights present in the container.
Equal masses of H2, He and CH4 are mixed in empty container at 300 K, when total pressure is 2.6 atm. The partial pressure of H2 in the mixture is:-
choose answer:
1) 0.5 atm
2) 1.22 atm
3) 0.8 atm
4) 0.2 atm
1) 0.5 atm
2) 1.22 atm
3) 0.8 atm
4) 0.2 atm
A straight glass tube has two inlets X and Y at the two ends. The length of the tube is 200 cm. HCl gas through inlet X and NH3 gas through inlet Y are allowed to enter the tube at the same time. White fumes first appear at a point P inside the tube. The distance of P (in cm) from X is:
Calculate the final volume (in L) of one mole of an ideal gas initially at 0oC and 1 atm pressure, if it absorbs 2000 cal of heat during a reversible isothermal expansion.
Set the following solutions in increasing order of vapour pressure:
3m Na2SO4, 1m Urea 0.4m AlCl30.2m NaCl
An iron ball of radius 0.3 cm falls through a column of oil of density 0.94 g cm−3. If it attains a terminal velocity of 0.54 m s−1, what is the viscosity of oil? Density of iron is 7.8 g cm−3.
A viscous force of 1.018×10−7 N acting on a raindrop makes it fall through air with a terminal velocity of 1 ms−1. If the viscosity of air is 0.018×10−3 PI, what is the radius of the raindrop ?
Aerosol cans carry a clear warning of the heating of the can. Why?
One mole of an ideal gas expands reversibly and adiabatically from a temperature of 27C. If the work done during the process is 3 kJ, then final temperature of the gas is:(CV=20J/K)
(a) 100 K (b) 150 K
(c) 195 K (d) 255 K
Certain amount of a gas occupies a volume of 0.4litre at 17oC. To what temperature should it be heated so that its volume gets (a) doubled (b) reduced to half, pressure remaining constant.
The pressure in a bulb dropped from 2000 to 1500 mm of mercury in 47 min when the contained oxygen leaked through a small hole. The bulb was then evacuated. A mixture of oxygen and another gas of molecular weight 79 in the molar ratio of 1:1 at a total pressure of 4000 mm of mercury was introduced. Find the molar ratio of the two gases remaining in the bulb after a period of 74 min.
State and explain Gay Lussac's law of combining volumes.
The volume occupied by 3.5g of O2 gas at 27oC & 740 mm of Hg pressure[O=16]
What are the main postulates of kinetic molecular theory of gases?
400 mL of oxygen at 27oC were cooled to - 15oC without the change in pressure. Calculate the contraction in volume.
Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8g of CO2 at 31.1oC and 1 bar pressure. (R=0.083 bar dm3K−1mol−1)
A mixture of gases have O2 and N2 at the ratio of 1 : 4, then what will be the ratio of no. of molecular in mixture of gases?
A certain mass of a gas occupies a volume of 0.2dm3 at 273K. Calculate the volume (in dm3)of the gas if its absolute temperature is doubled at the same pressure. (Round off to 1 decimal places)
Solids have infinite free surfaces while liquids have only one upper free surface.
A spherical balloon of 21 cm diameter is to be filled with H2 gas at STP. From a cylinder, containing the gas at 20 atm and 17oC. If the vol. of cylinder is 2.82 L, what will be the no. of balloon that can be filled up by this pressure?
State and explain Gay Lussac's law.
At constant volume of 0.0821 litres for an ideal gas if ddT(PT)=300 at 150K. The number of moles of that gas is___
A bulb of tree litre capacity filled with air is headed from 27oC to toC. The air thus expelled measured 1.45 litre at 17oC considering the pressure to be 1 atm, throughout the experiment and ignoring the expansion of bulb, calculate t.
Two flask A and B of equal volumes maintained at temperature 300K and 700K contain equal mass of He(g) and N3(g) respectively. What is the ratio of total translational kinetic energy of gas in flask A to the flask B?
A gas occupies 100.0mL at 50oC and 1 atm pressure. The gas is cooled at constant pressure so that volume is reduced to 50.0mL. What is the final temperature of the gas?
250ml of nitrogen gas maintained at 650mm pressure and 380 mL of oxygen gas maintained at 650 mm pressure are out together in 1 L flask.If temperature is kept constant, what will be the final pressure of the mixture?
The volume expansivity of a gas under constant pressure is 0.0037 or (1273). Calculate its volume at −100oC if its volume at 100oC is 685cm3 .
Write down all the postulates of kinetic molecular theory of gases.
If 200mL of N2 at 25oC and a pressure of 250mm are mixed with 350mL of O2 at 25oC and a pressure of 300mm so that, the volume of resulting mixture is 300mL, what would be the final pressure of the mixture at 25oC?
At a constant temperature, 250 mL of argon at 760 mm pressure and 600 mL of nitrogen at 500 mm pressure are put together in a one litre flask. Calculate the final pressure.
Some faculty members of XYZ classes were trying to simplify a problem for students by mentioning data explicity about a gaseous mixture. Information given by them is as follow.
Faculty - 1 : Mixture consist of three gases A, B and C.
Faculty - 2 : Molar mass of B is twice of A & Molar mass of A is 4 times of C.
Faculty 3 : The gas that is neither heaviest nor lightest is 16% by mass.
Faculty - 4 : Molar ratio of heaviest to lightest gas is 2:5
Based on the above information, answer the question that follows.
What would be the average molar mass of mixture.
A gas occipies 700ml at S.T.P. Find the volume occupied by the gas when its pressure is 400mm of Hg and its temperature 15oC
A balloon is filled with hydrogen at room temperature, it will burst if pressure exceeds 0.2 bar. If at 1 bar pressure the gas occupies 2.27 L volume, upto what volume can the balloon be expanded?
A gas occupies 100mL at 50degree C at 1atm pressure.The gas is cooled at constant pressure so that volume is reduced to 50mL.What is the final temperature of the gas
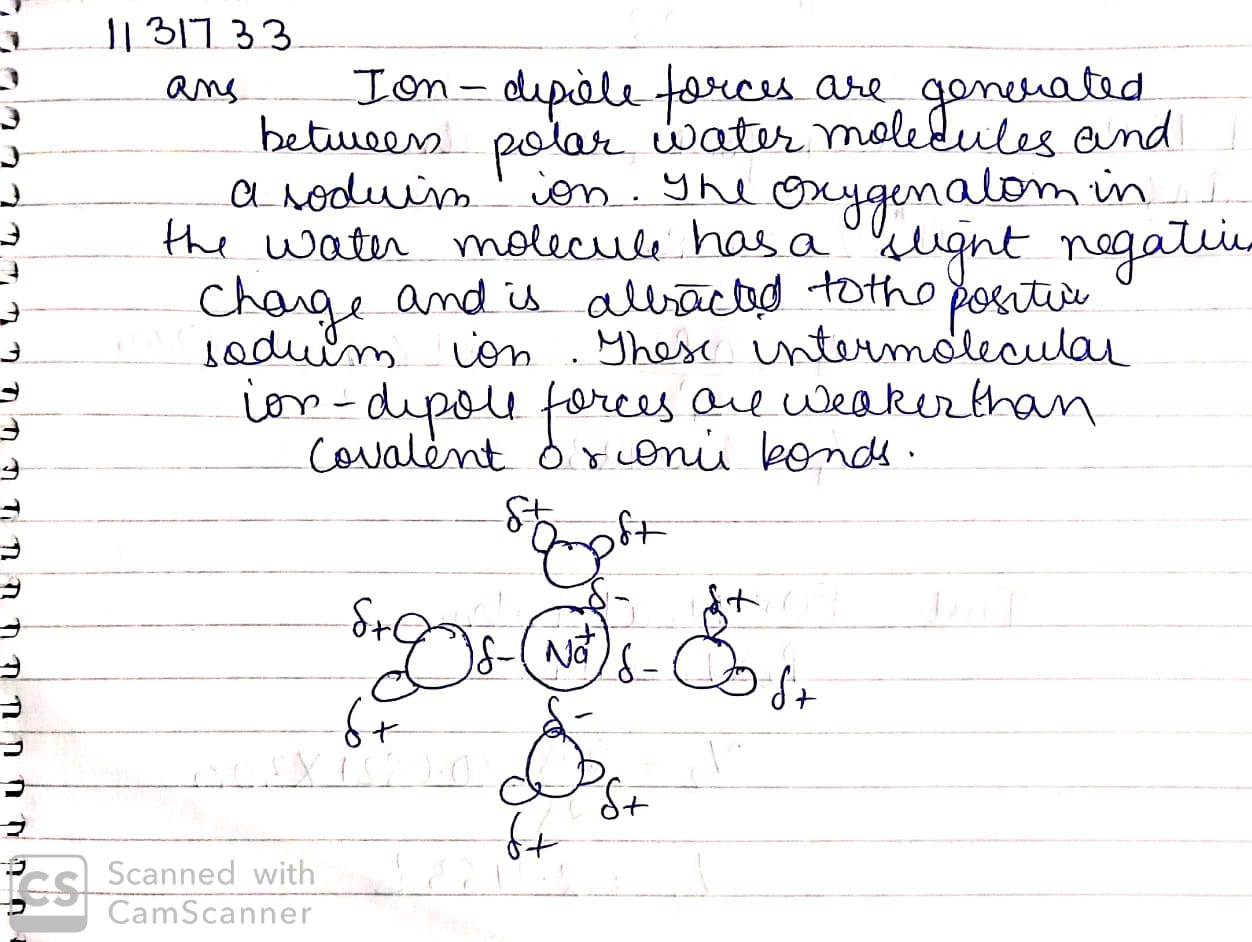
Explain ion-dipole interaction with suitable example.
Write note on Laws of multiple proportions.
Write note on Dalton's atomic theory.
The density of 3 M solution of NaCl is 1.25 g\ml. Calculate the molality of the solution.
A compound contains 4.07% hydrogen, 24.27% carbon and 71.65% chlorine. Its molar mass
is 98.96 g. What is its empirical and molecular formula?
Calculate number of atoms present in 500 ml 0.05 M aqueous solution of H2SO4?
Explain ion-dipole interaction with the help of suitable example.
The density of a gas is 3.80 g L−1 at S.T.P calculate is density at 270C and 700 torr pressure.
O2 is present in 1 litre flask at a pressure of 1.52 x 103 mm of Hg. Calculate mass of O2 at 0C.
What percent of a sample of nitrogen must be allowed to escape if its temperature, pressure and volume are to be changed from 220C, 3atm and 1.65litre to 110C, 0.7atm and 1.00litre respectively?
What will be the volume of a given mass of a gas at a pressure 50 cm of Hg. If it occupies 250 ml at a pressure of 98 cm of Hg, keeping the temperature constant.
Two closed bulbs of equal volume (v) containing an ideal gas initially at pressure P4 and temperature T1 are connected through a narrow tube of negligible volume as shown in the figure below. The temperature of one of the bulbs is then raised to T2. What is the final pressure Pf?

A 5 lit flask containing N2 at 1 bar and 25oC is connected to a 4lit flask containing N2 at 2 bar and 0oC. After the gases are allowed to mix keeping both flasks at their original temperature, what will be the pressure and amount of N2 in the 5 lit flask assuming ideal gas behaviour.
Find out the numerical value of gas constant (R).
An open bulb containing air at 190C was cooled to a certain temperature at which the no. of moles of gaseous molecules increased by 25%. What is the final temperature?
Calculate the percentage of free volume available in 1 mole gaseous water at 1 atm pressure and 373 K.
Calculate the volume occupied by 7.0 g of nitrogen gas at 27oC and 750 mm Hg pressure,
According to Henrys Law, in gases, an increase in pressure increase______.
5.40 gm of an unknown gas at 27∘C Occupies the same volume as 0.14 gm hydrogen at 17∘C and same pressure. The molecular weight of unknown gas is
Write the postulates of "kinetic theory of gases' .
Kinetic energy of oxygen molecule at0∘C is 5.64×10−21J. Calculate the value of Avogadro's number. GivenR=8.31J mole−1K−1.
Write ideal gas equation for one mole of a gas.
At 525K, the equilibrium constant of the reaction, PCl5⇌PCl3+Cl2 is 1.78 atm (Kp). At what pressure should an equimolar mixture of Cl2 and PCl3 be taken for the pressure of PCl5 to be 5×104 Pa at equilibrium, volume remaining constant?
Give two characteristic properties of a liquid.
Match the graphs between the following variable with their names:
"One of the assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases is that there is no force of attraction between the molecules of a gas". State and explain the evidence that shows that the assumptions are not applicable for real gases.
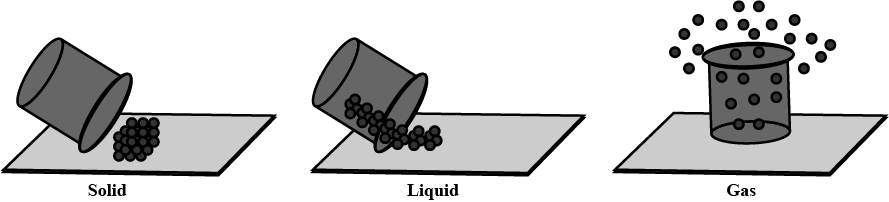
Why do liquids flow ?
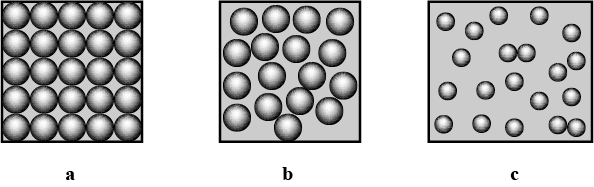
Define the three states of Matter
Define matter
For each of the following statements, say whether it describes a solid, a liquid, or a gas. (a) Particles move about very quickly.
(b) Particles are quite close together.
(c) Particles are far apart and move in all directions.
(b) Particles are quite close together.
(c) Particles are far apart and move in all directions.
Name the three states of matter.
Give the occurrence of water in the three different states i.e. solid, liquid and gaseous.
State three main characteristics of the particles of matter.
.......... deals with the study of matter and the changes it undergoes.
For the following statement, say whether it describes a solid, a liquid or a gas.
Particles are quite close together.
The different forms of a substance are called ............... of matter.
Give reason for : Tyres of automobiles are inflated to lesser pressure in summer than in winter.
Write a short note on Gay Lussac's Law.
Give two examples of substances that are rigid and not compressible.
State Dalton’s law of partial pressure.
What is Dalton's law of partial pressure?
What assumption can be made regarding the possibility of collision between gas molecules?
The drops of liquid take spherical shape. Why?
The boiling point of liquid changes on increasing the pressure. Why?
Mixture of NH3 and HCl gases do not follow Dalton's law of partial pressure. Why?
Complete the table
| Energy of gas molecules | Very high |
| Distance between the molecules | ......... |
| Freedom of moment of molecules | .......... |
| Attractive force between molecules | ........... |
State Ideal gas equation and law.
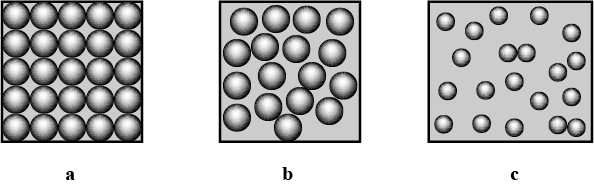
Identify and picturise the arrangement of particles in different states of matter.
Explain the peculiarities of materials.
At 25oC and 760 mm of Hg pressure, a gas occupies 600 mL volume. What will be its pressure at a height where temperatures is 10oC and volume of the gas is 640 mL?
Match the following.
| State of matter | A | B | |
| 1 | Gas | Soil | Milk |
| 2 | Solid | Kerosene | Oxygen |
| 3 | Liquid | Carbon Monoxide | Peas |
For hydrogen gas Cp−Cv=a and for oxygen gas Cp−Cv=b,
so the relation between a and b is a=nb. Value of n is:
so the relation between a and b is a=nb. Value of n is:
Match the items of List 1 with those in List 2.
Match the following from Column−I to Column−II.
300 litres of ammonia gas at 200C and 20 atmosphere pressure are allowed to expand in a space of 600 litres capacity and to a pressure of one atmosphere .Calculate the drop in temperature.
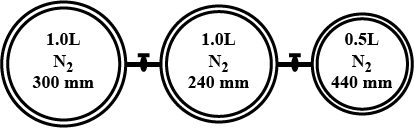
Consider the of bulbs shown arrangement below.
If the pressure of the system when all the stop cocks are opened is x (in atm) then find 100 x ? (760 mm = 1 atm)
16gm of O2 was filled in a container of capacity 8.21 lit. at 300K. Calculate
(i) Pressure exerted by O2
(ii) Partial pressure of O2 and O3 if 50% of oxygen is converted into ozone at same temperature
(iii) Total pressure exerted by gases if 50% of oxygen is converted into ozone (O3) at temperature 50K
Two flask of equal volume have been joined by a narrow tube of negligible volume. Initially both flasks are at 300K containing 0.60 mole of O2 gas at 0.5atm pressure. One of the flask is then placed in a thermostat at 600K. Calculate final pressure and the number of O2 gas in each flask.
20\ mL of a solution containing 0.2\ g of impure sample of H_{2}O_{2} reacts with 0.316\ g of KMnO_{4} (acidic). Calculate:
(i) Purity of H_{2}O_{2}.
(ii) Volume of dry O_{2} evolved at 27^{\circ}C and 750\ mm\ P.
There are n connected container having volume V, 2V, 3V, ......, nV separated by stopcock. All container have same moles of gas at same temperature. If pressure of first container is P, then final pressure when all stop cocks are opened is ?
A mixture in which the mole ration of {H}_{ 2 } and {O}_{ 2 } is 2:1 is used to prepare water by the reaction
{ 2H }_{ 2 }\left( g \right) +{ O }_{ 2 }\left( g \right) \longrightarrow { 2H }_{ 2 }O\left( g \right)
The total pressure of the container is 0.8 atm at 20 before the reaction. Determine the final pressure at 120 after reaction assuming 80% yield of water.
The kinetic molecular theory attributes an average kinetic energy of 3/2\ KT to each particle. What rms speed would a mist particle of mass 10^{12}\ gm have at room temperture (27^0{\circ}C) according to the kinetic molecular theory.
At 817^0C, K_p for the reaction between pure CO_2 and excess hot graphite to form 2CO(g) is 10 atm.
What is the analysis of the gases at equilibrium at 817^0C & a total pressure of 4.0 atm? What is the partial pressure of CO_2 at equilibrium?
Calculate the value of R in S.I unit for one mole of a gas.
(Given P={10}^{5}N/{m}^{2}\,V=0.0227098{m}^{3},\,T=273.15K,\,n=1mole)
Pure PCl_5 is introduced into an evacuated chamber and it comes to equilibrium at 250^oC and 2\ atm. The equilibrium contains 40.7\% chlorine by volume. Calculate the partial pressures of all the gases present at equilibrium.
A quantity of an ideal gas is collected in a graduated tube over the mercury in a barometer type arrangement. The volume of gas at 20^oC is 50 ml and the level of mercury is 100 mm above the outside of the mercury level. The atmospheric pressure is 750 mm. Volume of gas at STP is :(Take R=0.083 it. atm/K/mole).
Calculate the total pressure in a 10 litre cylinder which contains o.4g He,1.6g oxygen and 1.4g nitrogen at{ 27 }^{ 0 }C. Also calculate the partial pressure of He gas in the cylinder. Assume ideal behavious for gases :
An open container of volume V contains air at temperature 27^oC or 300K. The container is heated to such a temperature so that amount of gas coming out is 2/3 of
(a) amount of gas initially present in the container.
(b) amount of gas finally remaining in the container.
Find the temperature to which the container should be heated.
Find out the temperature at which vessel was heated.
A gaseous mixture containing equal masses of He and CH_4 is a total pressure of 2 \ atm. Calculate partial pressure of He.
A gaseous mixture containing equal amount of nitrogen and methane has total pressure 7.86 mm Hg at 300K. Calculate the partial pressure (in mm Hg) of methane in the mixture.
Two litres of an ideal gas at a pressure of 10 atm expands isothermally to a final volume of 10 litres against a constant external pressure of 1 atm. What will be the work done if process is done reversibly?
An evacuated bulb of known volume is filled with H_2 gas at room temperature (30^oC). The pressure of the gas in the bulb is 750 mm Hg. A portion of the gas is transferred to a different flask and found to occupy a volume of 50.0 mL at 1 atm pressure and at the same temperature. The pressure of the H_2 gas remaining in the original bulb drops to 600 mm Hg. What is the volume of the bulb assuming H_2 gas is an ideal gas ?
Match the description in Column I with graph provided Column II. For n moles of ideal gas at temperature T.
If the pressure and absolute temperature of 2 liter of carbon dioxide are doubled, the volume of carbon dioxide would become (in litres)?
The density of liquid nitrogen is 0.807 \, g \, mL_{-3}. If a person acidently swallowed a .028mL drop of liquid nitrogen. What volume of nitrogen gas would be evolved in their body at 100.0kPa and 27^oC?
If the kinetic energy of an electron is increased 9 times then the wavelength associated with it would become.
For a gas adsorbed on a particular adsorbent at
{O^ \circ }C, the plot of \log \frac{x}{m} versus log P where P is
in atm has a slope and intercept as shown in the fig.
Find the mass of the gas adsorbed by 10 g of the adsorbent at 0.2 atm.

1L flask containing vapour of methyl alcohol at a pressure of 1atm, and 25C was evacuated till the fill pressure was { 10 }^{ -3 } mm.How many molecules of methyl alcohol were left in the flask?
At one bar pressure, the volume of a gas is 0.6 liter. If the gas receives 122 Joules of heat at one atmosphere pressure, the volume becomes 2 liters, then calculate its internal energy. (1 liter bar=101.32 Joule)
A mixture of helium and neon gases is collected over water at {28.0^0}C and 745mm of Hg, If the partial pressure of helium is 368mm of Hg, what is the partial pressure of neon? (Vapour pressure of water at {28.0^0}C = 28.33 mm of Hg)
At 400\ K temperature in a closed vessel the \% by volume of He,Ne and Ar are 40\%, 40\% and 20\% respectively. If the total pressure is 25 bar, then find the partial pressure of each gas. (Total pressure is 25 bar)
When the size of a soap bubble is increased by using more air in it, the surface area increases. Does it mean that the average separation between the surface molecules is increased?
All the substances are formed by small ............
What are the three states of matter ? Define each of them with two examples.
State the following
(c) Gas equation.
Give the assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory
Deduce the relation PV = nRT, where R is a constant called universal gas constant.
How is the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture related to the total pressure of the gaseous mixture?
Explain the following observation : The tyre of an automobile is inflated at lesser pressure in summer than in winter.
Briefly explain Pressure-Temperature Law.
State and explain Daltons law of partial pressures. How is this law applied in the determination of the pressure of dry gas from that of the moist gas?
Class 11 Medical Chemistry Extra Questions
- Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Extra Questions
- Classification Of Elements And Periodicity In Properties Extra Questions
- Environmental Chemistry Extra Questions
- Equilibrium Extra Questions
- Hydrocarbons Extra Questions
- Hydrogen Extra Questions
- Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Extra Questions
- Redox Reactions Extra Questions
- Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry Extra Questions
- States Of Matter Gases And Liquids Extra Questions
- Structure Of Atom Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- Thermodynamics Extra Questions
- The S-Block Elements Extra Questions
.bmp)